Lab 1 - Introduction to Animals (Invertebrate Classification)
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
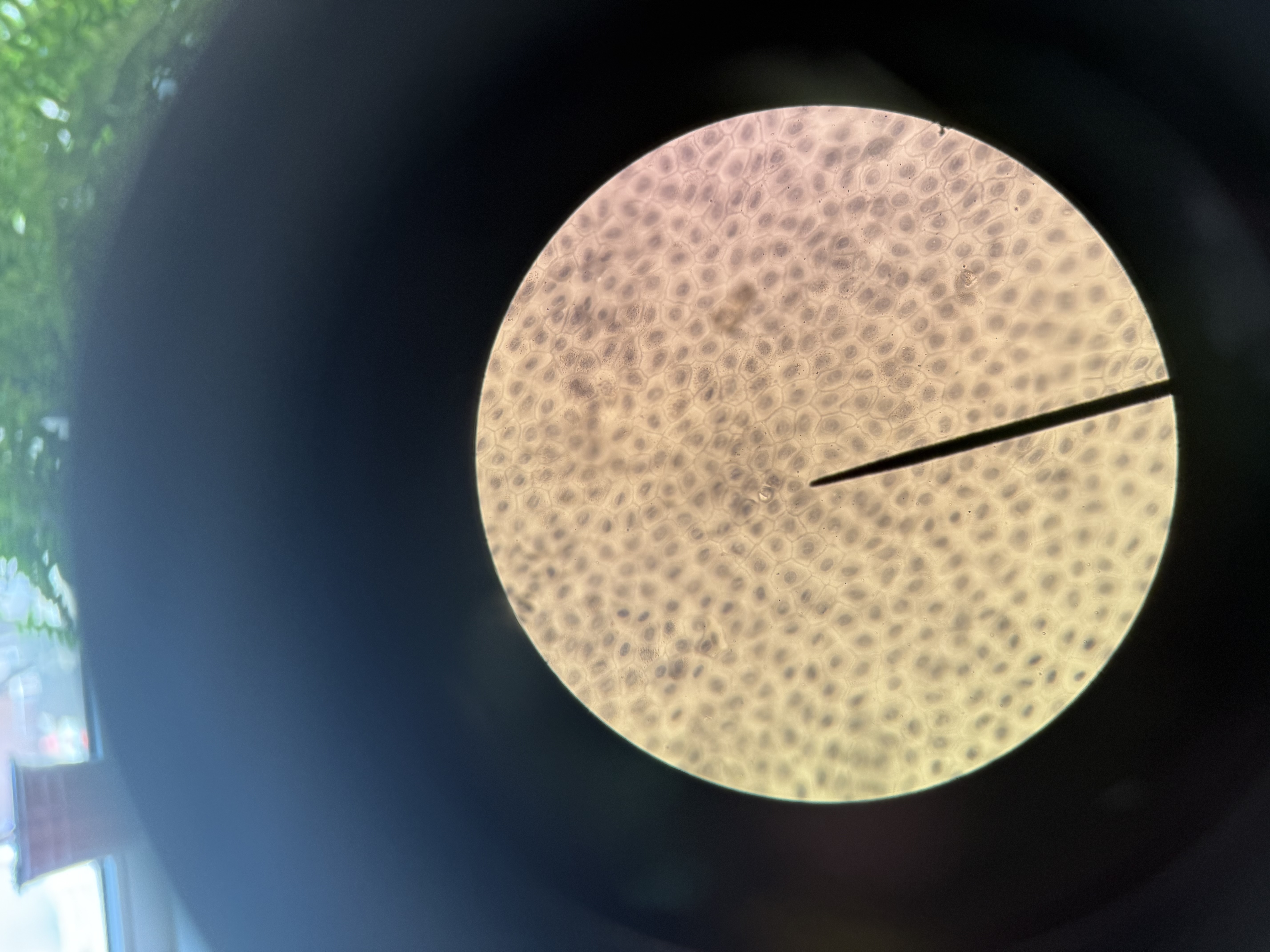
Simple Squamos
Epithelial
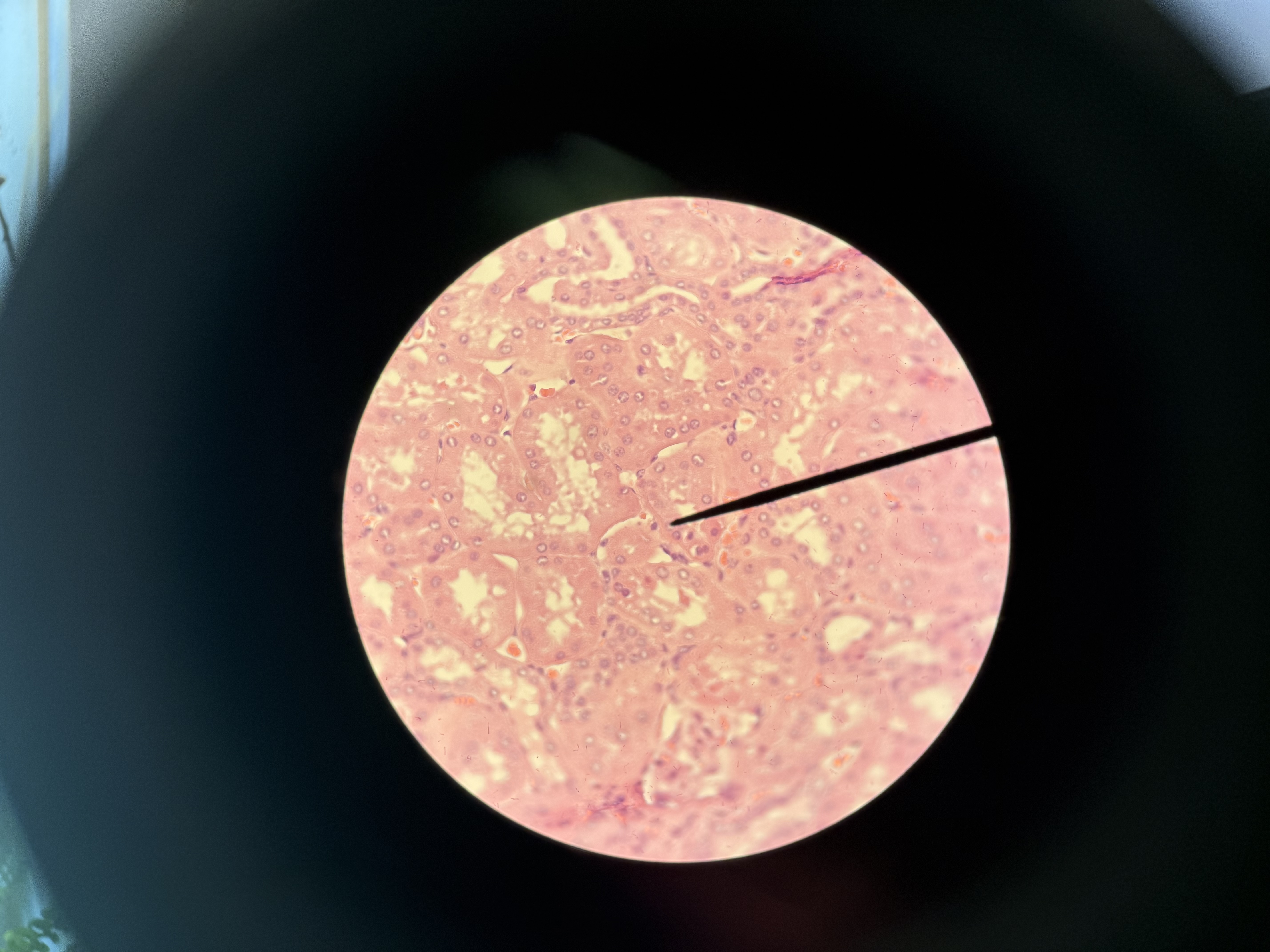
Simple Cuboidal
Epithelial
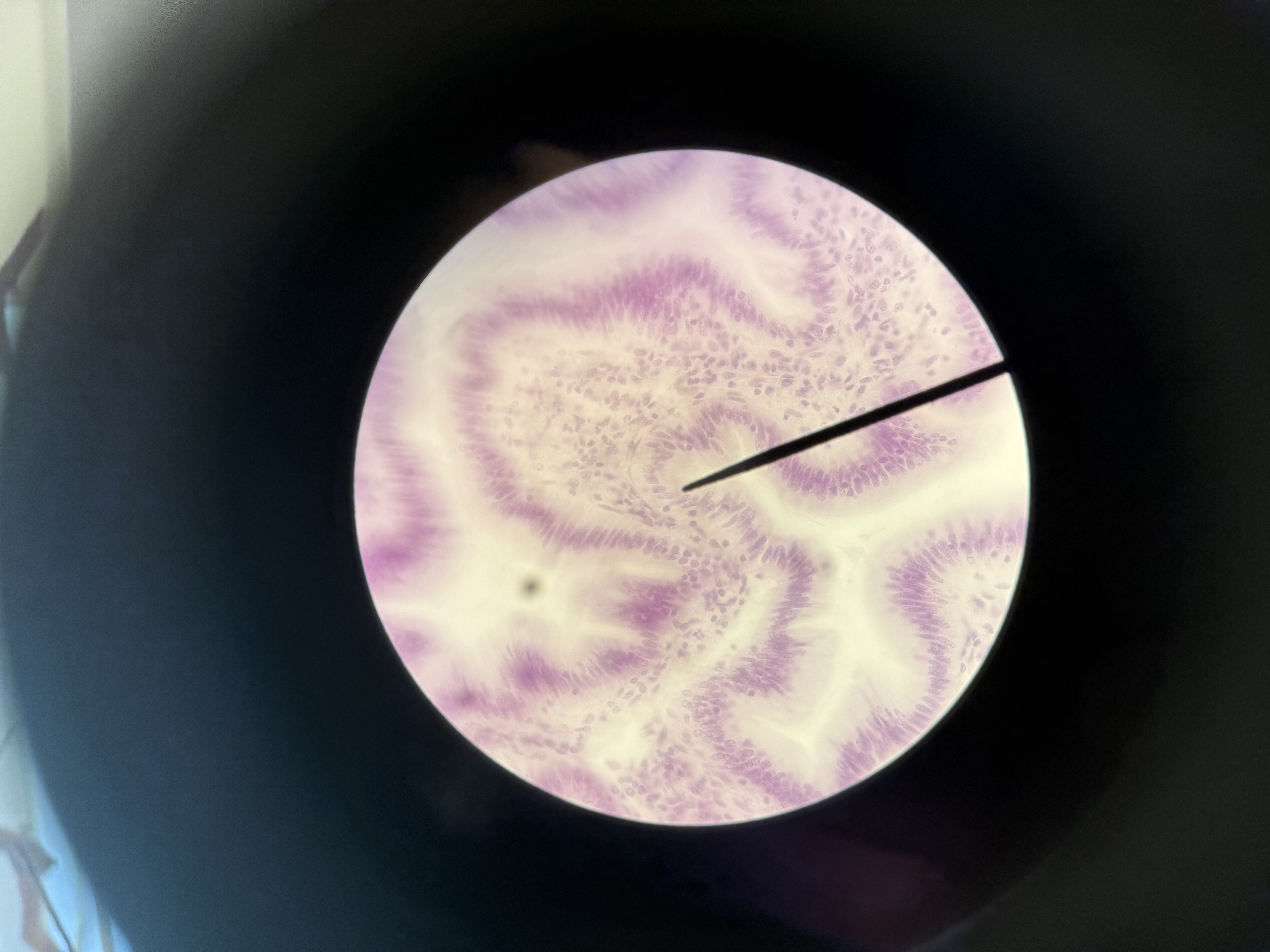
Simple Columnar
Epithelial
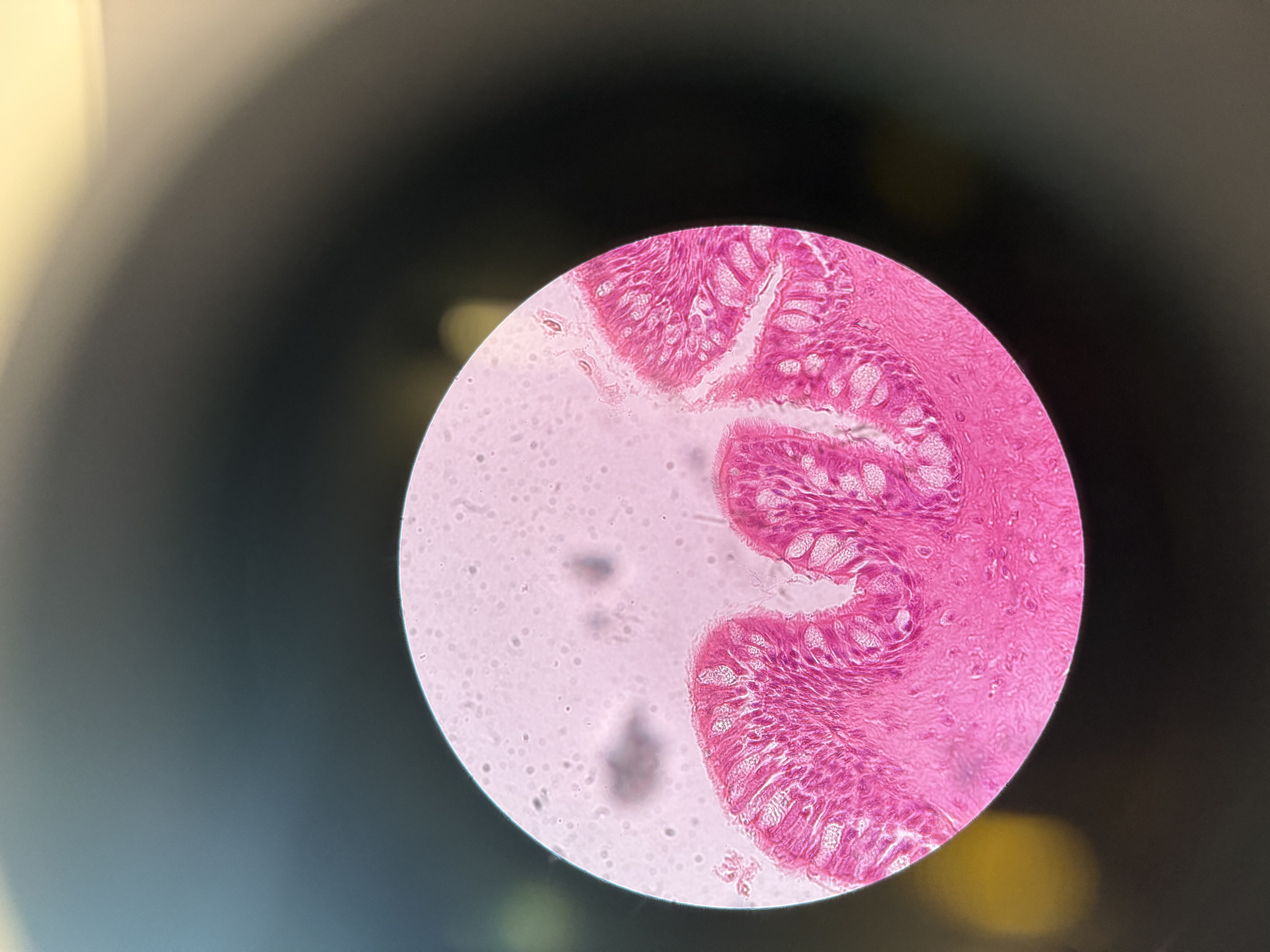
