Lecture 34 - Methylxanthines Pt 2, Lead Pt 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How do you diagnose methylxanthine toxicity?
history: potential exposure usually is
MUST DO THE MATH if can
clinical signs in order: GIT..+PU/PU…+hyperexcitability…+CV….+CNS
nonspecific clin path and lesions (myocardial necrosis)
chemical analysis: can use lots of samples, accidental/malicious
What are the treatment aims for the asymptomatic methylxantine toxicity?
big D = decontaminate
emesis - up to 6 hours post ingestion or longer, esp if you see bloat
lavage - not as popular for AS patients
AC repeated - ½ dose, for theobromine: 3x in 24 hours, cathartic for first dose only, well hydrated
What does PPH say with regards of AC use to decontaminate an asymptomatic methylxanthine toxicity?
reserve for high dose exposures or if emesis did not work — high sugar content can increase risk of hypernatremia
What does Dr. T. recommend with regards to AC use to decontaminate a methylxanthine toxicity?
do repeated ½ doses of AC 3x in the first 24 hours,
ensure WELL hydrated and monitor for 3-4 hours post usage for hypernatremia
What are the treatment aims for the symptomatic methylxanthine toxicity?
consider antiemetic, then gastric lavage, AC — based on clinical presentation
control tremors, agitation, seizures via benzodiazepines, methocarbamol, acepromazine, butorphanol
monitor ECG-HR/BP - treatment of arrhythmia/tachycardia via propranolol, esmolol, lidocaine
IV fluids - to flush out caffiene in urine especially
lots of walks to urinate // catheter with theophylline only
What parameters should you be monitoring with methylxanthines toxicity?
HR, BP, CNS status, Na levels
hydration status especially in first 24 hours
True or False? Dr. T says to only consider IV lipid rescue therapy for methylxanthine toxicities if not responding to other treatments and is about to die.
True
What is the prognosis for methylxanthine toxicities?
Good, can see fatalities due to cardiac arrest
How long is the treatment for methylxanthine toxicities?
24 hours is typical, 72 hours in severe cases
Remember with chocolate, there tends to be a __ half life and delayed __ and __. So need to wait __ hours of no problems to send home.
long,
gastric emptying/delayed absorption,
8-12

What is the toxic substance in glow jewelry?
dibutyl phthalate
What animals are susceptible to dibutyl phthalate in glow jewelry?
cats due to biting into them, others

Exposures to the toxic substance __ in glow jewelery, is typically __ onset, with the __ from the toxic substance tending to cause __ exposures.
dibutyl phthalate,
acute,
irritation,
self-limiting
What are signs a cat may exhibit with dibutyl phthalate exposures?
excessive salivation, behavior change: catnip-like
The dibutyl phthalate is an __ irritant as well so important to __ as __ is the solution to pollution.
eye,
rinse (mouth, eye, bathe body),
dilution
What other compounds besides dibutyl phthalate can be found in glow jewelery?
zinc sulfate // strontium aluminate
irritant, neurologic, cardiac irregularities, acute respiratory arrest

Never call it a junk pile, it is a ___ ___!
resource pile

Blind cow think ___!
LEAD
What is the most common source of lead in cattle? What is the second most common? What is the third?
Batteries, Batteries, Batteries

What is lead?
natural element, ubiquitous, hard to get rid of
What animals are susceptible to lead toxicity?
All animals, companion, LA cattle, waterfowl, raptors, indoor avians, humans
What are common sources of lead toxicity in companion animals?
paint (dust-renovation), sinkers, shot, solder (stained glass), linoleum, roofing material, flashing material…

A dog is presenting with the severe GIT signs with intermittent seizures and hyperexcitability. The owner declines any use of chemical pesticides or any exposures but is concerned that the dog could have ingested glass pieces from a broken Tiffany lamp. What toxic principle are you concerned about?
LEAD in the stained glass (NAVLE Q per Dr. T)
What are common sources of lead toxicity in cattle?
BATTERIES, way less often is paint, grease…
What are common sources of lead toxicity in waterfowl?
sinkers/fishing equipment, shot
What are common sources of lead toxicity in raptors?
lead shot via scavenging
What are common sources of lead toxicity in indoor avians?
paint, misc. (lead solder on Tiffany lamps)
What are common sources of lead toxicity in humans?
everywhere! crayons, bread wrappers, toys, herbal medicines…

