Ch 9. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Use of drugs to treat infections caused by microbes.
Selective Toxicity
Ability to target pathogens without harming host cells.
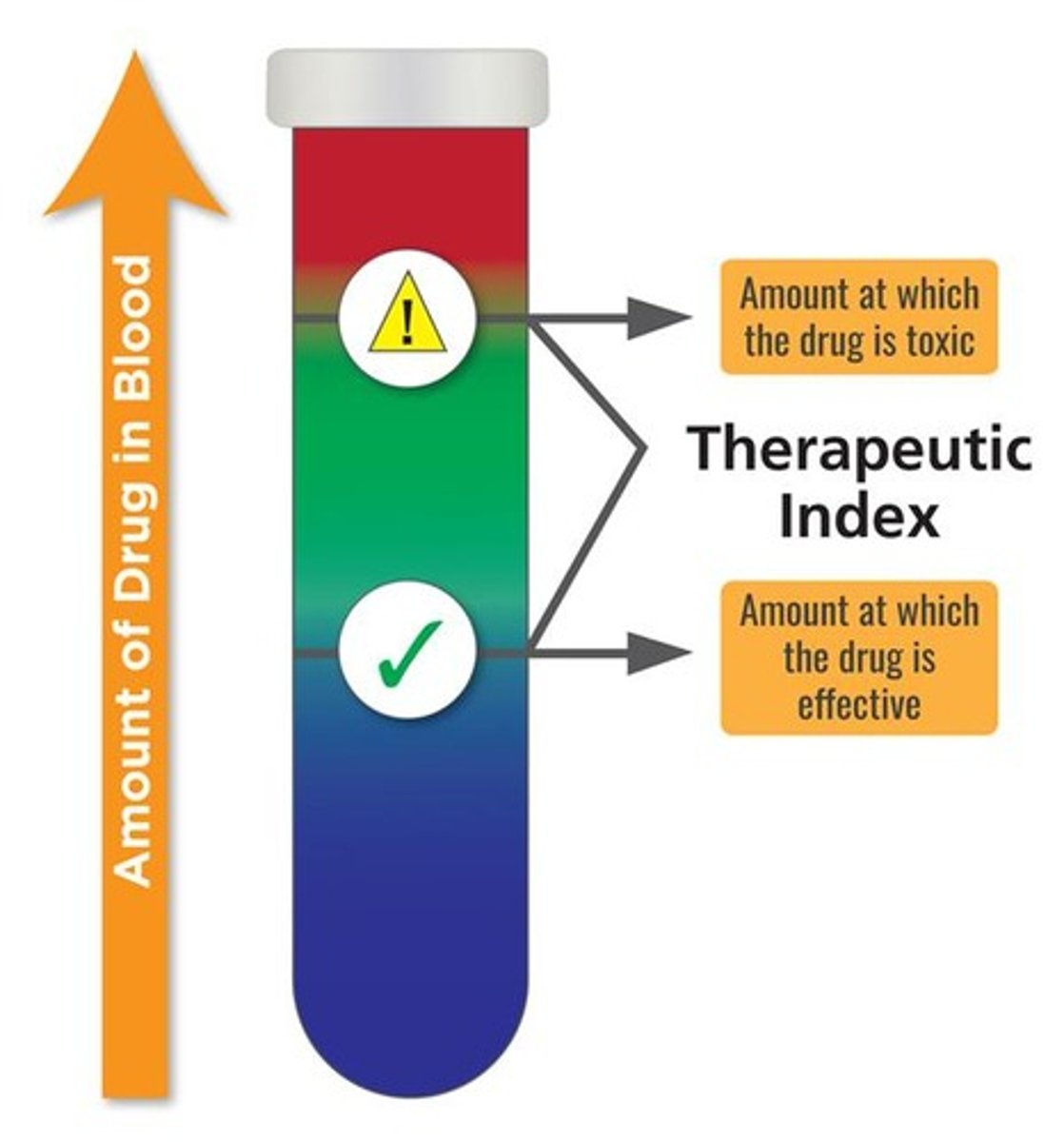
Therapeutic Index
Ratio of toxic dose to therapeutic dose.
Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Lowest concentration preventing microbial growth.
Minimal Lethal Concentration (MLC)
Lowest concentration killing the microorganism.