Stratified Columnar
Epithelial
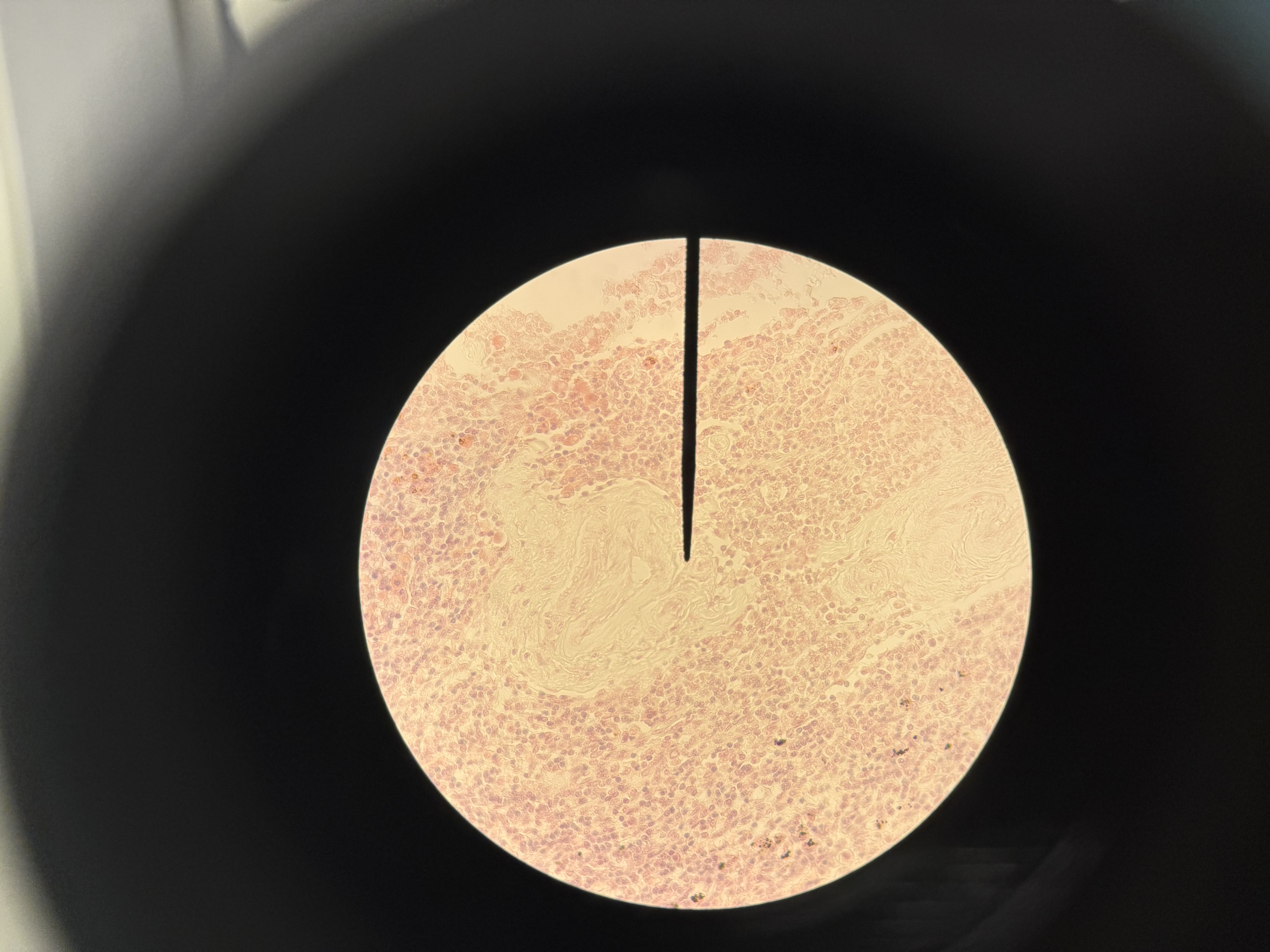
Pseudostratified columnar
Epithelial
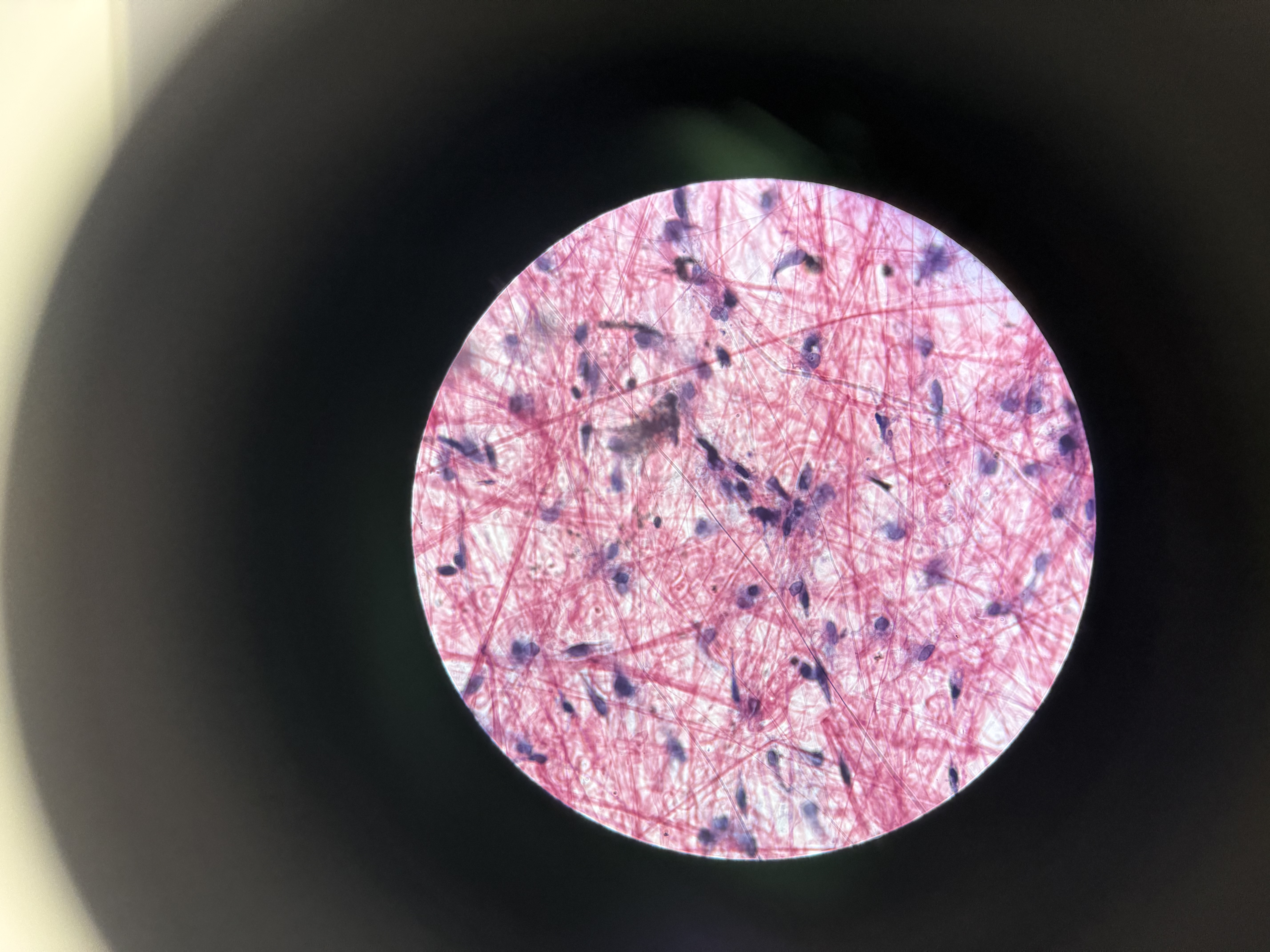
Loose Connective
connective
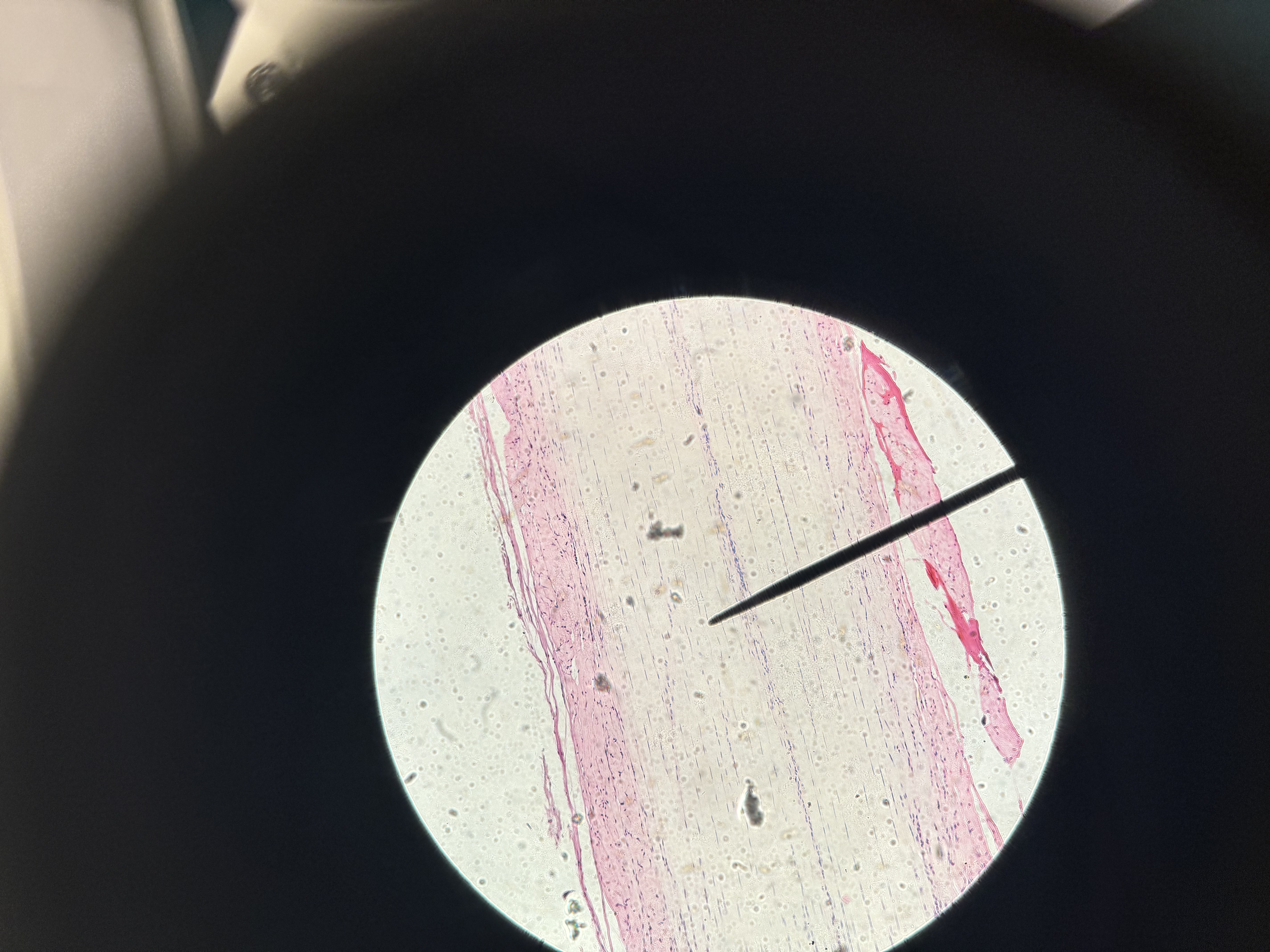
Fibrous connective
connective
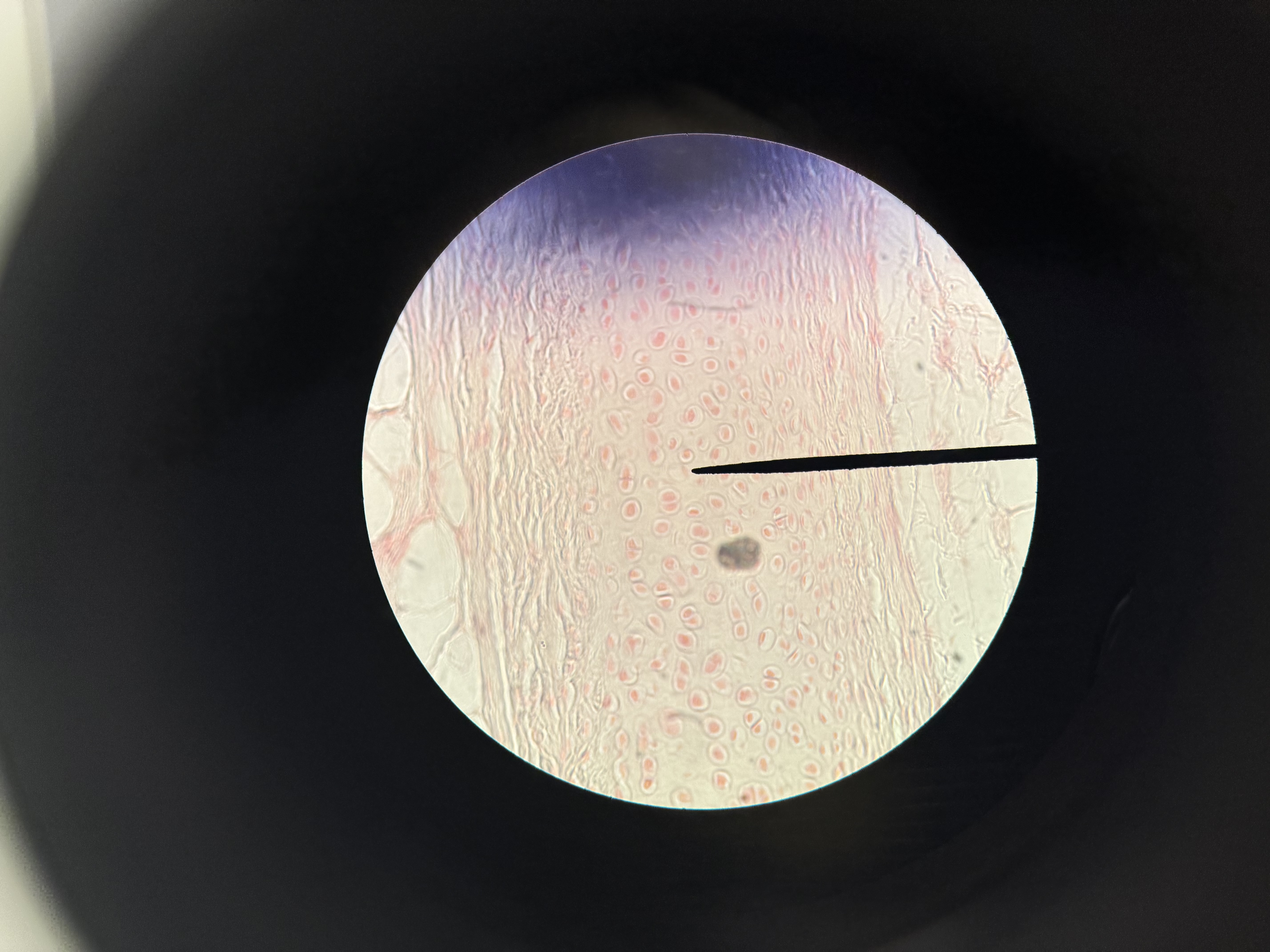
Cartilage
connective
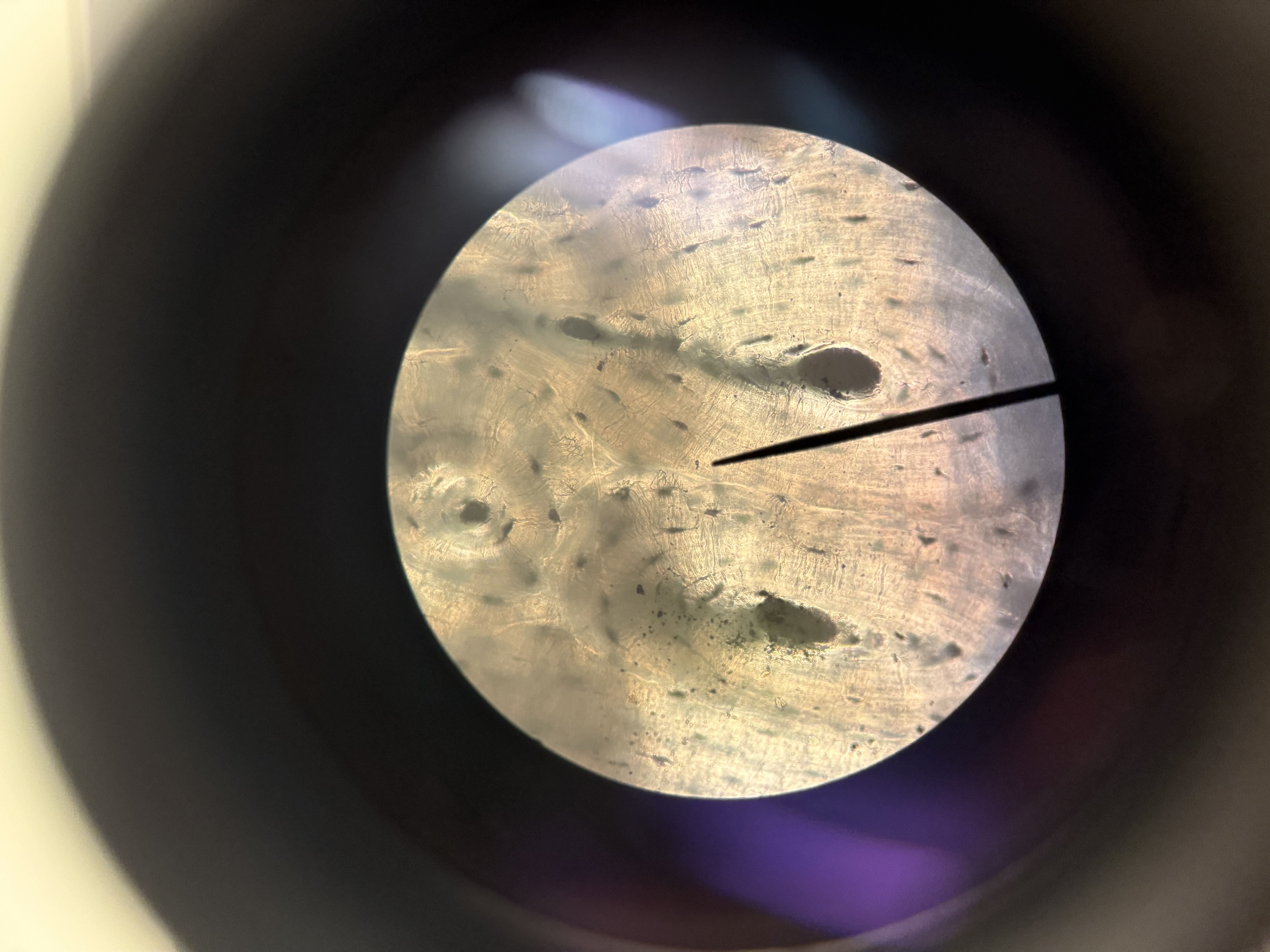
Bone
connective

