Chapter 12.1: General Functions, Organization, Nerves and Ganglia
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
General functions
communication and control system
collect information (sensory input): receptors detect stimuli and send sensory signals to spinal cord (sc) and brain
process and evaluate information (integration): brain and sc determine response to sensory input
initiate response to information (motor output): brain and sc send motor output via nerves to effectors (muscles or glands)
Structural organization
central: brain and spinal cord
peripheral: nerves and ganglia
Functional organization: sensory nervous system
sensory nervous system: afferent nervous system, receives sensory info from receptors, transmits to CNS
somatic motor system: detects stimuli consciously perceives
visceral sensory: stimuli not consciously perceived (heart, kidneys)
Functional organization: motor nervous system
motor nervous system: efferent nervous system, initiates motor output and transmits from CNS to effectors
somatic motor: send signlas to skeletal muscles
autonomic motor (visceral): involuntary commands to heart, smooth muscle and glands
sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
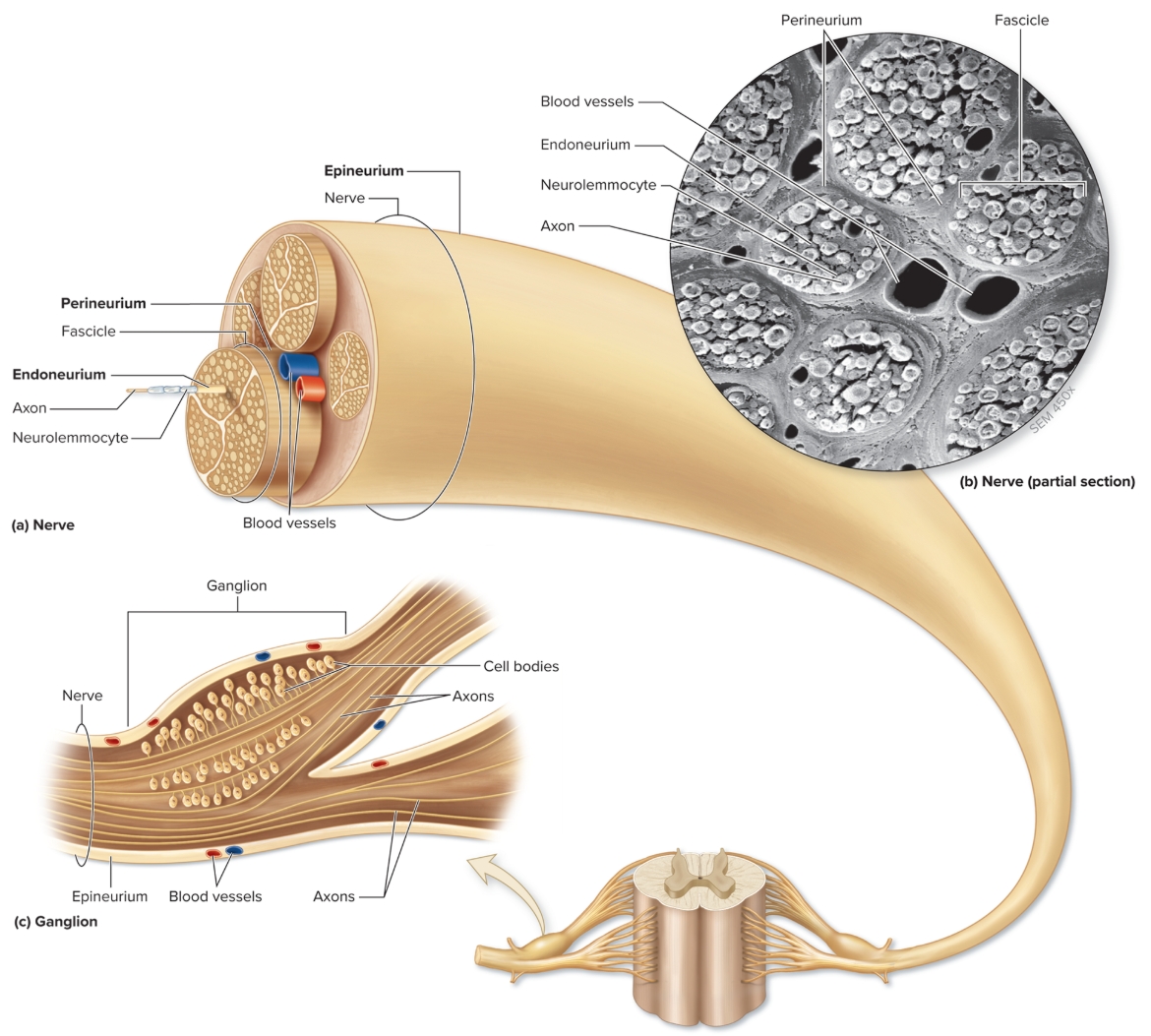
Nerve
bundle of parallel axons in PNS, connective tissue wrappings similar to muscle
very vascular
epineurium: encloses entire nerve, thick layer of DICT
perineurium: wraps fascicle (bundle of axonz), DICT
endoneurium: wraps individal axon, layer areolar CT, separates/electrically insulates axon
Structural classification
cranial nerves: extend from brain
spinal nerves: extend from spinal cord
Functional classification of nerves
sensory nerves: sensory neurons signals to CNS
motor neurons: motor neurons sending signals from CNS
mixed nerves: both sensory and motor neurons
most nerves
individual nerves transmit only one type of info
ganglion: cluster neuron cell bodies in PNS