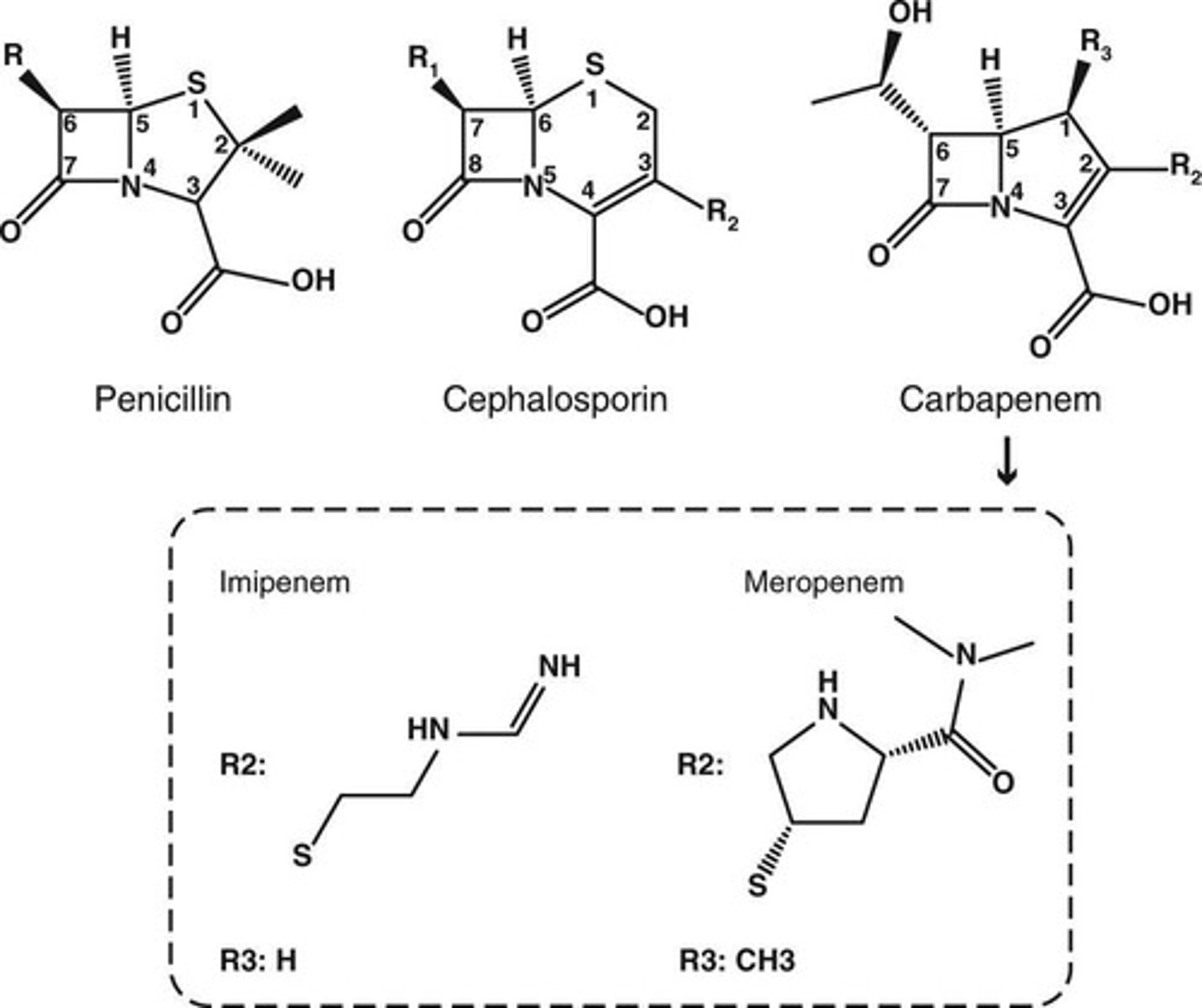
Penicillin
First true antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming.