Adipose
connective
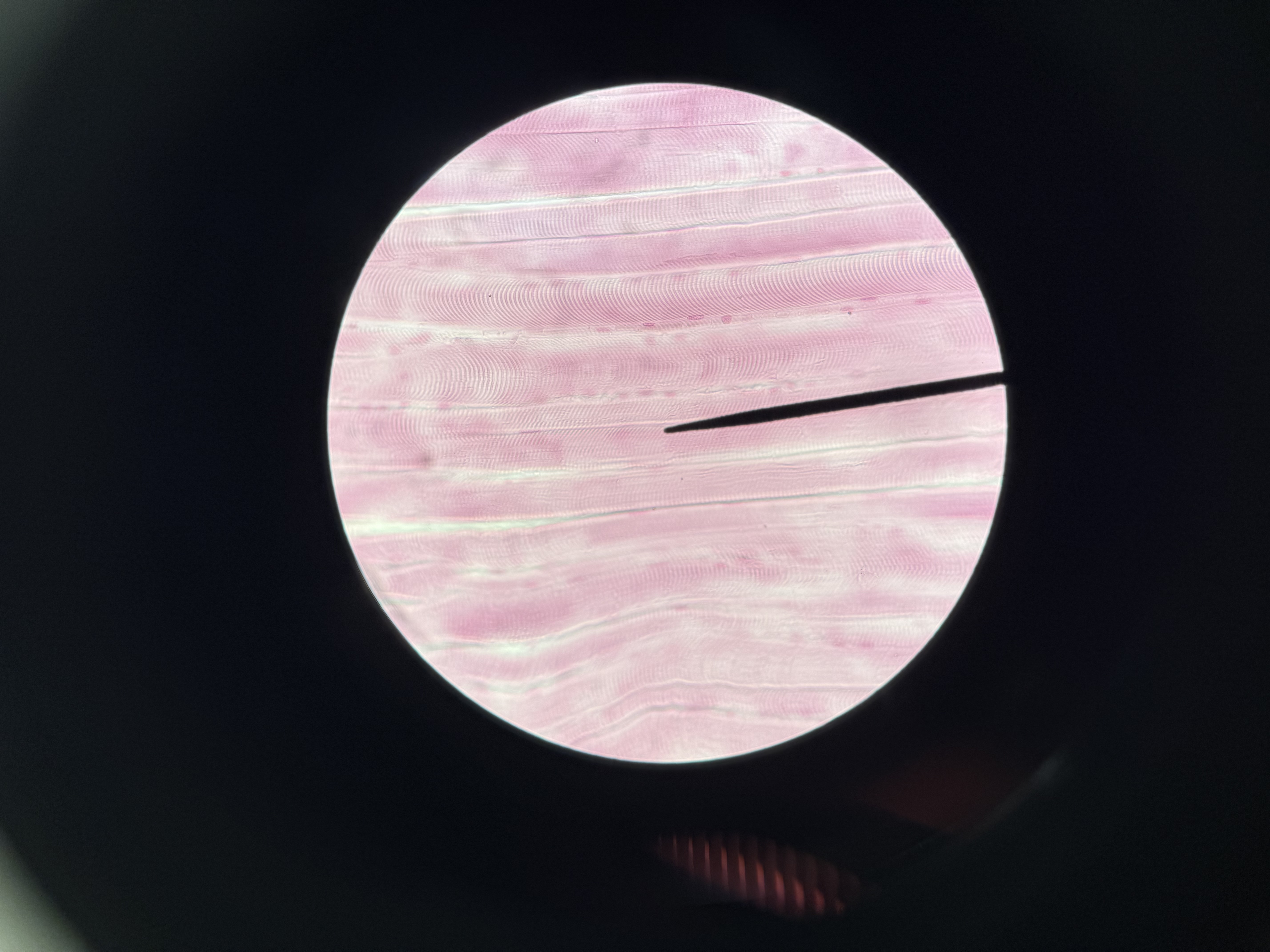
Skeletal muscle
muscle
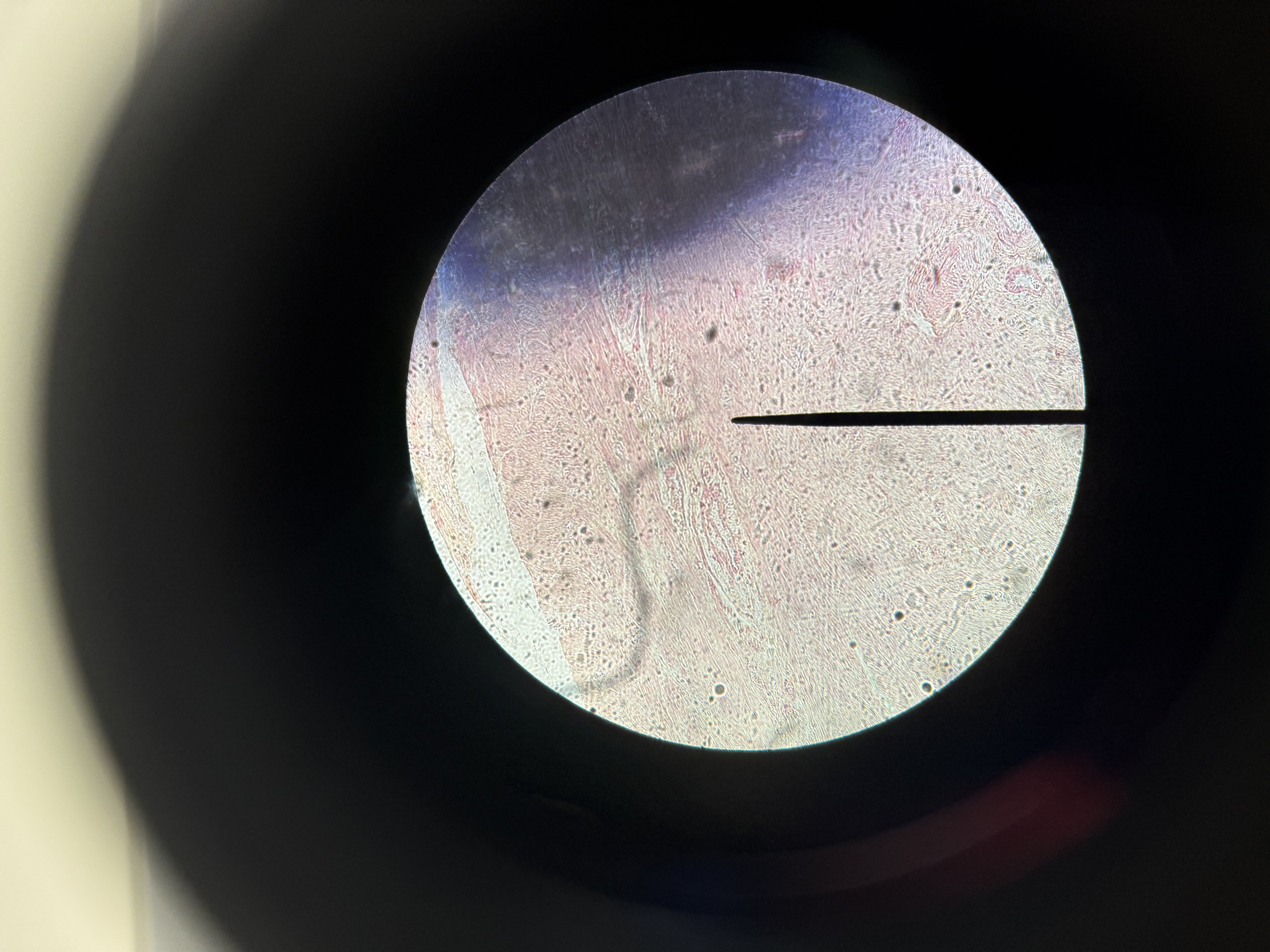
Smooth muscle
muscle
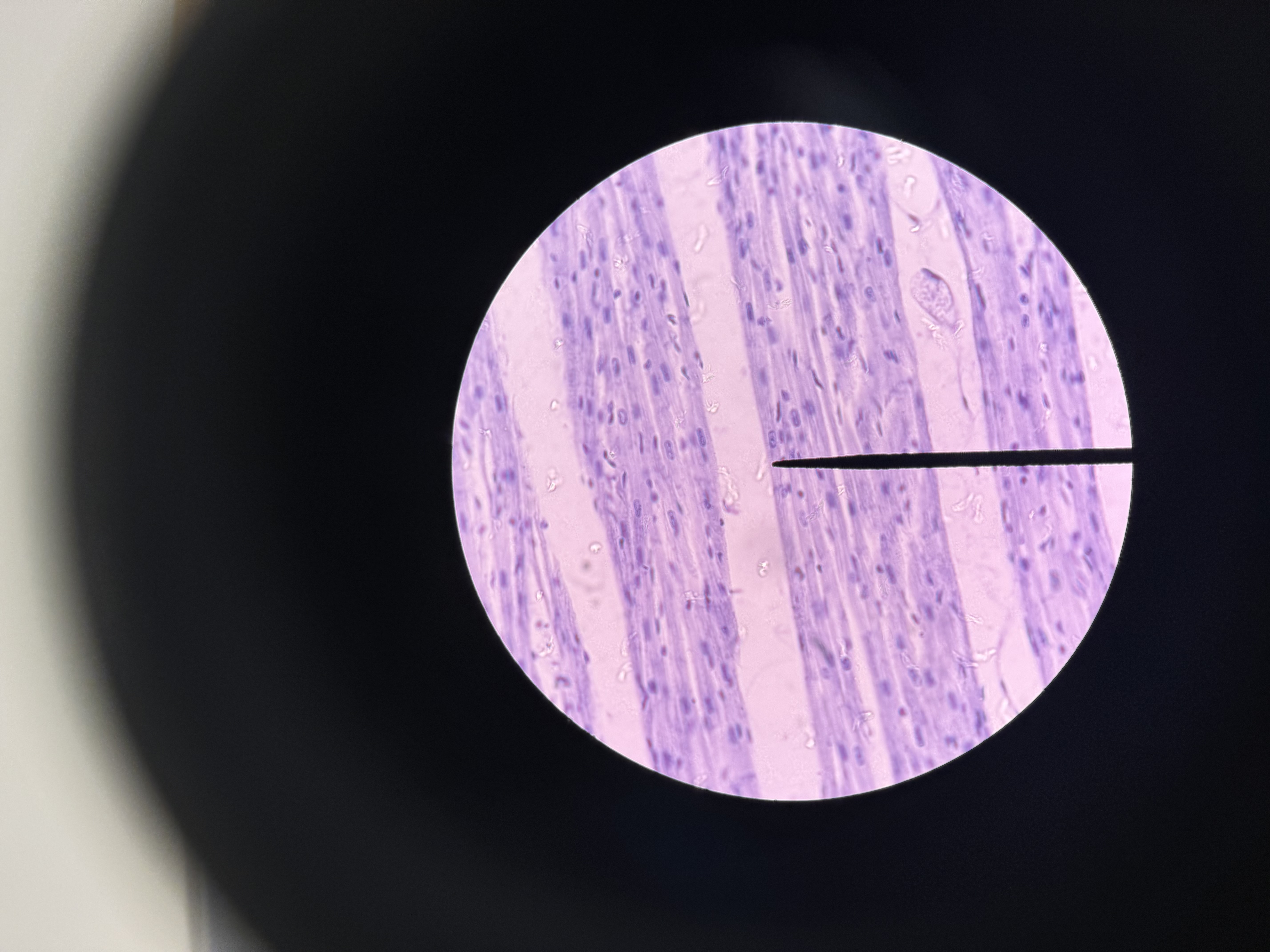
Cardiac muscle
muscle
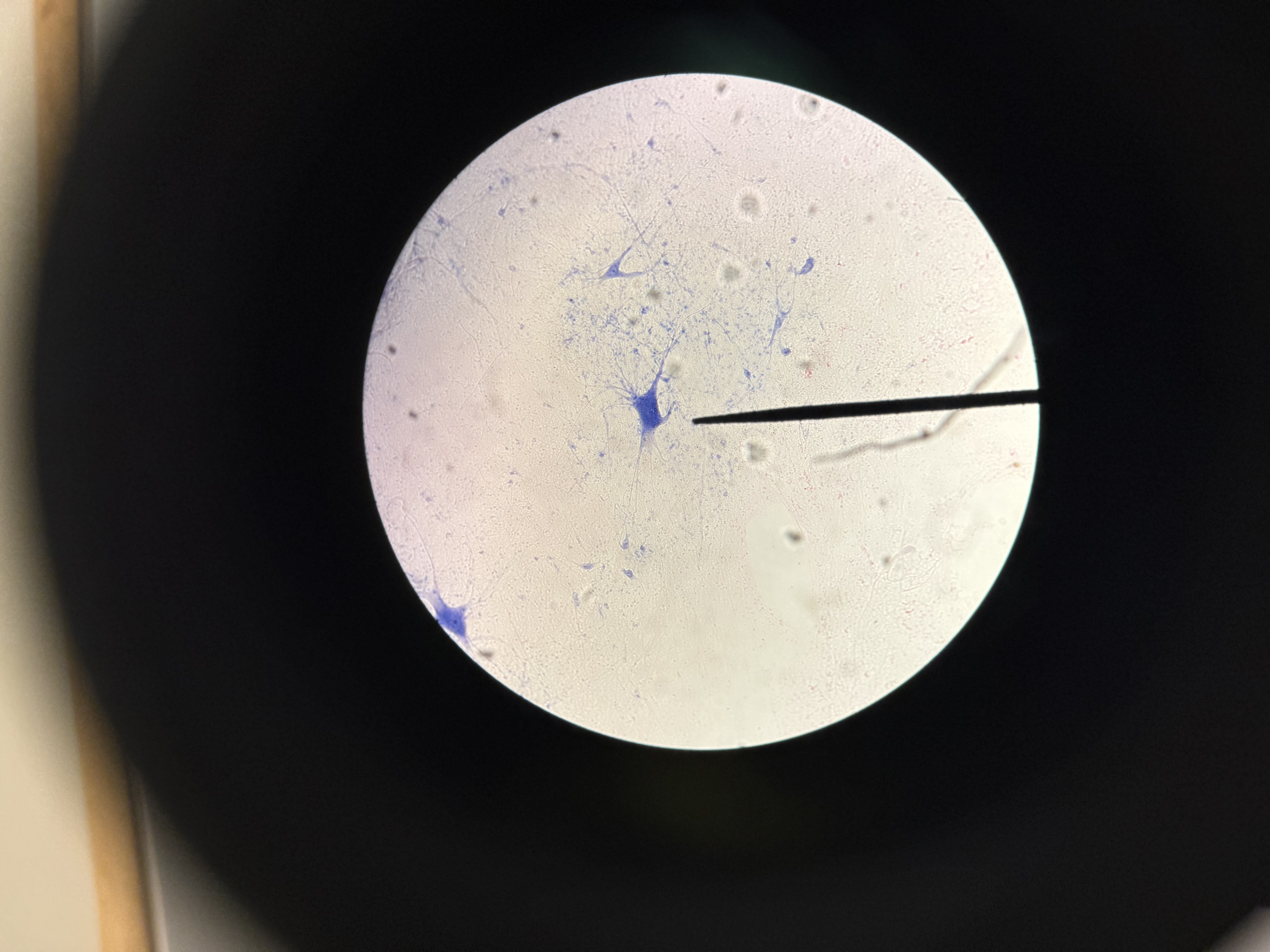
Neuron
Nervous tissue
Phylum: Porifera (Sponges) Characteristics
Loose aggregate of cells, no true tissues
Porifera; “pore bearers”, sponge full of holes
Choanocytes: flagellated cells
Cambrian
How are Phylum: Porifera classifed?
Classified into classes by canal systems and skeletal structures
What is the level of organization of Phylum: Porifera?
cellular level
What type of digestion does Phylum: Porifera have?
intracellular
Phylum: Porifera Asexual Reproduction
Budding or gemmules
Phylum: Porifera Sexual Reproduction
Eggs and Sperm
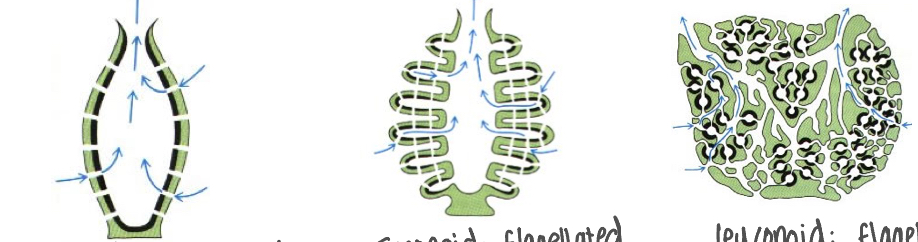
Sponge Body Types
3 Body Types:
Ascnoid: flagellated spongocoel
Syconoid: flagellated canals
Leuconoid: flagellated chambers
What is the name of the central cavity in a sponge?
Phylum: Porifera
Spongocoel: central cavity
What is the name of the large opening at the top of the sponge?
Phylum: Porifera
Osculum: large opening at the top of sponge
Sponge Skeletal Structures
Spicules: made up of calcium carbonate or silica
Spongin: made up of protein
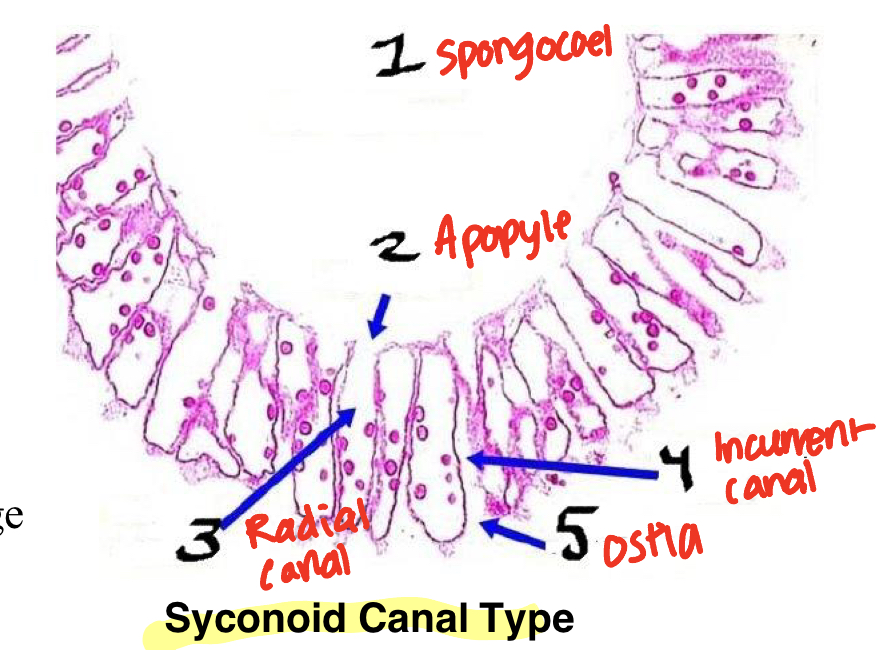
Synconoid Canal Type Structures
Spongocoel
Apopyle
Radial Canal
Incurrent Canal
Ostia
Osculum: at the top, where water comes out
Class Calcarea
Phylum: Porifera
Radially symmetrical vase shaped body types
Colonies of meshwork of thin tubes
Irregular massive forms
Class Calcarea Body Types
Phylum: Porifera
Ascnoid, syconoid, leuconoid
Class Calcarea Skeletal Structure
Phylum: Porifera
Calcium carbonate spicules
Class Hexactinellidae Body Types
Phylum: Porifera
Glass sponges
Syconoid, leuconoid

