Experiment 2: Buffer Solution and pH
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Water
~70% of human body, universal solvent.
Biochemical Reactions
Processes like metabolism and respiration occur in water.
pH
Measures hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
pH Scale
Ranges from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic).
pH Change
1 unit change = 10x change in [H⁺].
Buffer Capacity
Ability to maintain stable pH with added acids/bases.
Conjugate Base
Weak acid's counterpart that neutralizes added H⁺.
Ideal Buffer Ratio
1:1 ratio of acid to conjugate base.
pKa
pH at which acid and conjugate base concentrations are equal.
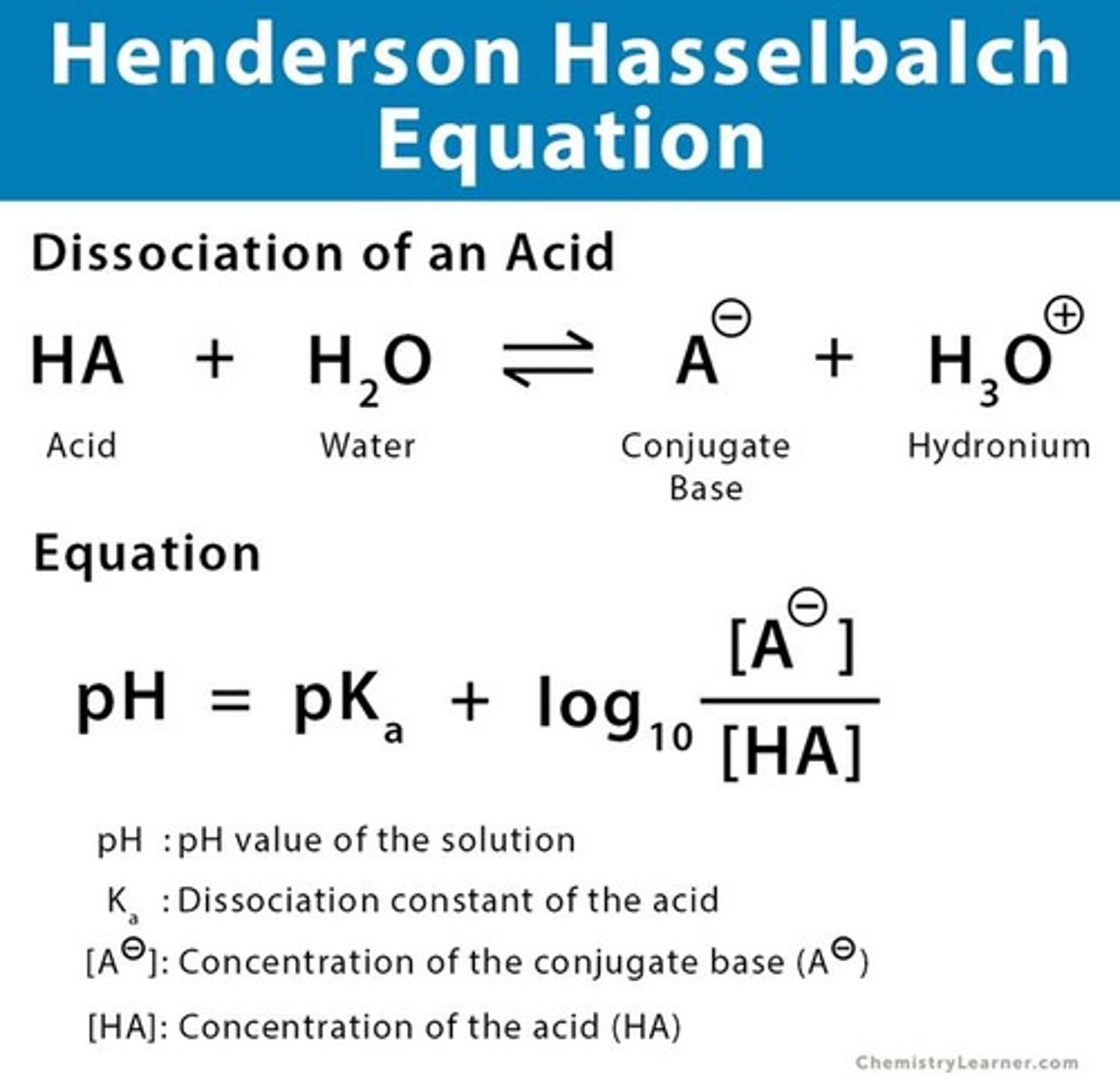
Acetate Buffer
Mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate.
Buffer Components
Weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa.
Neutralization Reaction
Conjugate base neutralizes added H⁺ from acids.
Acetic Acid
Weak acid component of acetate buffer.
Sodium Acetate
Conjugate base in acetate buffer solution.
pH Meter
Device providing precise pH measurements.
pH Paper
Approximate pH readings, rounded to 0.5.
Distilled Water
Should be boiled to remove dissolved gases.
Carbonic Acid
Forms from CO₂ in water, lowers pH.
Buffering Agents
Substances that stabilize pH in solutions.
Acidic Solutions
Soft drinks, vinegar, and pineapple juice examples.
Basic Solutions
Toothpaste neutralizes mouth acids, slightly basic.
Buffering System Strength
Stronger systems show smaller pH changes.
Homeostasis
Cells regulate pH tightly for biological function.
Buffering Factors
Concentration and acid-to-base ratio affect capacity.