Hesi A2 Biology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Hierarchic Organizational system for nomenclature
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species (Least)
"Keep Penguins Cool Or Find Good Shelter"
Scientific Method
Observation
Hypothesis
Experiment
Conclusion
Water
All life, and therefore biology , occurs in water.
Properties of Water
2 Hydrogen bonds Covalently bonded to Oxygen.
Hydrogen Bonding between molecules.
- High specific heat
- Large bodies or water stabilize climates
- Strong cohesive and adhesive properties
- Water freezes forms a lattice crystal resulting in ice floating in water.
- Polarity of water allows it to act as a universal solvent.
- Water can be used to dissolve different solvents.
Carbohydrates
Long chains, or polymers of sugar. Most importantly form the backbone of DNA and RNA.
Saturated
Clogs arteries. NO DOUBLE BONDS in their hydrocarbon tail. SOLID @ room temperature.
Unsaturated
Double bond in their hydrocarbon tail. LIQUID at room temperature.
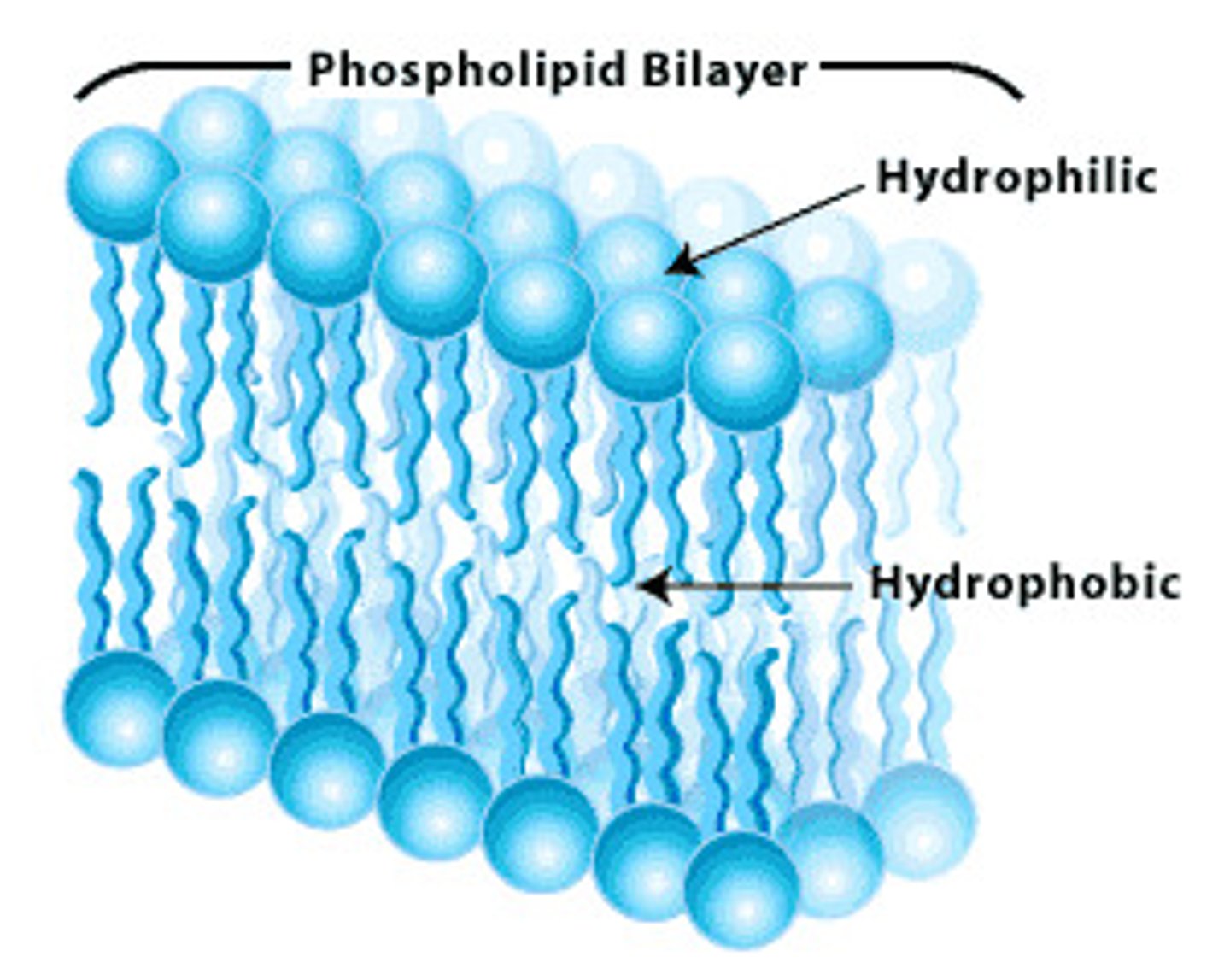
Phospholipids
Phosphate group (polar) soluble in water. Hydrocarbon tail of fatty acids is nonpolar and nonsoluble in water.
Ex. Cell Membrane
Steroids
Are lipids, which are precursors to hormones and drugs
Proteins
They are Polymers of 20 molecules called Amino Acids. Enzymes are a type of protein, which catalyze different reactions or processes. LARGEST Biological Molecule
Cell
Fundamental unit of biology
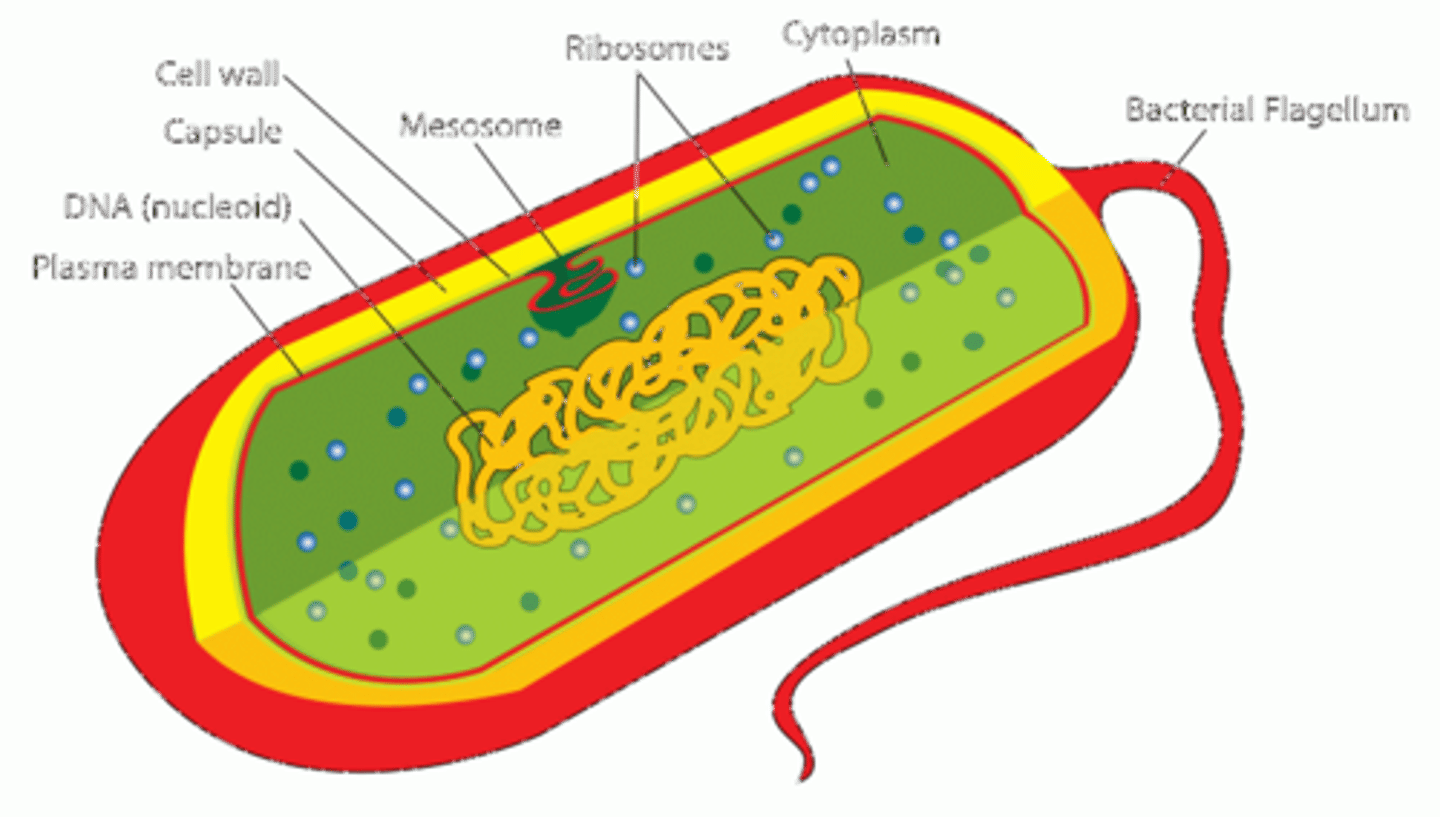
Prokaryotic Cells
NO defined nucleus and NO membrane- bound organelles.
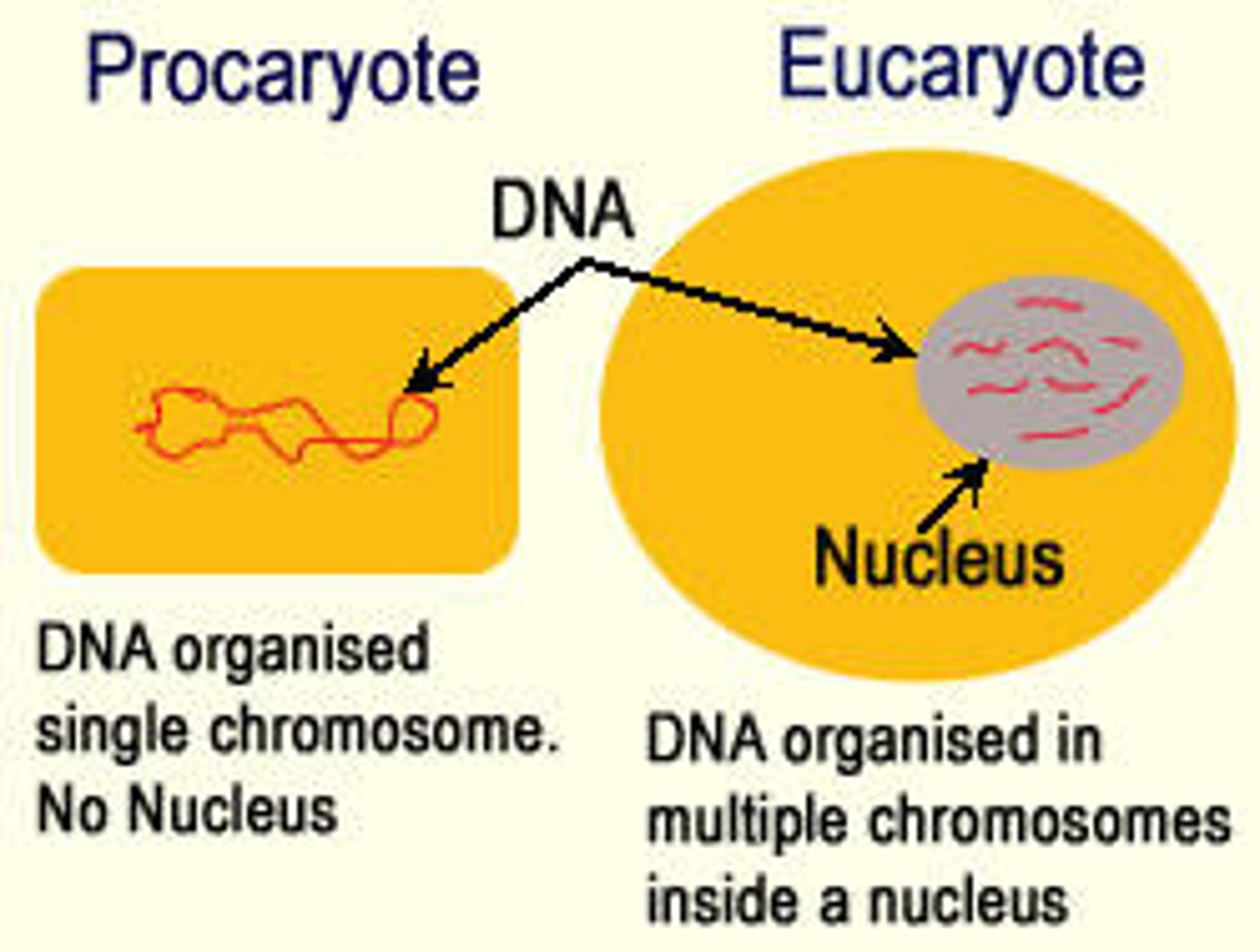
Eukaryotic Cells
Membrane-enclosed nucleus and series of membrane-bound organelles that carry out the functions of the cell as directed by the genetic information contained in the nucleus.