Class Hexactinellidae Skeletal Type
Phylum: Porifera
6 sided silica spicules

Class Demospongiae Body Type
Phylum: Porifera
Makes up 81% of this phylum
Bath sponges (most important)
Leuconoid

Class Demospongiae Skeletal type
Phylum: Porifera
Silica spicules and/or spongin

Phylum: Cnidara
Radial symmetry
Tissue level organization
580 MYA precambrian
How many tissue layers in Phylum: Cnidara?
Diploblastic: ectoderm (outer) and endoderm (inner) separated by mesoglea (2 tissue layers)
What body forms found in Phylum: Cnidara?
Polyp and medusa
What is the central cavity name of Phylum: Cnidara?
Gastrovascular cavity
What is the name of stinging capsule of Phylum: Cnidara?
Nematocysts: stinging cells used for protections and to capture prey
Class Hydrozoa Body Types
Phylum: Cnidaria
Polyp and medusa stage
What is the shelf seen on medusa Class Hydrozoa?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Velum
How are polyps arranged in Class Hydrozoa?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Polyps are colonial
What body form does Class: Hydrozoa Hydra posses?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Polyp form
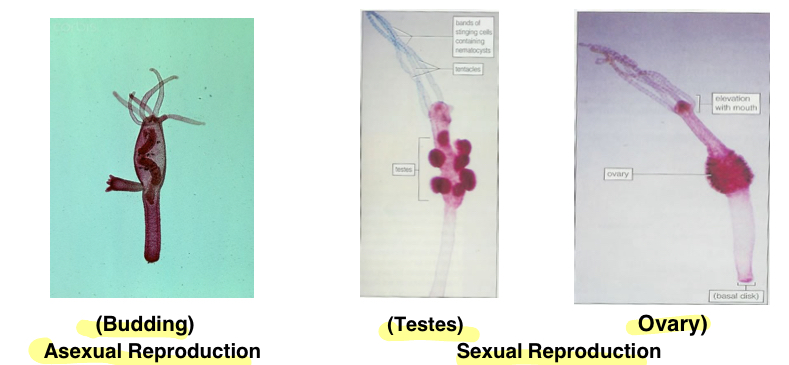
How does Class: Hydrozoa Hydra reproduce
Phylum: Cnidaria
Asexually: by budding
Sexually; have both males/females with testes and ovaries
Know 3 structures:
Budding
Testes
Ovary
Why are Class: Hydrozoa Hydra interesting to biologists? Their diet?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Have regenerative ability
Diet: aquatic invertebrates
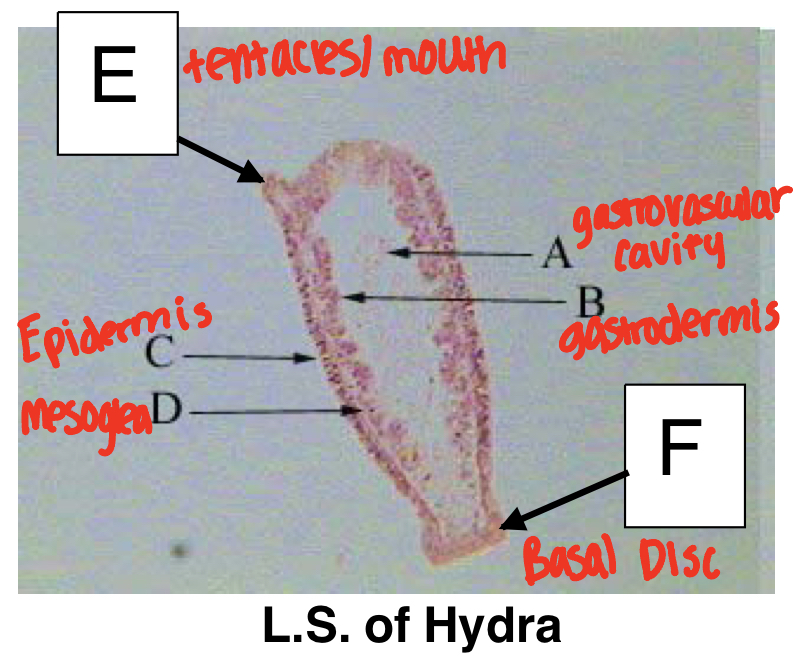
Class: Hydrozoa Hydra Structures
Phylum: Cnidaria
Tentacles/mouth
gastrovascular cavity
epidermis
mesoglea
gastrodermis
basal disk
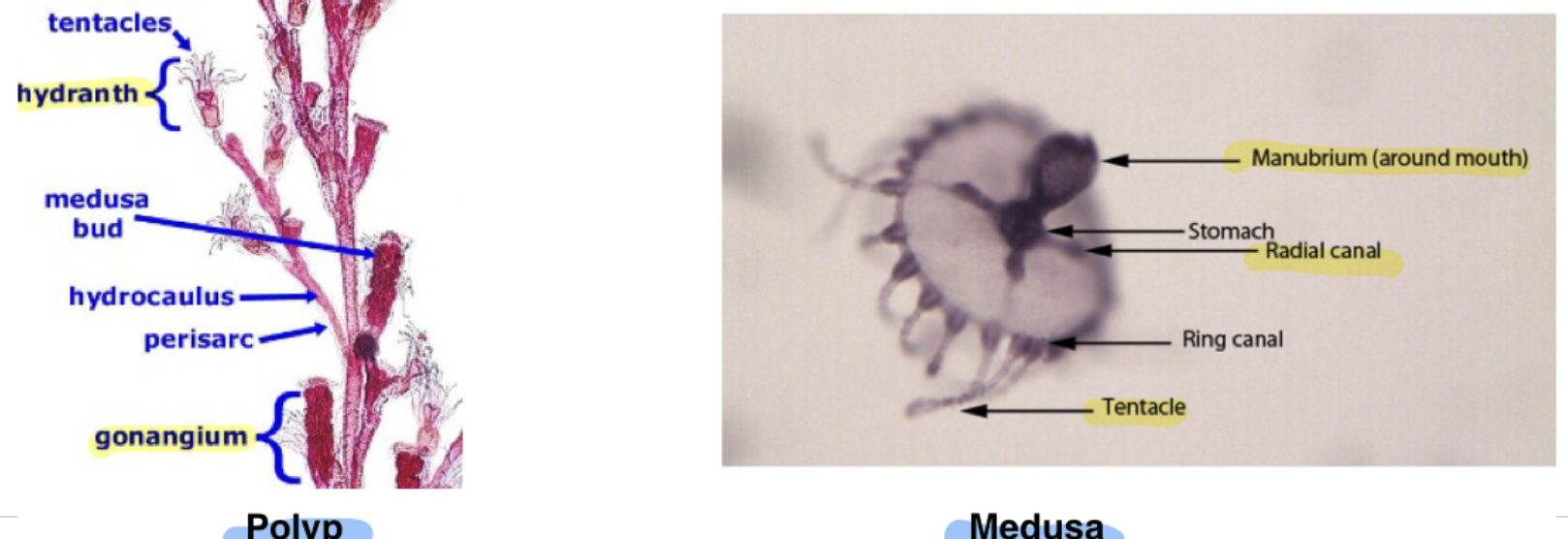
What body form do Class: Hydrozoa Obelia have?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Body form: polyp and medusa stages
What is the specialized structure Obelia use for feeding? Reproduction?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Hydranth: specialized structure for feeding
Gonagium; reproduction
Class: Hydrozoa Obelia Diet
Phylum: Cnidaria
Zooplankton, worms, crustaceans
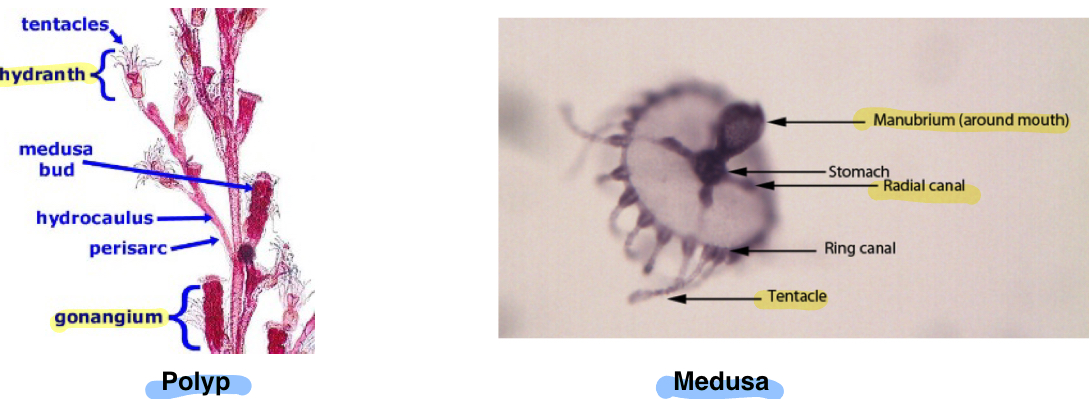
Class: Hydrozoa Obelia Structures
Phylum: Cnidara
Medusa
Manubrium (around mouth)
Gonads
Radial Canal
Tentacles
Polyp
Hydranth
Gonangium
Basal disc
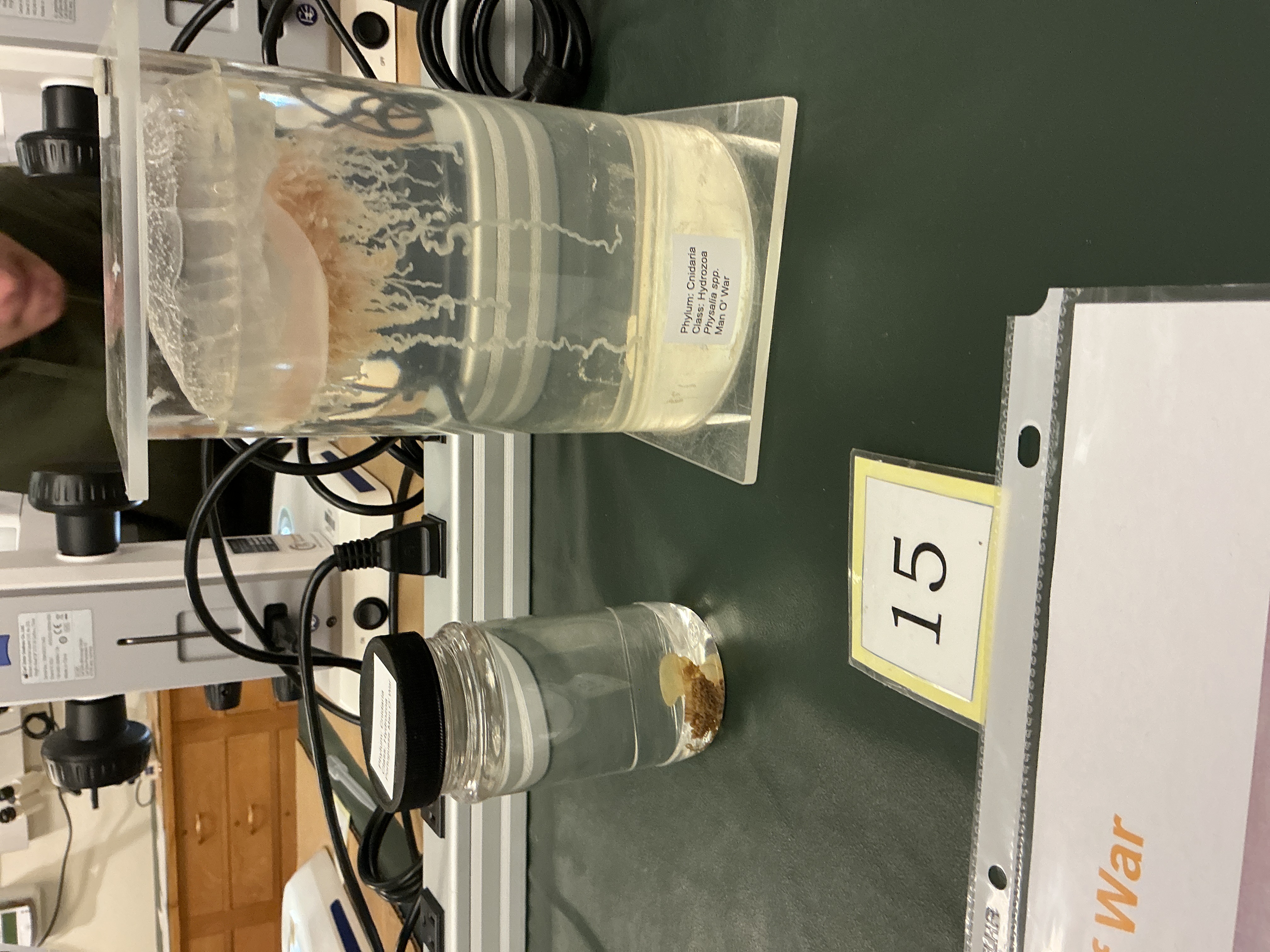
What is the body form of Portuguese Man of War ?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Siphonophore: made up of zooids
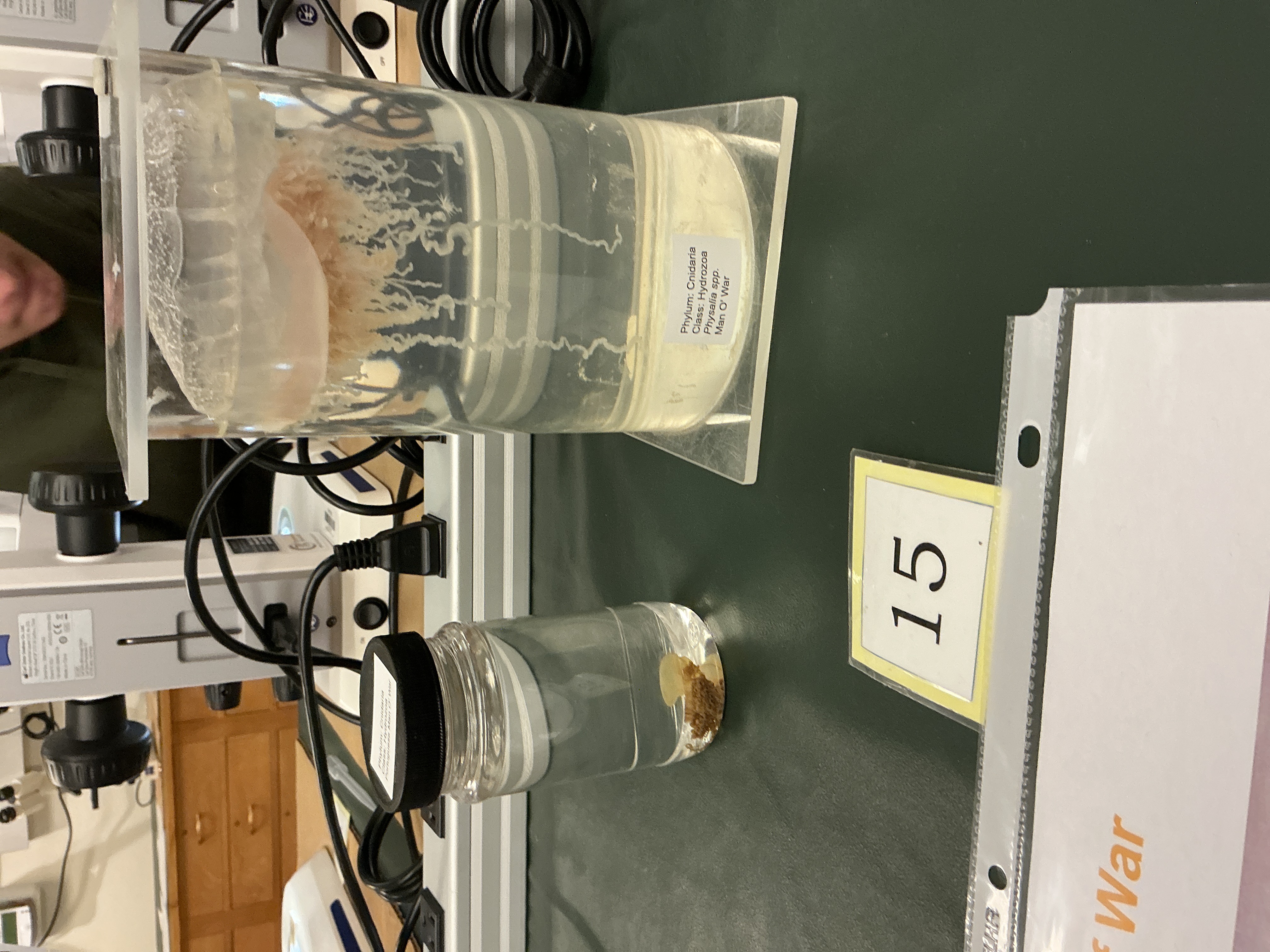