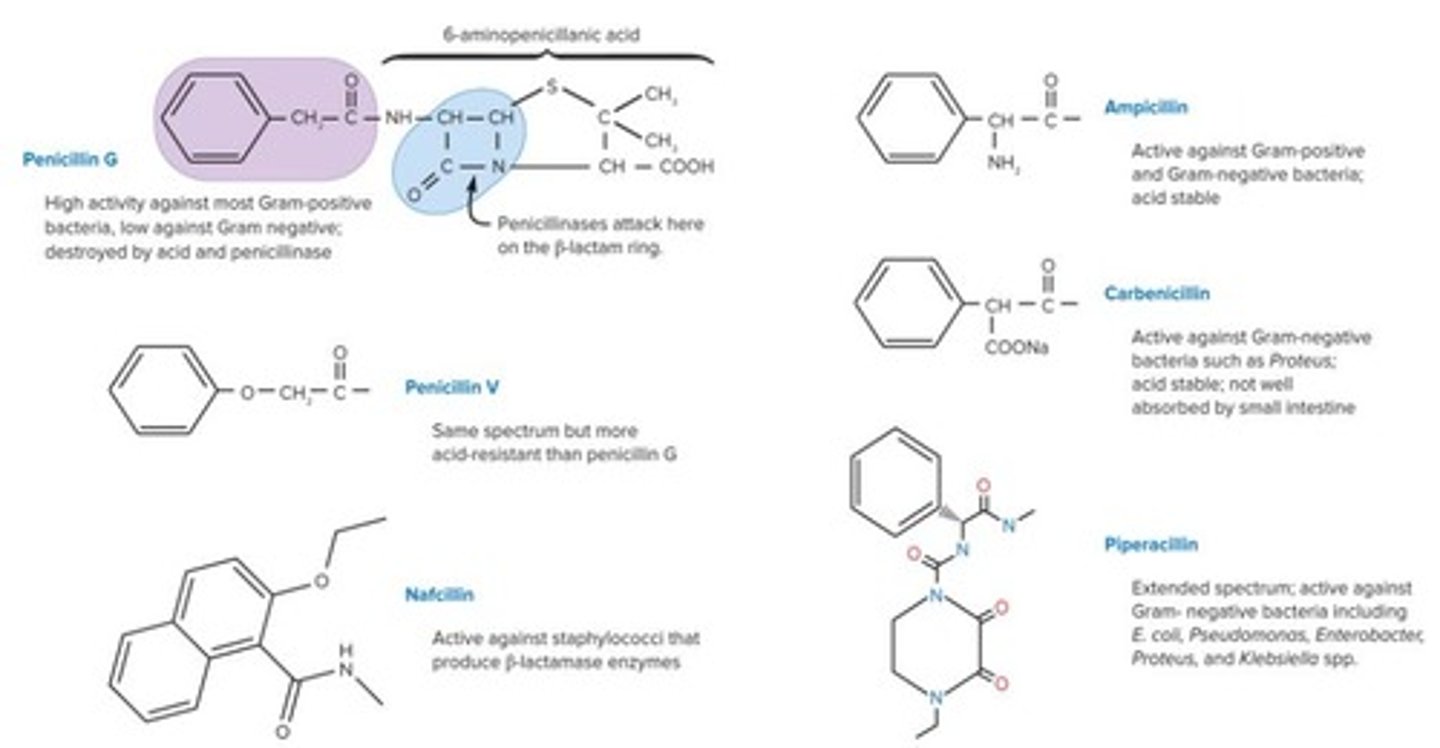
β-lactam Ring
Core structure in penicillin and cephalosporins.
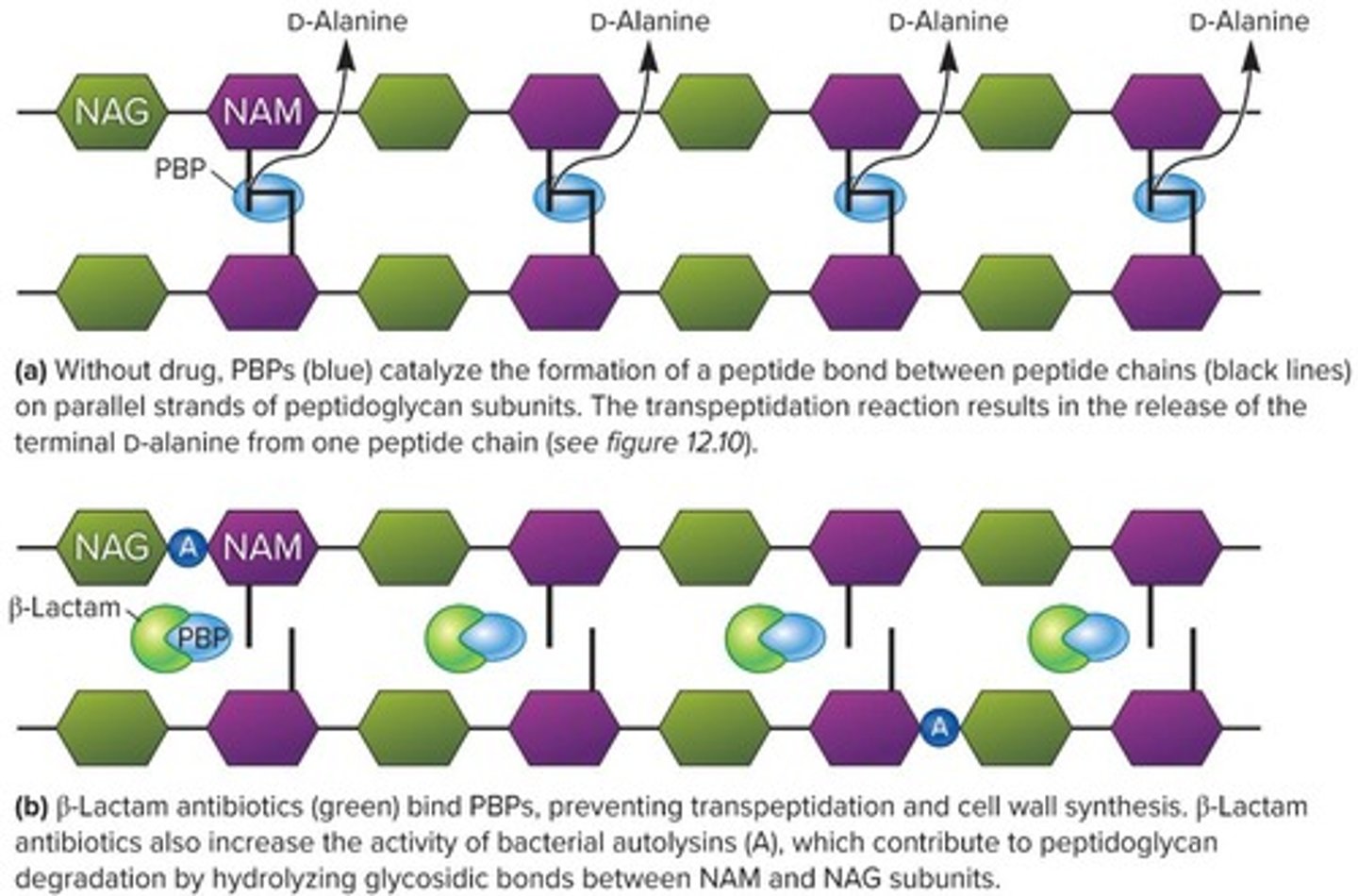
Transpeptidation
Process crucial for bacterial cell wall synthesis.