Nucleus
Contains DNA called Chromosomes.
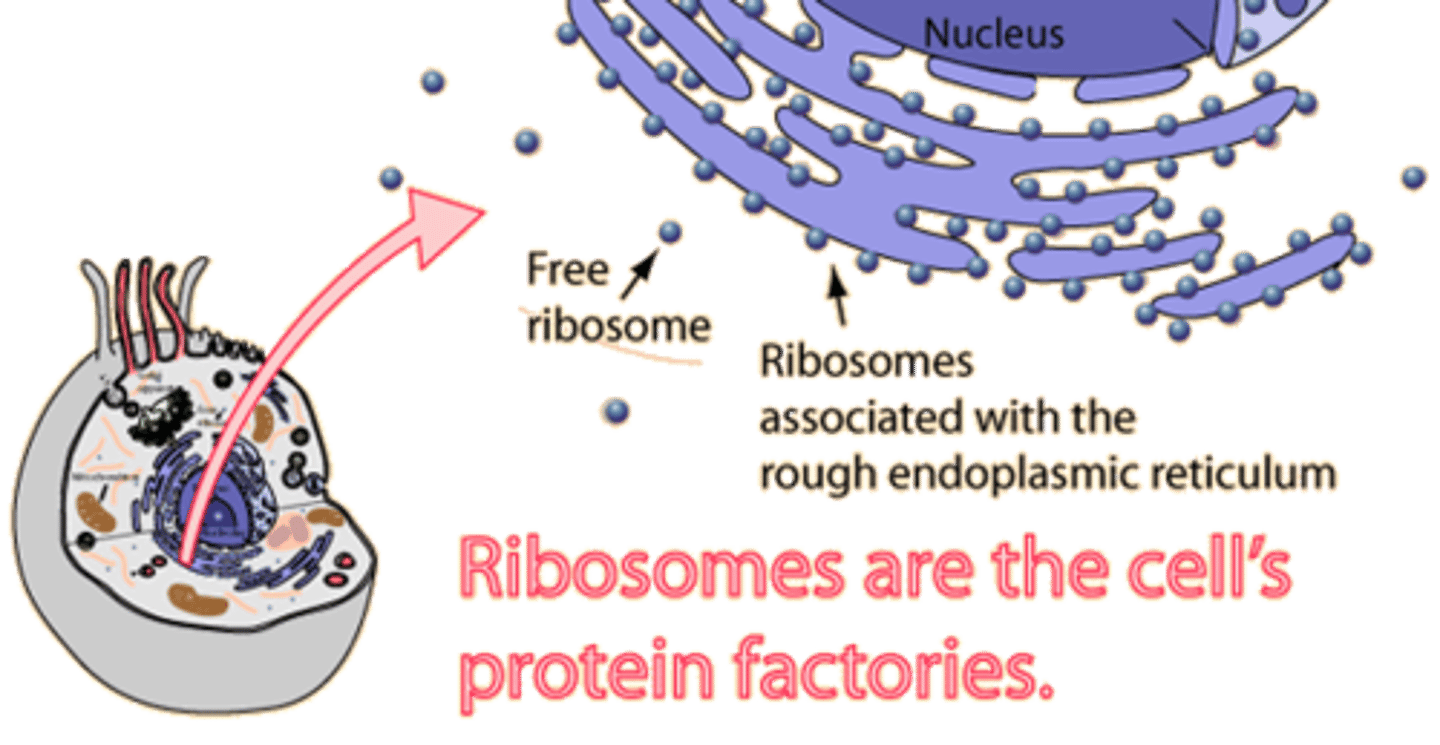
Ribosomes
Are organelles that read the RNA produced in the nucleus and TRANSLATE the genetic instructions to produce PROTEINS.
Bound ribosomes
Are found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
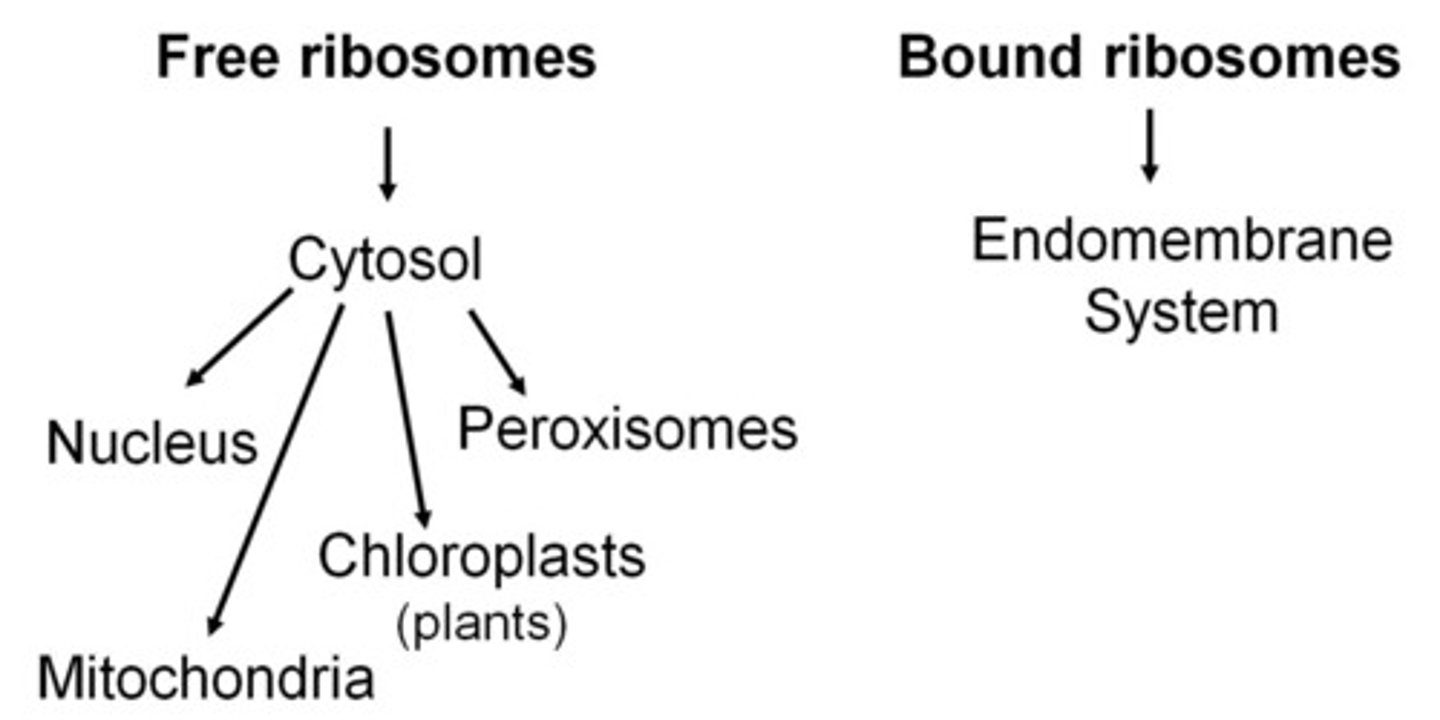
Free ribosomes
Are found in the cytoplasm
Endoplasmic reticulum
Attached to the nucleur membrane and consists of two continuous parts.
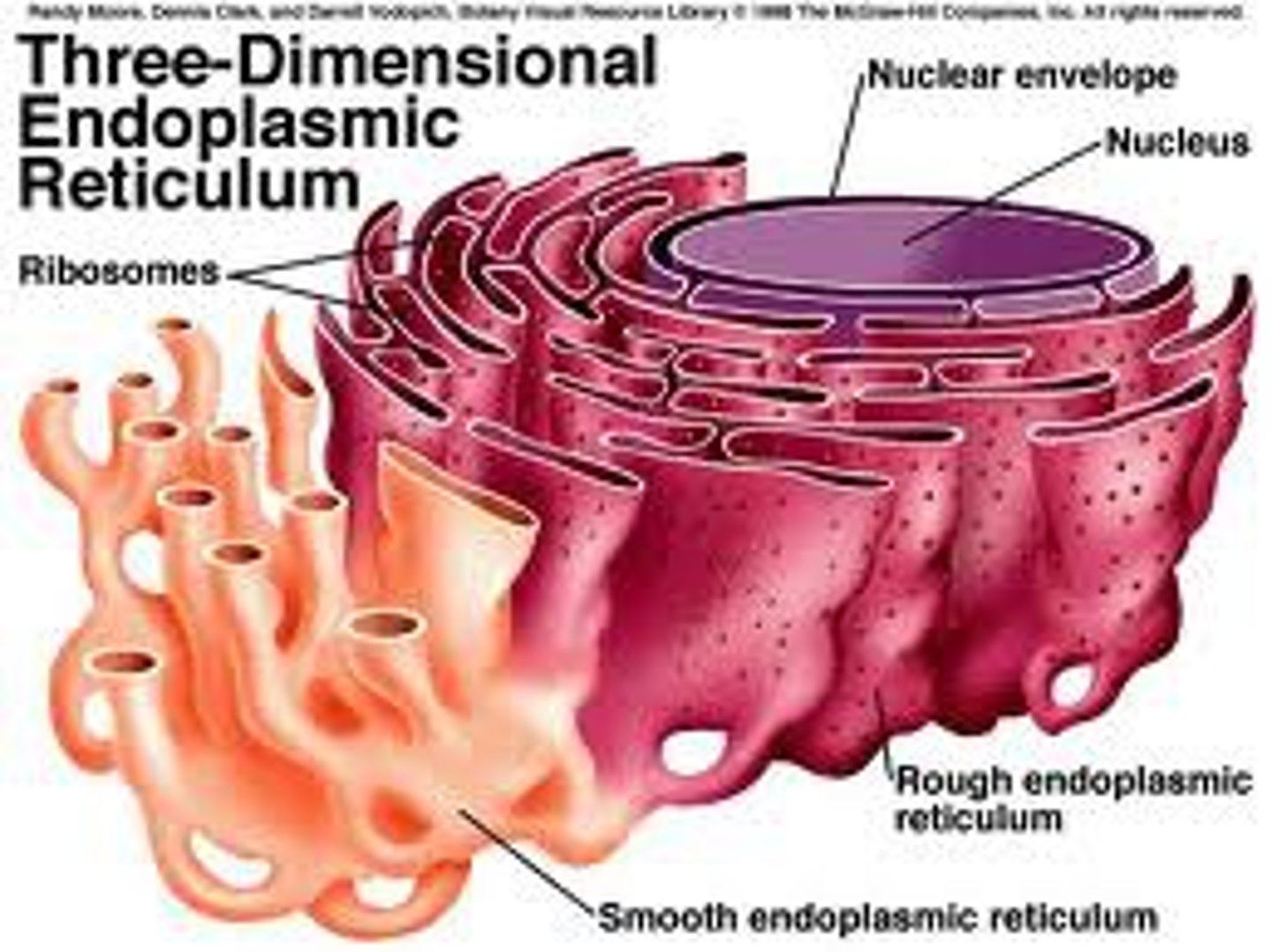
Rough ER
Covered in RIBOSOMES and is responsible for PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and membrane production.
