Rocks
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Teaches about Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
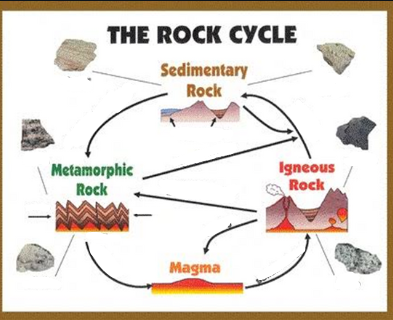
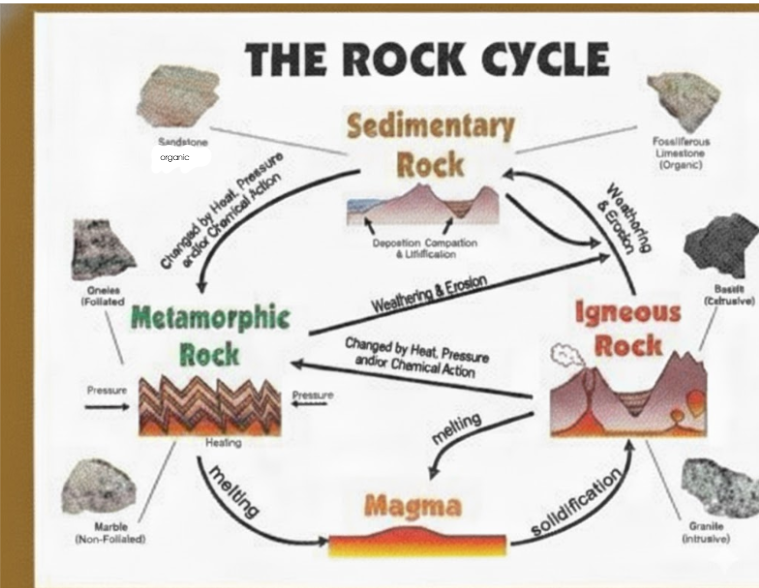
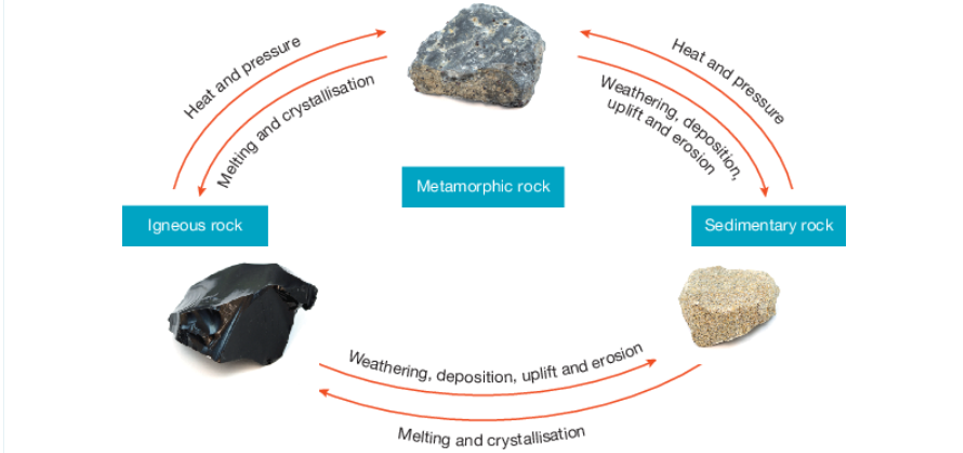
Igneous Rock.
Forms from molten magma or lava. As lava or molten lava cools, it becomes crystals. The slower the lava cools, the bigger the crystals are..
Sedimentary Rock
This rock is formed in layers near the Earth's surface. It begins when fragments of older rocks, minerals, or organic matter (called sediments) are broken down and moved by weathering and erosion. The sediments are then turned into solid rock through two main steps: the massive weight of layers above compresses or squeezes the sediments (compaction), and dissolved minerals then act as a natural glue or pressure to bind the grains together (cementation). Made from rocks shells and stones are weathered down into small grains called sediments. When these eroded sediments enter flowing water all these small sediments are glued together through a process called cementation and compaction.
Metamorphic Rock
This rock is formed when any existing rock (igneous, sedimentary, or an older metamorphic rock) is chemically and physically changed deep underground by intense heat and pressure, causing it to transform into a new, denser rock.