What is the specialized structure used as a float in Portuguese Man of War ?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Pneumatophore: specialized structure used as float

What do stings of Portuguese Man of War cause?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Stings cause severe pain; whiplike, red welts on skin lasting 2-3 days but pain should go away in hours
Portuguese Man of War Diet
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Diet: small fish, plankton, crustaceans
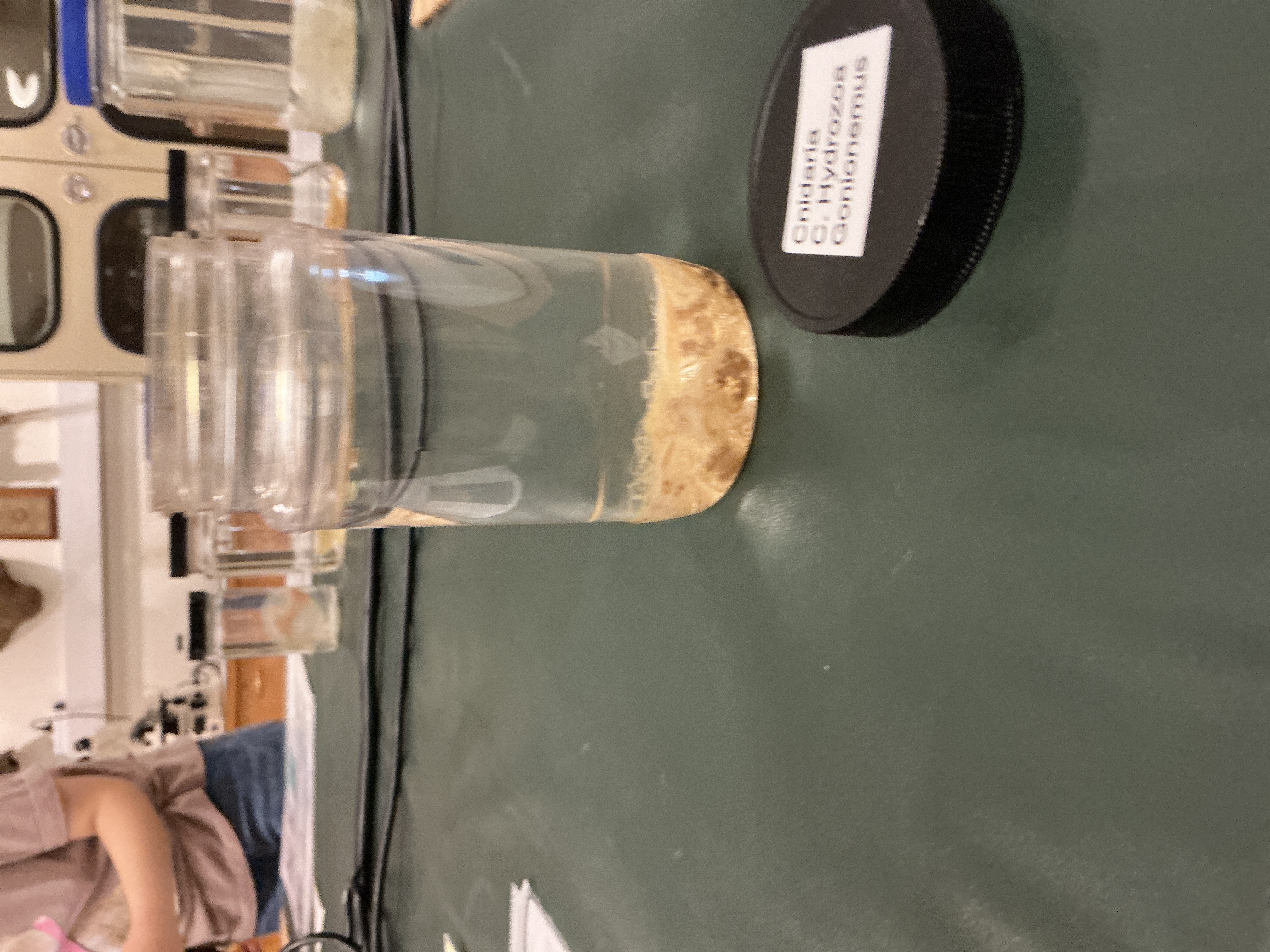
What is the body form of Gonionemus?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Clinging Jelly
Small jelly; colorful gonads, tentacles bent on ends, manubrium

Gonionemus Diet
Phylum: Cnidara
Class: Hydrozoa
Diet: small fish and zooplankton

How are Moon Jellies different from Class Hydrozoa
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class Scyphozoa
True jellies
Medusa different from Class hydrozoa; lack a vellum
How are Moon Jellies recognized?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Recognized by its 4 horseshoe shaped gonads

What are Moon Jellies only capable of when swimming?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Swimming; only limited motion and drifts with the current

Moon Jellies Diet
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Diet: medusae, plankton, mollusks
How is Class Anthozoa different from other cnidarians?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Anthozoa; “flower animal”
Don’t have medusa stage in development

How are is Class Anthozoa grouped?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Solitary or found in large colonies

What body shape do Class Anthozoa (Sea Anemones) have?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Body shape: coral disc at top and pedal disc at the bottom
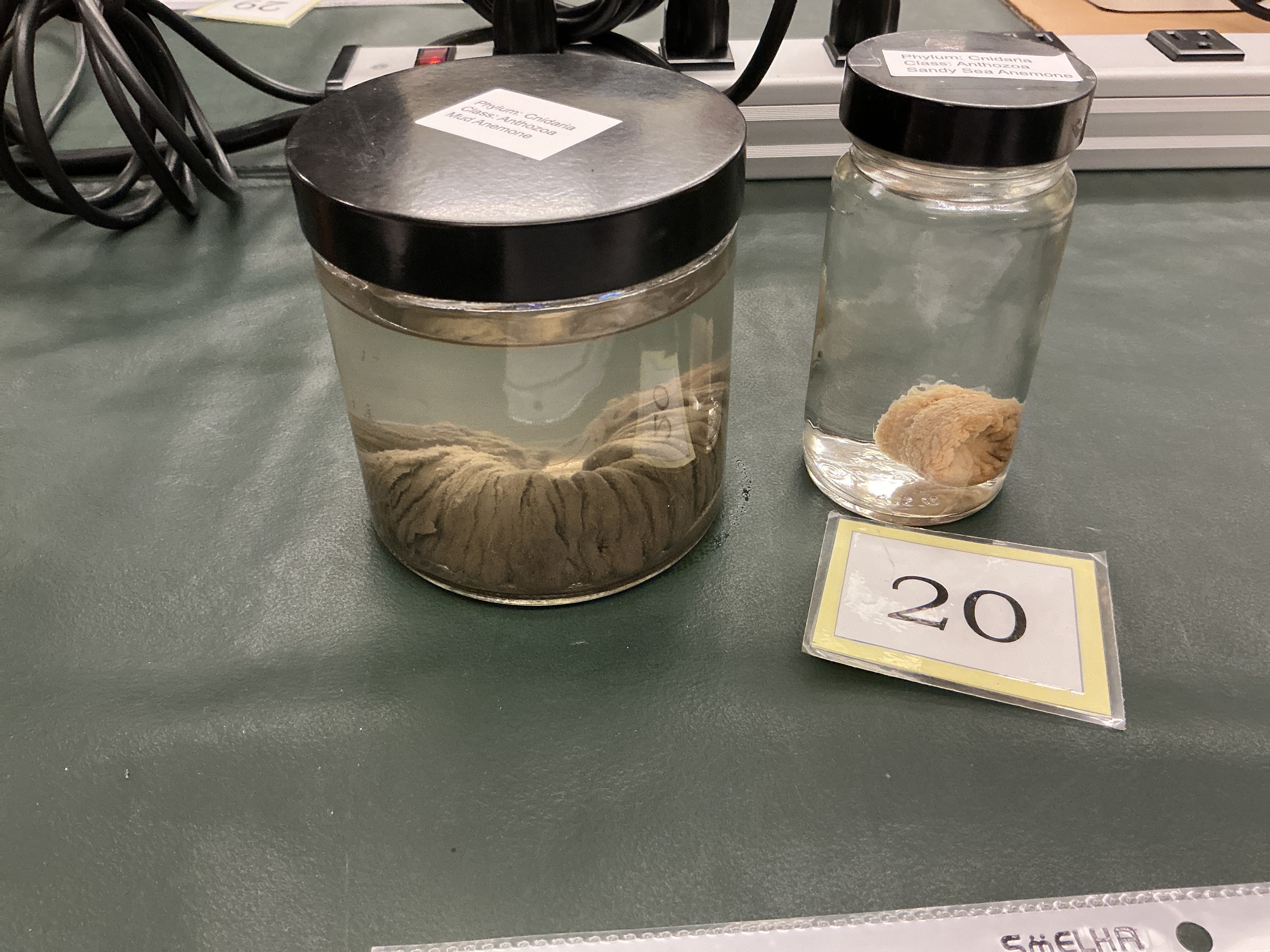

Class Anthozoa (Sea Anemones) Color
Phylum: Cnidaria
Color: green to light yellowish, and gray color

Class Anthozoa (Sea Anemones) Diet
Phylum: Cnidara
Diet: small fish, snails, limpets, crabs
What is the coral group of Coral?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa
Coral group: colony of myriad genetically identical polyps
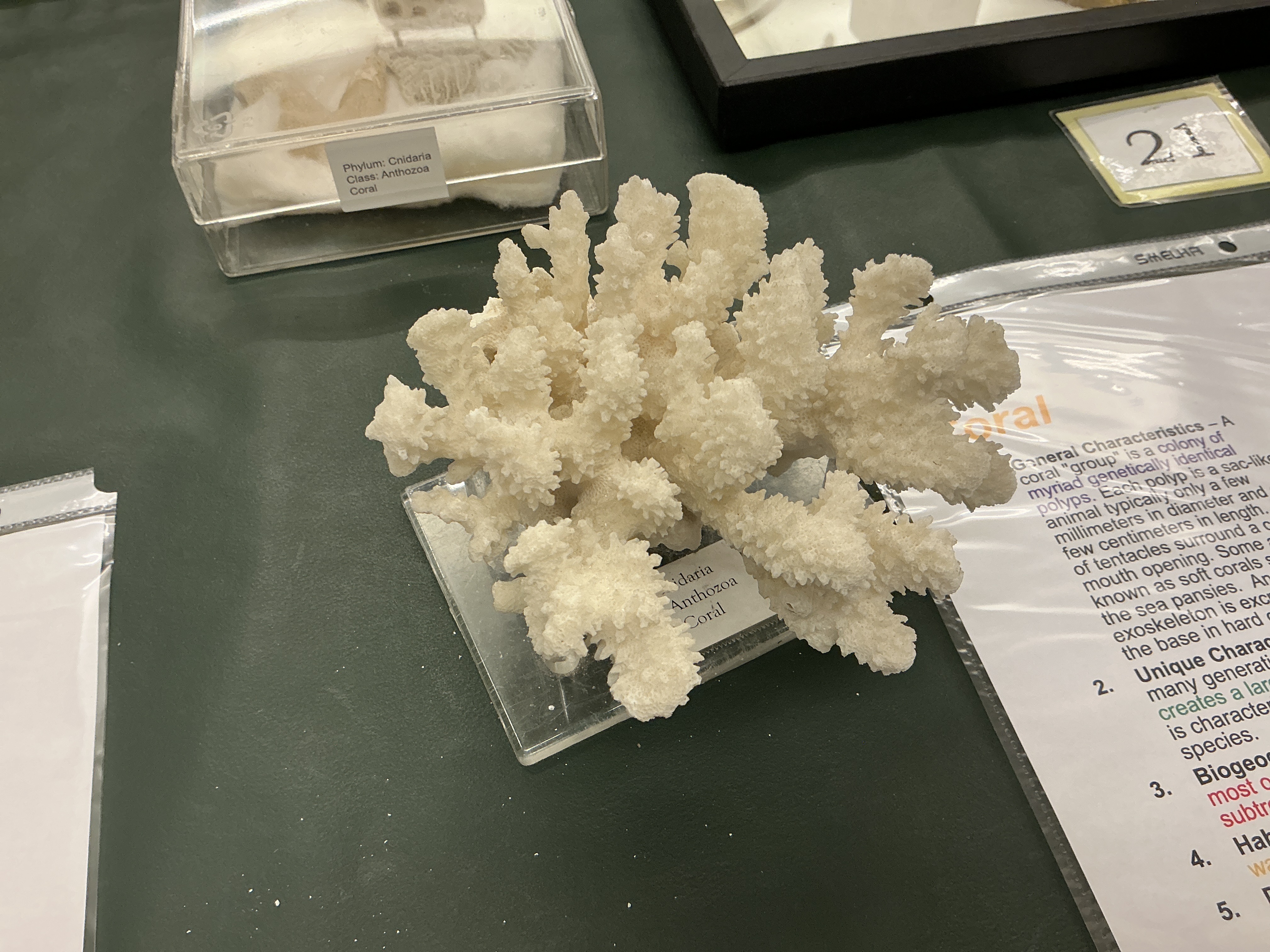

What does Coral create over generations?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa
Colonies create a large exoskeleton
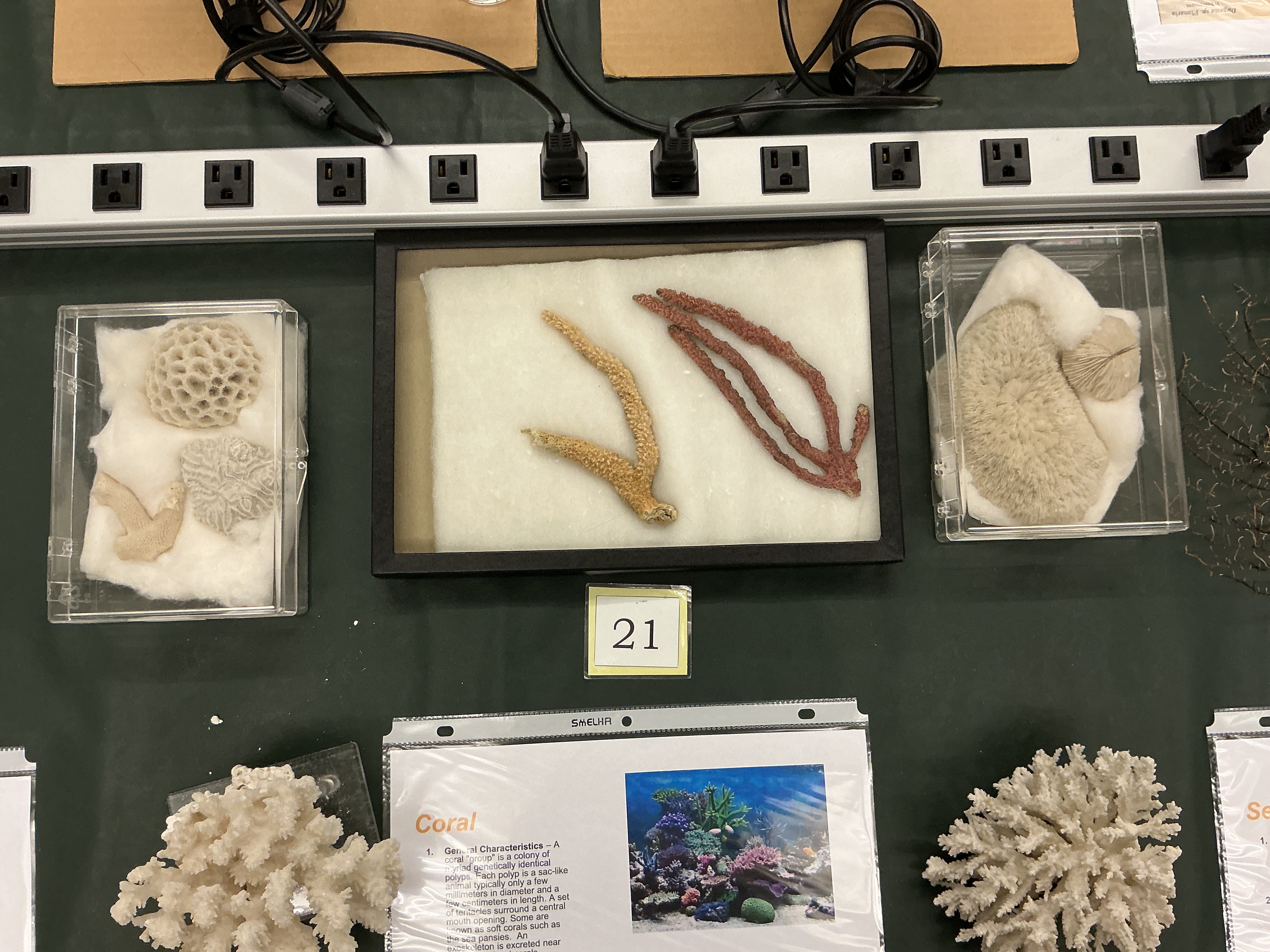