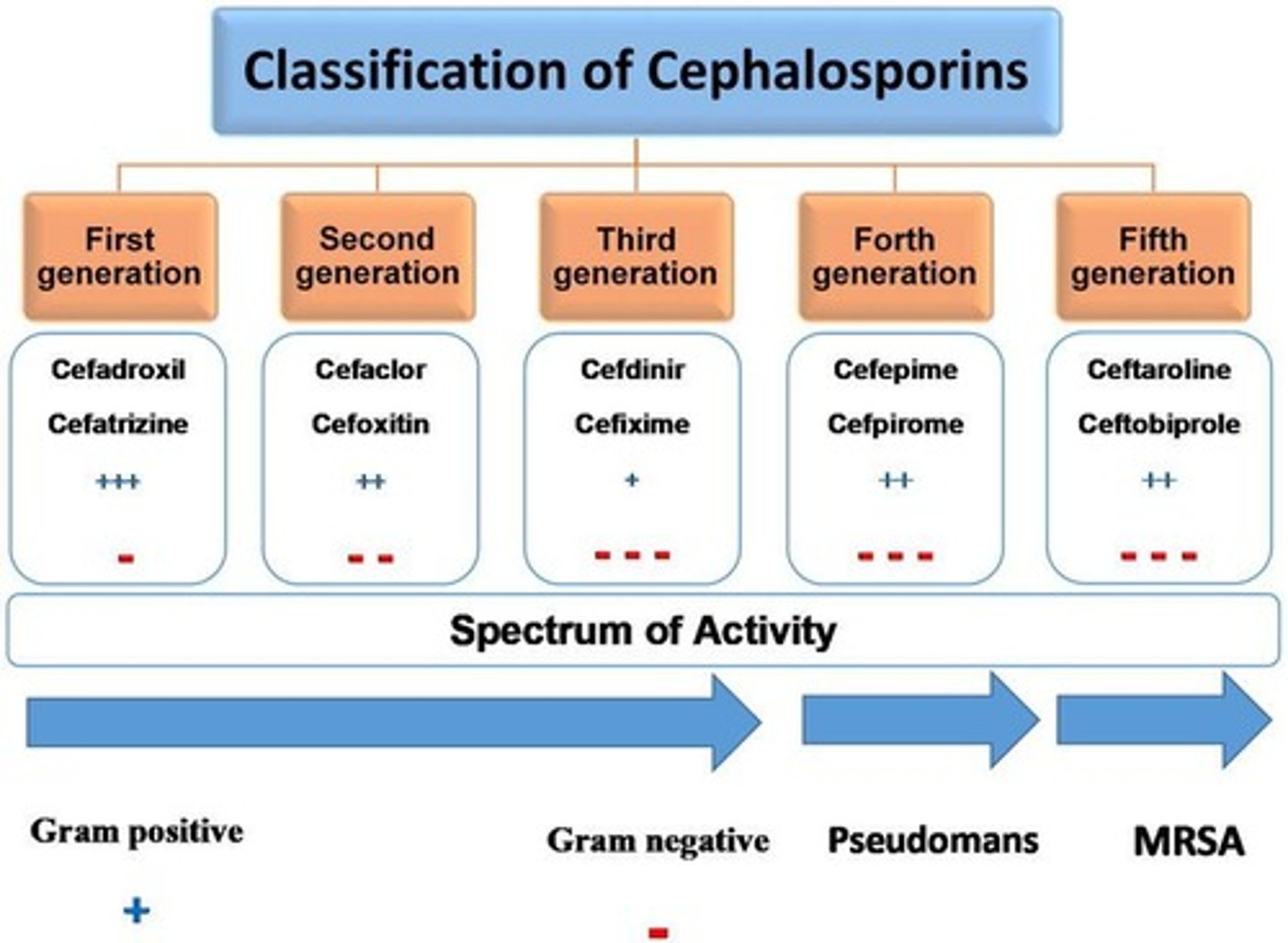
Cephalosporins
Broad-spectrum antibiotics derived from Acremonium fungus.
Carbapenem
Hybrid drugs combining penicillin and cephalosporin properties.
Vancomycin
