Blood and Hematocrit
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
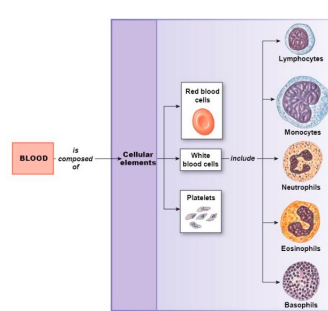
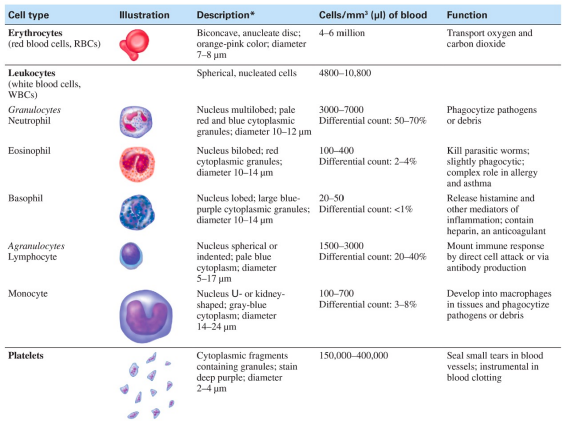
Erythrocytes
Use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to tissues throughout the body. They are the most abundant formed element in the blood.
Leukocytes
Have various immune functions and include granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes, monocytes). They can travel out of blood vessels into tissues by diapedesis.
Platelets
Critical in blood clotting.
Hematocrit Step 1
Place a capillary tube into a blood sample to draw up blood.
Hematocrit 2
Centrifuge the capillary tube.
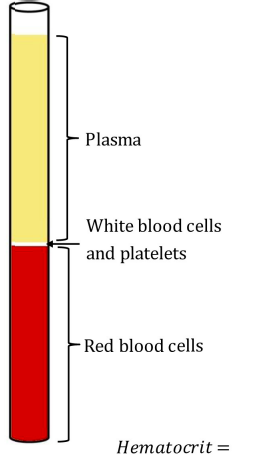
Hematocrit Calculation
Measure the length of RBCs, WBCs, and plasma in the tube and divide each by the total length of the fluid in the tube.
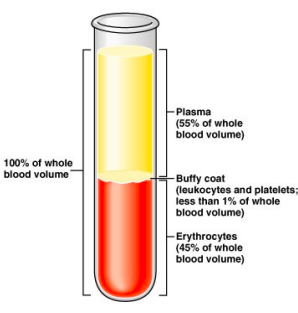
Blood Centrifugation
Erythrocytes sink to the bottom, the buffy coat (leukocytes and platelets) forms a thin layer in the middle, and plasma rises to the top.
Leukocytosis
Leukocyte count is too high; buffy coat >1%. Caused by infection and some types of leukemia.
Anemia
Erythrocyte count is too low; hematocrit value below average.
Types of Anemia
Aplastic anemia, iron-deficiency anemia, hemolytic anemia, sickle cell anemia. Hemorrhagic anemia is not detected by hematocrit.
High Altitude & Hematocrit
Individuals at high altitude have higher hematocrit due to lower oxygen levels.
Dehydration
Decreases plasma percentage due to the loss of water.
Blood Formed Elements
Formed Elements
Hematocrit
Height of RBC/height of all components of the blood x100
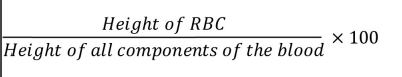
Hematocrit Range
Normal Adult Female Range: 37 – 47% Normal Adult Male Range: 42 – 52% Normal Newborn Range: 49 – 61%