Organic chemistry portion
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pictures and definition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
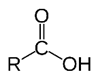
Carboxylic acid. R-C=O-OH
any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon (C) atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group (―OH) by a single bond. A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen (H) atom or to some other univalent combining group
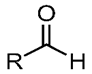
Aldehyde. R-C=O-H
carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom, a single bond with a hydrogen atom, and a single bond with another atom or group of atoms
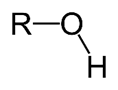
Alcohol. R-OH
organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl ( −OH) functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom
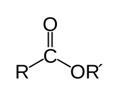
Ester. R‐C=O‐OR’
compound derived from an acid (organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group (−OH) of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (−R)
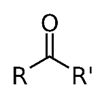
Ketones (R−C−R), diketones.
o ketone is a functional group with the structure R−C−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C−. The simplest ketone is acetone
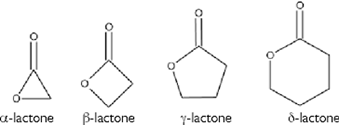
Lactones – heterocyclic, aromatic.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure, or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring

Phenols.
phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C. 6H. 5. OH
Macrocyclic compounds.
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Think mickey mouse ears as an example
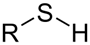
Sulfur compound
Thiol.
compound which contains an SH functional group. The -SH group itself is called a mercapto group

dithiol.
Basically two -SH groups instead of one
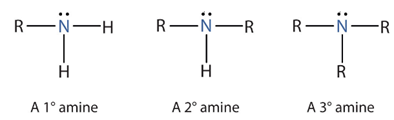
Amines.
derivative of ammonia in which one, two, or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydrocarbon groups
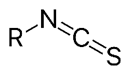
Isothiocyanate.
functional group −N=C=S, formed by substituting the oxygen in the isocyanate group with a sulfur.

Pyran.
Heterocyclic 6-member ring compound, usually non-aromatic. Contains an oxygen molecule and 2 double bonds. (lactone, maltol)
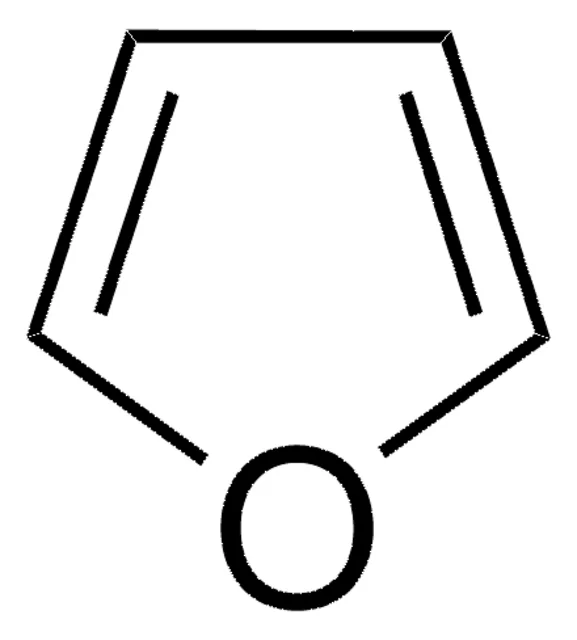
Furan.
5-membered ring containing an oxygen and 4 carbons.
Define Monoterpine
cyclical or ring shape that contains at least two isoprene units.
examples: myrcene, valencene
Define sesquiterpene
increased chain length over monoterpene. must contain at least 3 isoprene units.
example: humolene, bisabolene
define cis isomer
C arm of aromatic ring. can be labeled as Z-3-hexanol
Define trans isomer
Z shape arms on opposite sides of aromatic ring. can be labeled as E-3-hexanol
Define dextro isomer
Right sides isomer of aromatic ring. example D-carvone
Define Laevo isomer
Isomer that comes off the left side of a aromatic ring. Example: L-carvone
Define racemic amino acid isomer
Combo of D and L amino acids
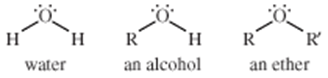
Ether
characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers are similar in structure to alcohols, and both ethers and alcohols are similar in structure to water.
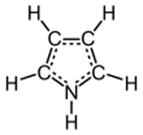
Pyrroles
Heterocyclic (two different molecules) series characterized by a ring structure composed of four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom.
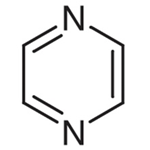
Pyrazine
azaheterocycle that is aromatic and contains two nitrogen atoms
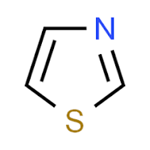
Thiazole
heterocycle containing sulphur and nitrogen atoms
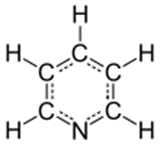
Pyridine
heterocyclic organic compound structurally similar to a benzene ring with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−).