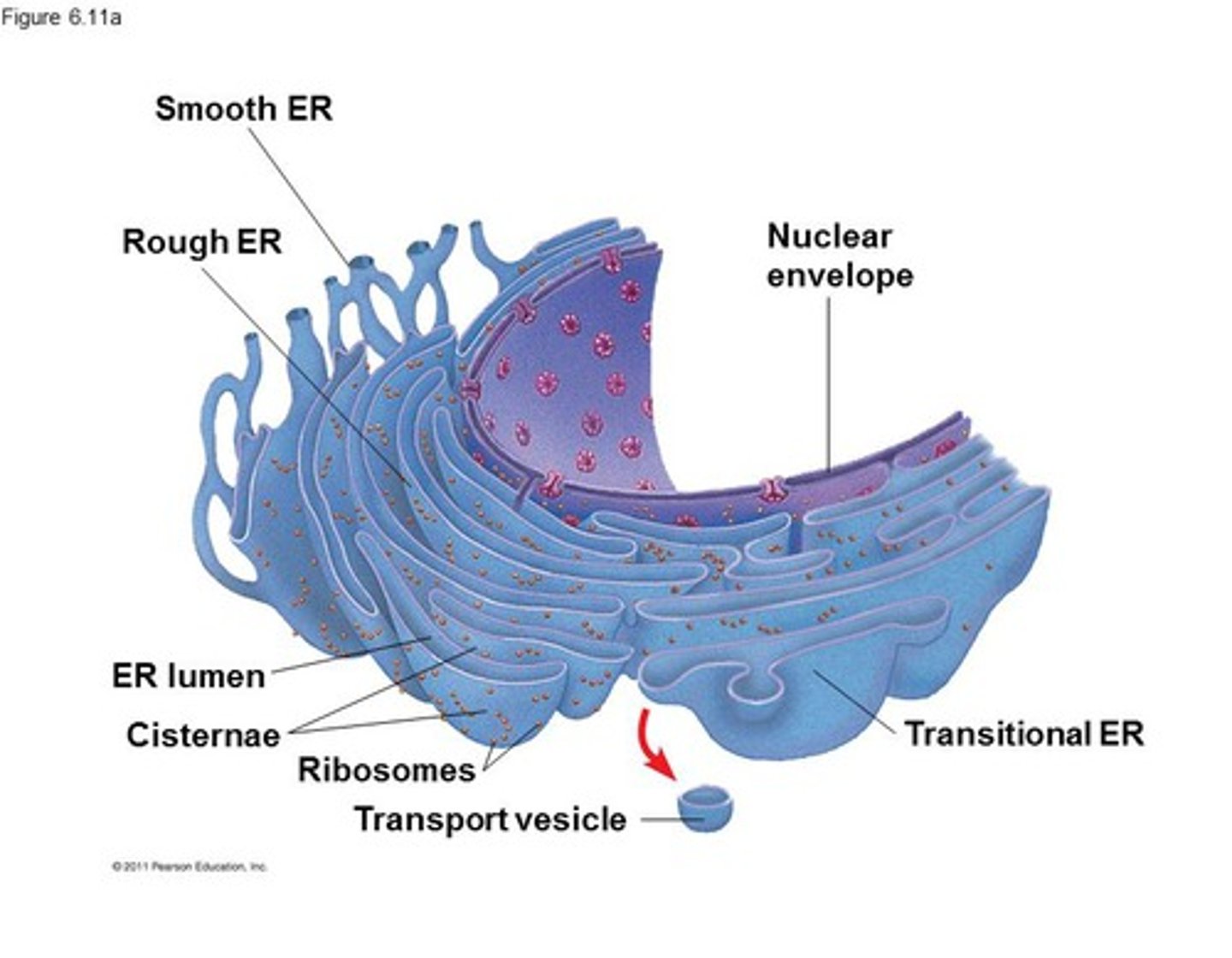
Smooth ER
NO ribosomes. It functions in the DETOXification and METABOLISM of multiple molecules.
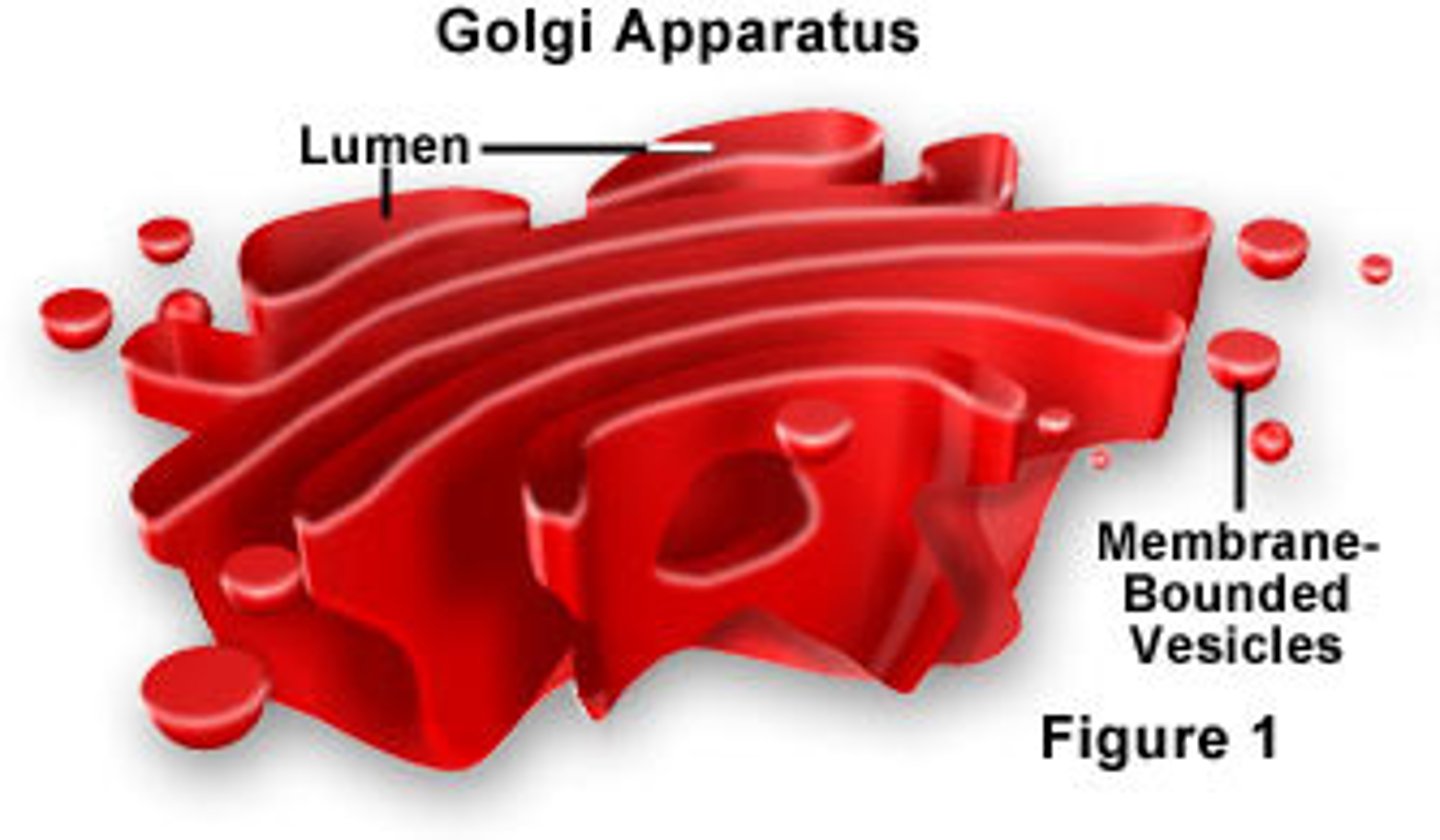
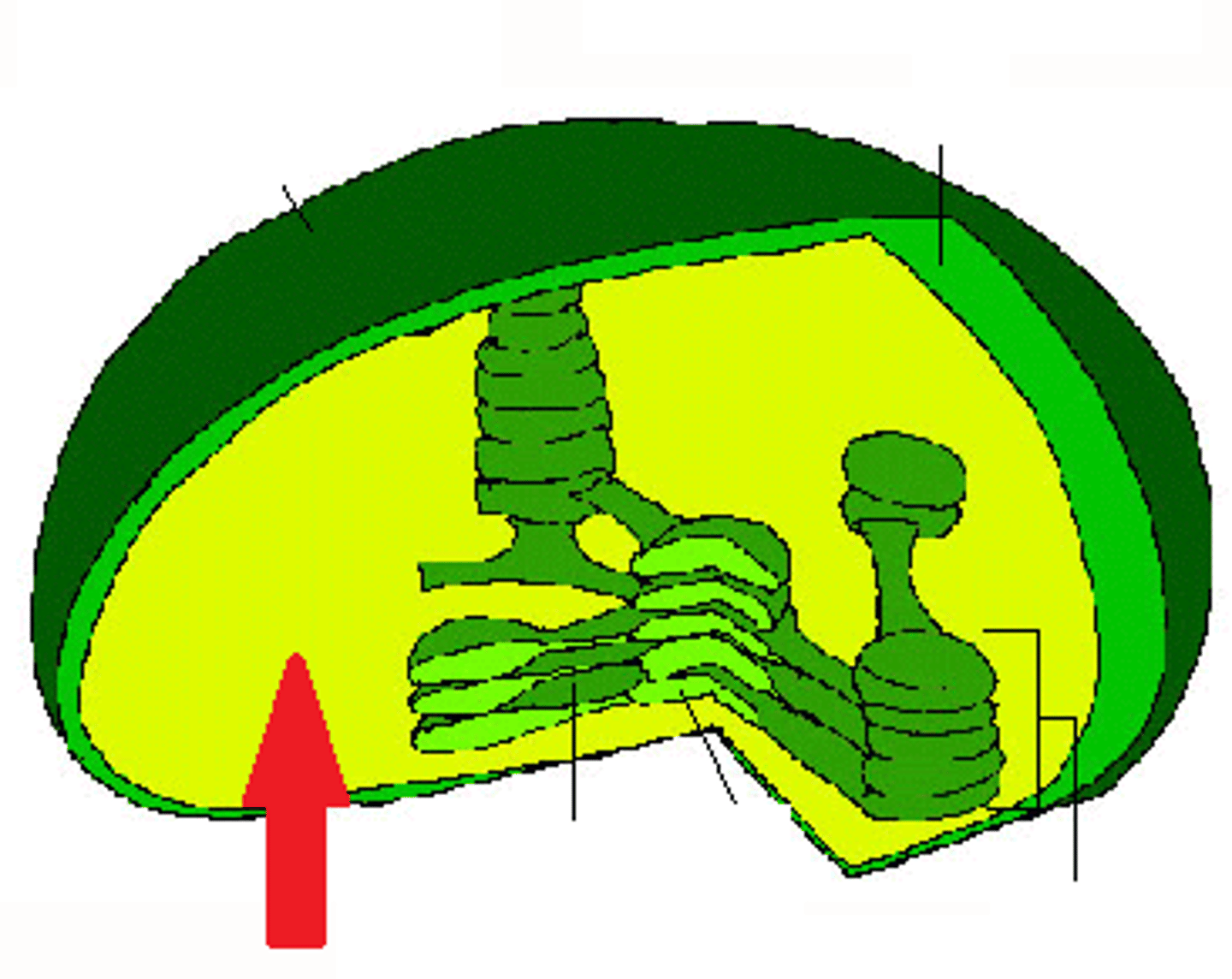
Golgi Apparatus
Packaging, processing and shipping. "UPS"
Lysosomes
Intracellular DIGESTION. hydrolyze proteins, fats, sugars, and nucleic acids.