Minerals
These make up the set out of rocks. These are solid substances that can include elements found in their pure state, also called native elements, such as gold or iron. However, most minerals in rocks are compounds like calcite, which is one carbon and three oxygen. The main type of mineral is called silicates, formed where oxygen is mixed in with carbon and possibly other minerals. A specific type of mineral will always have the same chemical makeup, even though its colours and shapes may change.

A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types
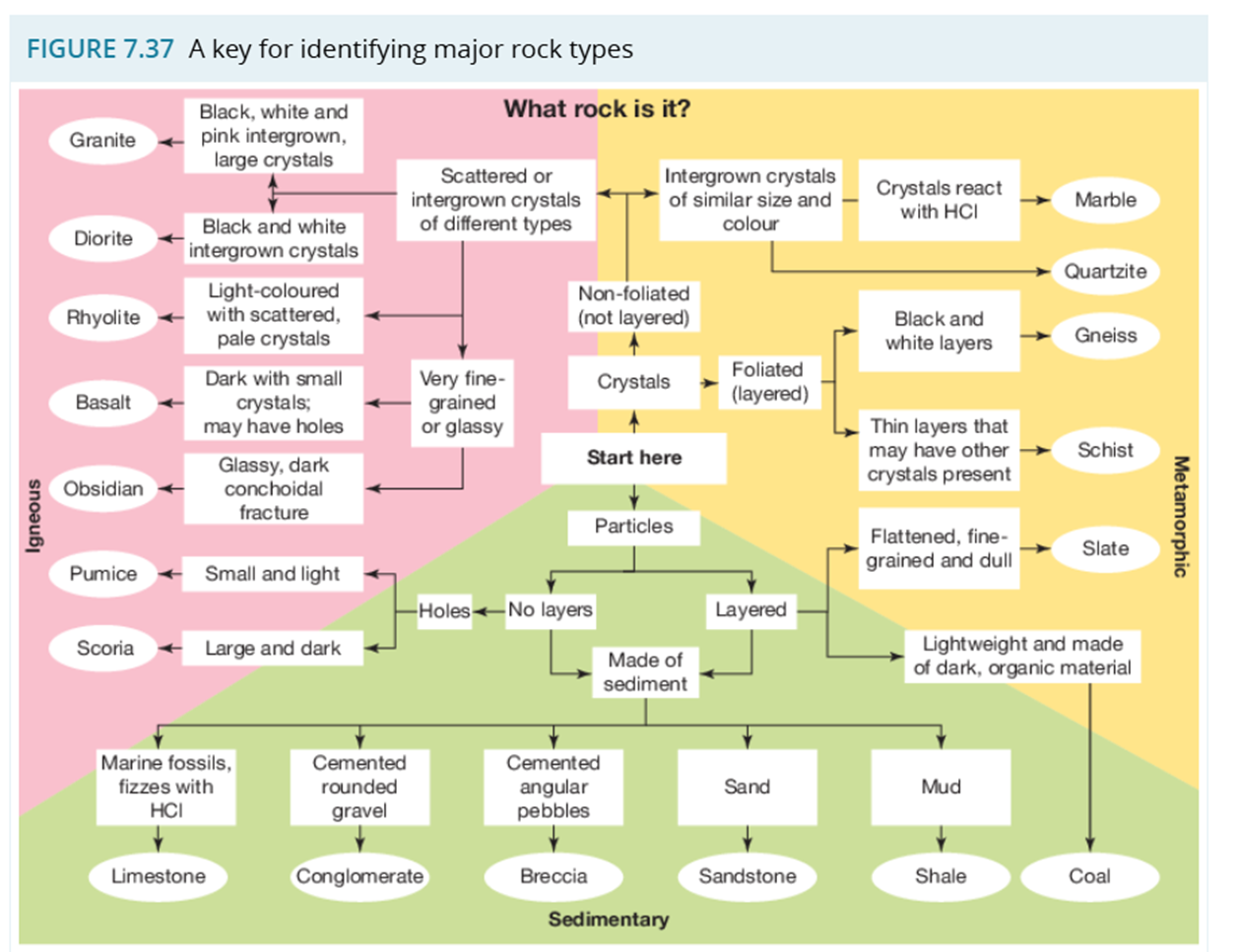
Identify and describe:
Granite and Pumice
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types
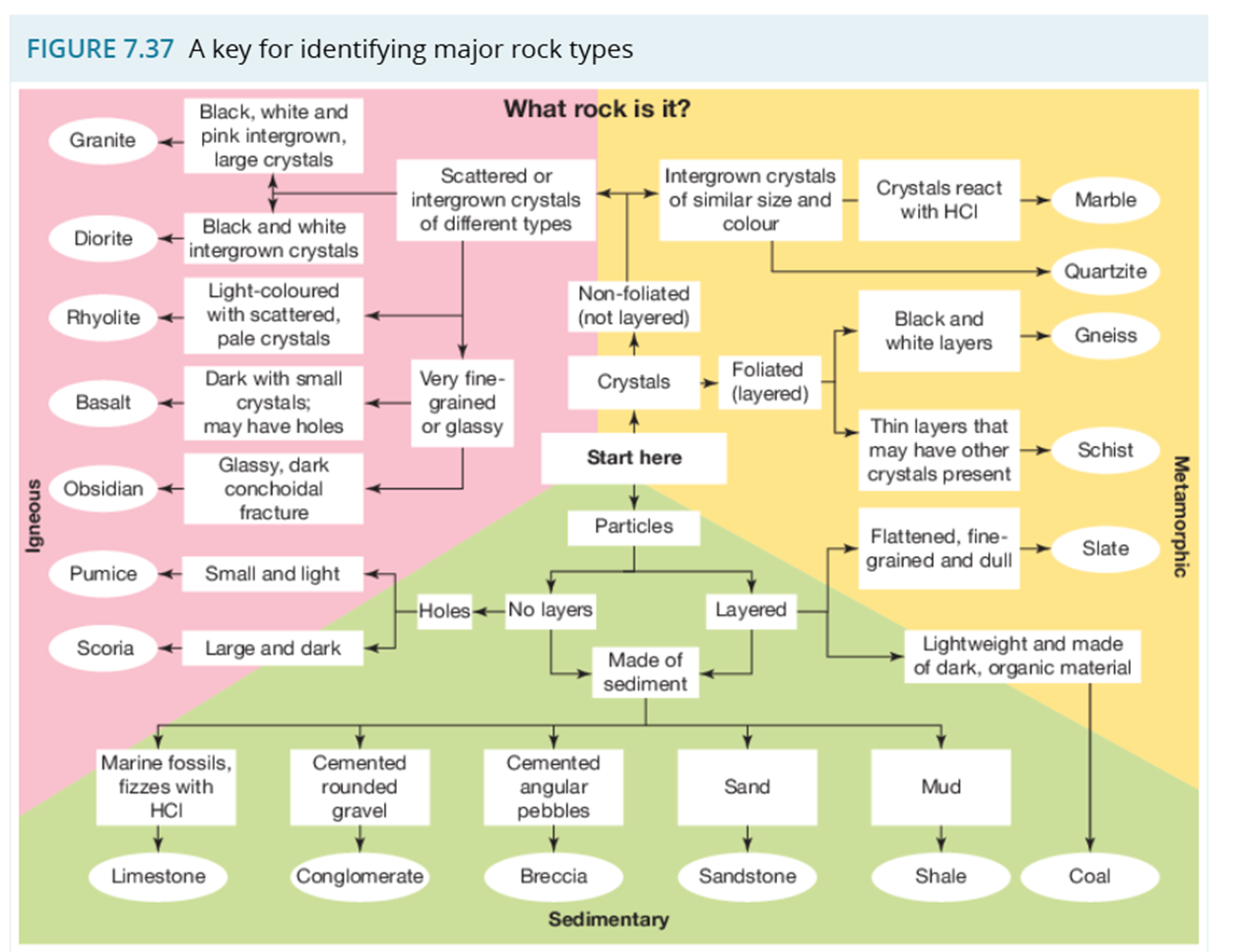
Identify and describe:
Diorite and Scoria
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Rhyolite and Basalt
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Obsidian
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Limestone and Coal
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Conglomerate and Shale
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Breccia and Sandstone
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Marble and Slate
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Quartzite and Schist
A Key For Identifying Major Rock Types

Identify and describe:
Gneiss
How different Sedimentary rocks are made.
TABLE 7.6The names of sedimentary rocks are based on their grain size.
Sediment clast size | Clastic sedimentary rock names |
|---|---|
 | Conglomerate contains large clasts surrounded by sediments of different sizes, all cemented together. |
Sandstone is formed from grains of sand that have been cemented together. | |
Siltstone particles are smaller than sand, but slightly larger and not as soft as those in mudstone. | |
Mudstone and shale are formed from muddy particles (clay and silt) deposited by calm water. |