Art Appreciation - Midterm
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Subject
Refers to the visual focus or the image that may be extracted from examining the artwork.
Abstract Art
An art that does not attempt to represent external reality, but seeks to achieve its effect using shapes, forms, colors, and textures.
Abstract Art
__________ is in itself a departure from reality, but the extent of that departure determines whether it has reached the end of the spectrum which is non-representational.
Content
Refers to the meaning that is communicated by the artist of the artwork.
Factual Meaning
The most rudimentary level of meaning for it may be extracted from the identifiable or recognizable forms in the artwork and understanding how these elements relate to one another.
Conventional Meaning
Pertains to acknowledged interpretation of the artwork using motifs, signs, symbols, and other cyphers as bases of meaning.
Conventional Meaning
Meanings that are strengthened through time, recurrent use, and wide acceptance by the viewers or scholars who study them.
Subjective Meaning
Meanings from a viewer’s circumstances that come into play when engaging with art.
Subjective Meaning
Meaning derived from what we know, what we learned, what we experienced, and the values that we stand for.
Nature, mythology, religious beliefs, and history.
What are the sources of subject in art?
Describe, Analyze, Interpret, Evaluate.
What are the 4 steps in critiquing an artwork?
Line, Shape, Form, Texture, Value or Tone, Color, Space.
What are the elements of art?
Emphasis, Contrast, Harmony, Balance, Pattern, Variety.
What are the principles of art?
Symmetrical, Asymmetrical, Radial
What are the sub-principle of Balance?
Emphasis or Focal Point
It is the first thing you see, dominant figure
Contrast
It’s any of the noticeable differences in light and dark shades; technique CHIAROSCURO (light/dark)
Harmony or Unity
It is the wholeness, feeling of completeness
Symmetrical
Both sides weigh about the same
Asymmetrical
Both sides does not weigh equally
Radial
Its elements equally distributed around a center point
Pattern
It’s the consistency of line or color; makes the artwork seem more active.
Variety
It’s the quality of having different forms, contrast, emphasis, size, and color.
Interpret
A step that bases on the analysis, interpret the meaning of the artwork using factual, conventional, or subjective levels of meaning.
Describe
A step that answers “What do you see?”
Describe
It’s like taking an inventory of what is seen in the artwork
Analyze
It uses the dominant elements and principles of art to reflect upon the artwork and why the artist used them.
Evaluate
It bases on the interpretation, evaluate the artwork
Evaluate
It derives relevance from the artwork to your own personal life or the society that you live in.
Describe
In critiquing an artwork, what step does this guide questions belong to:
What is the subject and what are the objects?
What sort of artwork is it?
What is the media used?
Analyze
In critiquing an artwork, what step does this guide questions belong to:
What kind of lines are present?
What shapes?
What colors?
How is space used?
What grabs your attention the most and why?
Do you see any relationship to the things described in step 1?
Interpret
In critiquing an artwork, what step does this guide questions belong to:
What is the artwork about?
What is the purpose of the artwork? Why did the artist create it?
What is the artist trying to say?
What is its meaning?
What kind of mood is being portrayed?
Evaluate
In critiquing an artwork, what step does this guide questions belong to:
What do you think about the artwork?
What is the value you find in it?
Why do you like or dislike the artwork?
Piet Mondrian
Who is the artist of Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow?

Rene Magritte
Who is the artist of The Treachery of Images?