Coral Diet
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa
Diet: small fish, plankton, zooanthellae
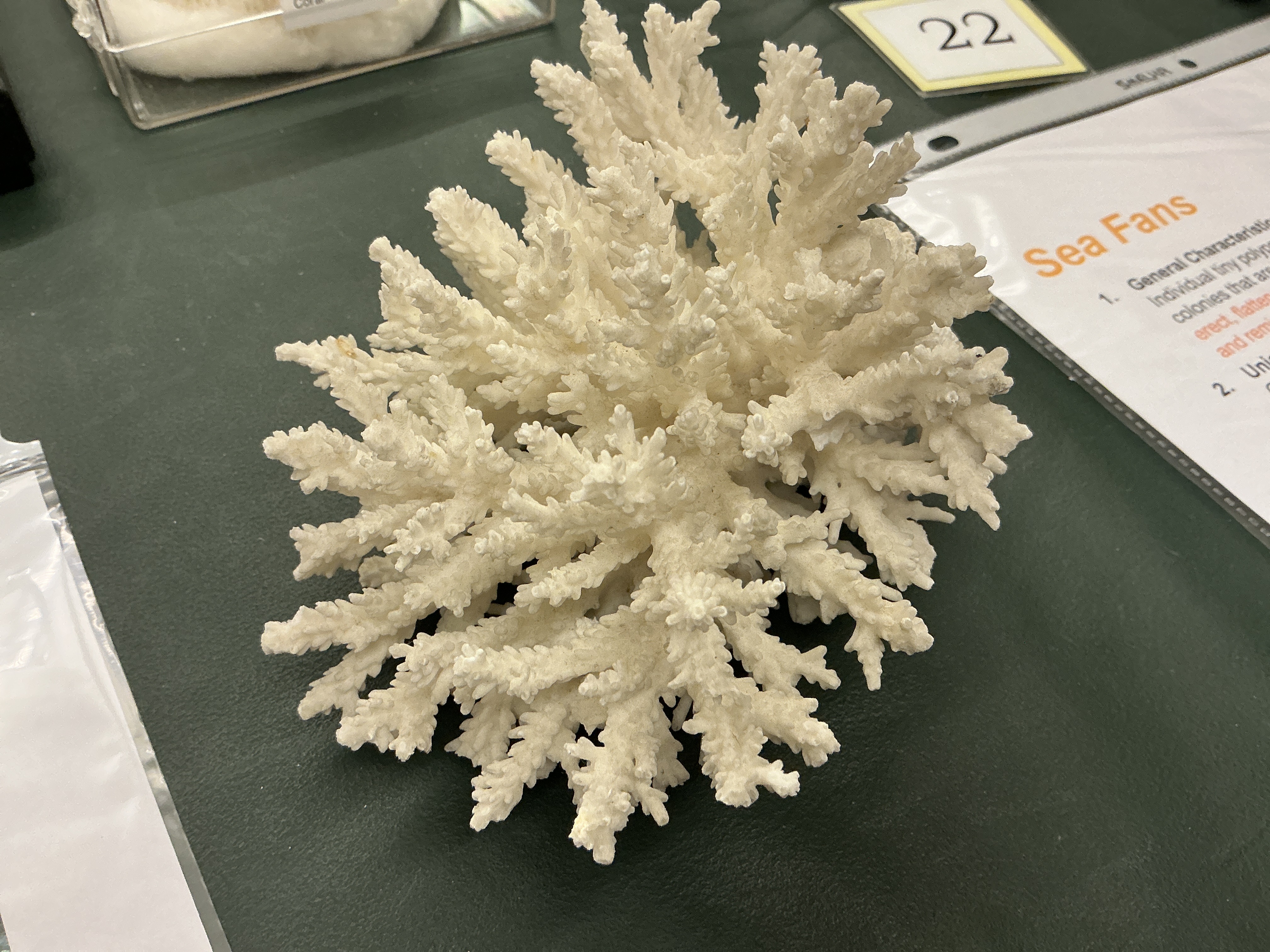

What is the structure of the polyps in Sea Fans?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa
Form colonies that are erect, flattened, branching, and similar to a fan
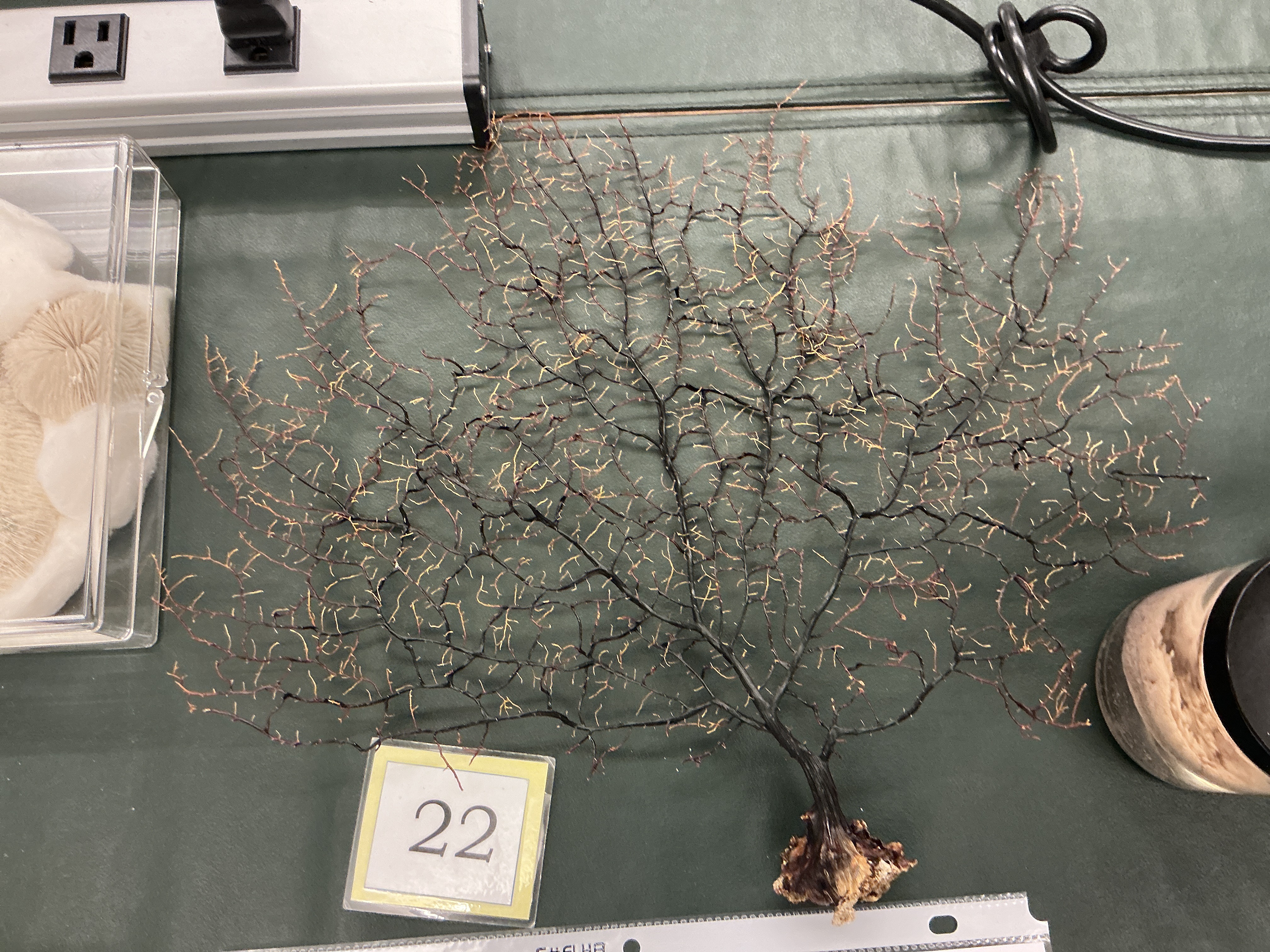

What chemical found in Sea Fans?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa
Chemical: diterpenes for protection and candidates for new drugs
Diet: plankton
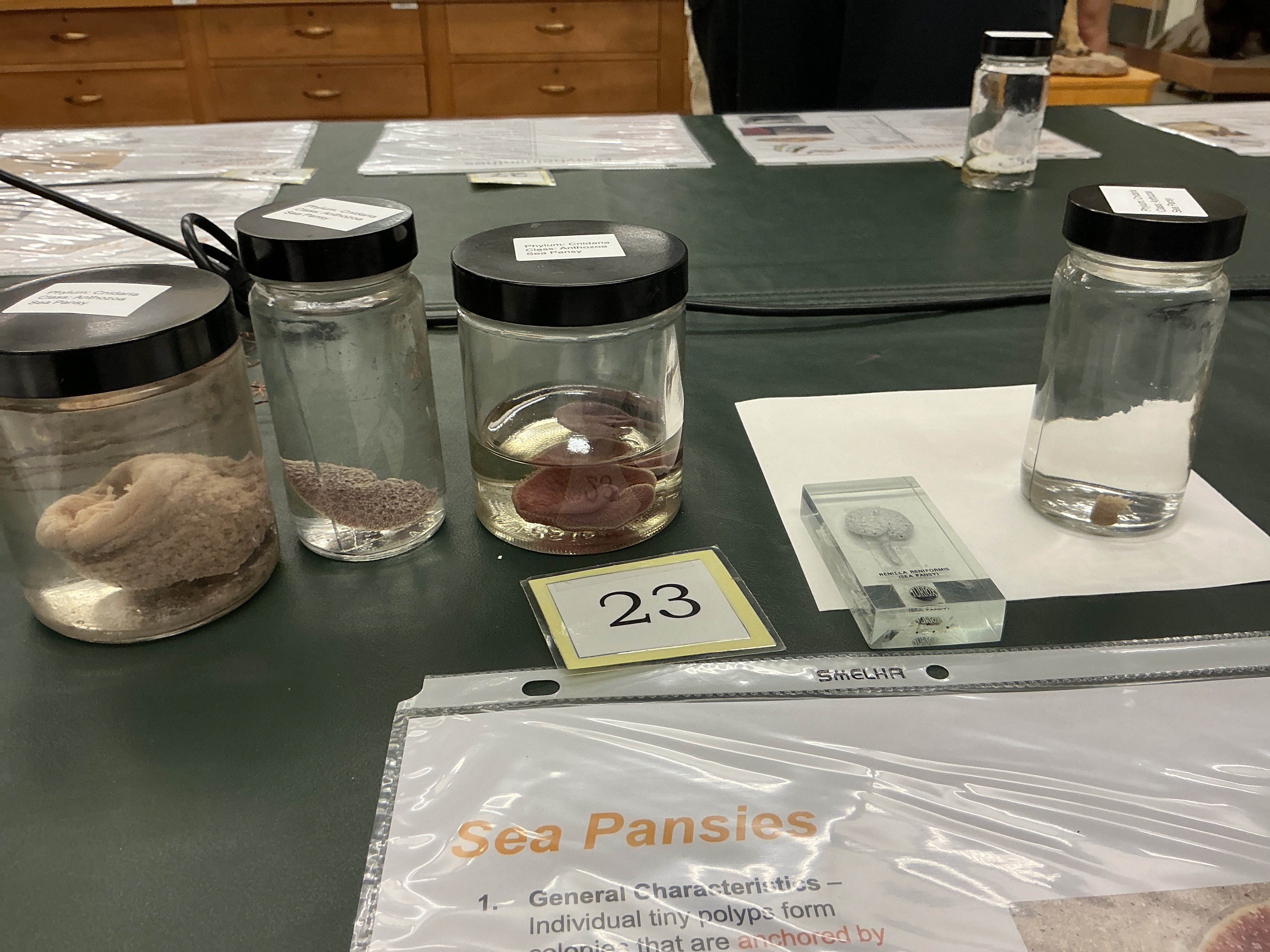
Sea Pansies
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Anthozoa

Phylum: Ctenophora
Radial Symmetry separates them from other animals
Tissue level of organization
Ctenophora; “comb-bearer”
510 MYA cambrian
Phylum: Ctenophora Body Plan
Body plan: sac surrounds gastrovascular cavity
How does Phylum: Ctenophora differ from Cnidarians?
Have radial symmetry
Comb plates with cilia
Colloblasts to capture prey
What are Phylum: Ctenophora known for?
Largest animals to move by cilia found on combs
What evidence proves protosome animals in Lophotrochozoans (Clade) are monophyletic?
Molecular evidence (rRNA)
What phyla belong to Clade Lophotrochozoans?
Platyhleminthes
Rotifera
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Nemertea
Mollusca
Annelida
What two main groups within Lophotrochozoans?
Trochozoans: larvae form with a ring of cilia around its middle
Lophophorates: horse shoe shaped structure covered with ciliated tentacles
What is the characteristic responsible for the branching off Phylum: Platyhelminthes from other animals?
Clade: Lophotrochozoans
Acoelomates: no space between gastrovascular cavity and muscles
1st to demonstrate bilateral symmetry

Phylum: Platyhelminthes Level of Organization
Organ system level of organization
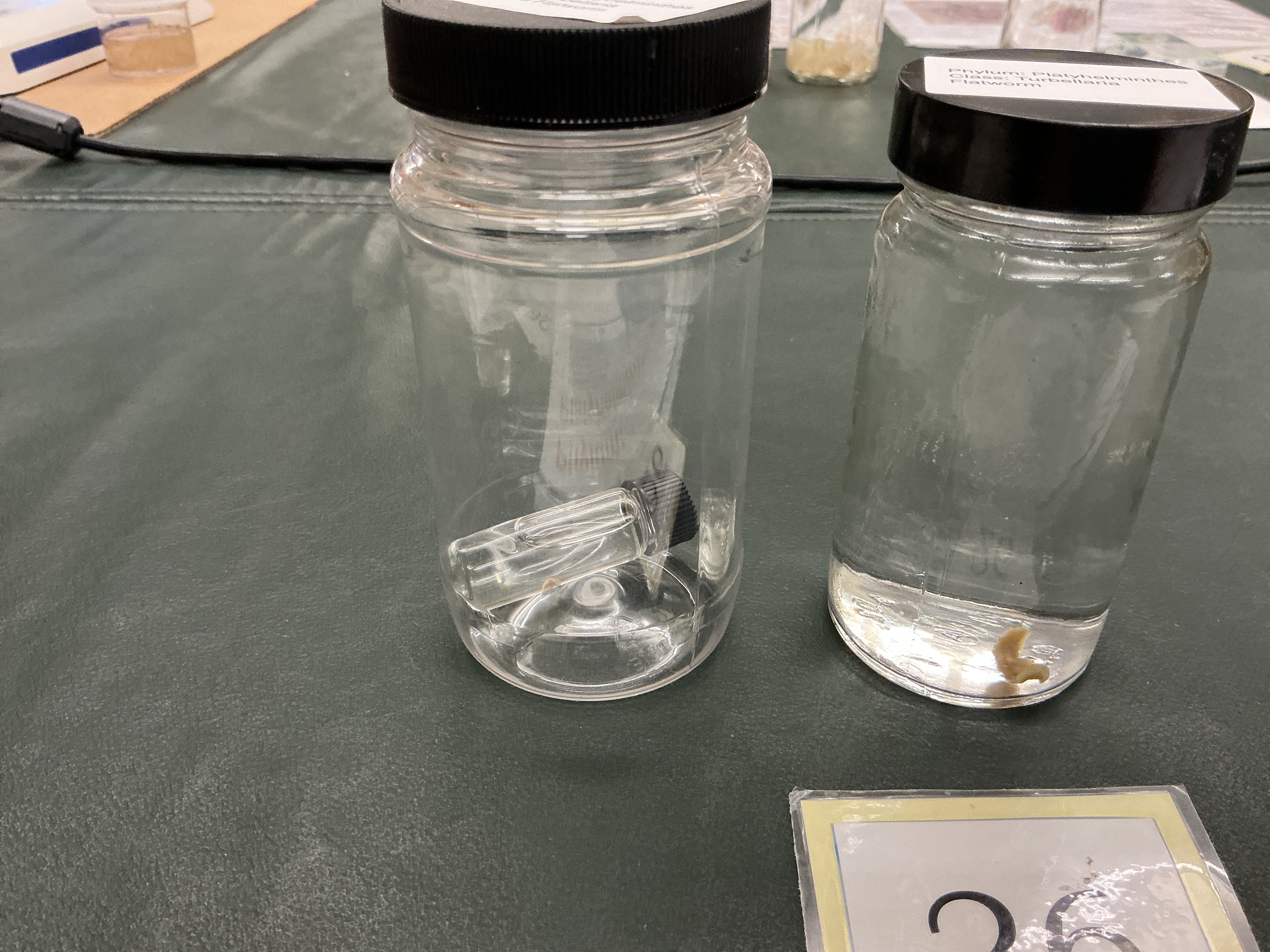

