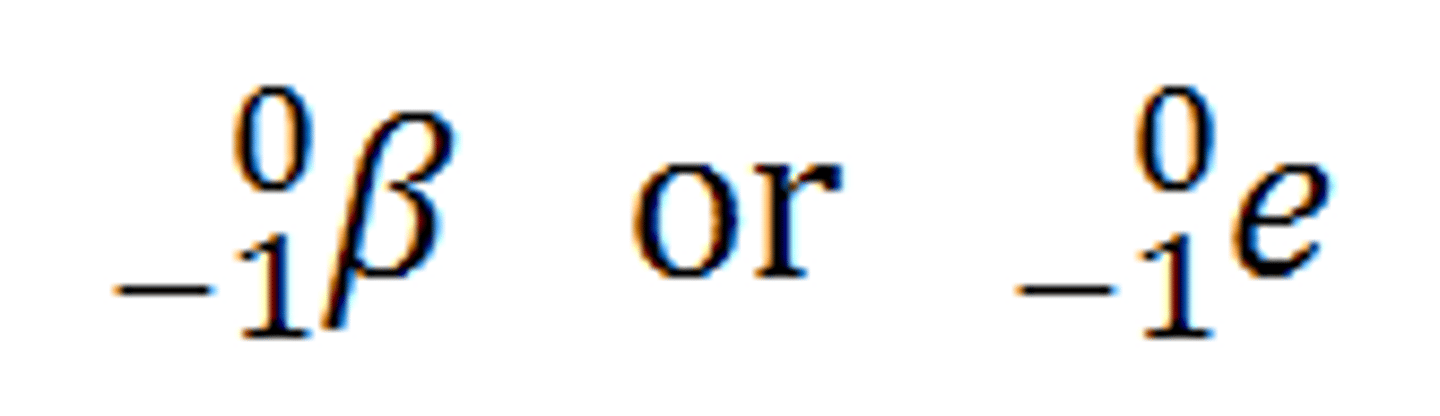Nuclear Decay
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
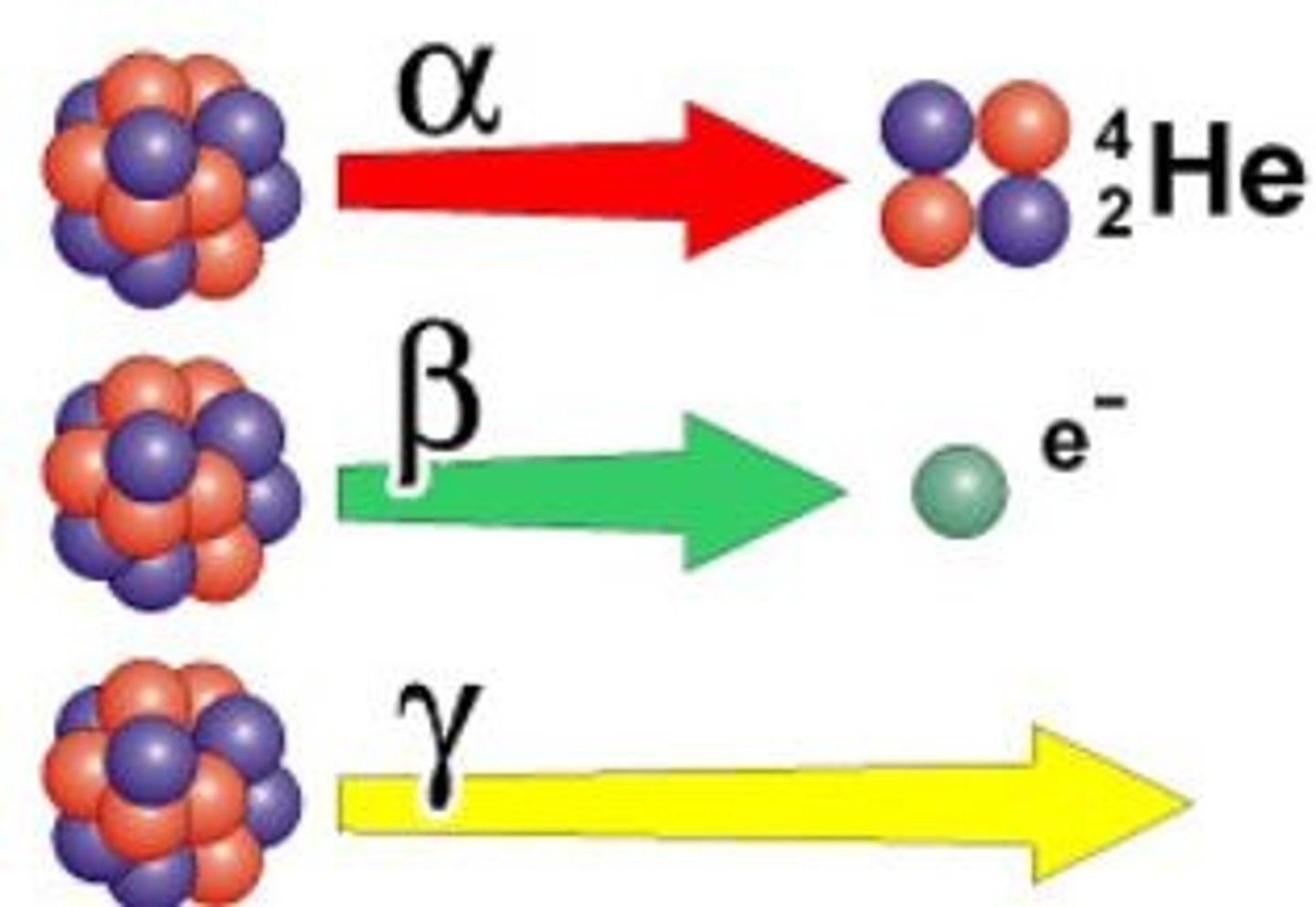
Beta Decay
Neutron breaks in to Proton plus Electron which escapes from the nucleus.
Gamma Decay
The release of energy to create a more stable atom in a lower energy state.
Alpha Decay
The release of a 4/2 He and can pass thru paper
A) Charge of alpha decay
B) Effects of an alpha decay on atomic mass and number
A) positive and
B) atomic mass down by 4 atomic number down by 2
