DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
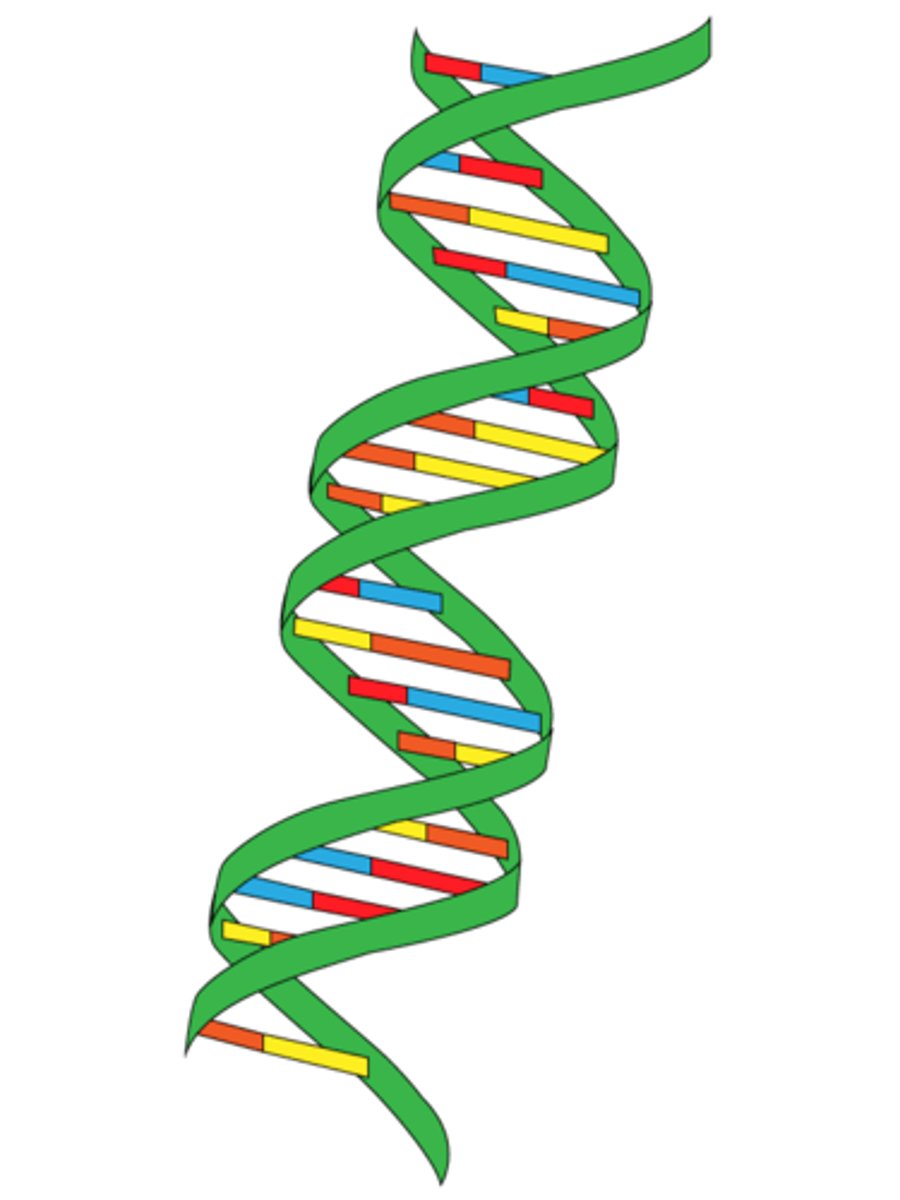
DNA
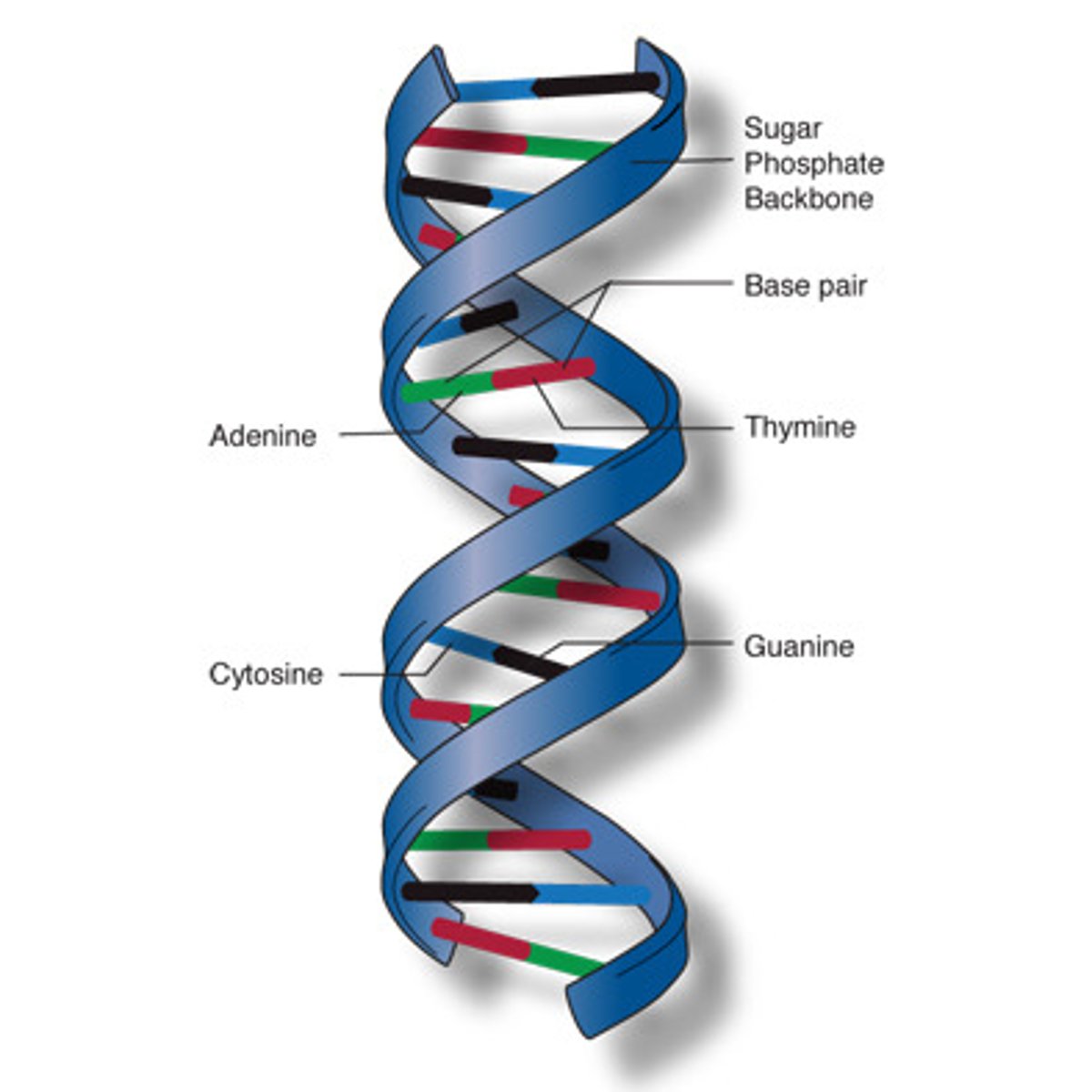
deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms. Double-stranded nucleic acid that carries genetic information.
RNA
