Muscular System
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
how many muscles in the human body
650
what is the main function of the muscular system
To generate force and movement in the body.
aponeuroses
Fibrous sheets that connect muscles to bones or other muscles, allowing for the transmission of force and providing stability and support; broad tendon sheaths
what is the basic unit of the muscle cell
sarcomere
Muscle Tone
The natural state of tension in muscles, even at rest
maintain posture, stabilize joints, and provide a base for movement.
regulated by the nervous system and influenced by factors like physical activity, age, and overall health.
_____ produced by muscle tone prevents muscle from weakening, allowing muscles to stabilize joints and maintain posture
tension
hypotonia
Abnormally low muscle tone, characterized by decreased resistance to passive movement and a floppy or limp appearance.
hypertonia
condition characterized by increased muscle tone or tension; excessive muscle tone
What are the two forms of hypertonia?
spasticity and rigidity
spasticity
type of stiffness related to uncontrolled reflexes
rigidity
stiffness of muscle not associated with reflexes
what are two types of skeletal muscle contractions.
isotonic and isometric
isotonic contractions
Muscle contractions where the muscle length changes while maintaining constant tension. These contractions are commonly seen during activities like weightlifting or carrying heavy objects.
what are two types of isotonic contractions
concentric and eccentric
concentric contractions
Muscle contractions where the muscle shortens as it generates force. It occurs when the force produced by the muscle is greater than the resistance.
example of concentric contraction
bicep muscle shortening as hand weight brought upward and angle of elbow decreases
Eccentric Contraction
muscle lengthens while generating force
It occurs when the external force applied to the muscle is greater than the force generated by the muscle itself
doesn’t produce adequate force to move load, but used for movement, balance, resisting movement
example of eccentric contraction
movement of bicep as it performs lowering portion of bicep curl
______ contraction brings arm upward, reducing angle of elbow while _____ contraction lowers arm, resisting gravity and increasing elbow angle slowly
concentric, eccentric
isometric contractions
muscle produces tension without changing length; do not produce movements or lift loads, maintain posture and joint stability
example of isometric contraction
ex. holding head in upright position to maintain stationary and not produce movement
epimysium
connective tissue that wraps around outer laryer of each muscle; allows muscle to contract and move powerfully while maintaining structural integrity; composed of thick layer of collagen fibers
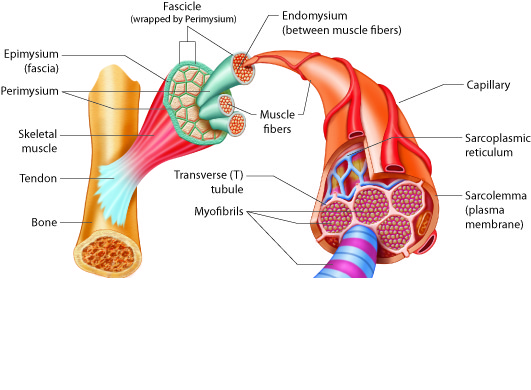
Fascia
Connective tissue that surrounds muscles, organs, and other structures, providing support and protection. It helps to separate and compartmentalize different body parts, allowing them to move independently; plays a role in facilitating the transmission of forces and maintaining structural integrity.
a single muscle cell is called a ________
muscle fiber
each______ contains many long muscle fibers bound by the perimysium
fascicle
perimysium
contains collagen fibers and elastin fibers; middle layer of connective tissue that surrounds each fascicle
endomysium
connective tissue layer that encases individual muscle fibers; thinner than other two layers, contains areolar and reticular tissues to form loose delicate networks; contain small blood vessels and motor neurons to support and activate each muscle fiber
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of skeeltal muscle fiber; located just under endomysium; site of action potential conduction
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of the muscle cell
muscular dystrophy
A progressive genetic disorder characterized by the weakening and degeneration of muscles. It leads to muscle wasting, loss of muscle control, and eventual disability.
what is most common type of muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
genetic disorder characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration; primarily affects boys and is caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene.
purpose of dystrophin
helps thin filaments of myofibrils bind to sarcolemma and maintains equal force transmission through muscle tissue; without sufficient amounts of this protein muscle contractions cause sarcolemma to tear
inheritance pattern of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
X-linked recessive
parallel muscles are arranged parallel to ______ axis of muscle
long
parallel muscles are
equidistant and run in the same direction
What type of muscle fiber organization do skeletal muscles follow?