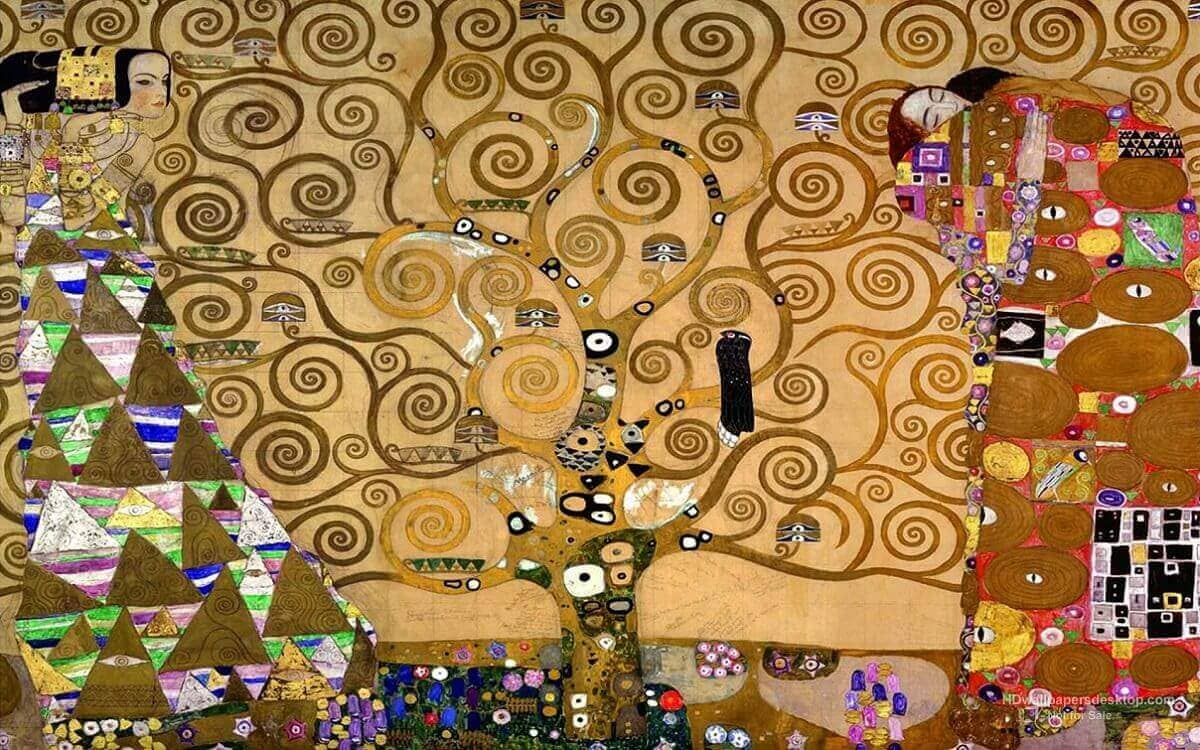
Gustav Klimt
Who is the artist of The Tree of Life, Stoclet Frieze?
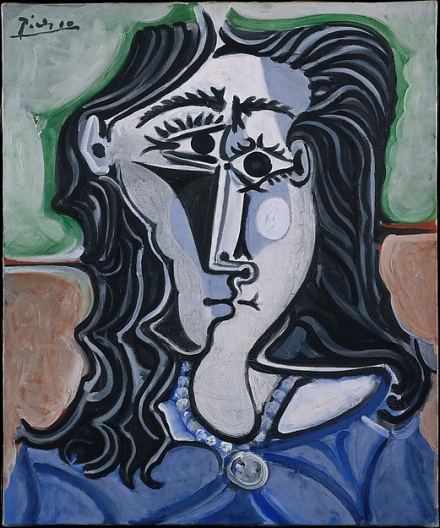
Pablo Picasso
Who is the artist of Head of a Woman?

Willem de Kooning
Who is the artist of Interchange?