Vacuoles
uptake food through the cell membrane by phagocytosis. Plant cells have a central vacuole that functions as storage, waste, disposal, protection, and hydrolysis
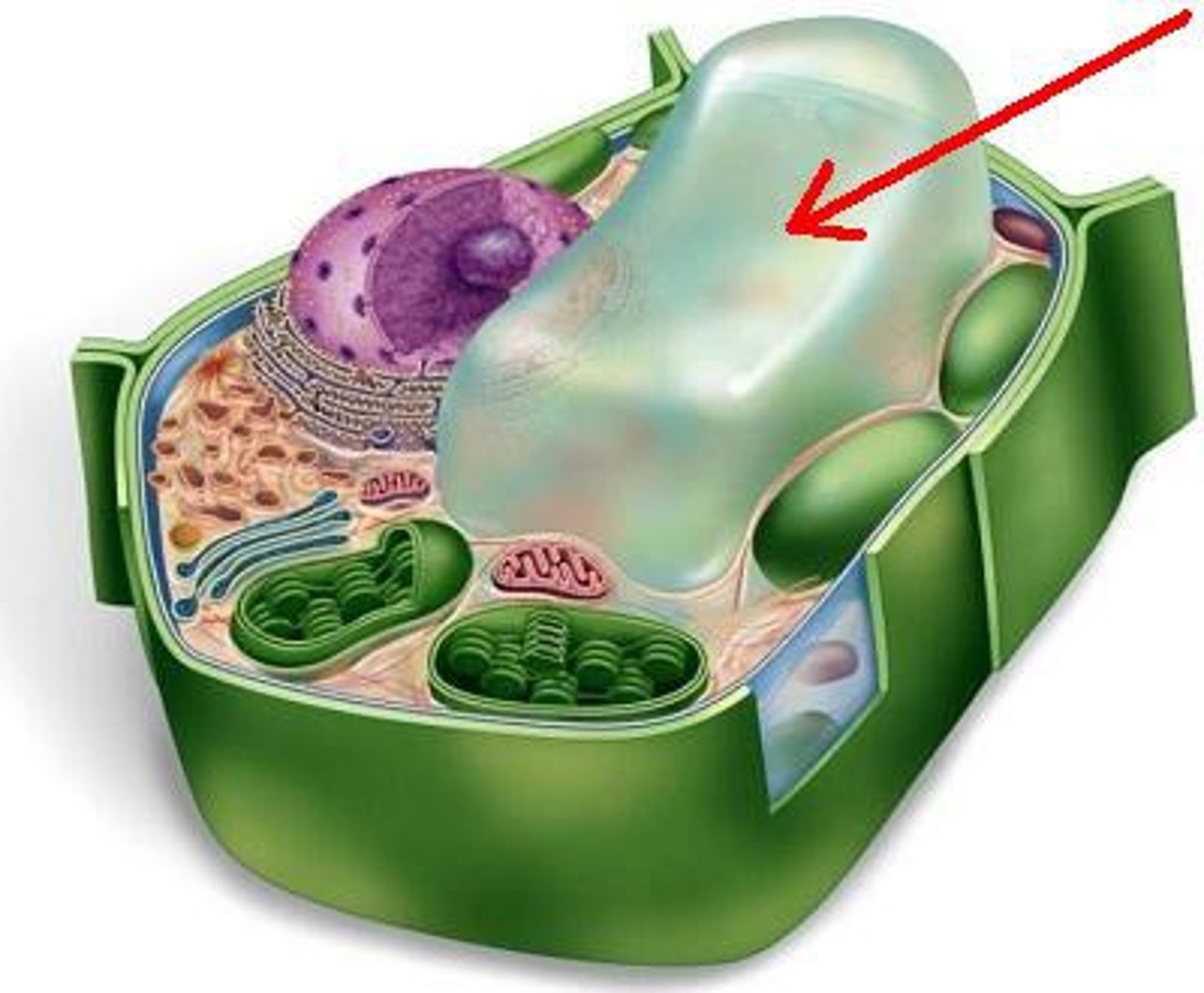
Mitochondria
Found in Eukaryotic cells and are the site of CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular Respiration Formula
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
Steps of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis, Kreb's Cycle, Electron Chain Transport
Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis and Fermentation
Asexual Reproduction (Mitosis)
Produces 2 daughter cells. "Everything stays the same"
Sexual Reproduction (Meiosis)
Produces 4 daughter cells 1/2 from mom 1/2 from Dad
Begin as diploid end as haploid
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle involves creating energy in the form of 2 GTPs (which convert to ATP) and NADH (and FAHD2 which donate the electrons to the ETC), not harvesting it, and it is not only used by plants. In addition, it is cyclical, not linear. ATP and Pyruvate are created by glycolysis.
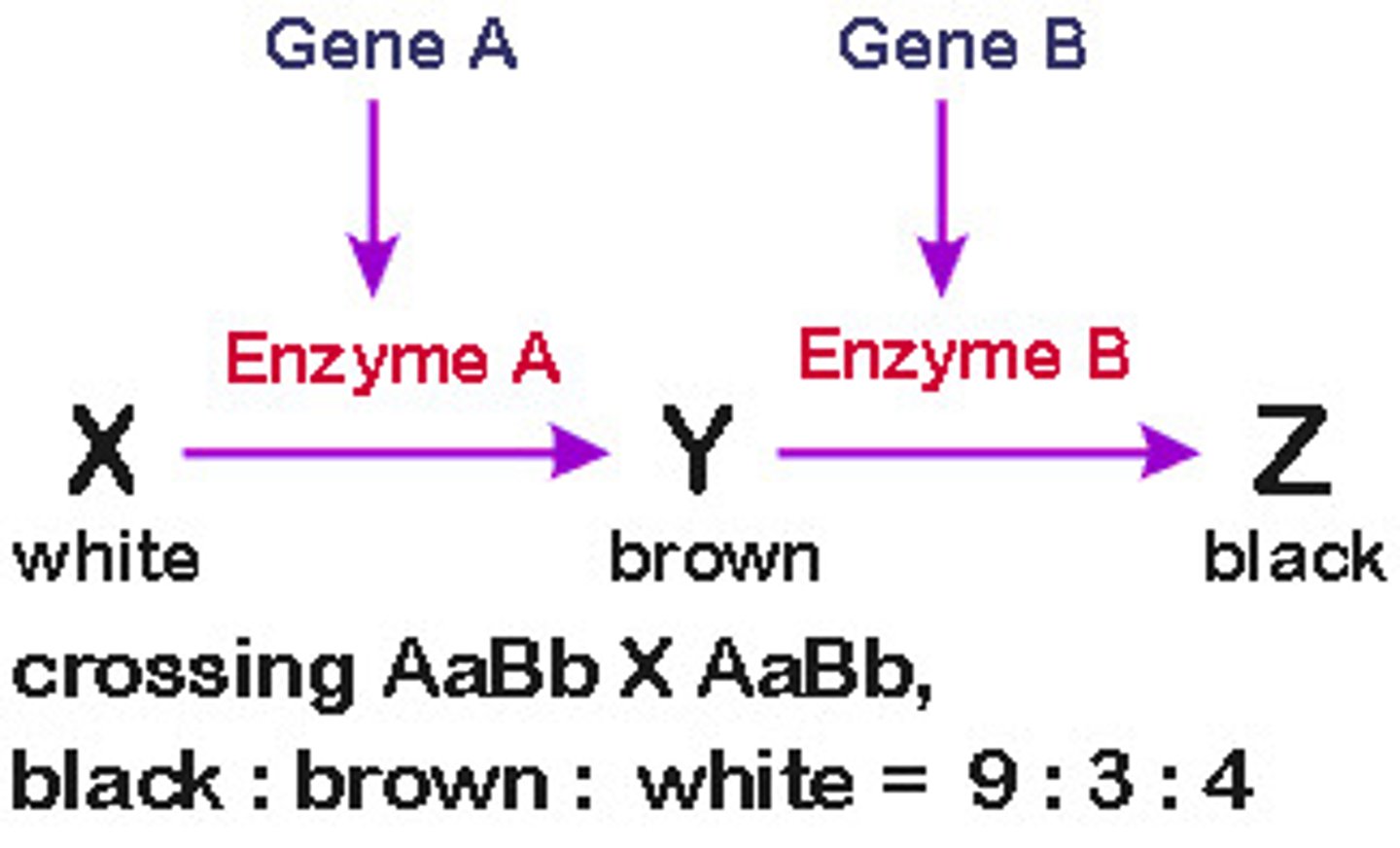
Epistasis
Epistasis is the interaction between two alleles which have different effects in combination than individually.
Worms lack
eyes and ears.
Which of the following is true with regard to eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria.
One of the major differences between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is that eukaryotic cells contain organelles, such as mitochondria, whereas prokaryotic cells do not.