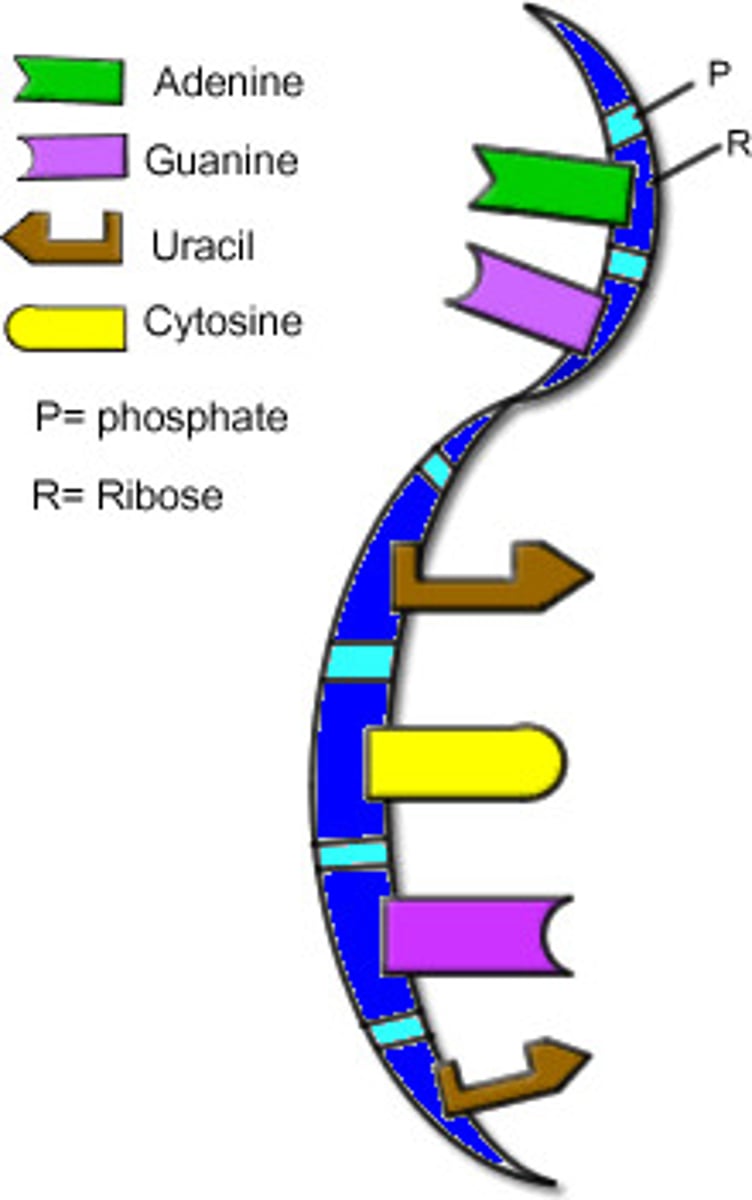
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
Nucleotide
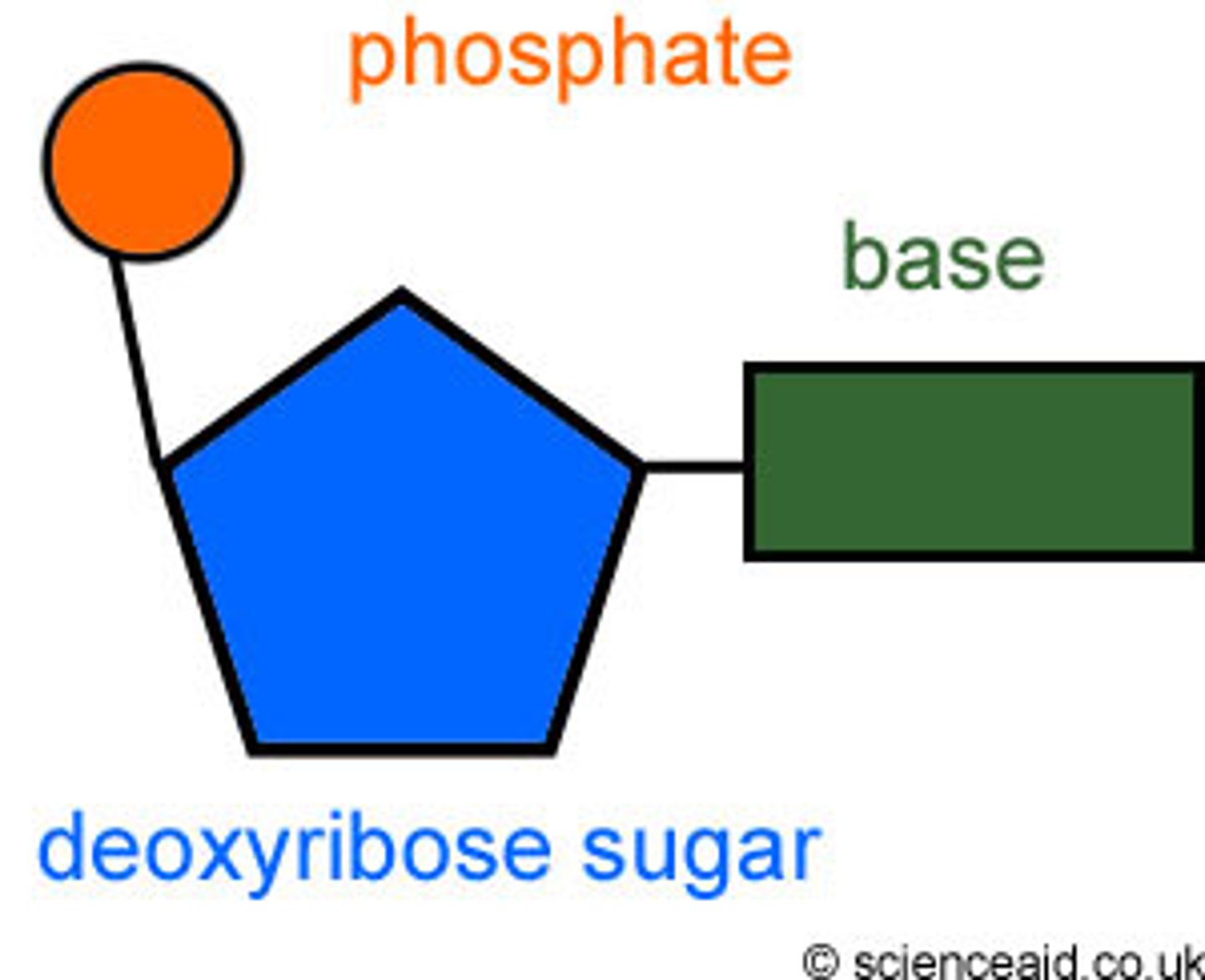
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Nucleotide structure
-deoxyribose sugar
-nitrogenous base
-phosphate group
DNA macromolecule