parallel muscle fiber organization
central body of muscle
large mass of tissue located in middle of the muscle
aka the belly
circular muscles
aka sphincters, arranged around an opening in rings
orbicularis oris muscle
circular muscle around the mouth under lips
orbicularis oculi muscle
circular muscle surrounding each eye
convergent muscles
fascicles extend from broad fan-shaped area and converge on single attachment site where muscle interacts with tendon; can be stimulated in different, smaller areas
example of convergent muscle
pectoral muscle on chest
example of parallel muscle
bicep muscle
pennate muscle
feather-shaped, form different fascicle arrangements at angle to tendon; contracting this msucle pulls at an angle and can produce high tension but doesn’t move tendons very far
subtypes of pennate muscles
uni, bi, multi
unipennate muscle type
fascicles located on one side of the tendon
ex. extensor digitorum in forearm
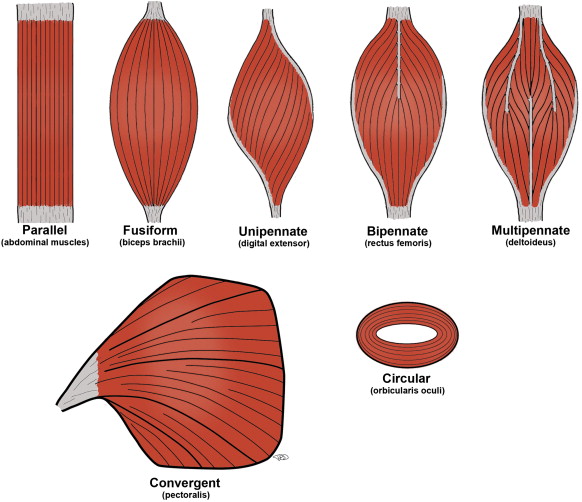
bipennate muscle type
fascicles on both sides of the tendon
ex. rectus femoris in thigh
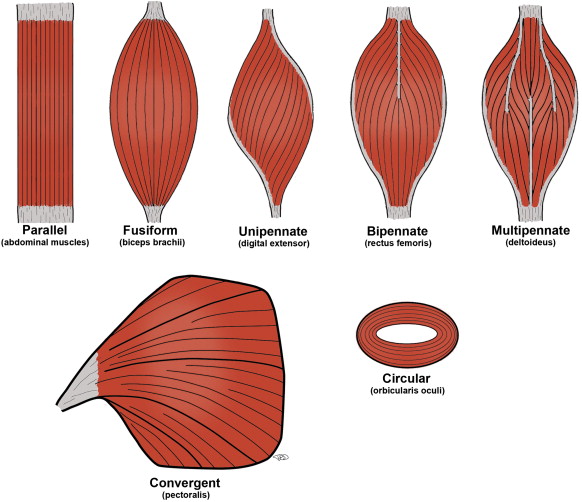
multipennate muscle type
tendon branches within pennate msucle
ex. deltoid muscle of shoulder
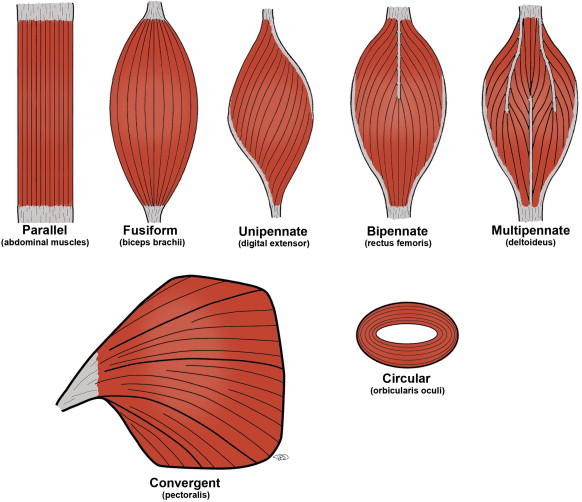
fusiform muscles
muscles that are spindle-shaped, with a thick belly and tapered ends; enable rapid and coordinated movements, such as running and jumping
example of fusiform muscles
biceps brachii or gastrocnemius
triangualr muscles
can be convergent or multipennate to create this muscle shape
ex. trapezius which extends from head down back and out the shoulder
5 types of muscle fiber organization
parallel, circular, convergent, pennate, fusiform (triangular as extra)
direct muscle attachment
The type of muscle attachment where the muscle fibers attach directly to the bone without any tendons or other connective tissues in between.