A) Charge of beta decay
B) Effects of an beta decay on atomic mass and number
A) negative and
B) atomic mass unchanged and atomic number up by 1
Ra-226 undergoes beta decay to make
Ac-226
Po-209 produces Pb-205 What type of decay is this?
Alpha
What decay results in a transmuted element with the same atomic mass and an increased atomic #?
Beta
Po -218 decays alpha to produce ?
Pb-214
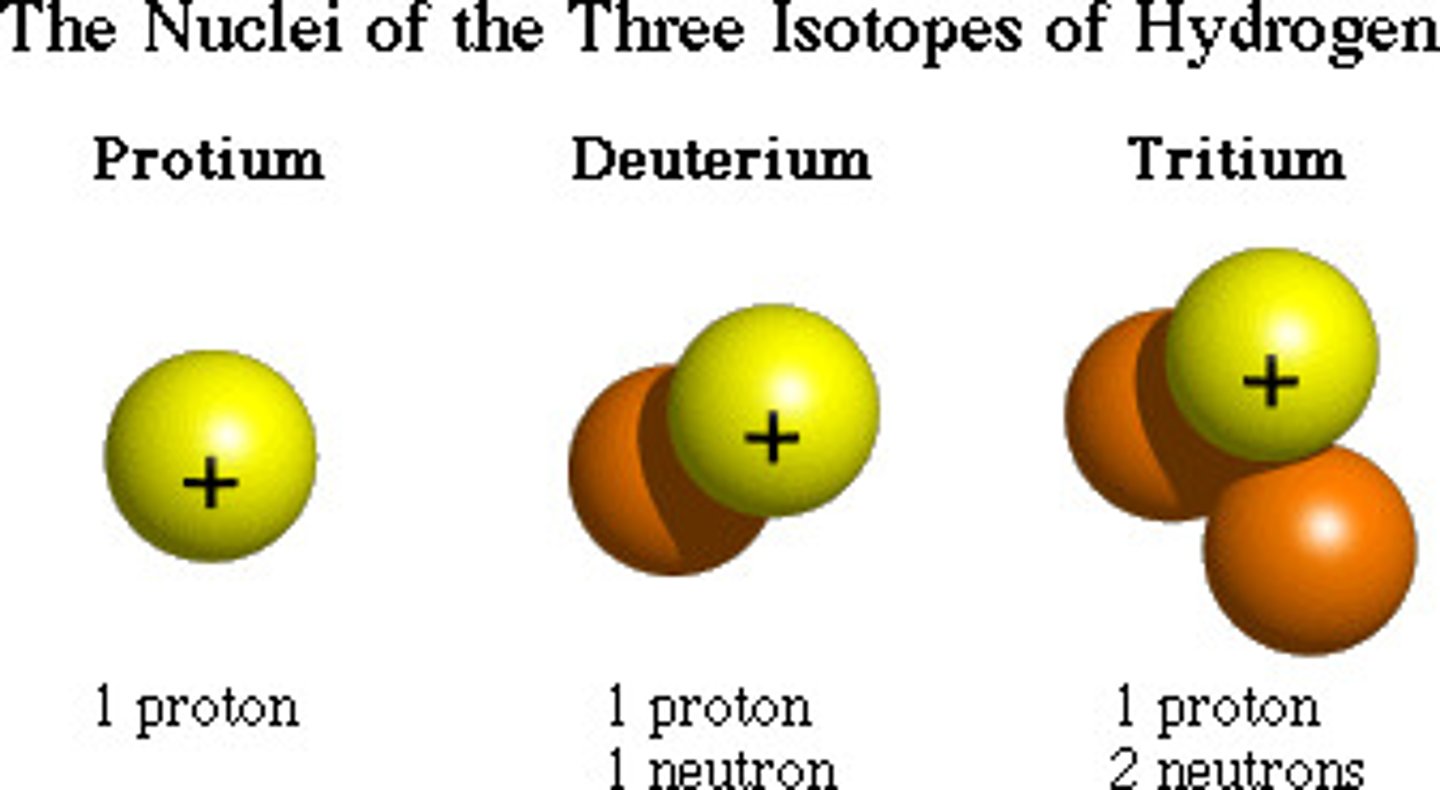
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in their number of