nucleic acid
DNA monomers are called
nucleotides
DNA sugar
deoxyribose
RNA sugar
ribose
Nobel Prize Winners for DNA structure
James Watson and Francis Crick
DNA structure and shape
double helix (twisted ladder)
Polypeptide
chain of amino acids
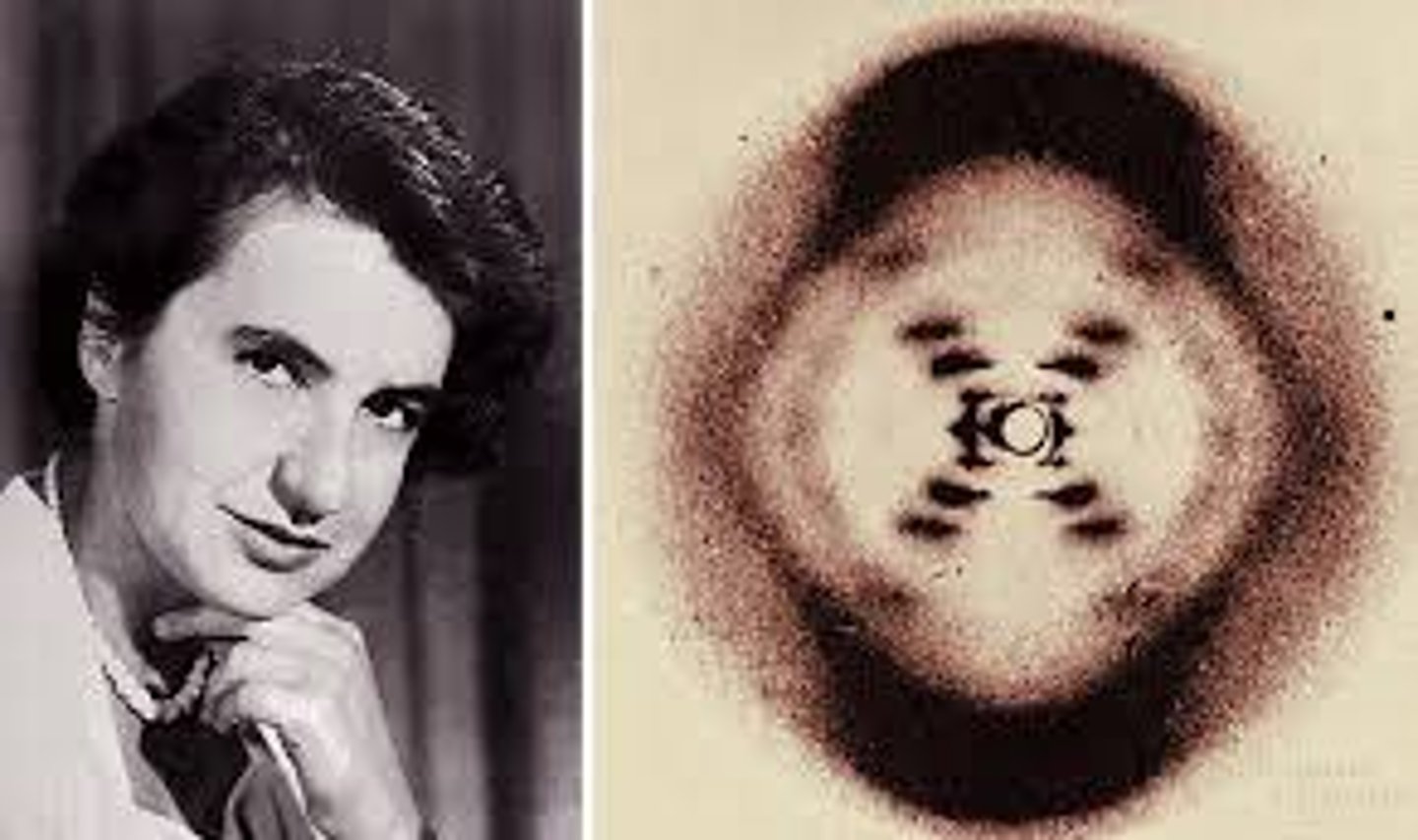
Rosalind Franklin
Woman who generated the famous Photo 51 x-ray image of DNA, she povided Watson and Crick with key data about DNA (was not credited until after her death and did not receive the Noble Prize)

protein synthesis
The creation of a protein from a DNA template.