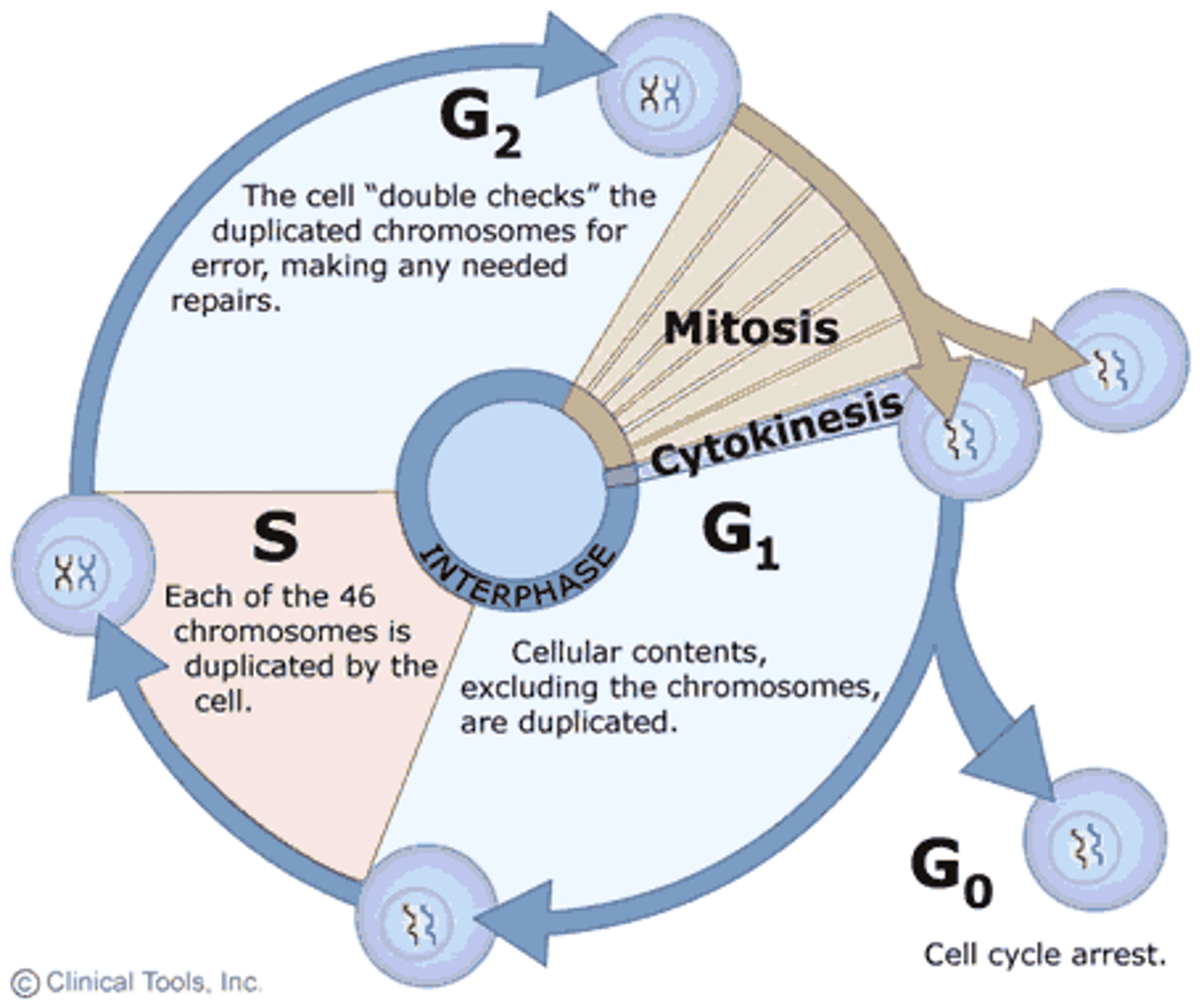
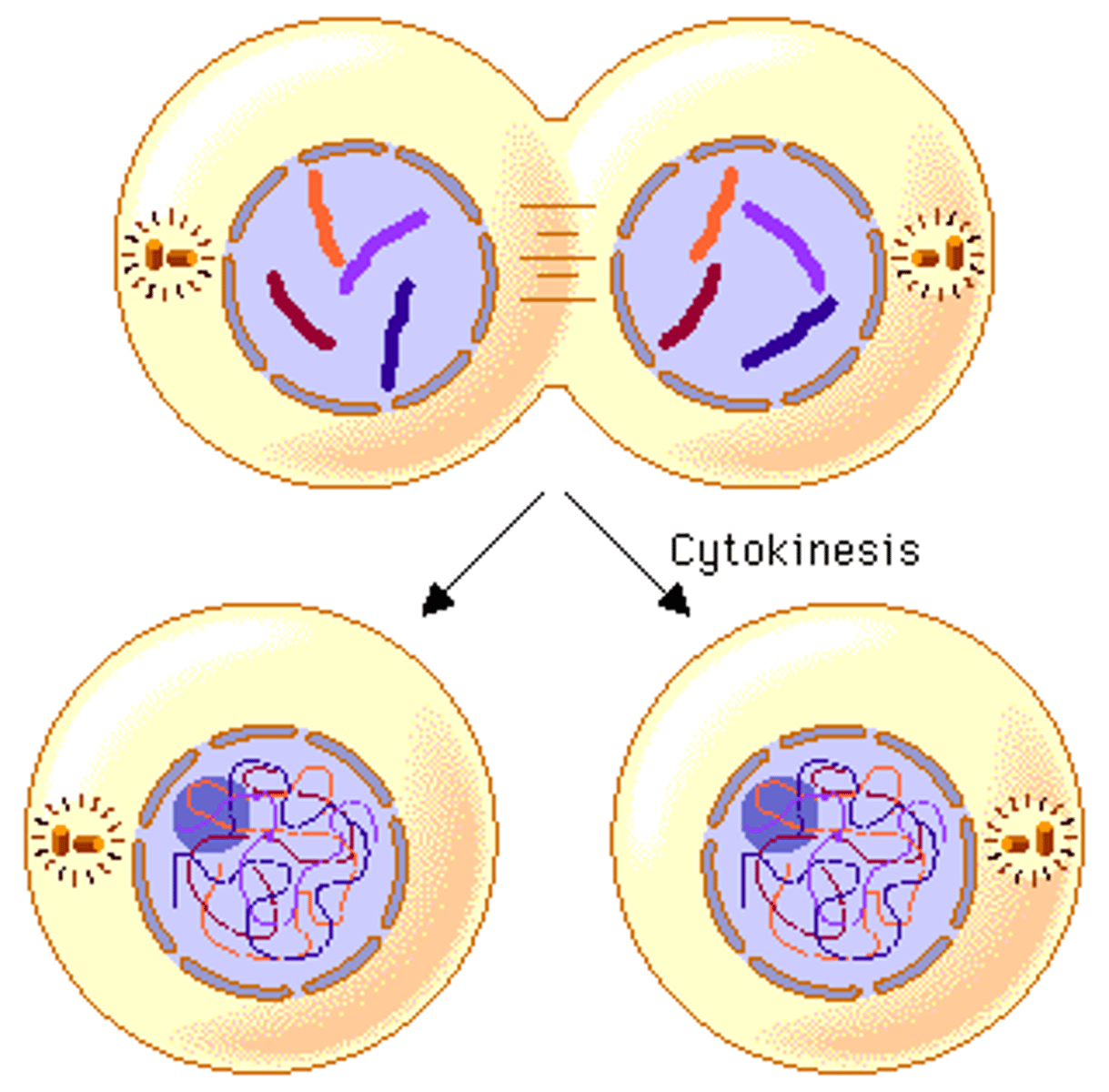
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis occurs late in the process of mitosis and is marked by a single cell splitting into two daughter cells.
In a bird or a bee, the crop is responsible for what?
The crop is a muscular pouch that is part of the bird's digestive system.
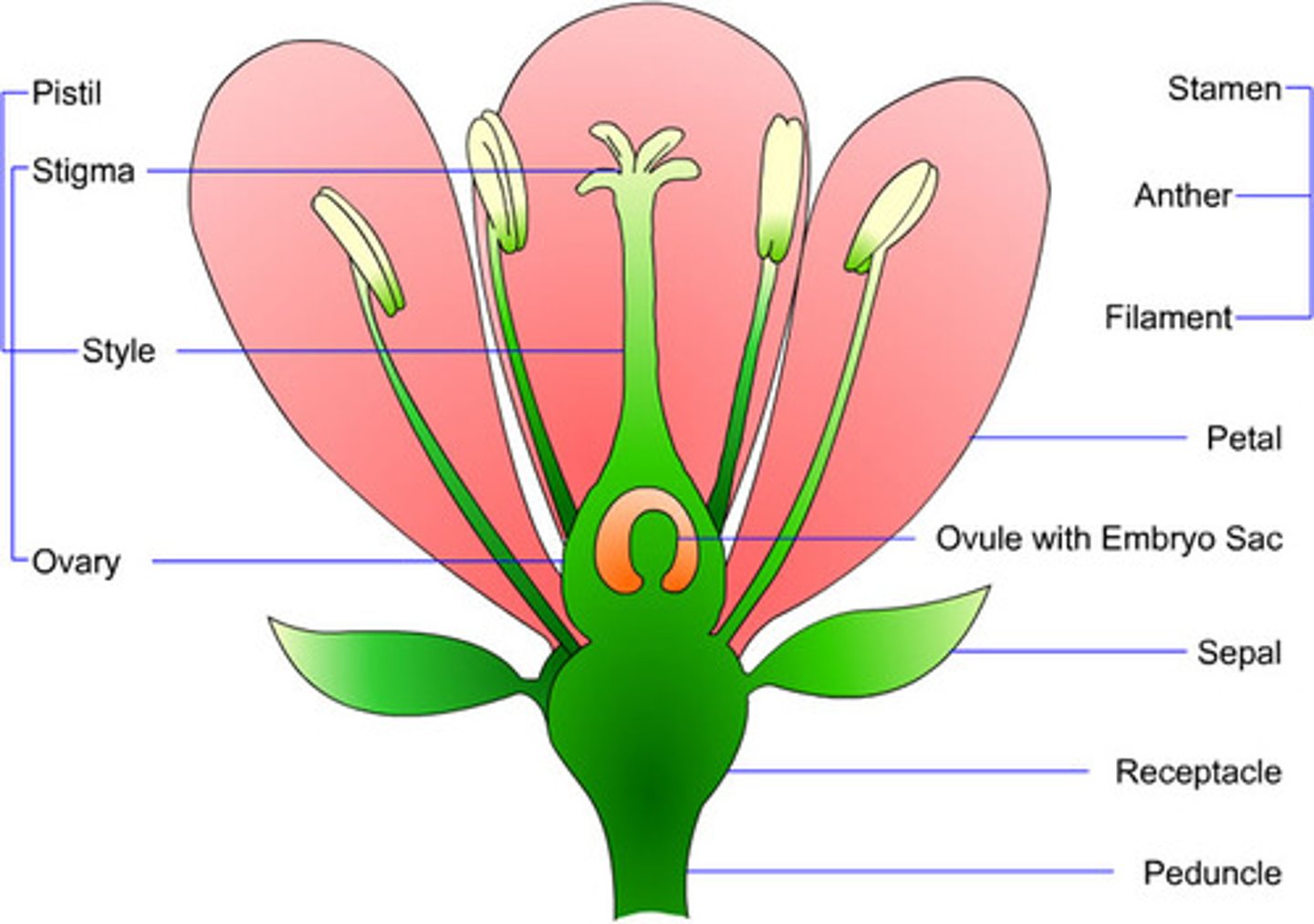
Stigma of a plant does what?