indirect muscle attachment
Type of muscle attachment where the muscle connects to the bone indirectly via a tendon or aponeurosis
aponeurosis
Sheet-like, fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscles to bones or other muscles. Provides strength and support, allowing for efficient transmission of muscle force.
tendon sheath
Structure surrounding a tendon, providing lubrication and reducing friction during movement.
example of direct muscle attachment
abdominal wall muscles attach directly onto brim of pelvis; temporalis muscle to skull
example of indirect muscle attachment
bicep attaching to humerus and radius and ulna via tendons
bursae
fluid filled sacs join tendons to reduce friction as tendon moves
bursitis
inflammation of bursae caused by overuse of joint or other mechanical stress which can result in pain and swelling
common in knees, elbows, shoulders
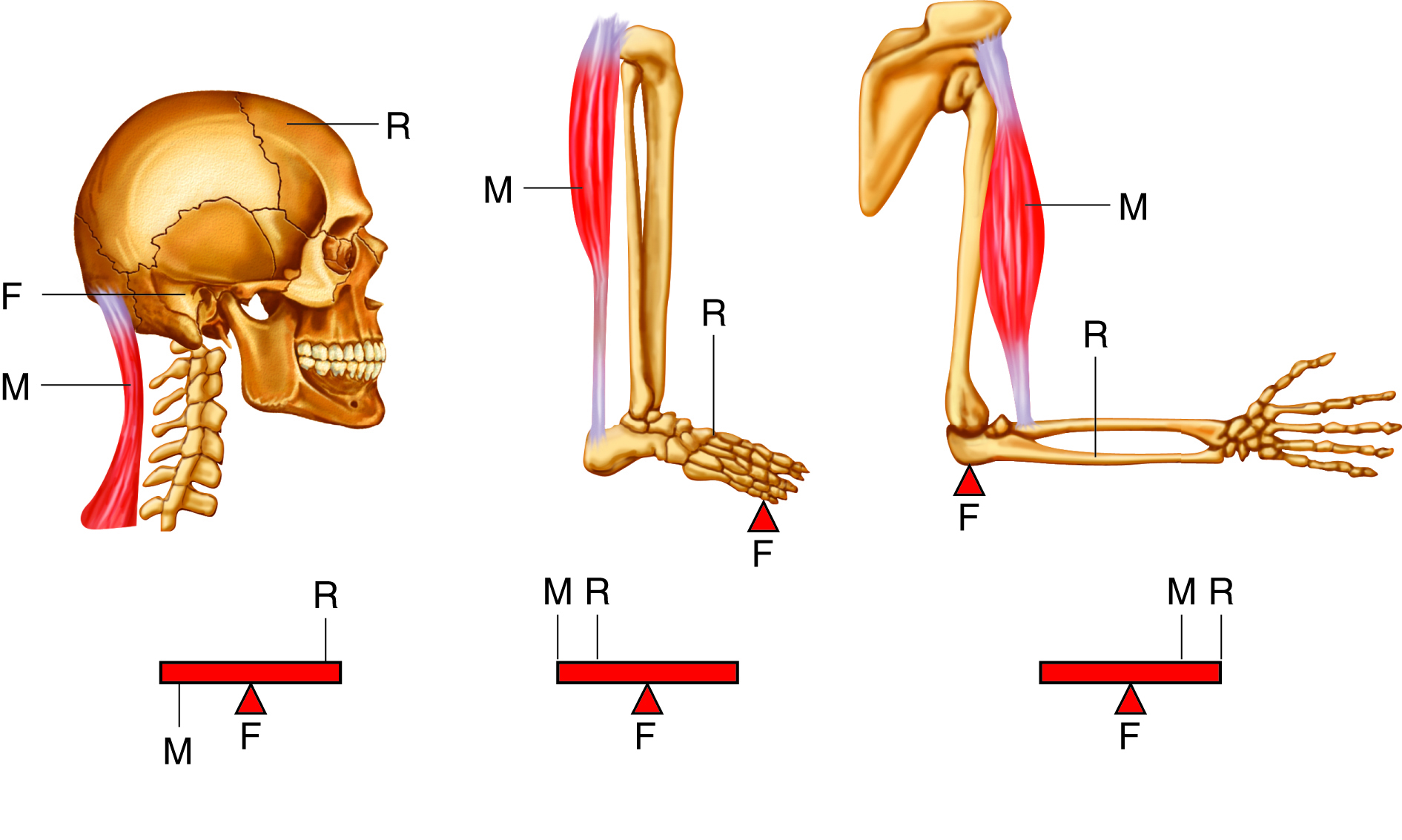
lever in muscular system
a rigid structure (like a bone) that rotates around a fixed point (joint) when muscles contract, allowing movement
each _____ is a lever and each ____ is a fulcrum, ______ supply the applied forces
bone, joint, muscles
first class levers
only few located in body, fulcrum located between force and load