Nitrogen bases in DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
A->T
C->G
Nitrogen bases in RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
A->U
C->G
Where are the nitrogen bases found on DNA & how are they bonded?
inside or middle of the double helix; bonded by hydrogen bonds
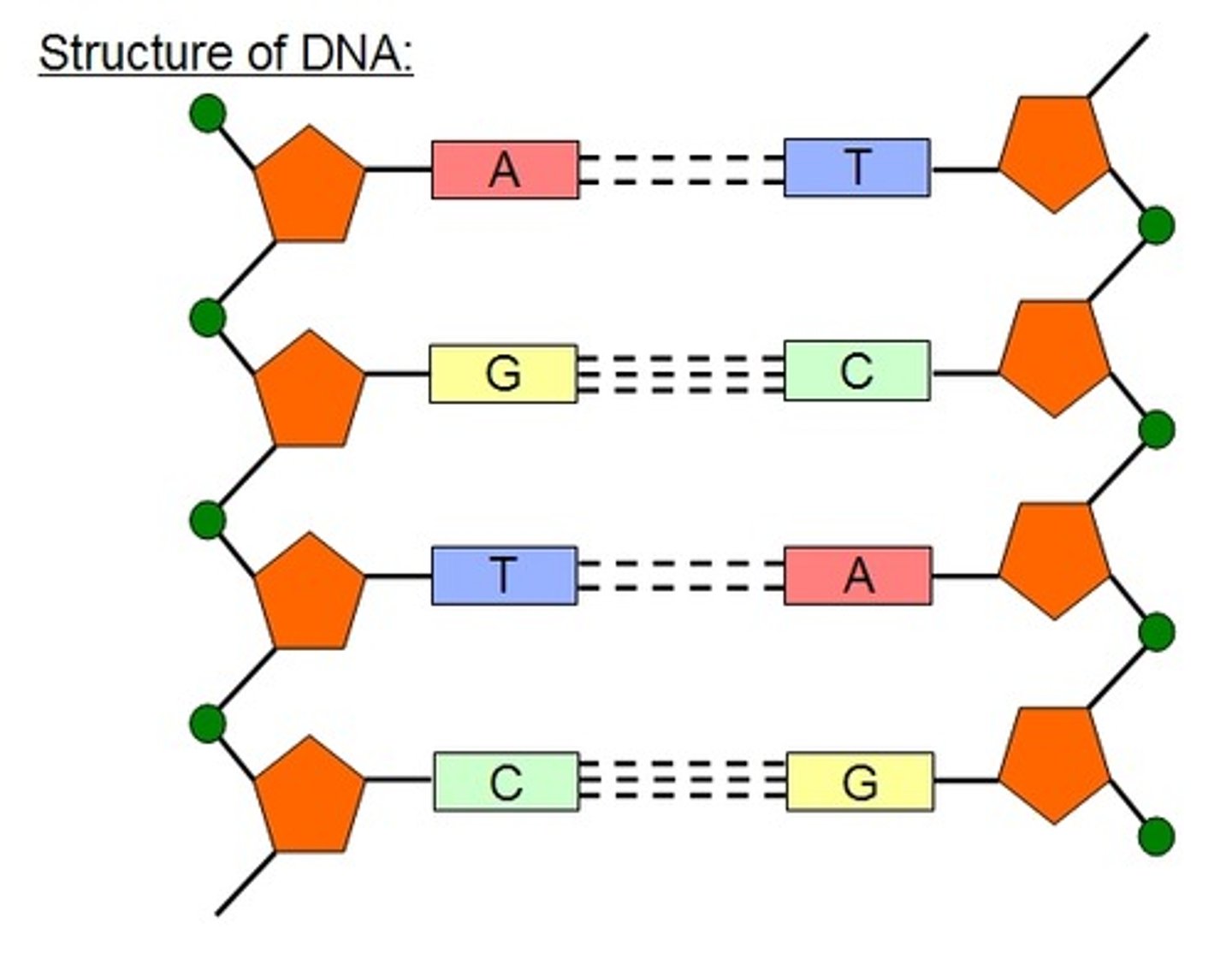
Where are the sugars and phosphates found on DNA?