The stigma collects pollen at pollination. Stigmas can either be long and thin or globe-shaped.
Halophile archaebacteria only survive in which type of environment?
Salt loving environment
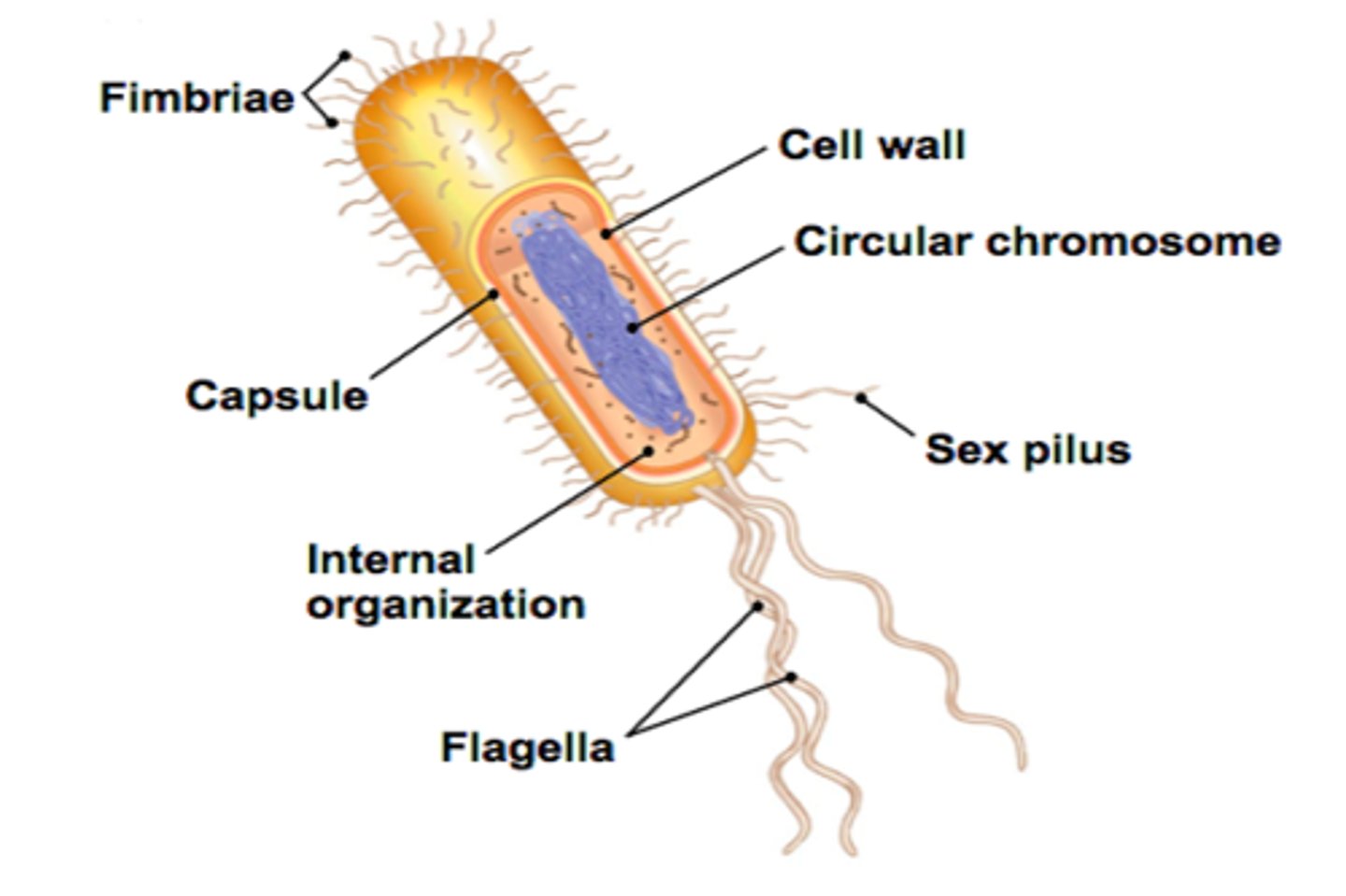
What is the cilium-like structure present in certain bacteria cells that allows them to attach to a host tissue?
Fimbria- are appendages found on many Gram-negative (and some Gram-positive) bacteria that allow them to attach to other bacteria, cells, or inanimate objects.
Virus
Viruses can be composed of either DNA or RNA, but not both. If they are composed of RNA, they are called a retrovirus. Viruses are typically much smaller than bacteria
Viruses are considered acellular because they do not have organelles or cytoplasm. All viruses are parasitic, as they depend on a host source to be able to reproduce
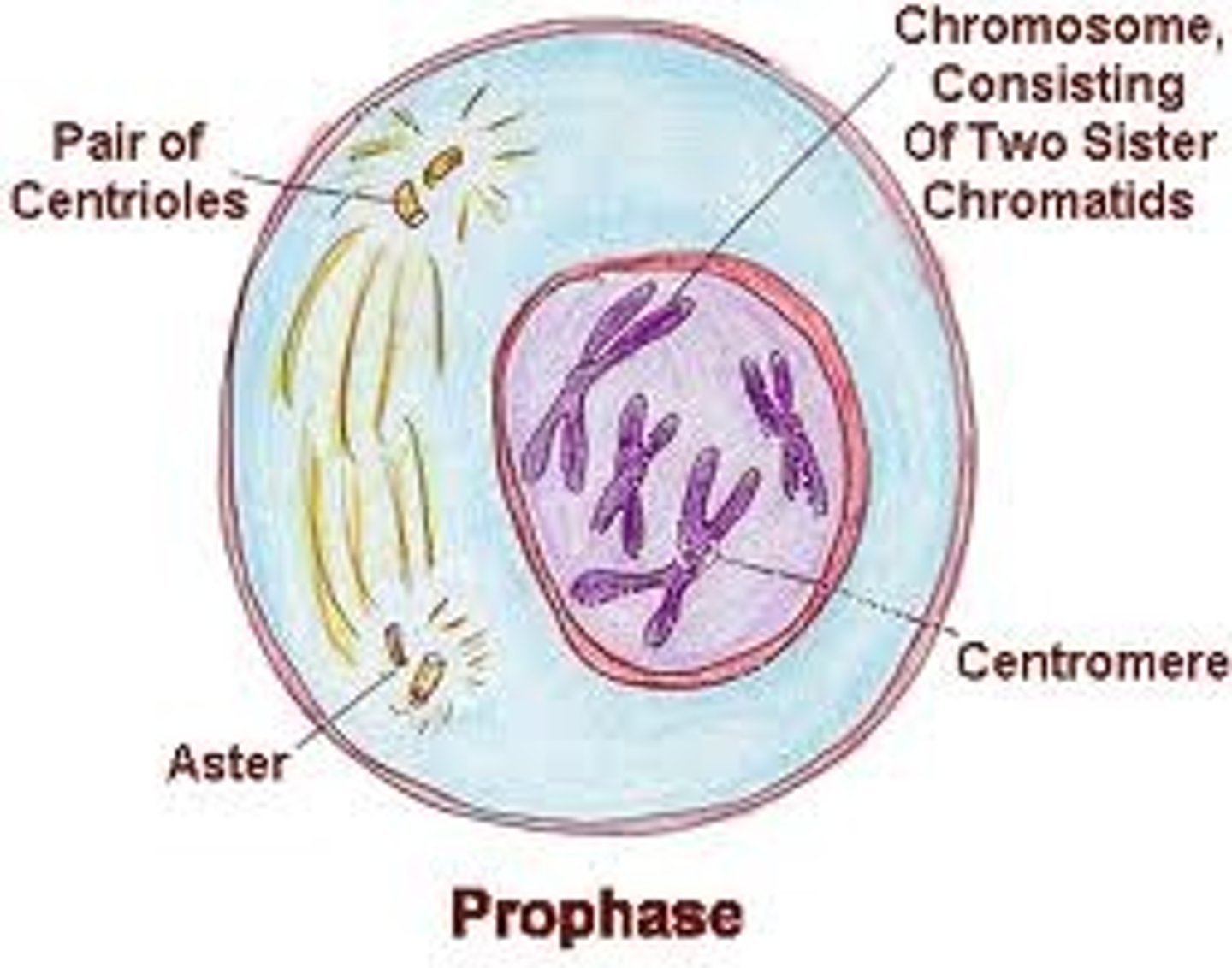
Prophase
Chromosomes are visibly separate, and each duplicated chromosomes has two noticeable sister chromatids
