Alcohols
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
How are alcohols are produced?
Produced industrially by hydration of alkenes in the presence of an acid catalyst
How is ethanol produced and what’s the formula?
By the fermentation of glucose
Glucose→Ethanol+Carbon dioxide
C6H12O6 → C2H5OH+CO2
How can ethanol produced by fermentation be seperated?
Fraction distillation
When the ethanol is separated what can it be used as?
Biofuel
Define biofuel
A fuel derived from organic matter like plants
Can be considered a renewable source of energy
What are the conditions needed for fermentation?
Temperatures around 30-40 degrees
Yeast (which produces an enzyme)
No air (presence of oxygen would lead to aerobic respiration instead of fermentation)
Explain why the optimum temperature for fermentation is 38 degrees
At lower temperatures the reaction is too slow
At high temperatures the enzymes will denature
Why is fermentation done in the absence of air
Oxygen can oxidise the ethanol
producing ethanoic acid (Vinegar) instead
Advantages of fermentation
Sugar (glucose) is a renewable source
Production uses cheap equipment
Disadvantages of fermentation
Uses up land that could be used for food
Batch process is slow and raises production costs
Ethanol made is not pure and needs purifying by fractional distillation
Why is a batch process used in fermentation?
Allows for a high ethanol yield
Fermentation stops when ethanol concentration becomes toxic to yeast
Batch process ensures fermentation occurs for an optimal time before the yeast becomes inactive
Define the term carbon neutral
An activity that has no net carbon emissions to the atmosphere
Why is the production of ethanol considered carbon neutral
Its a biofuel formed from fermentation
Any carbon dioxide given off when the biofuel is burned would have been extracted from the air via photosynthesis by the plants grown
Meaning there is no net carbon emission
Equations showing that the production of ethanol is carbon neutral
Removal of CO2 by photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6o2
Production of CO2 by fermentation and combustion
C6H1206 → C2H5OH + 2CO2 (fermentation)
C2H5OH + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O (Combustion)
For every 6 molecules of carbon dioxide absorbed, 6 molecules of carbon dioxide are emitted
Why may the production of ethanol not be considered carbon neutral?
The equations that show it being a carbon neutral process do not take into consideration
Energy required to fractionally distil the ethanol
Energy required to irrigate( water) the plants.- Water pumps are powered by fossil fuels
What does dehydrating an alcohol do?
Removes a water molecule to form an alkene and water
Conditions for dehydration
Alcohol is heated under reflux (heating a reaction without losing the volatile substances)
Heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric (v) acid
Acid act as a catalyst
Dehydration of alcohols is an example of an…
Elimination reaction
Products of dehydration of alcohols
Alkene
H2o
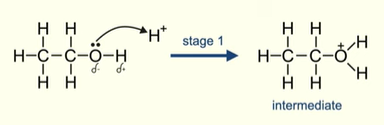
First stage of dehydration of alcohols
Lone pair of electrons on oxygen atom will be attracted to the positive hydrogen ion from the acid catalyst
Lone pair forms a covalent bond with the hydrogen ion
Forming an intermediate molecule with a positive oxygen atom
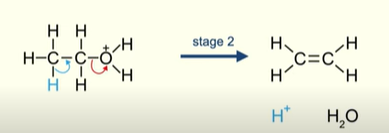
Second stage of dehydration of alcohols
Pair of electrons in the covalent bond between the C-O move onto the oxygen
This releases the molecule of water to be released
At the same time the pair of electrons between a C-H bond move between 2 carbon atoms
Hydrogen is now released as H+ (regenerating the acid catalyst
What can alkenes produced from dehydration of alcohols be used for ?
used to produce addition polymers (without using monomers derived from crude oil)
Describe a primary alcohol
Carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group (OH) is bonded to one more carbon atom
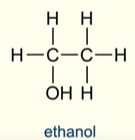
What alcohol is considered a primary alcohol despite not fitting the definition?
Methanol
Describe a secondary alcohol
The carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is bonded to 2 other carbon atoms
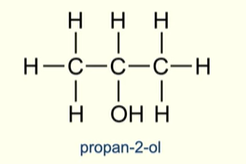
Describe a tertiary alcohol
The carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms
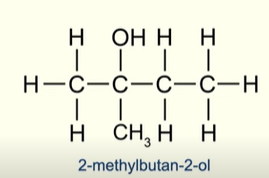
What does volatility of a molecule tell you?