they make up the side of the double helix
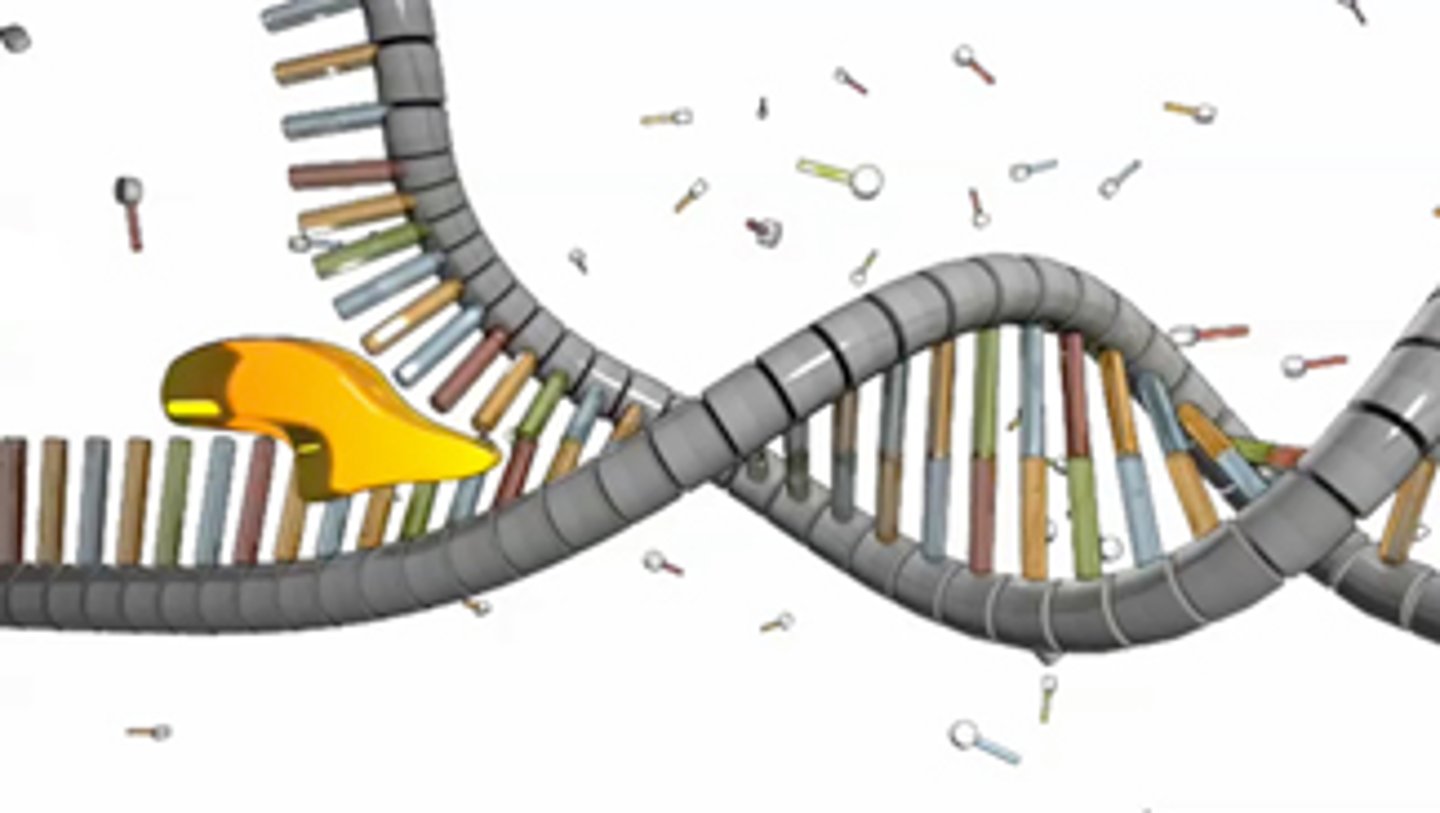
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the DNA double helix during DNA replication
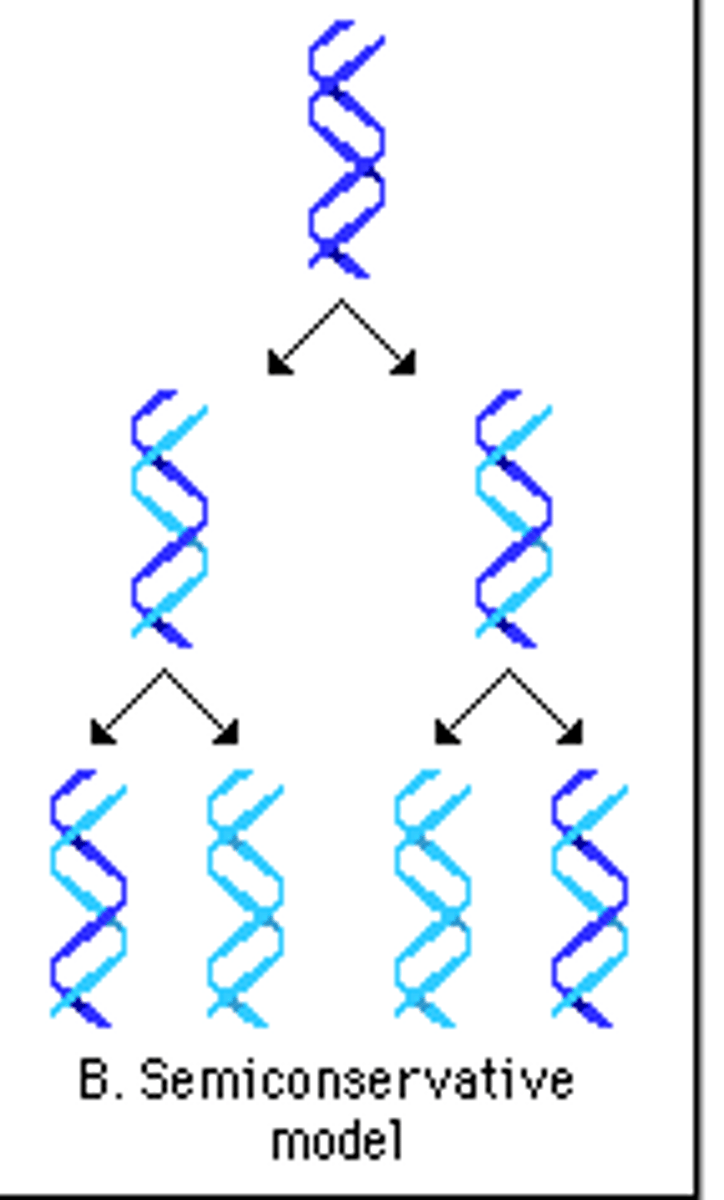
semiconservative replication
each new DNA molecule consists of one new strand and one old strand
DNA polymerase
produces the new DNA strand
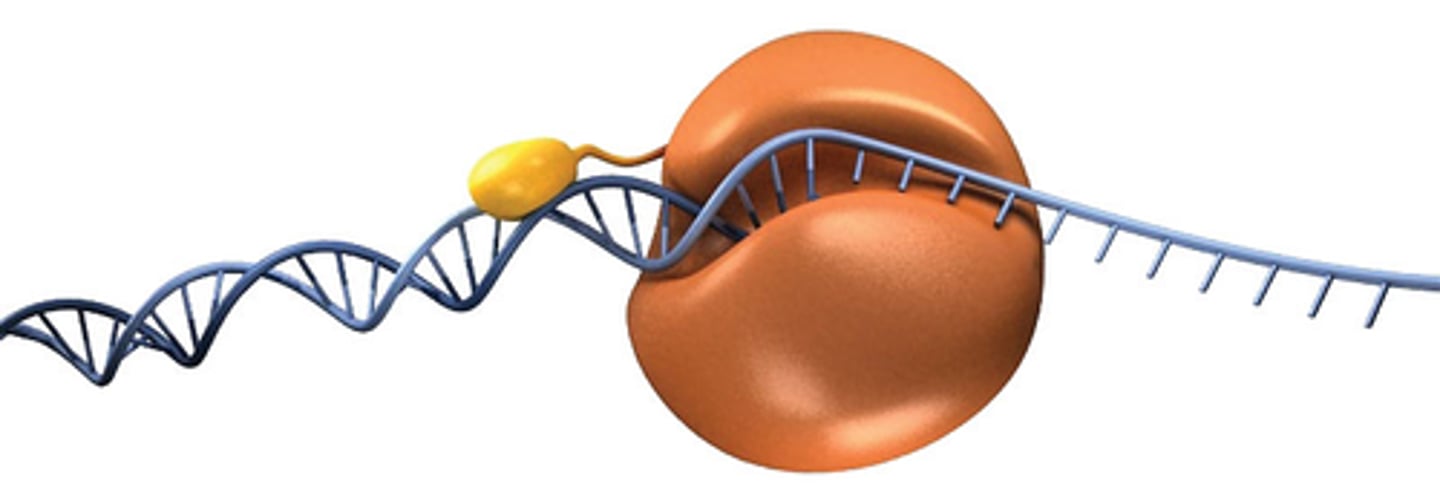
Overall process of protein synthesis
DNA > RNA > polypeptide (protein)
RNA polymerase
the enzyme responsible for creating RNA from a DNA template
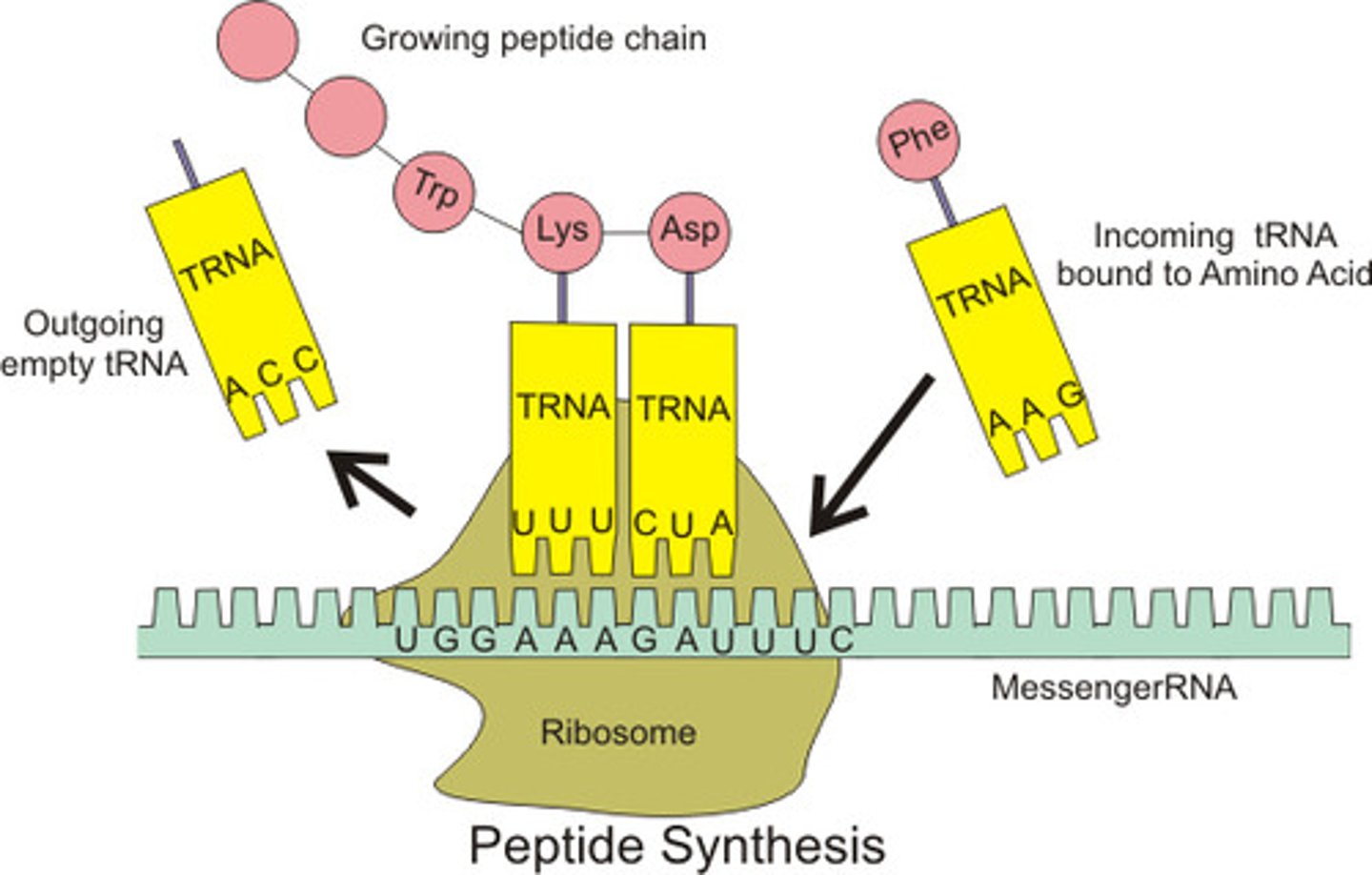
mRNA (messenger RNA)
a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
"start" codon
AUG (methionine)
"Stop" codon
UAA, UAG, UGA
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
DNA > RNA
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
RNA > Protein
genetic code is non-ambiguous
each codon specifies one amino acid
genetic code is redundant
more than one codon may for a particular amino acid
Mutation
a change in nucleotide sequence of DNA. A change in a gene or chromosome.
substitution mutation
Mutation in which a single base is replaced, potentially altering the gene product.
insertion mutation
the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence
deletion mutation
a mutation in which one or more pairs of nucleotides are removed from a gene
silent mutation
alters a base but does not change the amino acid
missense mutation
a nucleotide-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid
nonsense mutation
changes a normal codon into a stop codon; most damaging mutation
frameshift mutation
mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
Mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
number of amino acids
20 amino acids
tRNA (transfer RNA)
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome; contains the anticodon
Central Dogma
theory that states information in cells only flows from DNA to RNA to proteins
DNA > RNA > Protein
Fred Griffith (1928)
found a "transforming principle" (DNA) that changed a harmless bacteria (R Bacteria) into deadly bacteria (S Bacteria), but didn't know what it was
Avery, MacLeod, McCarty
Determined that DNA was Griffith's "Transforming Factor" using mice in their experiment
Chargaff's Rule
the number of Adenine will equal the number of Thymine and the number of Cytosine will equal the number of Guanine