Narrow-spectrum antibiotic effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
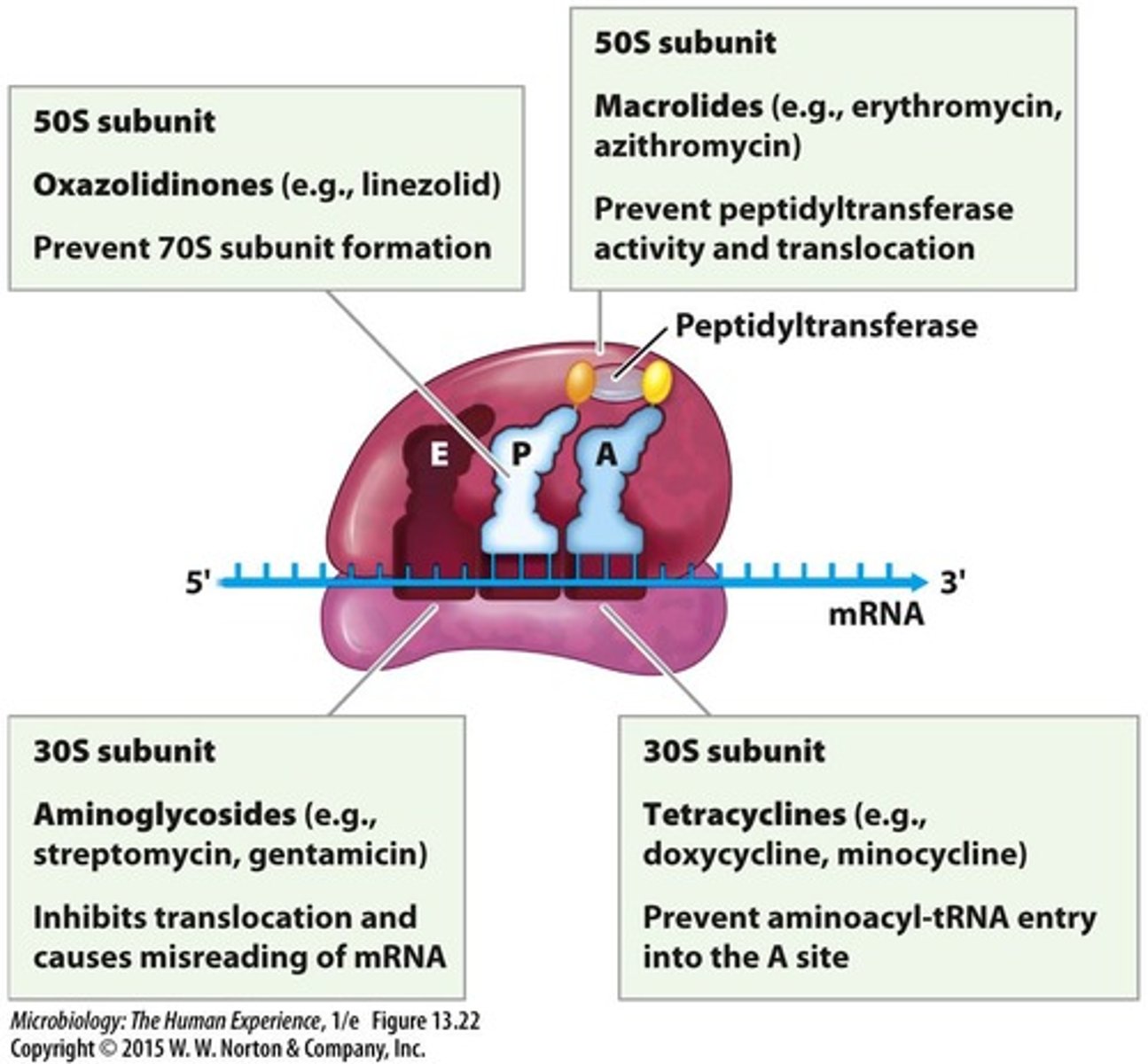
Aminoglycosides
Bactericidal antibiotics binding to 30S ribosomal subunit.