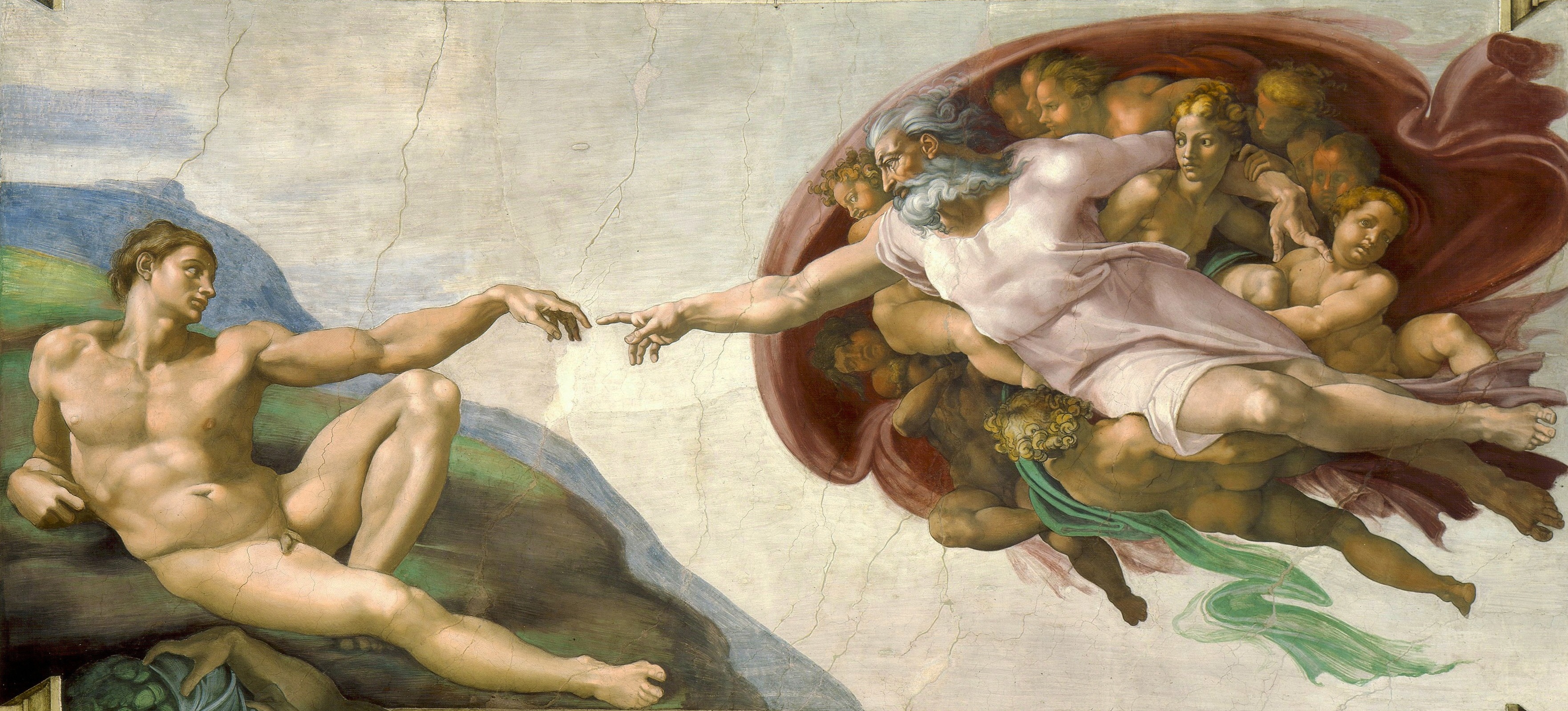
Specific poses of both figures allude that man was created in the image and likeness of God. Silhouette of the form behind God looks like a human brain, which signifies how the most important qualities imparted to man is intellect – Dr. Meshberger, Oct. 1990.
What is special about the depiction in The Creation of Man?

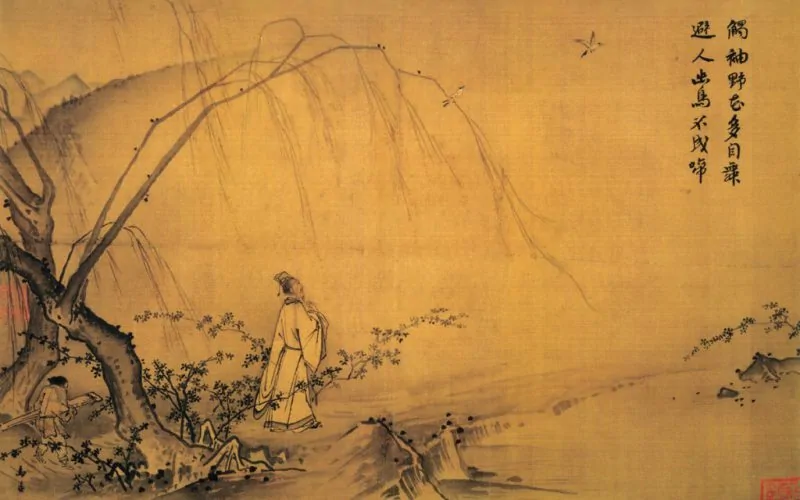
Ma Yuan
Who is the artist of On a Mountain Path in Spring?

Auguste Rodin
Who is the artist of The Gates of Hell?