Neutrons
Why does radioactive decay occur?
The nucleus is larger than the nuclear force can keep stable
Element Identity
Based on the number of Protons in the Nucleus of an Atom. The proton is the only subatomic particle you can use for this with 100% accuracy
Radiation
Matter or Energy that has been emitted from a radioactive nucleus. Alpha Particles, Beta Particles, and Gamma Rays are all forms of Radiation.
Isotopes
Different versions of atoms with the same element identify. The only difference between these versions of the same element is the amount of neutrons in the nucleus, this results in a different atomic mass.
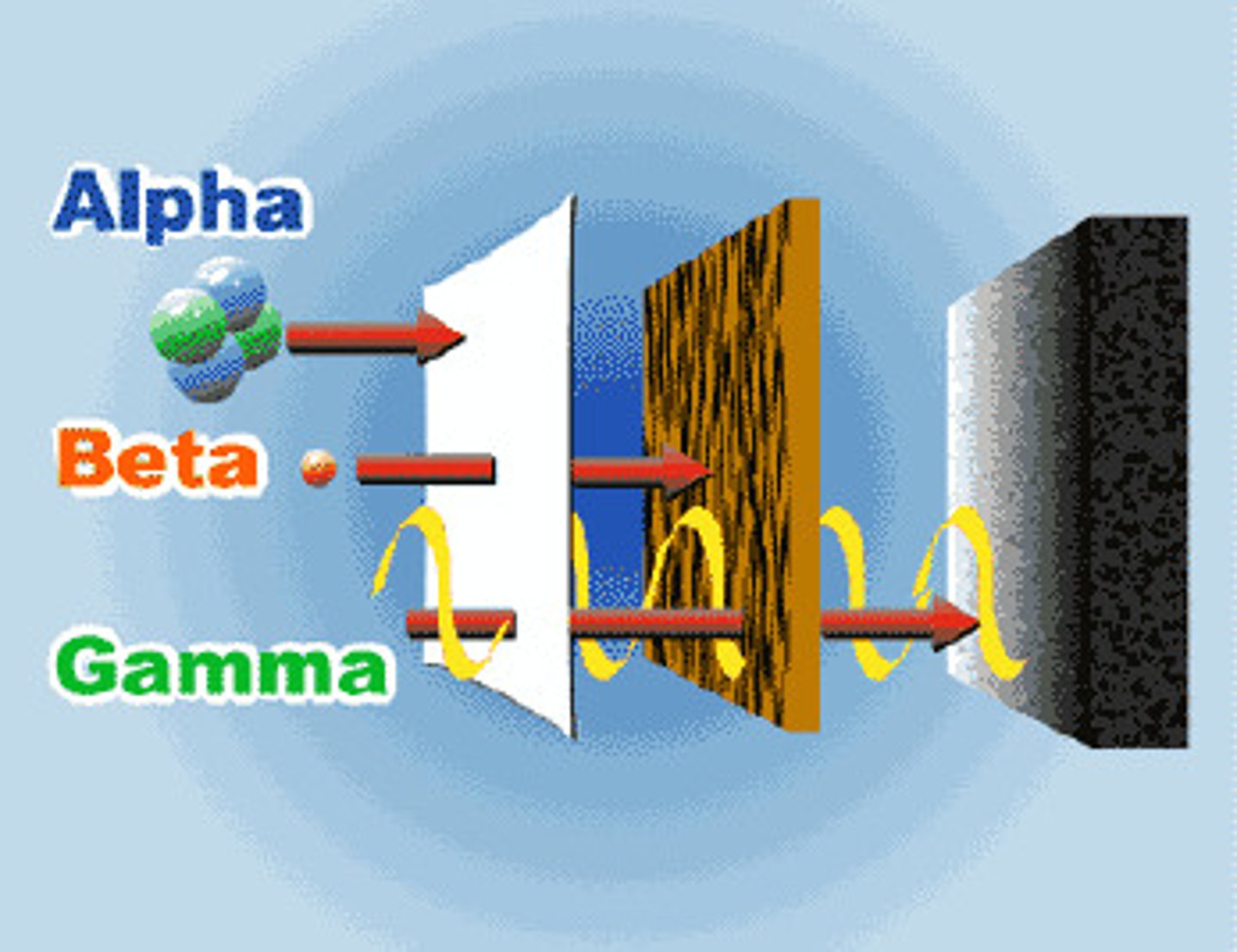
Gamma Ray
Radiation in the form of the highest frequency and highest ENERGY wave. It has NO Mass, NO Charge, and nearly unstoppable except by very dense materials such as lead, or a couple feet thick of concrete.
Radioactive
An Atom that can actively radiate Particles/Energy via nuclear decay processes.
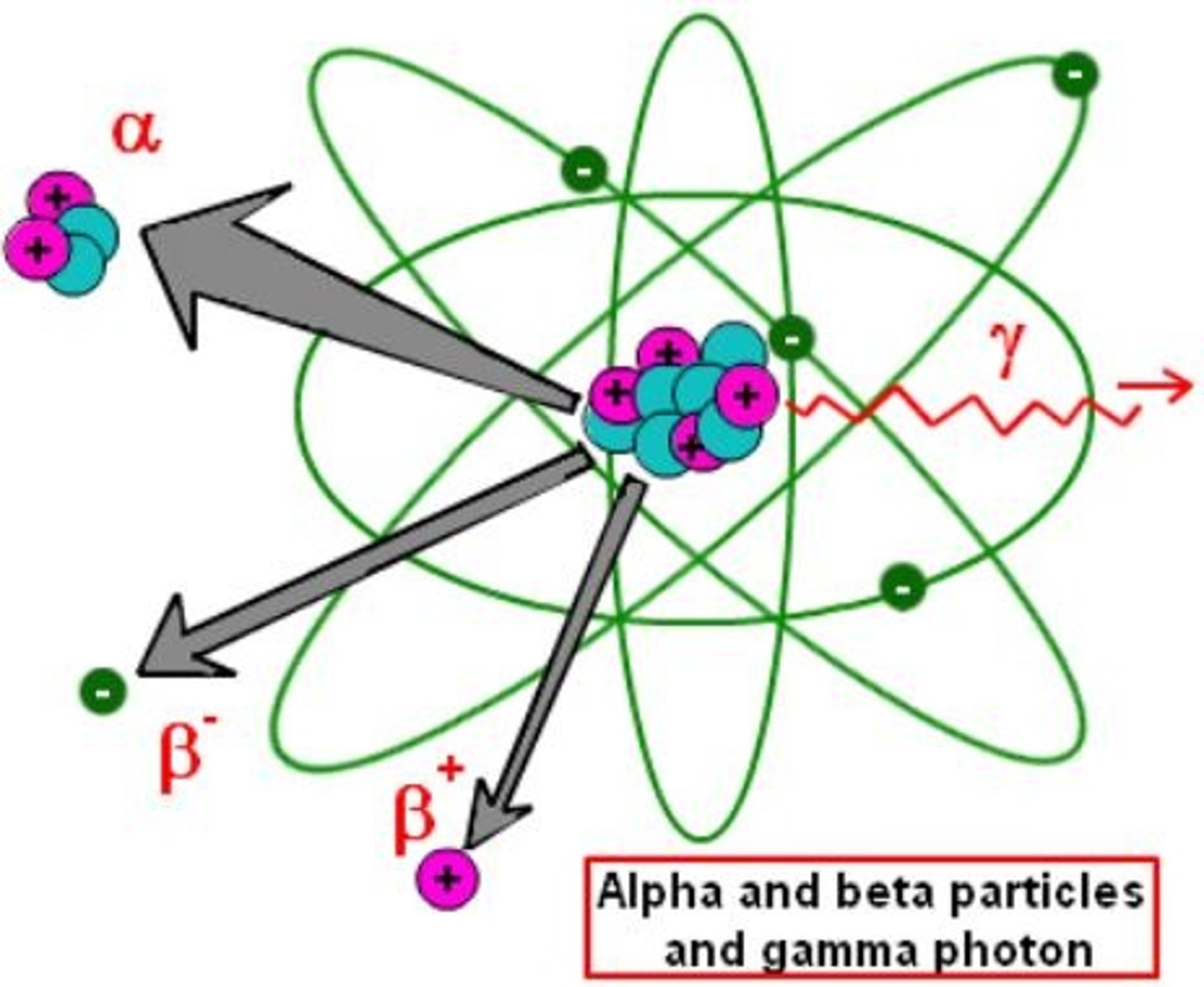
Nuclear Decay