Streptomycin
First antibiotic effective against tuberculosis (TB).
Sulfonamides
First synthetic antibiotics discovered by Domagk and Trefouel.
Prontosil Red
First sulfa drug effective against streptococcal infections.
Actinomycetes
Bacteria known for producing antibiotics like streptomycin.
Deep Learning in AI
Used to screen compounds for antimicrobial effectiveness.
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a drug-resistant bacterium.
Dilution Susceptibility Tests
Method to determine MIC of antimicrobial agents.
Disk Diffusion Test
Kirby-Bauer method for testing antibiotic effectiveness.
Etest
Method combining dilution and diffusion for MIC determination.
Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics
Effective against specific types of bacteria.
Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Effective against a wide range of bacteria.
Aerobic Gram-negative
Includes Proteus, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Serratia.
Semisynthetic antibiotics
Modified versions of natural antibiotics.
Renal damage
Potential toxicity from certain antibiotics.
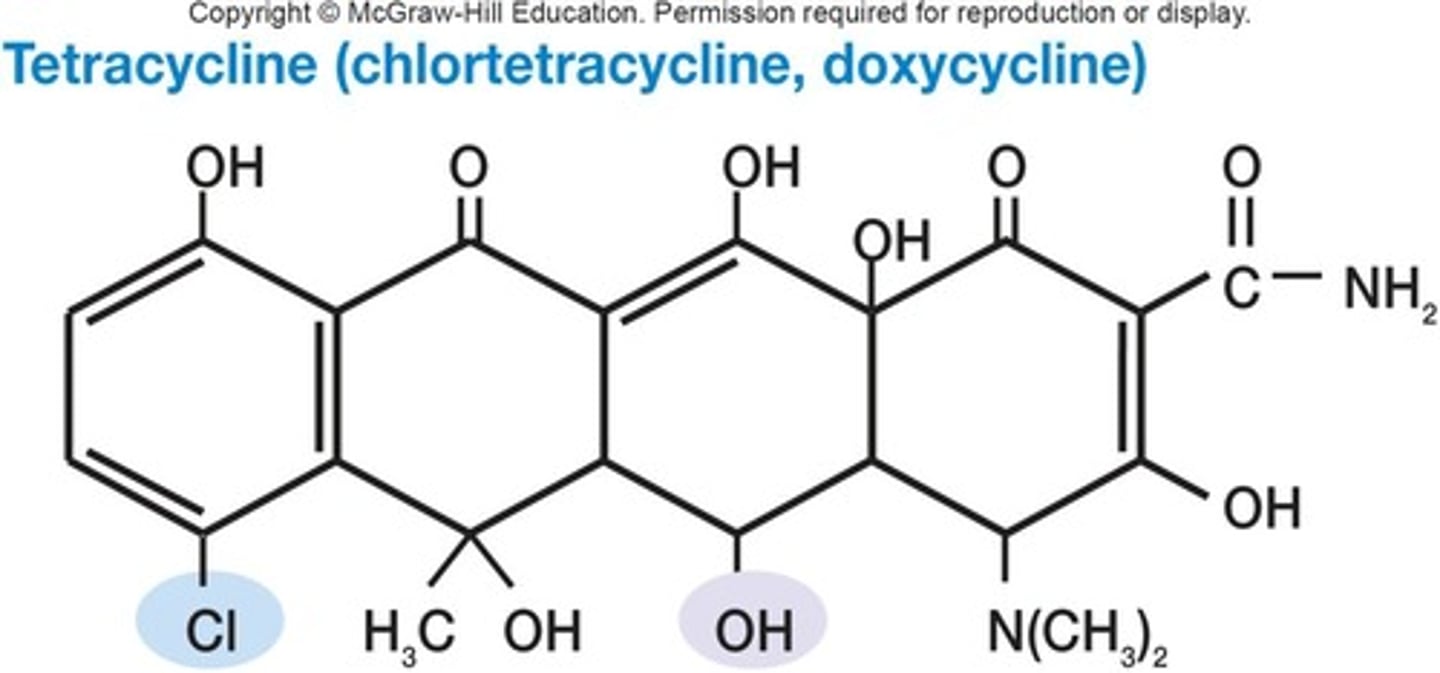
Tetracyclines
Bacteriostatic antibiotics targeting 30S ribosome subunit.