How readily a molecule turns into a gas
Why are alcohols highly soluble in water
Alcohol functional group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
Why do long carbon chain alcohols become less soluble in water?
The non polar carbon chain cannot form hydrogen bonds
So as carbon chain is increases a larger part of the molecule is unable to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
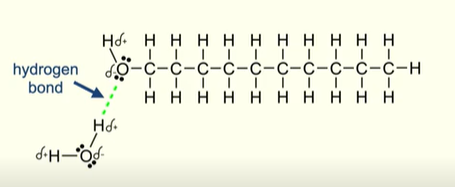
What can primary alcohols be oxidised to make?
Aldehyde
(and a molecule of water is produced)
What is the chemical needed for oxidation called and give an example?
Oxidising agent
Acidified potassium dichromate K2Cr2O7/H+
What happens in the oxidation of primary alcohols?
The oxidising agent is reduced from the dichromate(VI) ion which is orange in colour to the Chromium (III) ion which is green
oxidation in terms of hydrogen means a loss of hydrogen (alcohol is losing 2 hydrogens)
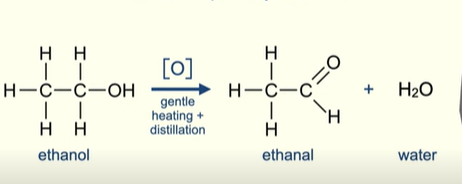
What is the problem with the oxidation of primary alcohols?
Aldehydes are extremely easy to oxidise further
So if only aldehyde is wanted from this reaction it must be removed as soon as it forms.
How and why can you remove the aldehyde from the reaction?
Through distillation
Aldehydes have low boiling points
Explain the method of distillation
By gently heating the alcohol and the oxidising agent we produce the aldehyde
The aldehyde evaporates and passes through the condenser
Where it condenses back to a liquid and is removed
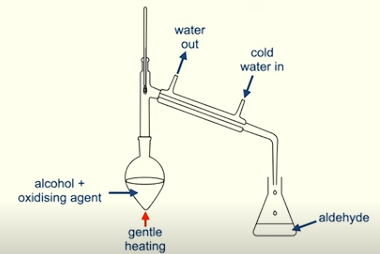
Why does an excess of alcohol and a limiting oxidising agent favour the production of an aldehyde?
If there’s too much oxidising agent the aldehyde will get oxidised further into a carboxylic acid.
What happens when aldehydes are oxidised?
They make a carboxylic acid
How do you get from a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid?
Using 2 molecules of oxidising agent

How can you ensure that all the aldehyde produced is then oxidised to a carboxylic acid?
Use excess oxidising agent
Heat the reaction under reflux
Use concentrated sulfuric acid instead of dilute in acidified potassium dichromate (oxidising agent)
What happens when you heat the reaction under reflux?
When you heat a reaction under reflux any volatile products are condensed and return to the reaction mix
The aldehyde will keep condensing back down until it forms a carboxylic acid

What will be obtained in the end after heating the reaction under reflux ?
A mixture of chemicals containing carboxylic acid and any unreacted alcohol and aldehyde '
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes so they can be separated using distillation
What does the oxidation of secondary alcohols produce?
Ketone
Molecule of water
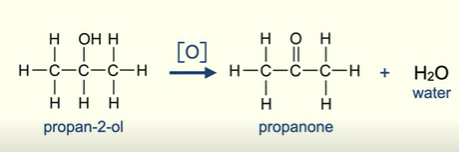
Why cant you oxidise ketones further?
The carbon atom bonded to the oxygen is not bonded to any hydrogen atoms
Why cant a tertiary alcohol be oxidised?
The carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is not bonded to any hydrogen atoms
How do you use tollens reagent to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones?
Tollens reagent is formed by mixing aqueous ammonia and silver nitrate. Forming a complex ion Ag(NH3)2+
Only aldehydes are oxidised by tollens reagent into a carboxylic acid. Silver ions are reduced to silver atoms
With aldehydes a silver mirror forms inside the test tube. Ketones result in no visible change
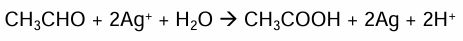
How do you use Fehling’s solution to distinguish aldehydes and ketones?
Fehling’s solution contains blue Cu2+ ions
Only aldehydes are oxidised by Fehling’s solution into carboxylic acid. Copper ions are reduced to copper(I) oxide
With aldehydes blue Cu2+ ions in solution change to a red precipitate of Cu2O
Ketones do not react