CSB329 (Stem Cell Biology) - Lecture Two Content
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What body plan do cnidarians exhibit?
Radial symmetry
Definition of radial symmetry
Absence of the dorsoventral axis, and the right to left axis.
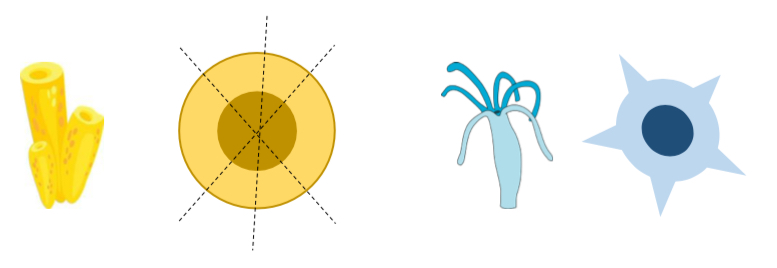
What is the number of germ layers present in poriferans and cnidarians?
Two or fewer
Anatomical characteristic of poriferan germ layers
Absence of discrete germ layers (i.e., specialized tissues)
Anatomical characteristic of cnidarians germ layers
Absence of the mesoderm layer (i.e., discrete organs)
What type of feeding behaviour do poriferans perform?
Filter feeding
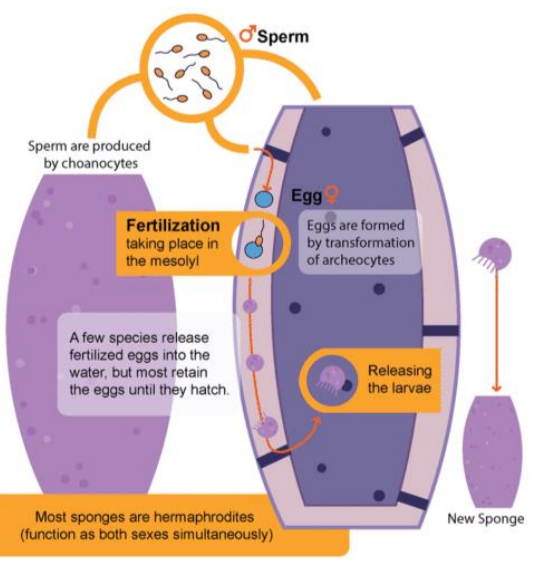
What cell is responsible for facilitating the movement of water in poriferans? What structure of the cell is responsible for generating the propulsive force necessary for the movement of water?
Choanocytes, and the movement of their flagella
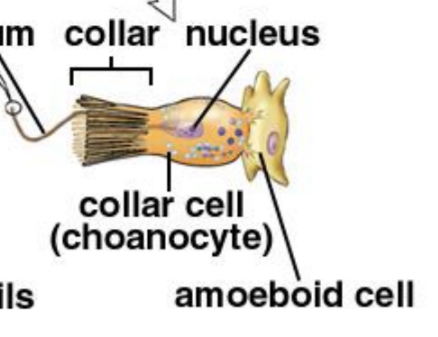
What cell are choanocytes derived from?
Archeocytes
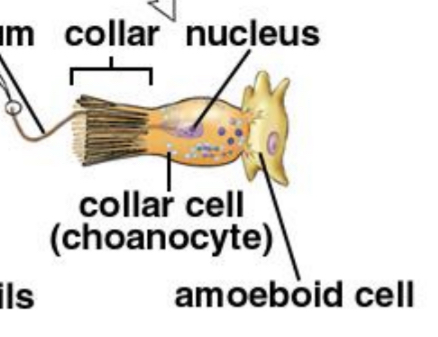
How are choanocytes identified?
Expression of EfAnnexin gene
How are archeocytes identified?
Distinct, morphological characteristics (e.g., enlarged nucleus and cell size)
Location of archeocytes
Mesohyl, a semi-fluid matrix.
Cell required for tissue regeneration in poriferans?
Archeocytes
Definition of phylogeny
Describes the evolutionary relationships between two individual or collection (i.e., classification) of species.
What do the leaves represent in a phylogenetic tree?
Individual organism or species, or collection (i.e., classification) of species.
What do the nodes represent in a phylogenetic tree?
Shared common ancestor between two individual species or two collections (i.e., classification) of species.
What does the root represent in a phylogenetic tree?
The common ancestor shared by all species represented in the phylogenetic tree.
Definition of germline
Cells that contribute to the genetic material of subsequent progeny (i.e., reproductive cells, not somatic cells)
Mutations that occur in somatic cells are [inherited/not inherited] by progeny, while mutation that occur in reproductive cells, such as gametes, are [inherited/not inherited]
Not inherited, inherited.
What are the two methods in which asexual reproduction occur in poriferans?
Fragmentation (e.g., budding), or production of gemmules (i.e., structures filled with dormant archeocytes).
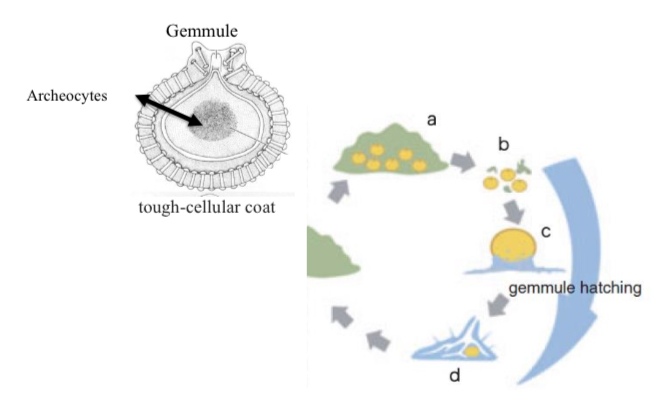
What is the primary method in which sexual reproduction occurs in poriferans?
Choanocytes differentiate into sperm (i.e., male gamete), while archeocytes differentiate into egg (i.e., female gamete), with fertilization occuring in the mesolyl.