Broad-spectrum
Effective against a wide range of bacteria.
Oxytetracycline
Produced by Streptomyces spp., a tetracycline antibiotic.
Chlortetracycline
Another tetracycline from Streptomyces spp.
Doxycycline
Semisynthetic tetracycline antibiotic.
Black teeth
Side effect of tetracyclines due to calcium chelation.
Liver toxicity
Potential adverse effect of tetracyclines.
Macrolides
Bacteriostatic antibiotics binding to 50S ribosome subunit.
Erythromycin
True antibiotic from Saccharopolyspora, a macrolide.
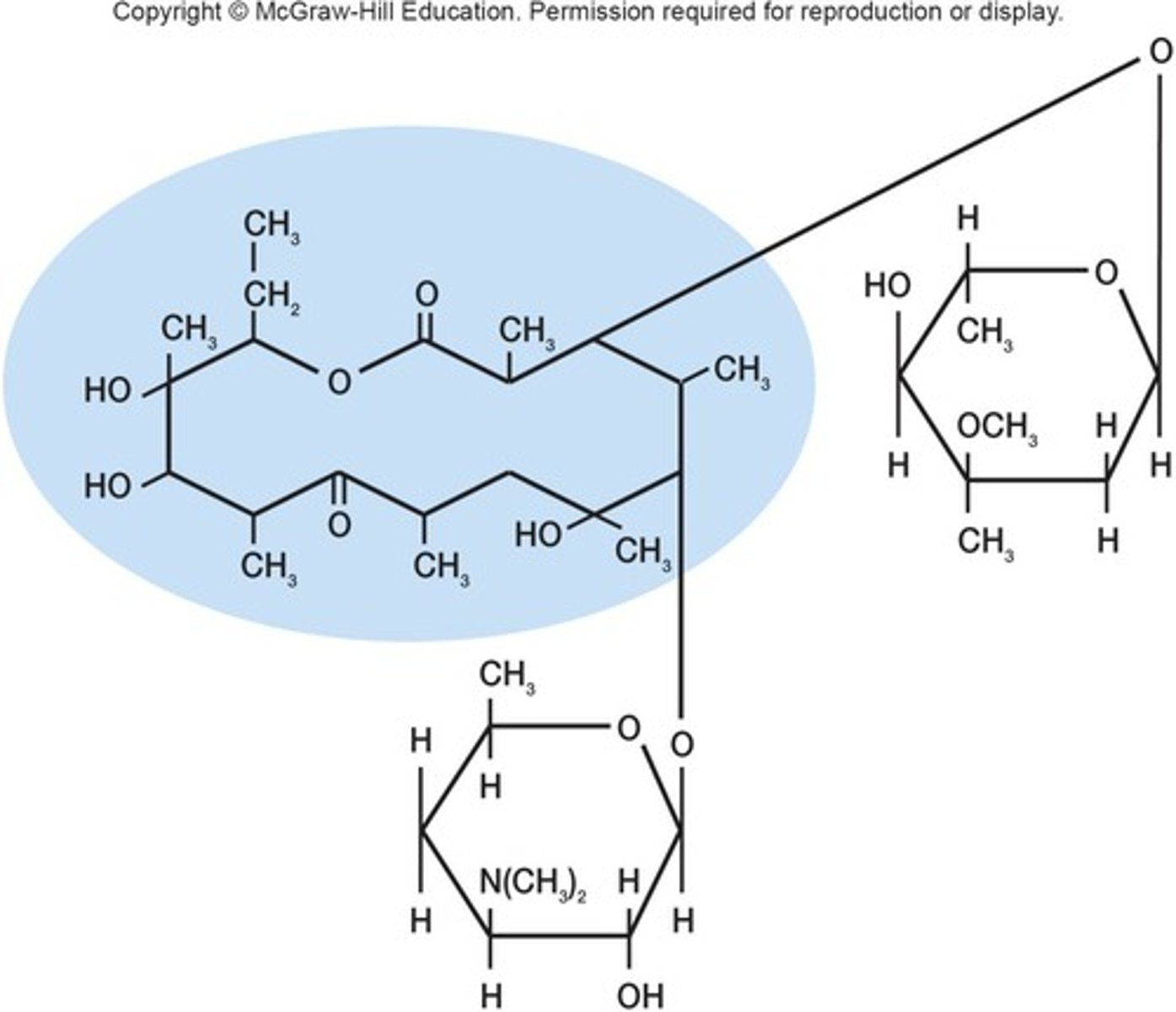
Azithromycin
Macrolide used for chlamydia treatment, known as 'Z-pack'.
