Next generation sequencing (15)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Illumina sequencing
PCR in a very small space
Gap between original strand and copy
Original is covalently bound and other is washed away
Fluorescent imaging
By adding fluorescently labeled dNTPs (one binds)
What does next gen sequencing allow?
-Multiple sample runs
-High sensitivity
Illumina sequencing
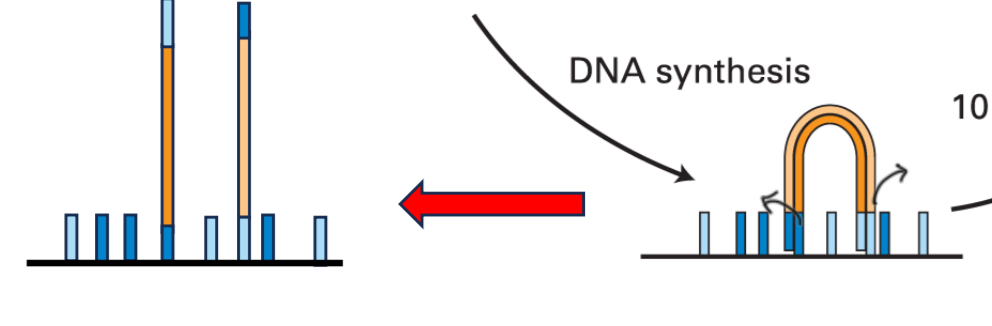
PCR for copies of the same molecule in a very small place (DNA clusters)
Step 1
Ligate linkers
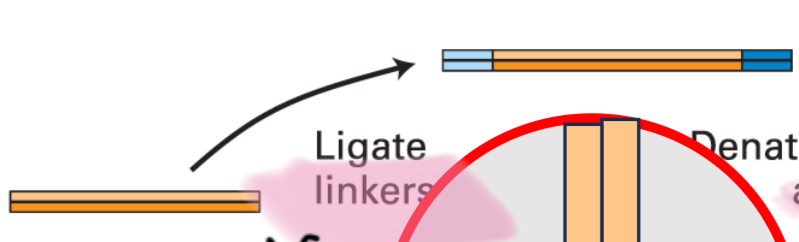
Step 2
Denature and anneal to primers
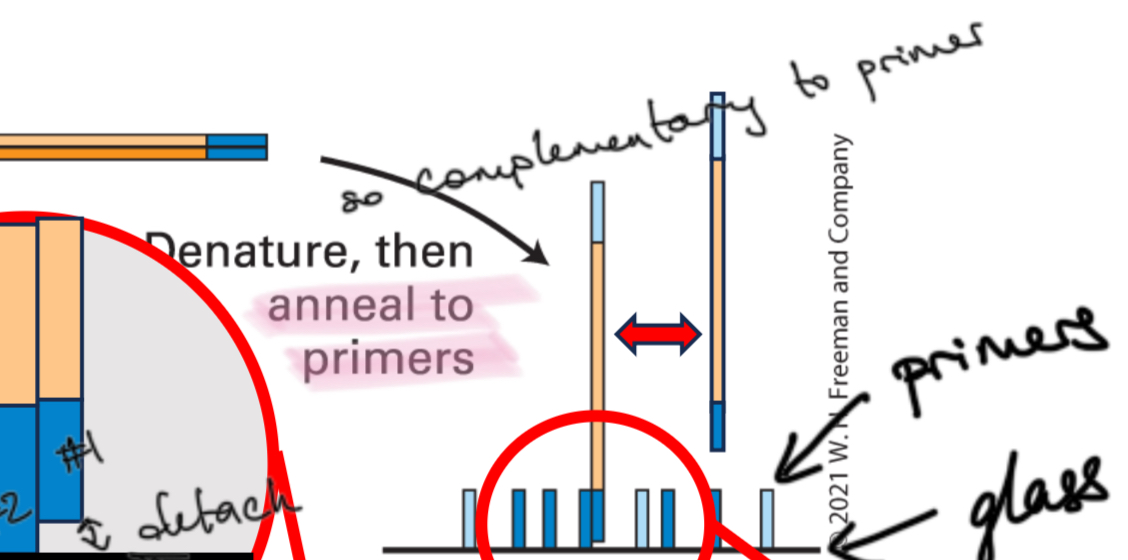
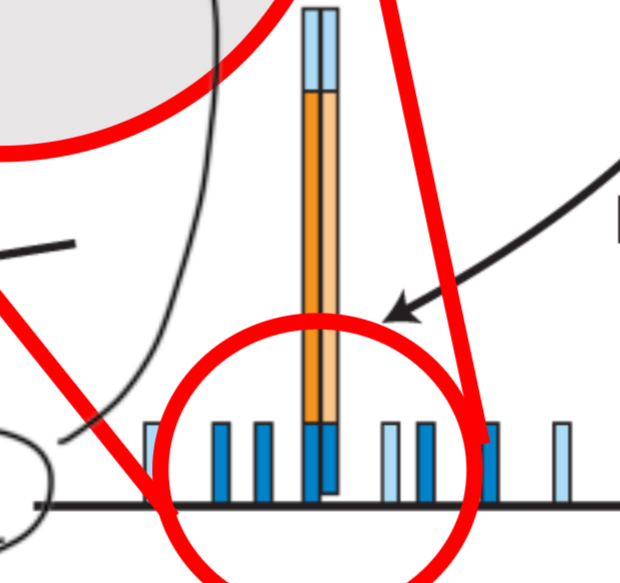
Step 3
DNA synthesis
Step 4
Denature and wash
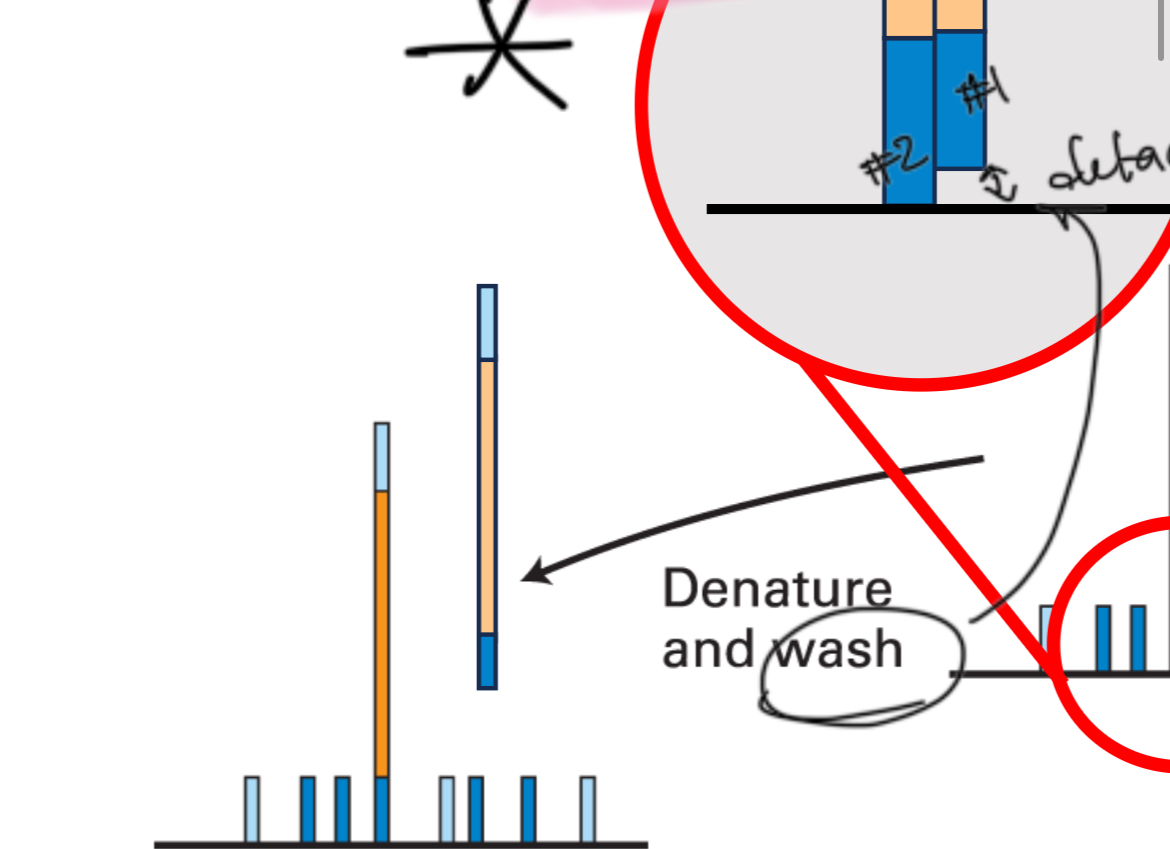
Step 5
Anneal
Step 6
DNA synthesis part 2
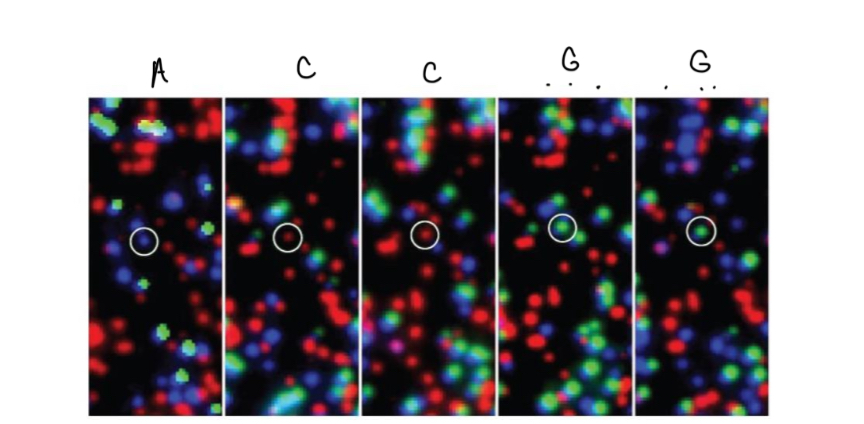
Sequencing of each strand (6)
dsDNA is cut
Fluorescently labeled dNTPs and new primer are added
Wash away excess dNTP
Fluorescent imaging = NTP determination
Chemically remove unbound fluorophore
Repeat
Sequence analysis info (4)
Common ancestry
Shared function
Timing events in evolution
Identify mutations
Purpose of sequence analysis
Homologous between 2 sequences
Sequence similarity
Degree of match between 2 sequences (%)
Homologous sequences
2 or more sequences derived from a common ancestral sequence
Analysis if length is not the same
Gaps are introduced to maximize the match
Programs for sequence analysis
Types of BLAST or basic local alignment search tool
BLASTN
Nucleotide sequence similarity
Steps of BLASTN (3)
Exact match
Extend match locally
Allow for short gaps in alignment
DNA shape for nanopore sequencing
Leader-Hairpin template
Does nanopore sequencing require PCR?
No
Change in current passing through a pore is…
proportional to the size of molecule (nucleotide)
Advantages of nanopore (4)
Sequencing single molecules
Very long reads = easier to map
Detects modifications (methylation)
Portable
Studying DNA methylation
Associated to generation and progression of cancer