When an unstable nucleus decays to a more stable form, during this process radiation is emitted (shot out).
Alpha Particle
Largest Mass and Charge, but the weakest form of radiation. Emitted from the nucleus as 2 protons and 2 neutrons, could also be referred to as a Helium Nucleus.
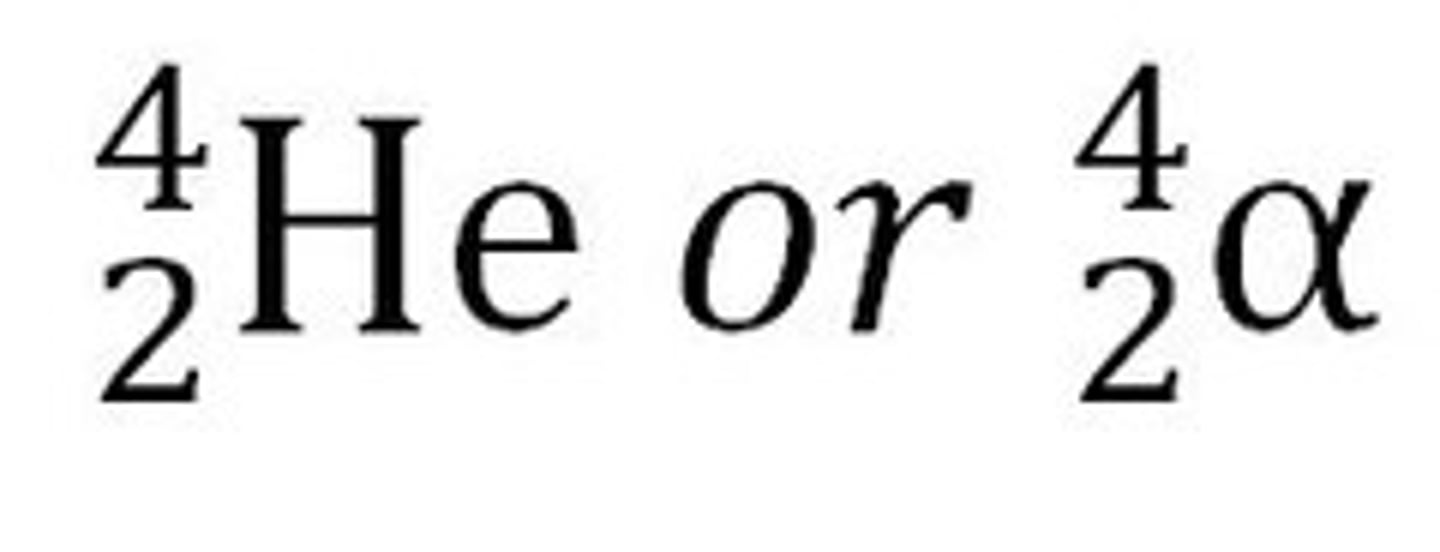
Beta Particle
a high-speed electron with a 1- charge that is emitted during radioactive decay. Yes, This Electron comes from the nucleus, and NO there are not electrons in the nucleus.