How many tissues found in Phylum: Platyhelminthes?
Triploblastic: outer epidermis and inner endodermis separated by 3rd layer of mesodermis
What type of digestive system found in Phylum: Platyhelminthes?
Gastrovascular cavity
Extra and intracellular
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Reproduction
Asexual; regeneration
Sexual; gametes, monoecious
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Nervous System
Pair of anterior ganglia with longitudinal nerve cords
Phylum: Playhelminthes Excretory System
Protonephridia (flame cells)
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Body Cavity
Acoelomate
What is Class Turbellarians - Flatworms known for?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Regenerative skills
What is the name of the eyespots and function in Class Turbellarians Planaria?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Ocelli (eyespots): used for light detection
What is the name of bumps on side of head for Planaria?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class Turbellarians
Auricles (bump on side of head): chemical detectors
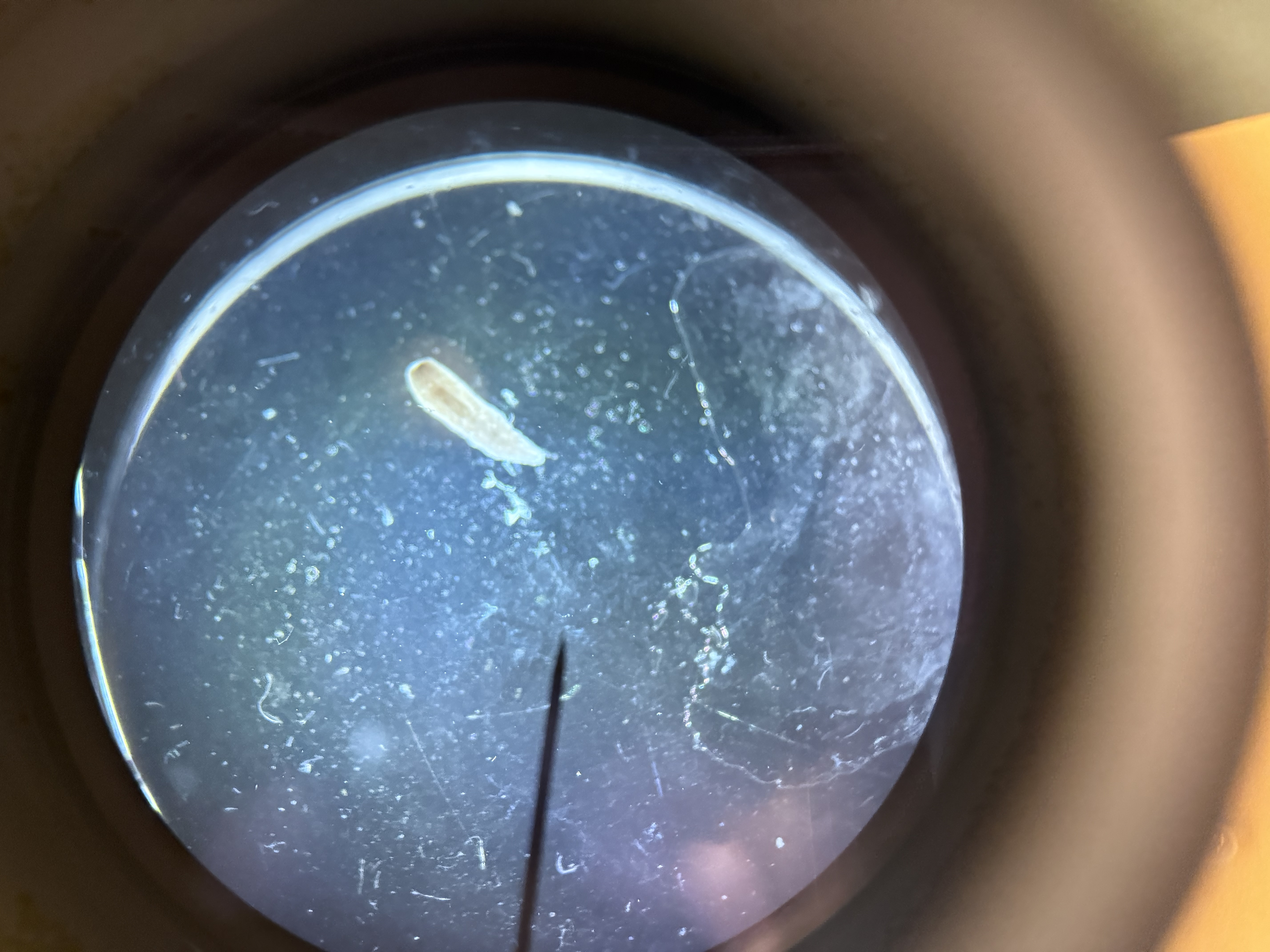
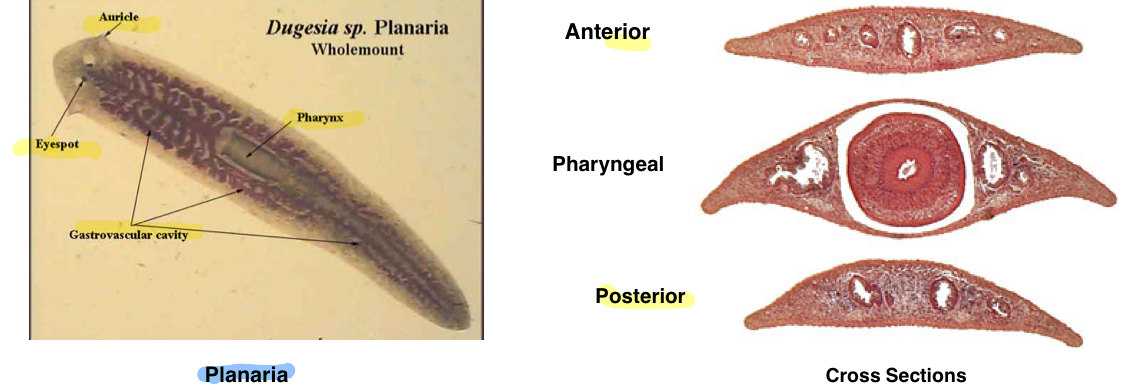
Class Turbellarians - Planaria Structures
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Auricle
Pharynx
Eyespot
Gastrovascular cavity

What hosts in Class: Trematoda - Flukes parasitize humans?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Invertebrates/vertebrates; snails, crabs, fish, birds
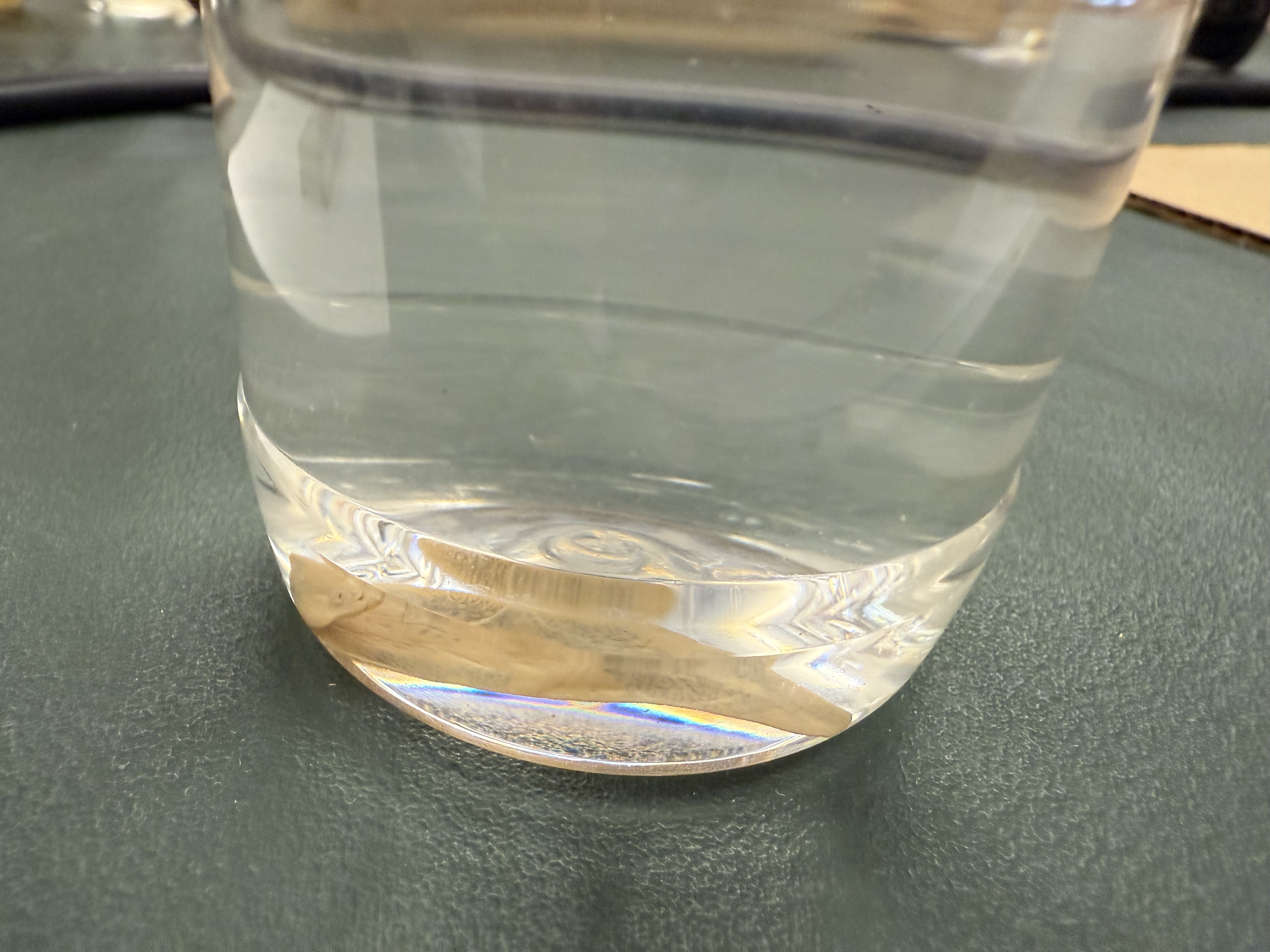