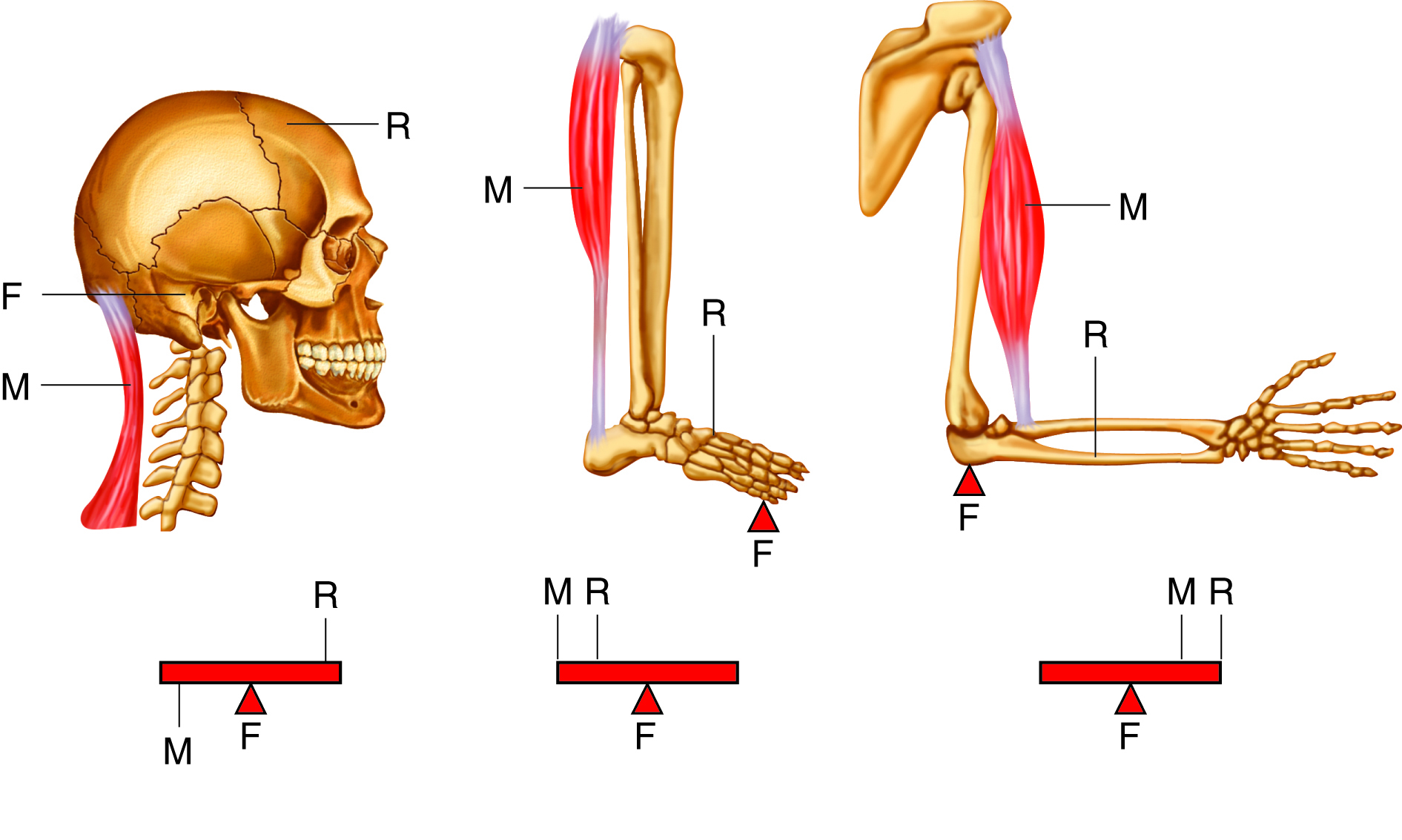
example of first class levers
the head resting on the neck, with the neck muscles acting as the effort, the joint as the fulcrum, and the weight of the head as the load
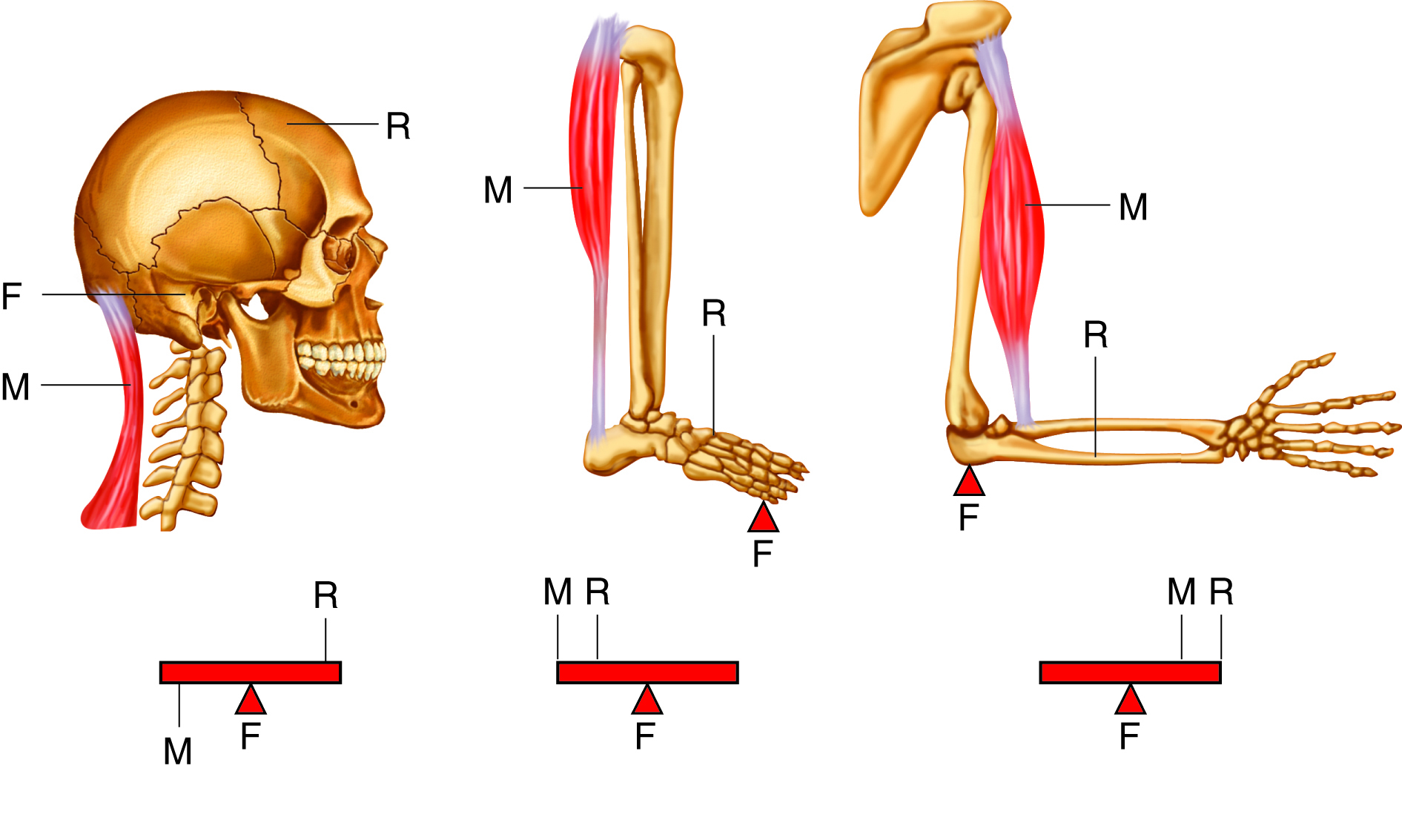
second class levers
load located between applied force and fulcrum; force further from fulcrum than the load so you can move larger weight with less effort
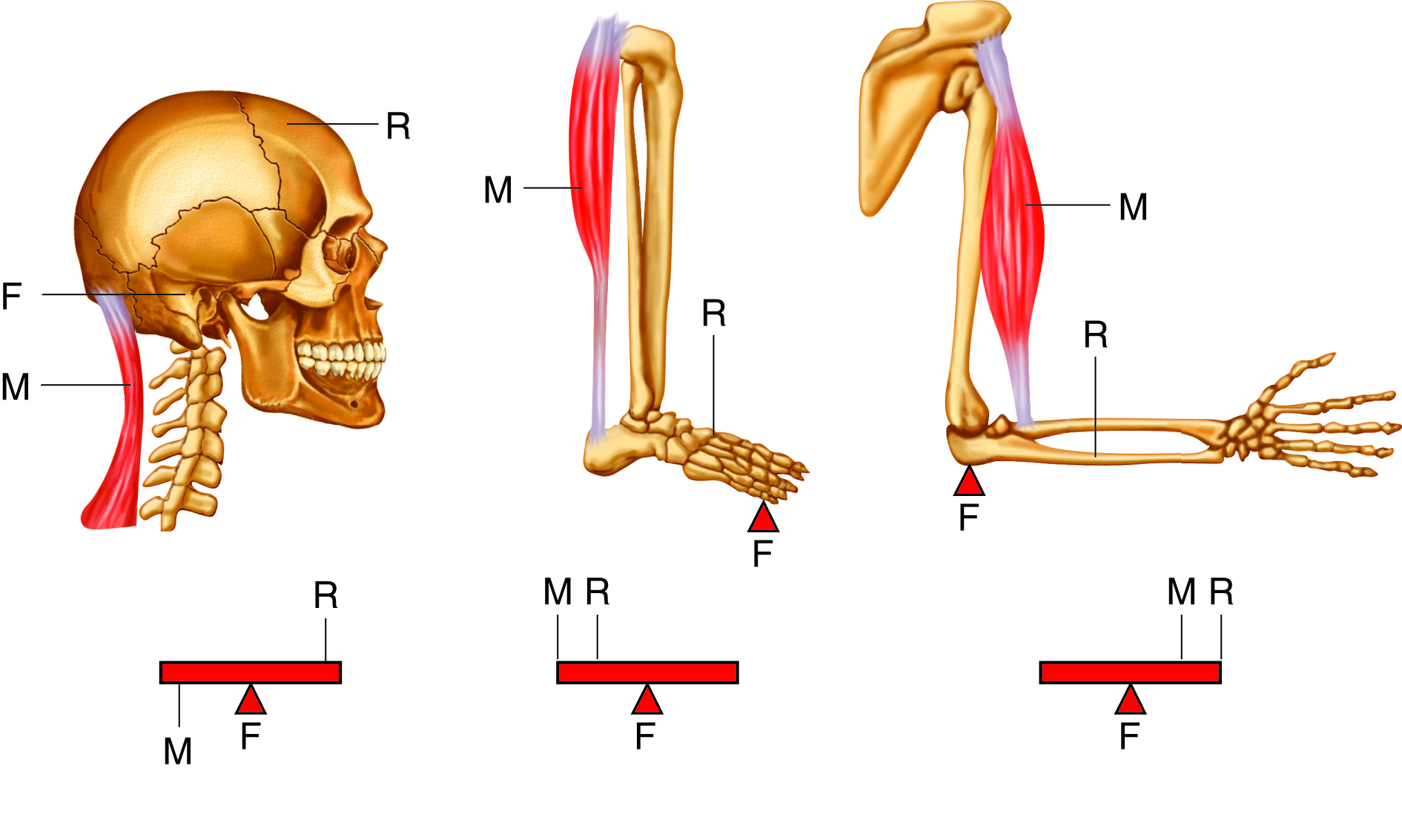
example of second class levers
when standing on your toes, fulcrum is ball of foot, load is body weight, and effort comes from muscles in back of leg