Donatello, Michelangelo, Bernini
What are the three famous depictions of David?
Pablo Picasso
Who is the artist of Guernica?
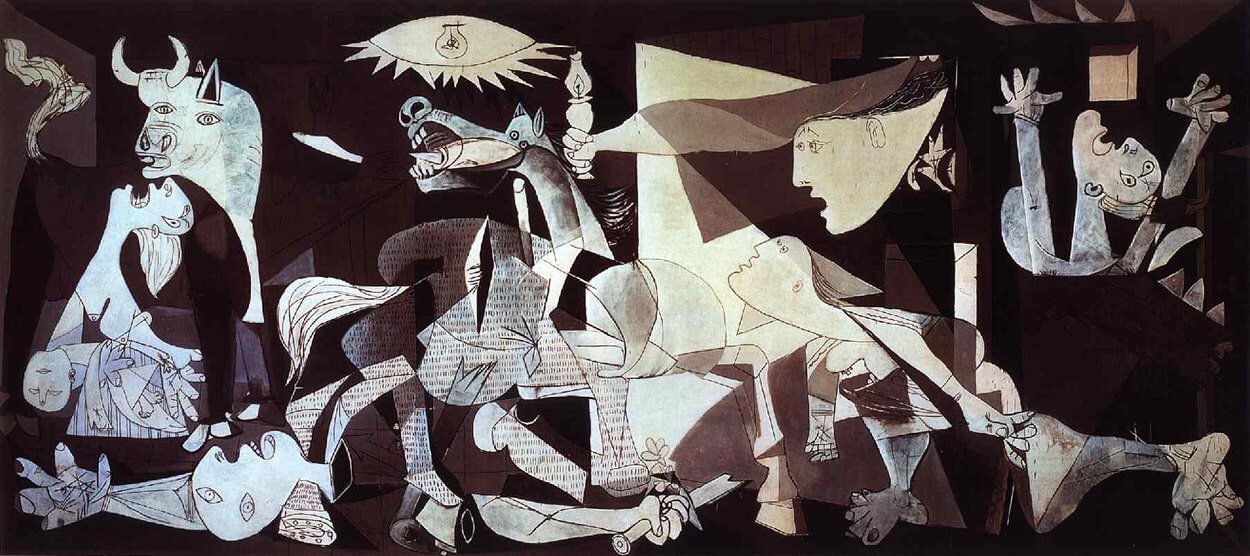

Picasso used cubist techniques, especially the fragmentation of objects and dislocation of anatomical features, to express condemnation of the Nazi bombing of the Basque Capital.
What is the significance of Guernica?

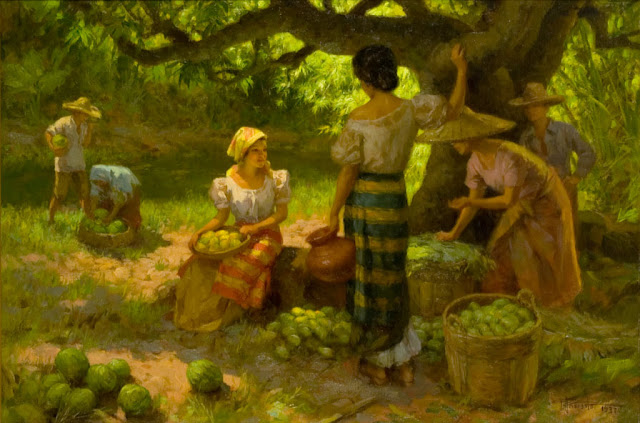
Fernando Amorsolo
Who is the artist of Fruit Pickers Harvesting Under The Mango Tree?

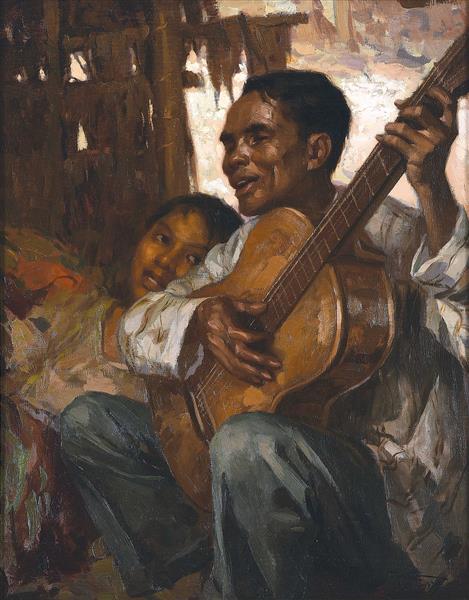
Fernando Amorsolo
Who is the artist of The Blind Man?