Propmetaphase
Nuclear Envelope begins to disappear and the chromosomes begin to attach to the spindle that is forming along the axis of the cell
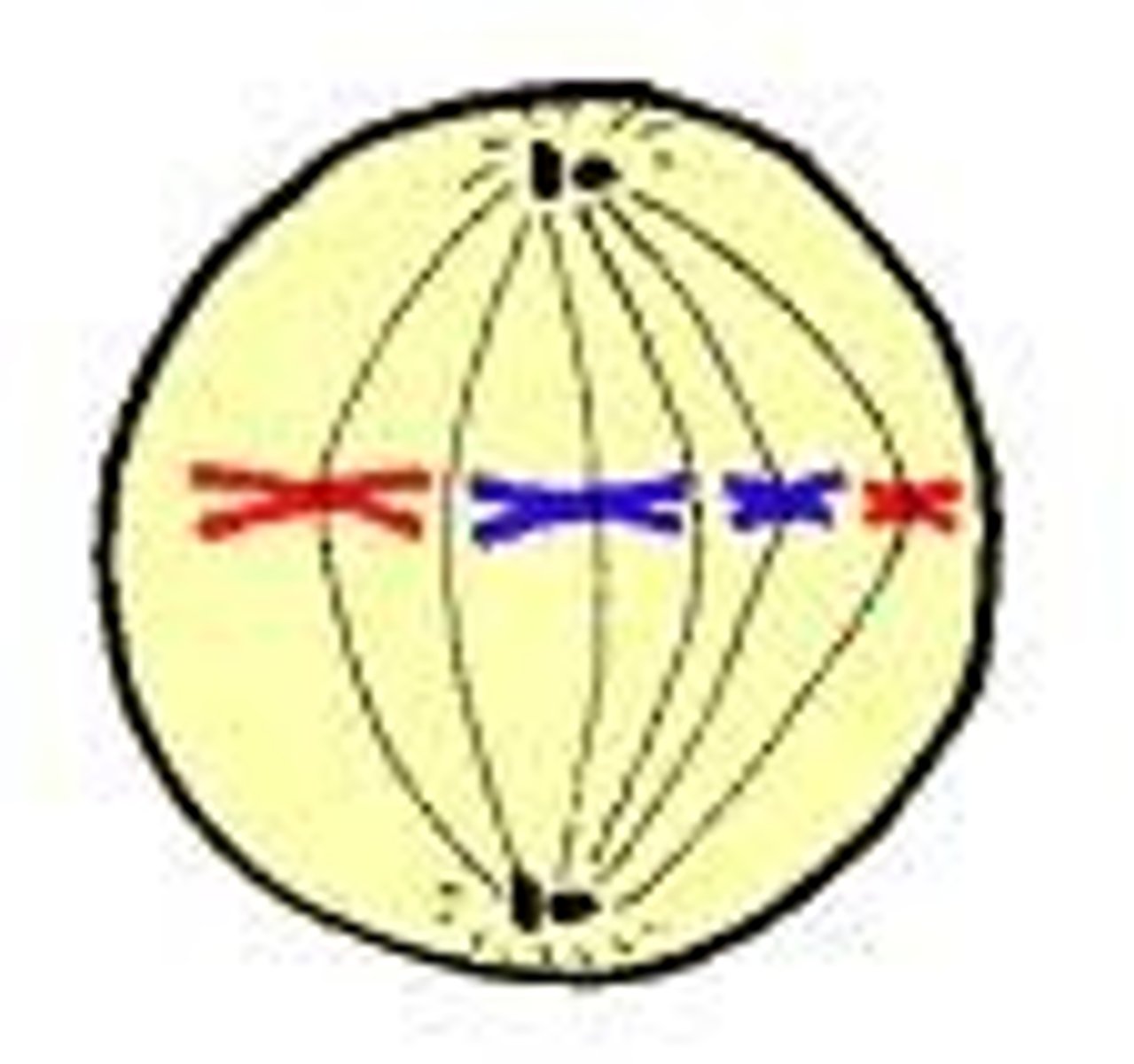
Metaphase
Aligning along the metaphase plate. "middle"
Anaphase
Chromosomes start to SEPARATE. "Chromotids" seperate chromosomes
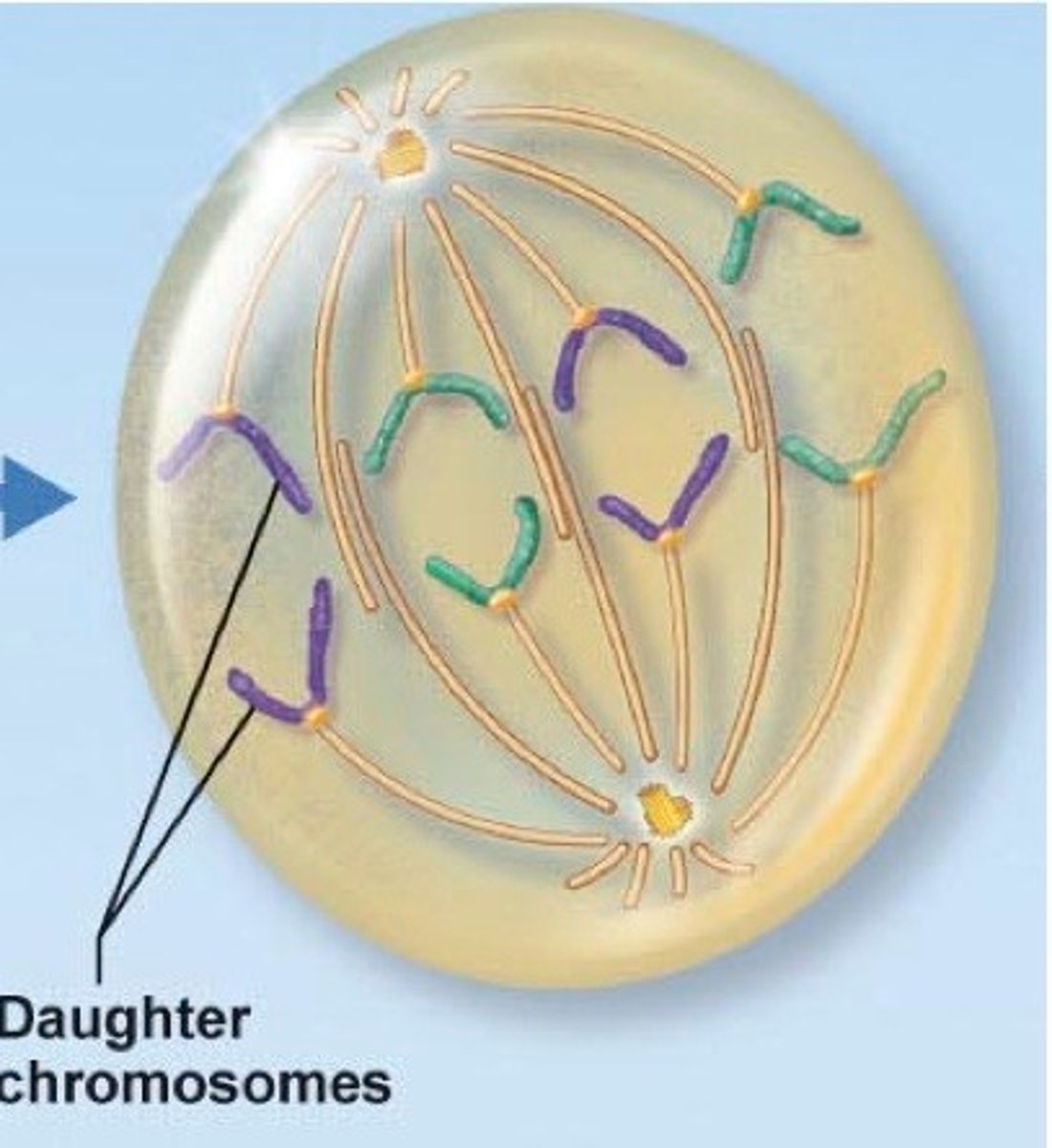
Telophase
Gather on either side of the now separating cell. END of mitosis.
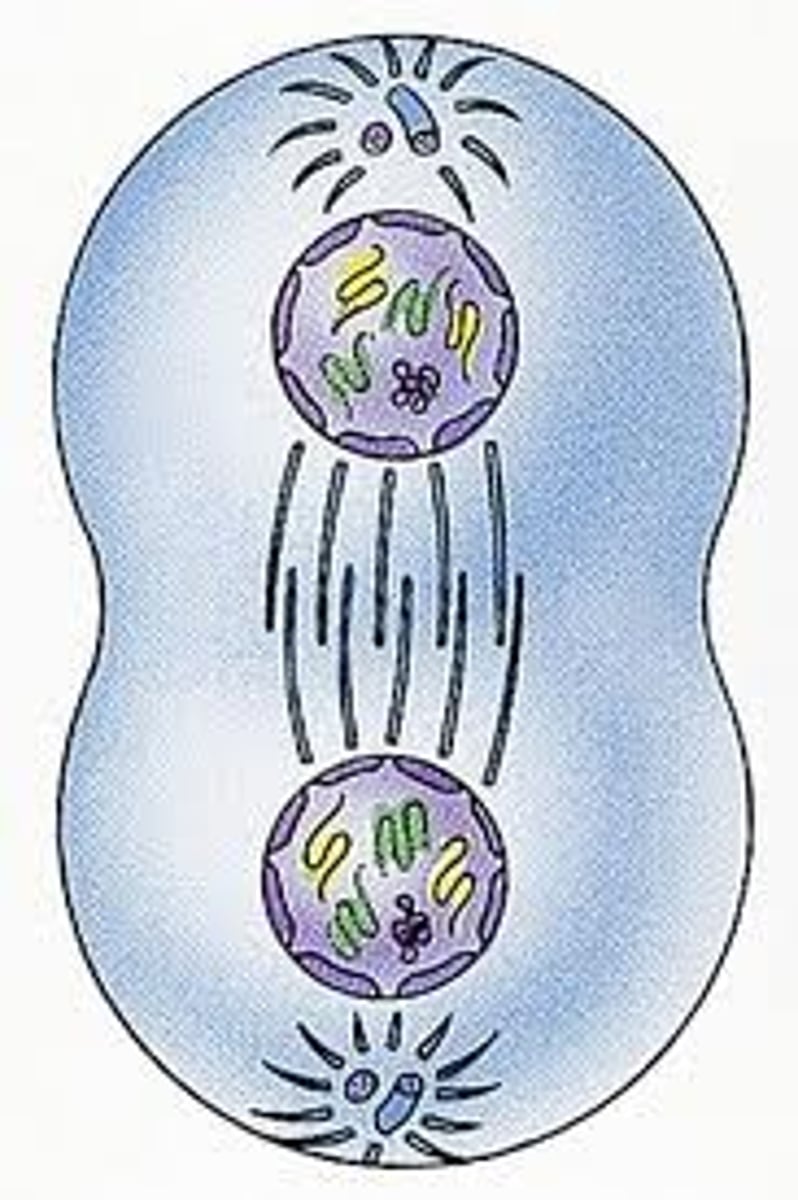
Cytokinesis (Mitosis)
2 diploid daughter cells from mitosis
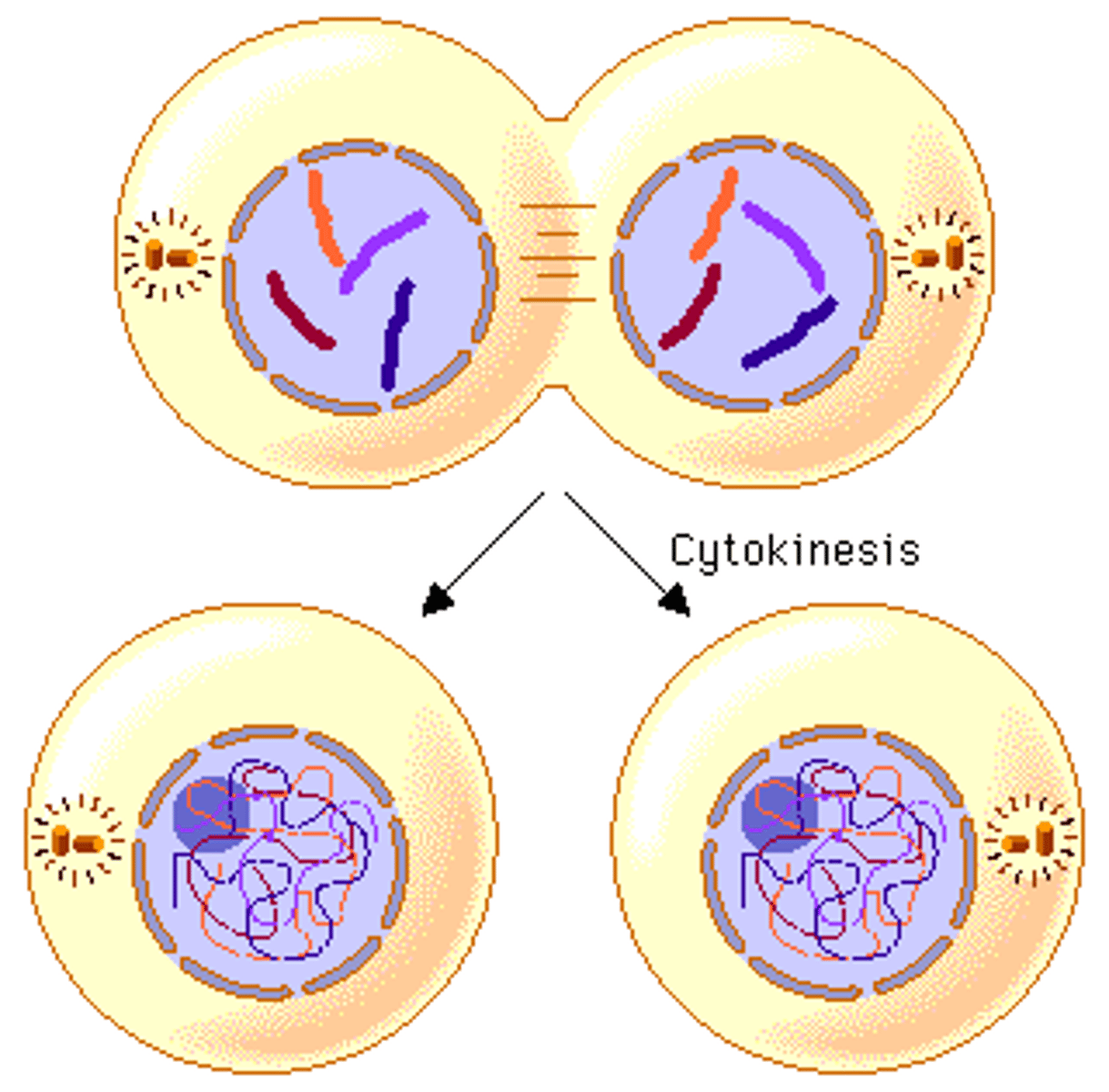
Meiosis I and II through cytokinesis
Results in 4 haploid daughter cells (haploid to diploid)
Interphase (IPMAT)
Chromosomes duplicate and cell prepares for division
Alleles
Alternative versions for a gene
Amino Acids
simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group. They are bonded together by a peptide bond and are the building blocks of proteins.
