Psych Notes Unit 3 Motivation and Emotion
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
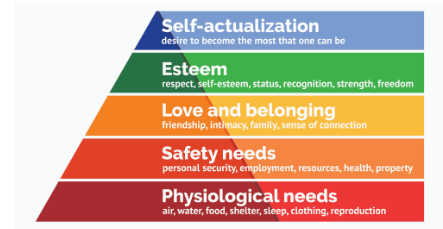
*Know Maslow’s Pyramid
“What drives us to seek a specific goal” is known as what?
Motivation
State of body that causes feelings (hate, love, fear, etc)
Emotions
Two examples of basic survival drive
Water and Food
How do we know we are hungry?
Our hypothalamus (with glucose monitors) signals our hunger when our blood sugar drops
How do we know we are thirsty?
Our hypothalamus detects our dryness of tongue
Hypothalamus: What part of the brain? What does it control? What happens when areas are stimulated?
The inner brain, controls pain and pleasure and emotions/motivations are increased if different areas are stimulated.
What are Gonads?
Sex Glands
What are the two types of Sex Glands (Gonads)
testes-male-produces sperm
ovaries-female-produces eggs
Testes and ovaries produce
hormones
Reticular Formation: Where in brain? Controls? How does this relate to motivation/emotions?
In base of brain, controls sleep but how high or low the level of activity is, any motivation or emotional state involves taking action
Reticular Formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
What are Pituitary Glands?
Controls chemical responses (in brain)
What are Adrenal Glands?
Gets signal from Pituitary Glands and produces adrenaline which changes breathing/heart rate
What is intrinsic motivation?
Comes from within, internal desires
Intrinsic motivation examples:
Growth, fun, enjoyment
What is extrinsic motivation?
comes from outside
Extrinsic motivation examples:
Winning, prizes, pay raises
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment
Extrinsic
What are the 3 theories of emotion?
James - Lange Theory
Cannon - Bard Theory
Schachter - Singer Theory
What is the James - Lange Theory?
See snake -> body reacts -> emotion/fear
What is the Cannon - Bard Theory:
See snake -> body reacts/emotions are felt at the same time
What is the Schachter - Singer Theory?
See snake -> emotion/fear -> body reacts
Harry Harlow
studied attachment in monkeys with artificial mothers
Psychological needs for change are what kind of drives?
Non Survival
The motivation to solve worthwhile problems
achievement
theory in which physiological reaction leads to the labeling of an emotion
James-Lange theory of emotion
manipulation motive
desire to handle/use objects in environment
sex, activity, exploration, manipulation and novelty are what kinds of needs?
Stimulation needs
Homeostasis
Body will try to keep in balance is known as
psychological need to have other people think highly of oneself
approval
the motivation to solve worthwhile problems
achievement