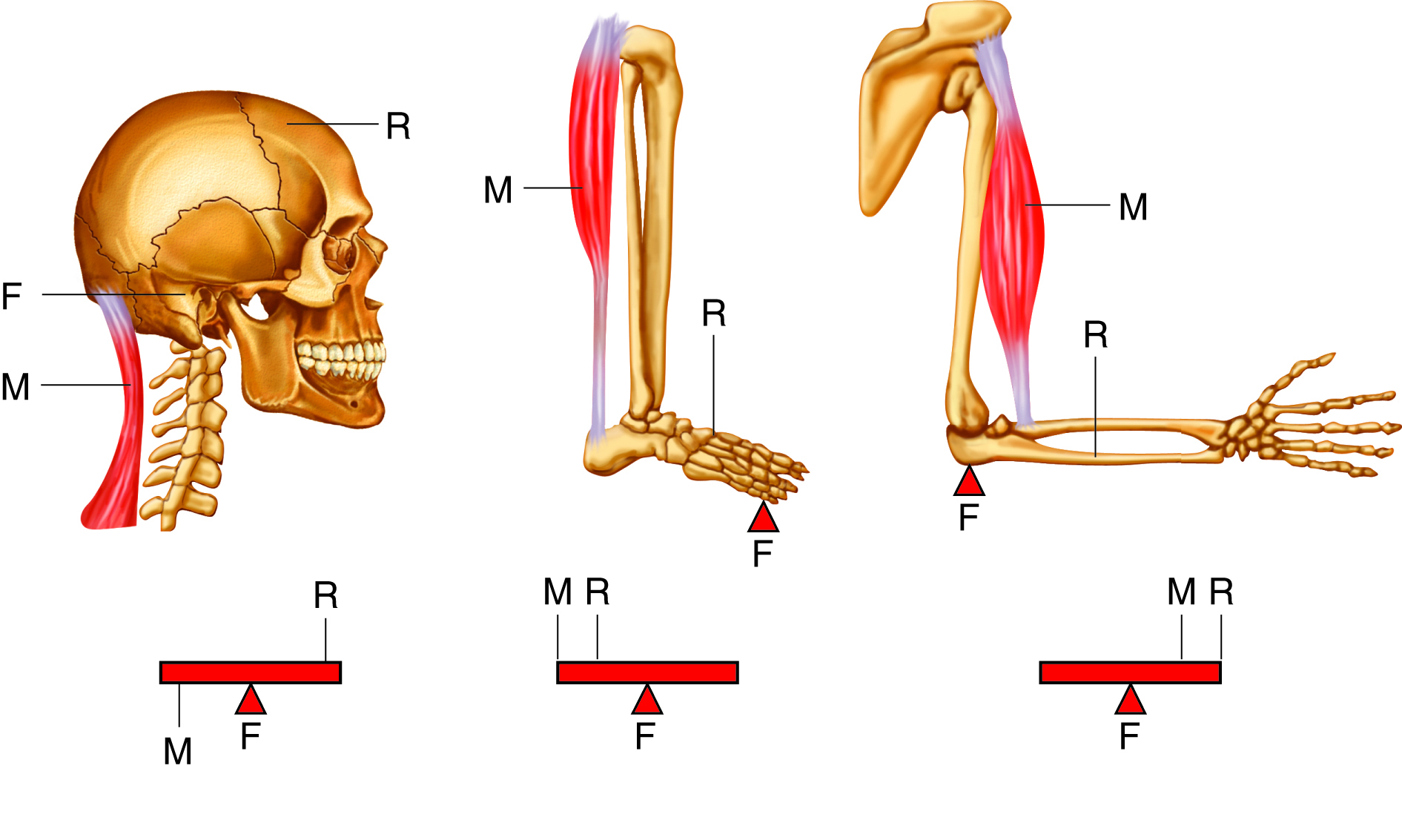
third class levers
force applied between load and fulcrum; most common levers in body
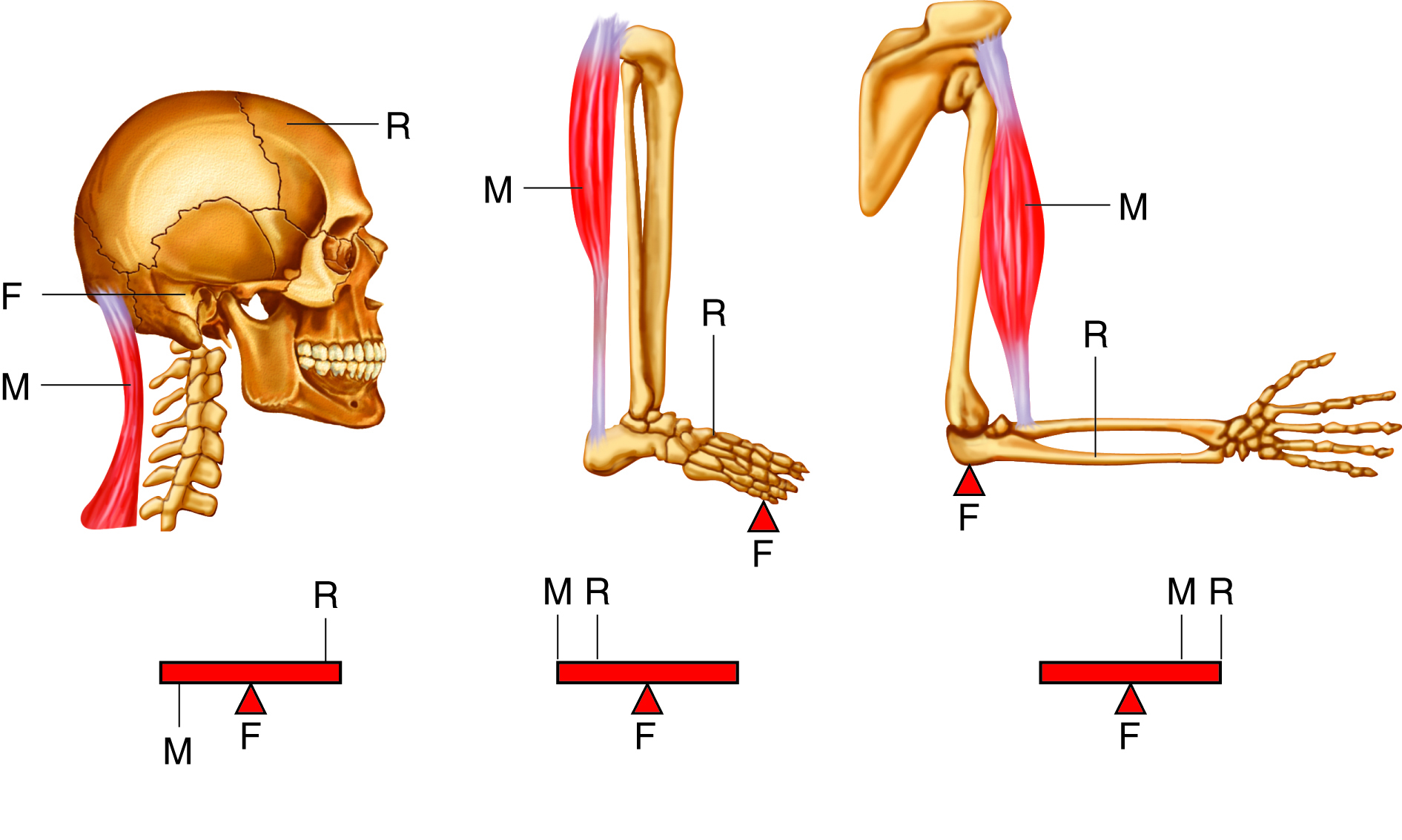
example of third class levers
biceps brachii in arm, load is the hand, fulcrum is the elbow joint, and biceps brachii attaches between the fulcrum and load
skeletal muscles are arranged in ______ for balance and to work efficiently
pairs
antagonist muscle
opposes the action of the agonist muscle
synergists
minor muscle that improves efficiency of agonist muscle or major muscle
brevis muscle
short
longus muscle
long
lateralis
lateral side or away from midline
medialis
toward the midline
flexor muscle
decrease angle at joint
extensor muscle
increase angle at joint
abductor muscle
moves bone away from midline
adductor muscle
moves bone towards midline
when naming muscles, location of ____ always named first
origin
rectus muscle direction means
straight
latissimus
widest
longissimus
longest
magnus, major, vastus
large, larger, huge
what shape is deltoid
triangular
what shape is trapezius
trapezoidal
what shape is serratus
serrated
what shape is rhomboid
diamond-shaped
what shape is pectinate
comb-like
what shape is piriformis
pear-shaped
what shape is platys
flat
what shape is gracilis
slender
supinator
turns palm anteriorly
pronator
turns palm posteriorly
muscle hierarchy
actin/myosin →sarcomeres →myofibrils →myofibers →fascicles → muscle
titin
large structural proteins in muscle cells; forms an elastic filament; helpss align myosin proteins and allows muscle cell to maintain structural integrity by resisting extreme stretching
dystrophin
protein that helps bind actin to muscle cell membrane; insufficient production of this protein results in inability ot transfer force of organized actin-myosin contraction
thick filament composed of
myosin
thin filament composed of
actin