Binary Fission
In this process, the chromosome binds to the cell membrane, where it replicates. The as the cell grows, it pinches in two, producing two identical cells.
Chromosomes
Contains all the DNA material necessary for the regeneration of the cell, as well as all instructions for the function of the cell. Every organism has a characteristic number of chromosomes specific to the particular species.
Codon
Every group of three bases along the stretch of RNA
Cytokenesis
This step is technically separate from mitosis, and occurs when the cell pinches in two, forming two separate identical cells.
Metabolic pathway
In a cell, it's a reaction that takes place in a series of steps progressing from a standpoint of high energy to low energy. All reactions are catalyzed by the use of enzymes.
Pleiotrophy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype
Polygenic Inheritance
Combined effect of two or more genes on a single character
Cilia
Paramecium, Vorticella and Stentor exhibit their locomotion with the help of ___________.
Autotrophs
is an organism that can feed itself i.e. produces its own food.
Heterotrophs
is an organism that feeds on another organism i.e. cannot produce own food.
Phototrophs
"plants" feed themselves with light.
Omnivores
Eat meat and plants
Herbivores
are the animals which feed on plants only. Typical examples of this category are insects, reptiles, birds and mammals.
Detritivores
animals which feed on detritus (organic debris from decomposing plants and animals) Earthworm is a common detritus feeder.
Fluid feeders
are organisms that feed on the fluid of other organisms. It can refer to: Hematophagy, feeding on blood. Nectarivore, feeding on nectar. Plant sap feeders.
Autocrine
The hormone which acts on the same cell that produced
Paracrine action
means that the hormone acts LOCALLY by diffusing from its source to target cells in the neighborhood. The hormone is distributed in blood and binds to distant target cells when it is acting through the endocrine pathways.
Exocrine action
Those hormones which secrete their essential product by way of a duct to some environment external to itself, either inside the body or on a surface of the body
Hydrogen and Helium
The 2 most ABUNDANT ELEMENTS in the chemical composition of the universe are:
Which of the following are the sites of ribosome production in the cell?
Nucleoli
How does the water on Earth regulate the Earth's temperature?
it absorbs heat, but only increases a few degrees in temp
The variations of the genes for a single trait are called
Alleles
Lycopods
first plants that formed true leaves and roots.
Which statement correctly describes a difference between the cytosol and the mitochondrion?
Mitochondrion which is also known as the power house of the cell is a membrane-bounded cell organelle while cytosol LACKS any definitive membranous outer covering.
Cytosol
The cytosol is the fluid in which organelles of the cell reside. This is often confused with cytoplasm, which is the space between the nucleus and the plasma membrane.
Which of the following processes does NOT lead to cellular energy production?
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. This process requires energy.
Gametes
Gametes carry half the genetic information of an individual, one ploidy of each type, and are created through meiosis.
One allele for each gene
The process of making mRNA using DNA as a template is called
Transcription
During cellular respiration, NAD+ serves as
a carrier of hydrogen atoms and electrons..
NAD+-----NADH
Isomers
Galactose, D-glucose and fructose are examples of
Which of the following CARRIED the GENETIC CODE from the nucleus to the ribosome in the cytoplasm?
MESSENGER RNA (mRNA) carries information about a protein sequence to the ribosomes, the protein synthesis factories in the cell. It is coded so that every three nucleotides (a codon) correspond to one amino acid.
Cytokinesis is
The division of cytoplasm is known as cytokinesis. This stage begins when the mitosis is near completion and results in the formation of two daughter cells.
ATP is able to power cellular work by undergoing a certain reaction. Which of these chemical equations best represents this reaction?
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + Energy
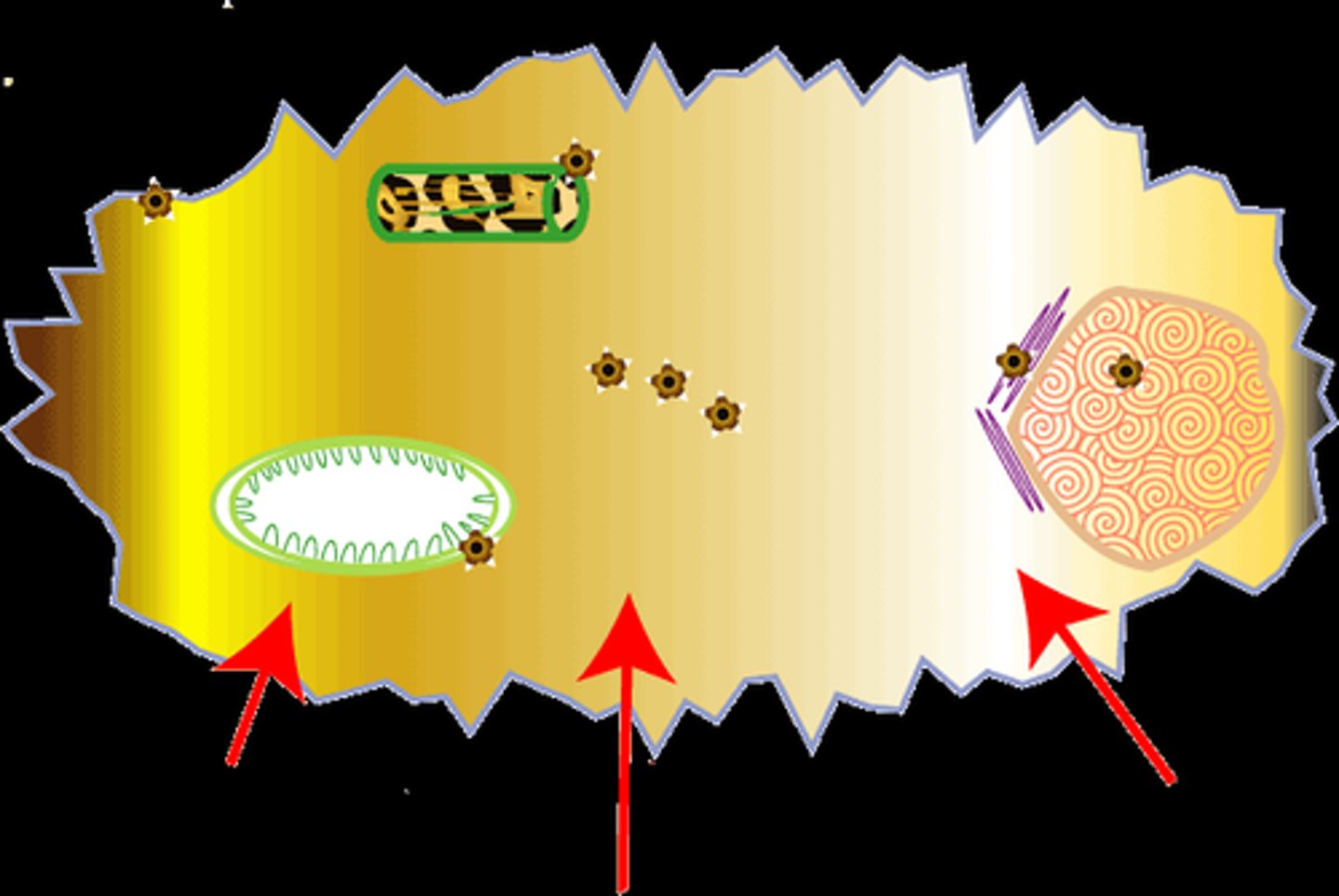
Which of the following are found in bacterial cells?
Ribosomes
The utilization of the products of digestion for production of energy or synthesis of cellular material is called:
Assimilation
The main factors affecting the process and rate of photosynthesis are:
Light
Temperature
Carbon dioxide
Water
Chlorophyll concentration
Photosynthesis takes place in the membranes of small sacs called
Thylakoids
DNA replication is called semiconservative because
each helix that is created contains one strand from the helix from which it was copied
In aerobic cellular respiration, oxygen serves as
oxidizing agent
Stratified squamos epithelium
Skin, mouth and esophagus are lined
transitional epithelium lines
the organs of the URINARY SYSTEM
pseudostratified epithelium
functions in the processes of absorption and secretion. It is often ciliated as in the RESPIRATORY TRACT
simple columnar epithelium
lines the DIGESTIVE TRACT. It consists of a single layer of tall cells. It often includes mucous producing goblet cells.
What are isomers?
Two or more compounds having the SAME MOLECULAR FORMULA but different structural formula and properties.
Mesosomes
The invagination of a cell membrane into the cytoplasm results in the formation of mesosomes. Mesosomes can be in the form of vesicles, tubules or lamellae.
Various functions of mesosomes are:
• DNA replication
• Cell division
• Export of extracellular enzymes
• Respiratory enzymes are also present in mesosomes
Which statement about pyruvate is most consistent with the diagram?
The formation of pyruvate is associated with the production of energy in the form of ATP molecules. Under aerobic conditions in the mitochondria, pyruvate is converted into acetyl-coA, which goes into the citric acid cycle to yield 2 molecules of ATP.
Maximum of 34 ATP molecules are produced in the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis process.
Aerobicrespiration37 41
It's formation yields ATP
The ultimate end product of glucose breakdown in glycolysis is:
Pyruvic acid
The breaking of the terminal phosphate of the ATP molecule releases about how many K calories of energy?
7.3 K calories
Stroma
What is the fluid-filled space that contains enzymes for the light-independent reactions called?
Which is a light-independent reaction?
Calvin Cycle
G1 Phase
The first phase within interphase
(G indicating gap). It is also called the growth phase.
Cellular contents are DUPLICATED