Amoxicillin
Commonly prescribed antibiotic alongside macrolides.
Lincosamides
Bacteriostatic antibiotics targeting 50S ribosome subunit.
Clindamycin
Lincosamide used to treat CA-MRSA infections.
C. difficile
Bacteria that can proliferate due to lincosamide use.
Oxazolidinones
Synthetic bacteriostatic drugs targeting 50S ribosome subunit.
Linezolid
Oxazolidinone effective against MRSA and VRE.
Chloramphenicol
First broad-spectrum antibiotic, binds to 50S ribosome.
Grey baby syndrome
Toxic reaction in infants from chloramphenicol.
Aplastic anemia
Serious side effect of chloramphenicol.
Neurotoxin reactions
Adverse effects associated with chloramphenicol.
Metabolic Antagonists
Act as antimetabolites to inhibit metabolic processes.
Structural Analogs
Molecules resembling others, affecting biological functions.
Bacteriostatic
Inhibits bacterial growth without killing bacteria.
PABA Analog
Mimics p-aminobenzoic acid to inhibit bacterial enzymes.
Dihydropteroate Synthase
Enzyme inhibited by sulfa drugs to block folate synthesis.
Trimethoprim
Synthetic antibiotic inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase.
Synergism
Combined effect of drugs enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Side Effects of Trimethoprim
Includes abdominal pain and photosensitivity reactions.
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibition
Mechanisms targeting RNA polymerase and topoisomerases.
Fluoroquinolones
Bacteriocidal drugs inhibiting DNA-gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
Ciprofloxacin
A fluoroquinolone effective against enteric bacteria.
Rifamycins
Bacteriocidal antibiotics blocking RNA transcription.
Rifampin
Most used rifamycin for treating TB and meningitis.
Red Sweat and Urine
Possible side effect of rifamycin use.
Antiviral Drugs
Inhibit virus-specific enzymes and life cycle processes.
Tamiflu
Neuraminidase inhibitor shortening influenza illness duration.
Xofluza
Blocks transcription in influenza viruses.
Resistant Viruses
Some viruses develop resistance to antiviral treatments.
Herpesviridae
DNA viruses using own enzymes for phosphorylation.
Acyclovir
Analog inhibiting herpesvirus replication.
Vidarabine
Another analog for herpesvirus replication inhibition.
NRTIs
Nucleoside inhibitors causing faulty DNA in HIV.
AZT
First NRTI used for HIV treatment.
NNRTIs
Prevent HIV DNA synthesis by blocking reverse transcriptase.
Protease inhibitors
Mimic peptide bonds targeted by HIV protease.
Integrase inhibitors
Prevent incorporation of HIV genome into host DNA.
Fusion inhibitors
Block HIV entry into host cells.
HAART
Combination therapy to prevent HIV drug resistance.
PrEP
Daily two NRTIs for HIV prevention.
Hepatitis C Virus
RNA virus with increased acute cases since 2010.
Interferon-α
Cytokine used in hepatitis C treatment.
Ribavirin
Antiviral drug used for hepatitis C.
Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir
Combination drug for hepatitis C (Epclusa).
Sofosbuvir-ledipasvir
Combination drug for hepatitis C (Harvoni).
Fungistatic
Drugs that inhibit fungal growth without killing.
Nystatin
Used to control superficial candidiasis.
Amphotericin B
Highly toxic polyene binding ergosterol in membranes.
5-flucytosine
Uracil analog disrupting RNA function in fungi.
Fluconazole
Low side effects, used prophylactically in immunocompromised.
Echinocandins
Inhibit β-1,3-D-glucan synthase in fungal cell walls.
Chloroquine
Antiprotozoal drug effective against Plasmodium.
Metronidazole
Activated by Entamoeba and Trichomonas for treatment.
Drug MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration for effective drug levels.
Drug resistance
Microbial ability to withstand effects of drugs.
Resistance mechanisms
Methods microbes use to evade drug effects.
Overcoming resistance
Strategies include using multiple drugs and appropriate concentrations.