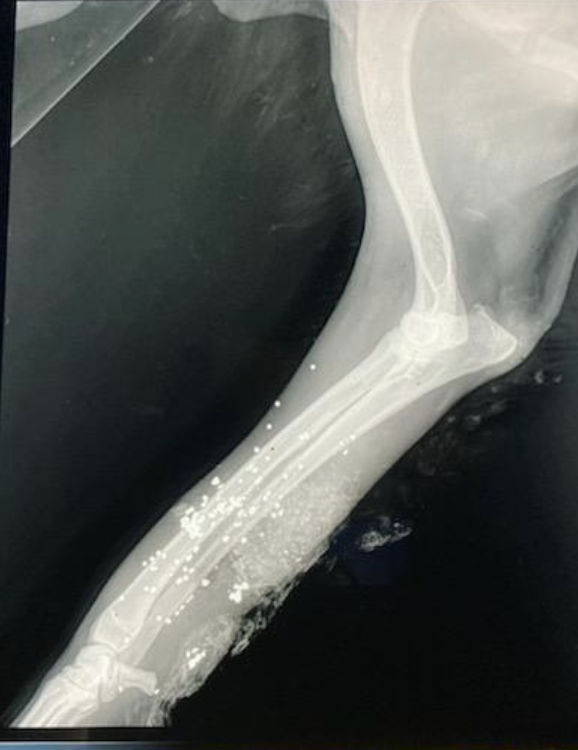
What should you tell the owner about this lead shot exposure?
Risk of toxicity is LOW because lead shot needs a low pH to leach
Expect granulomas to form
If granulomas get infected, can get more acidic and leach out, or if lead shot is in joint cavity
What types of animals do you most commonly see lead toxicities?
Young due to curious nature and small size and have enhanced absorption
cattle mostly acute, raptors + waterfowl more chronic (7-10days)
Describe the MoA of lead and the five major targets
Lead bound to protein on surface of RBC
LONG half life
targets all tissues: CNS or PNS, liver, kidney, bone marrow, GIT
depots in bone for years
excreted in bile primarily, urine
True or False? While lead can affect fetal development via the placenta, it is not excreted in the milk.
False. Lead found in both placenta and milk.
How does lead affect the bone marrow?
premature release of immature RBCs occur sometimes in dogs, cats
NO lysis, NO anemia unless chronic like in waterfowl, raptors
How does lead affect the CNS? PNS?
CNS: increase vascular permeability → edema
PNS: demyelination of peripheral nerves → GIT stasis, wing paralysis, difficulty swallowing from laryngeal/pharyngeal paralysis
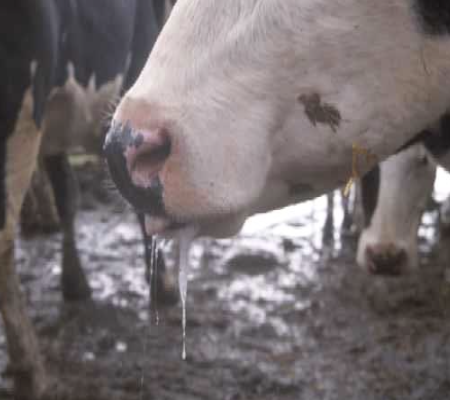

How does lead affect the GI?
GI irritant - “lead colic” may be the only sign you see in SA esp cats
How does lead affect the kidneys?
glucosuria, proteinuria
How does lead affect the liver?
liver necrosis
What are secondary affects of lead toxicity? (4)
aspiration pneumonia
immunosuppressant in chronicity (birds can die from secondary bacterial infections)
poor semen quality, embryotoxic, teratogenic, abortion? osteoporosis in lambs?
developmental disorders, hypertension, renal carcinomas etc (humans)