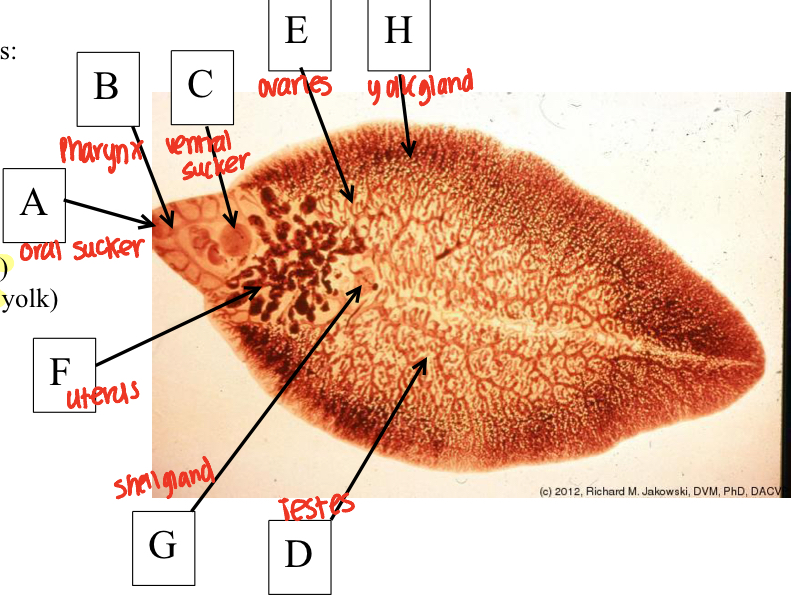
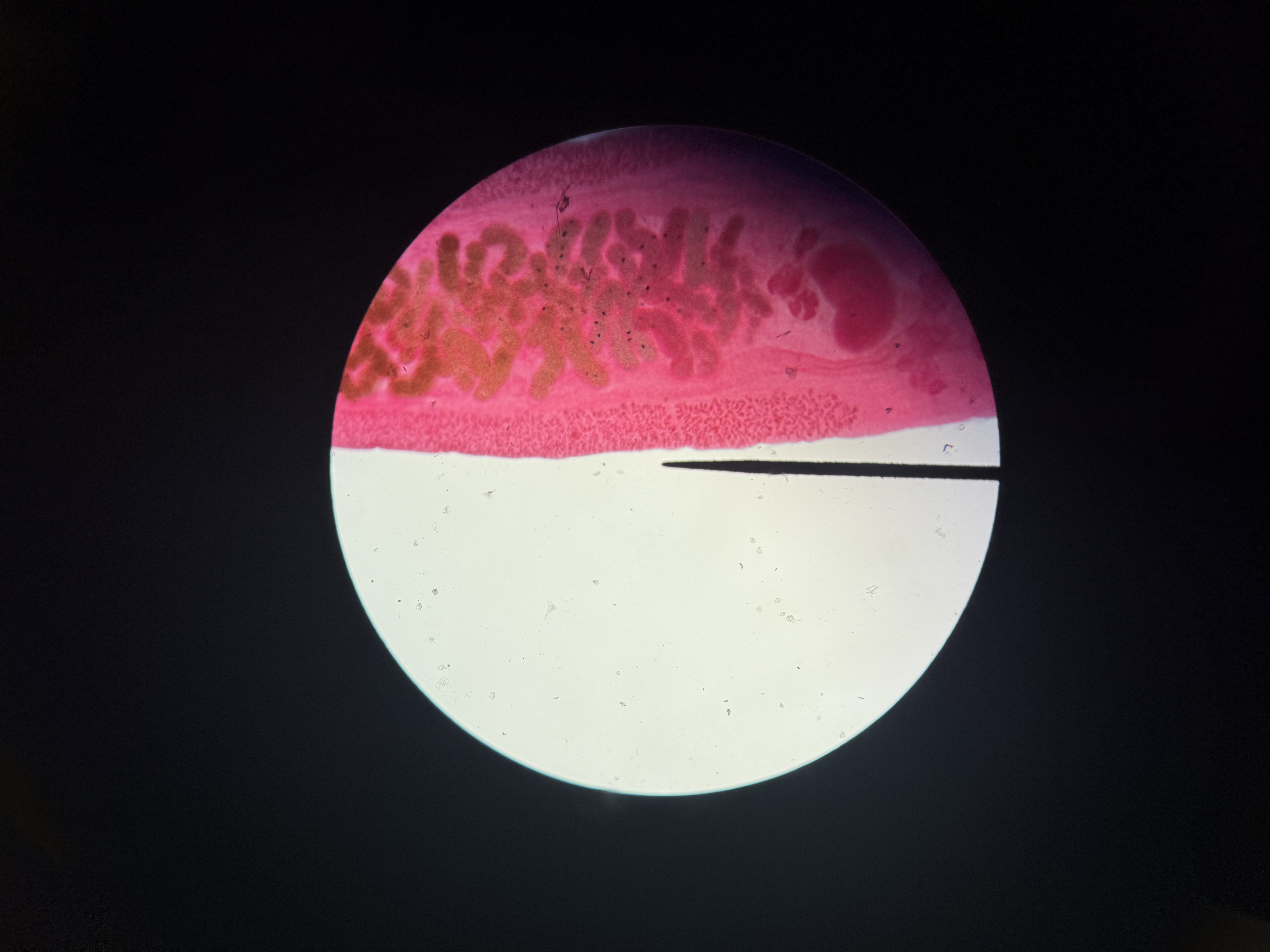
Class: Trematoda - Flukes Structures
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Oral sucker
pharynx
ventral sucker
testes
ovaries
uterus
shell glad
yolk glands
How many people does Chloronchis sp. infect?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Infect 30,000,000 humans
Infected when eating fish
85% of cases from China
Where is Chlonorchis sp. found in humans?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Found in humans; bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on bile
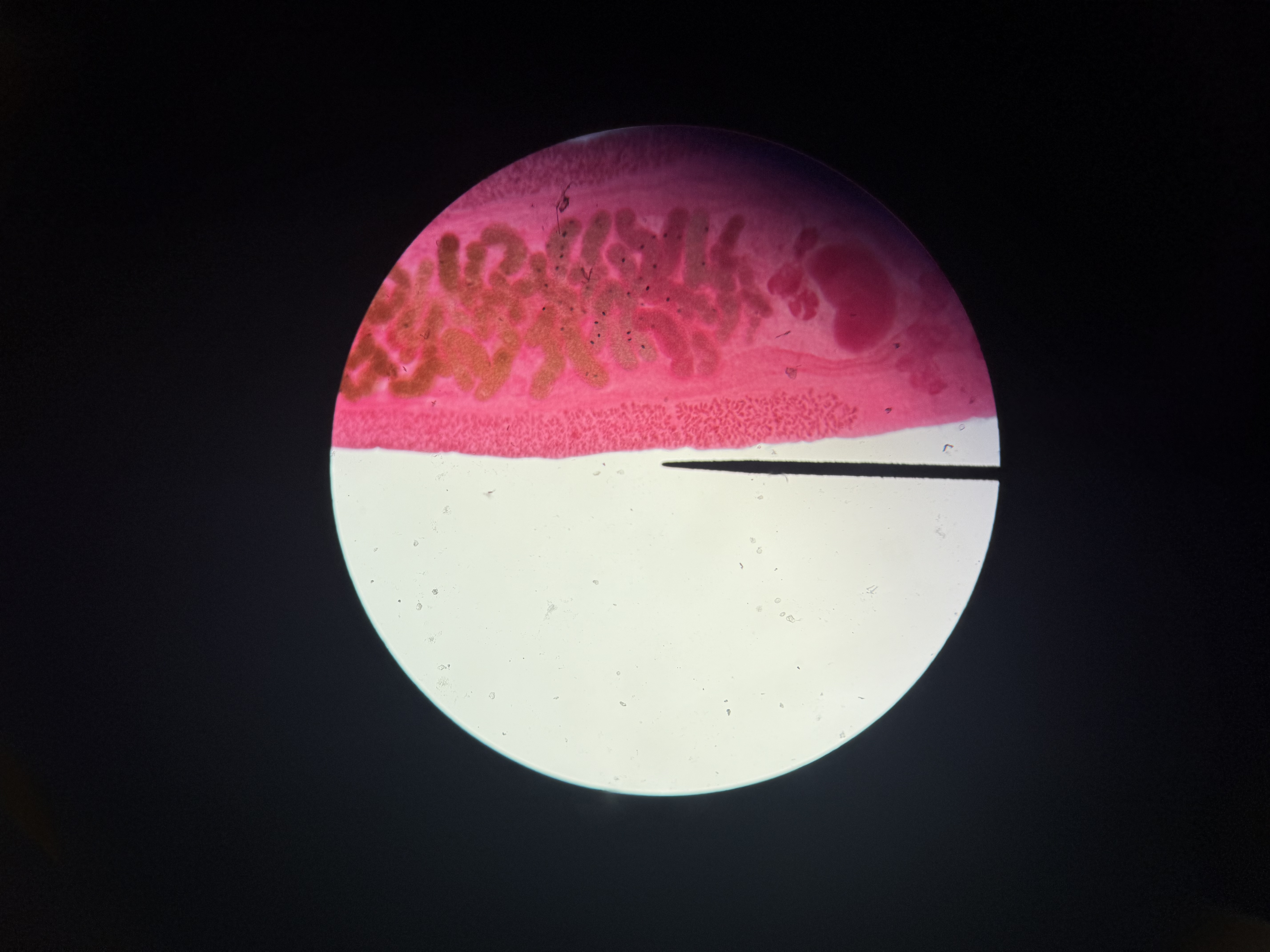
How are humans infected by Schistosoma?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Larvae recognize human skin, burrow into skin to lungs, then heart which carries them to circulatory system
Found in blood vessels
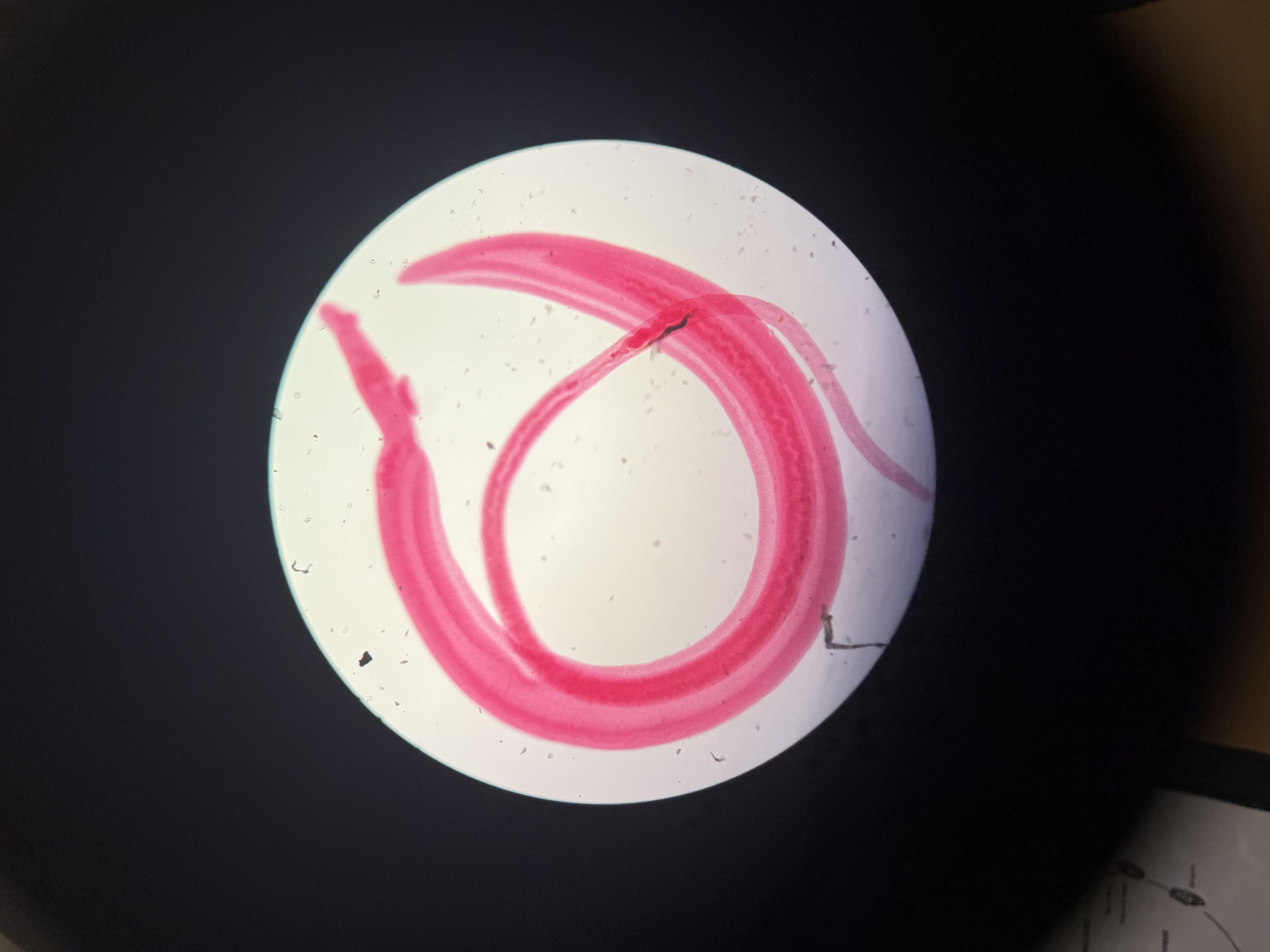
How many countries is Schistosoma found in?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
54 countries
South America and Carribbean, Africa, Middle East
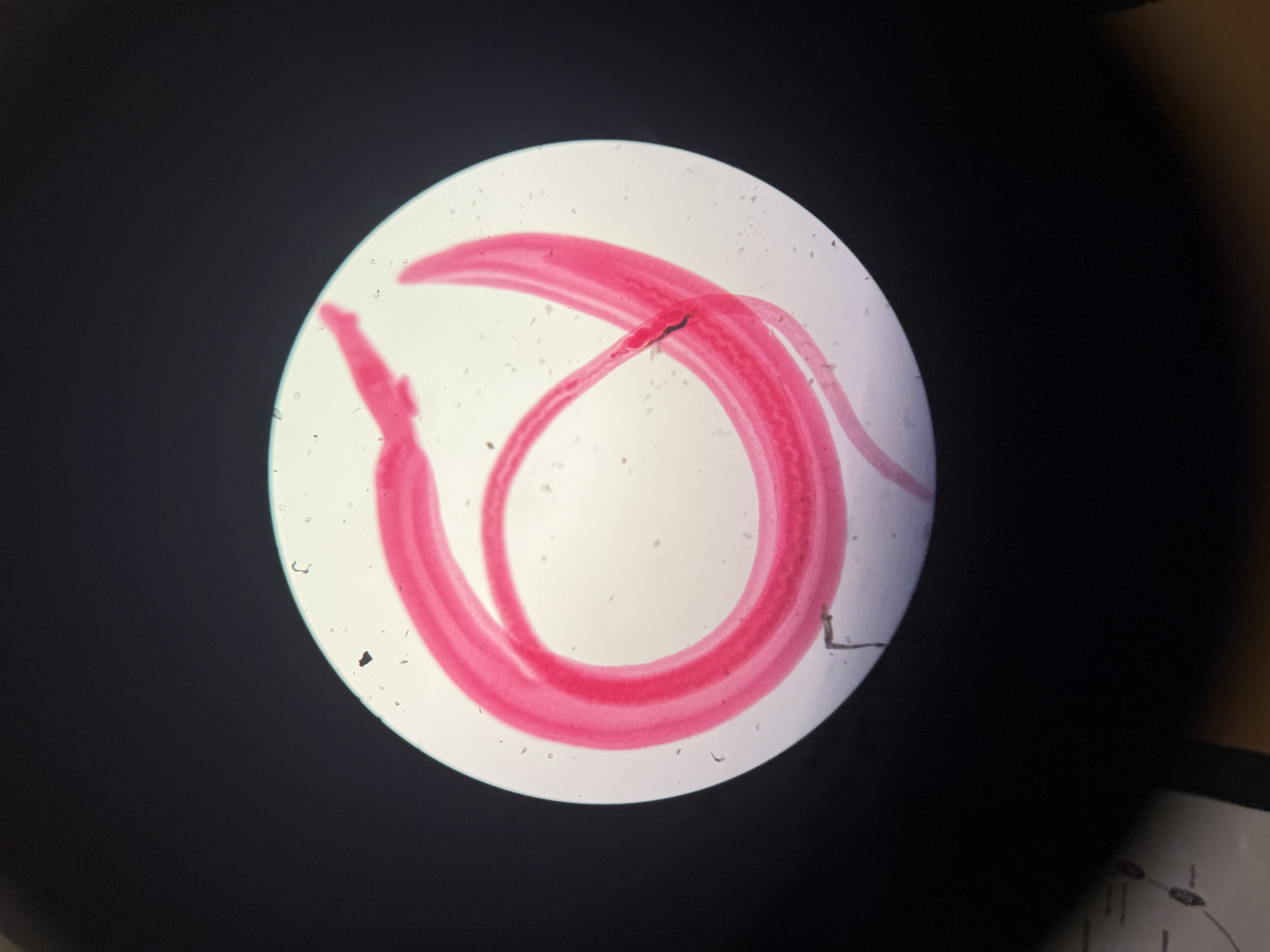
Hosts of Schistosoma
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Humans; parasite undergoes sexual reproduction
Snail: asexual reproductive stages
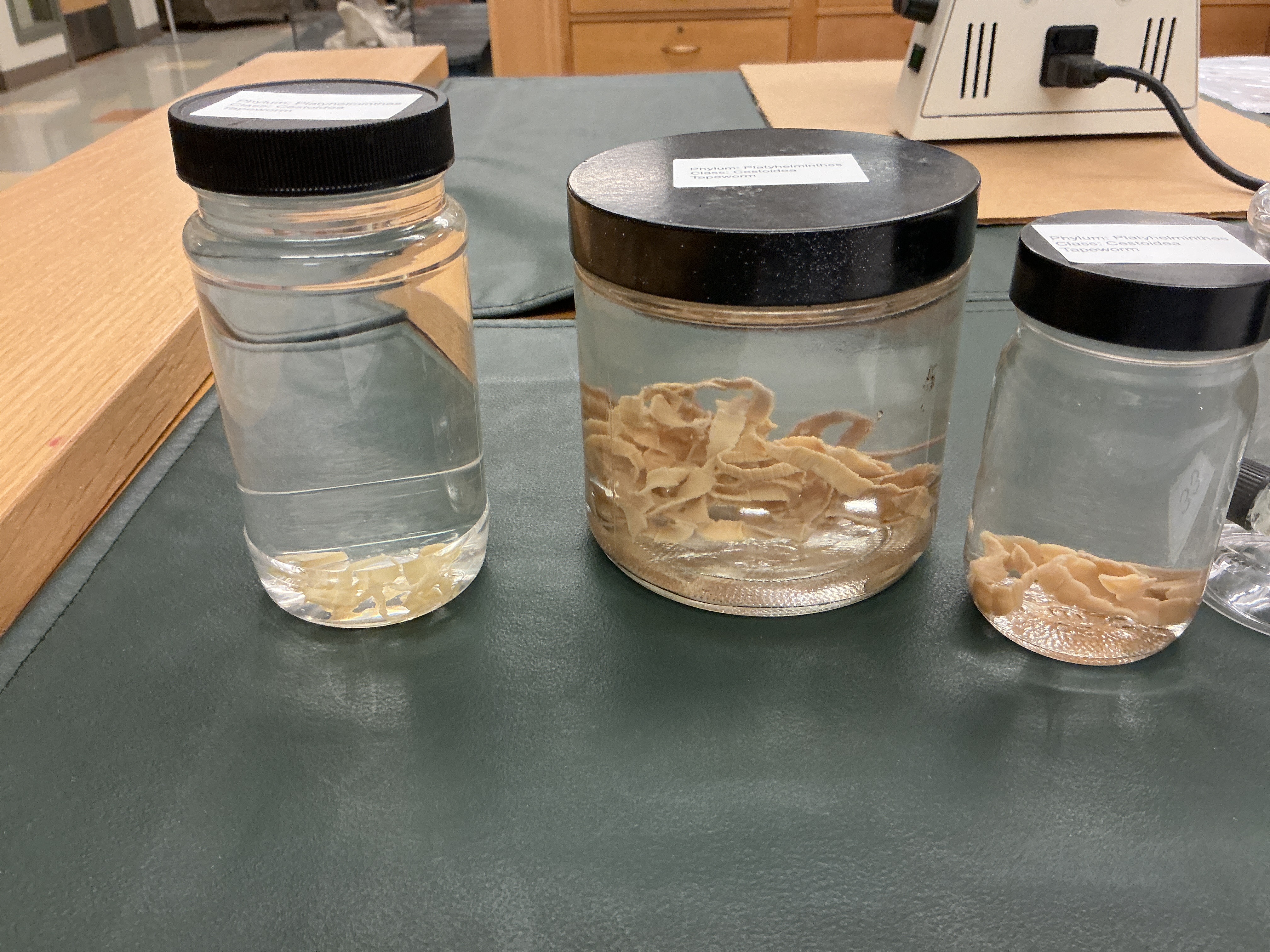
Where do Taenia (tapeworms) live?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class Cestiodea
Adults; digestive tracts of vertebrates
Juveniles; bodies of animals

What is name of the head of a Taenia (tapeworm)?
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class Cestiodea
Scolex
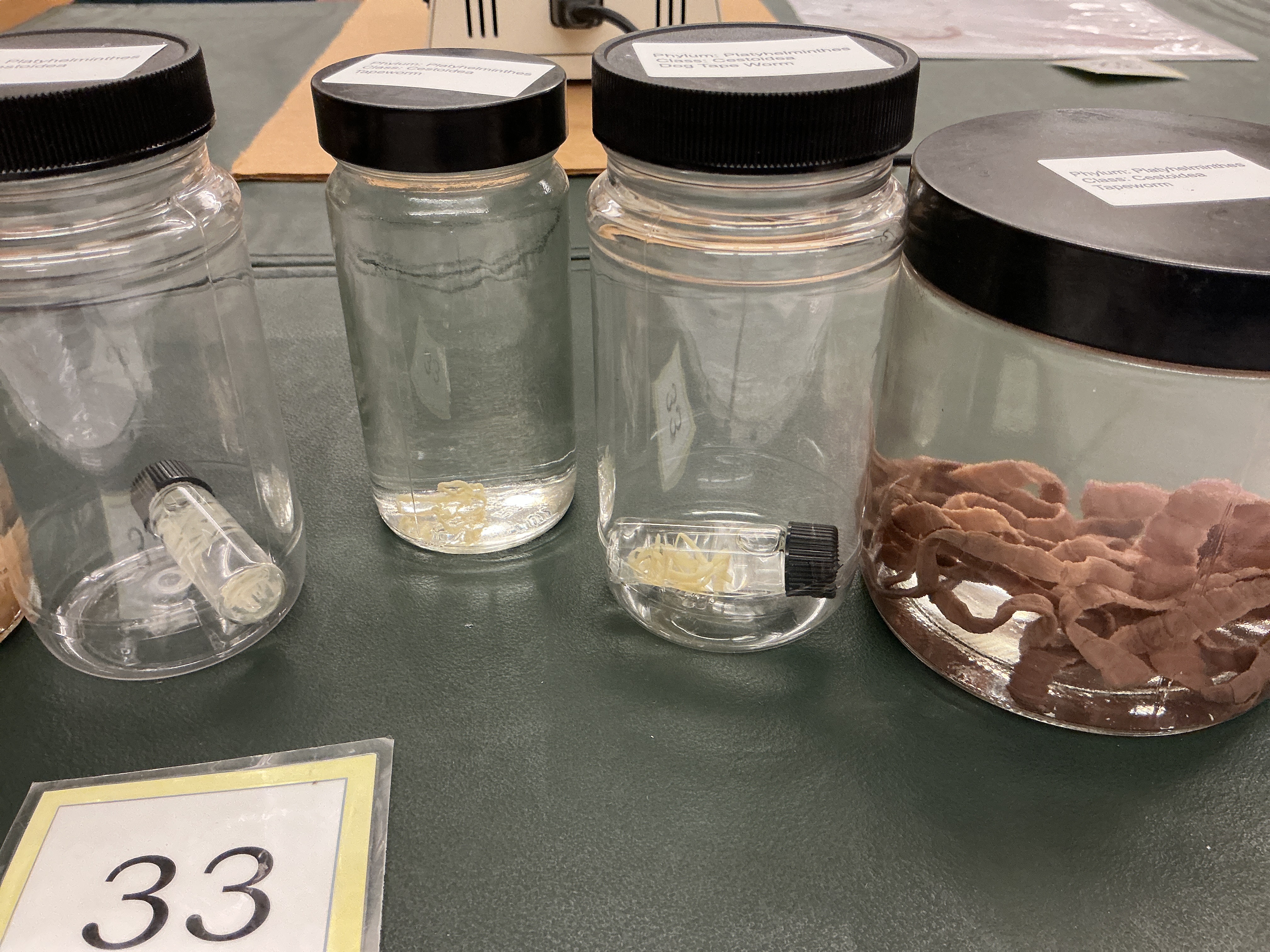

What is the name of the body parts of a Taenia (tapeworm)?
Class Cestoidea
Proglottids: body segments of tapeworm
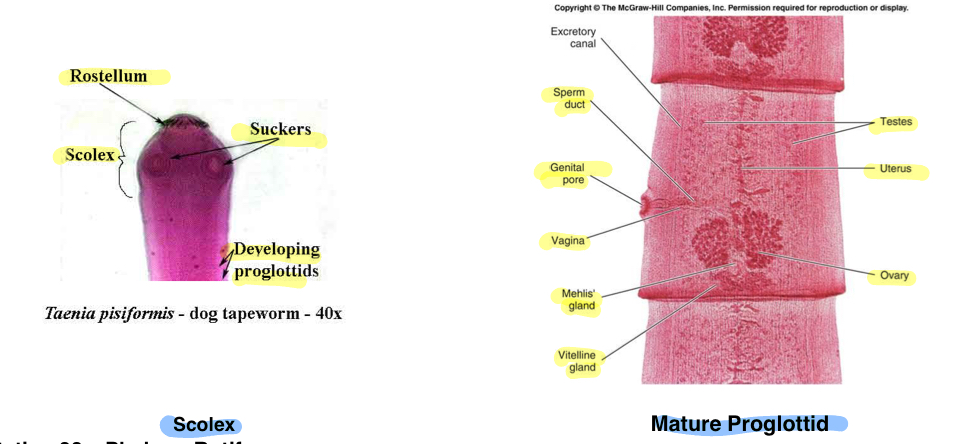
Structures of Taenia (tapeworm)
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Cestiodea
Scolex
Rostulum
Scolex
Suckers developing proglottids
Mature proglottid
Testes
Vagina
Uterus
Genital pore
Ovary
Yolk/mehilis gland
Sperm duct
What type of coelom do Phylum: Rotifera?
Pseudocoelomate body plan