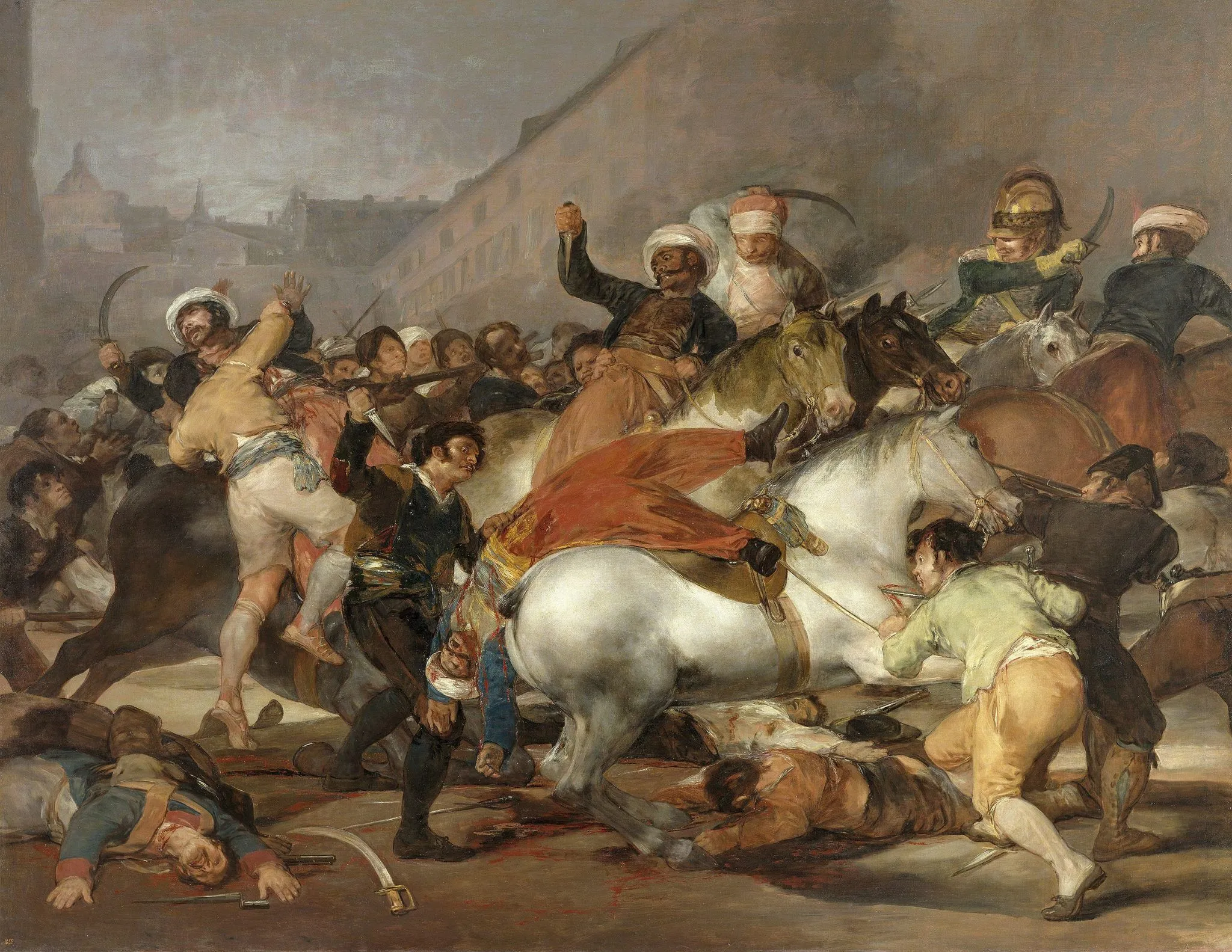
Francisco Goya
Who is the artist of The Third of May?

Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Who is the artist of Bal du moulin de la Galette?

Georges Seurat
Who is the artist of Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte?
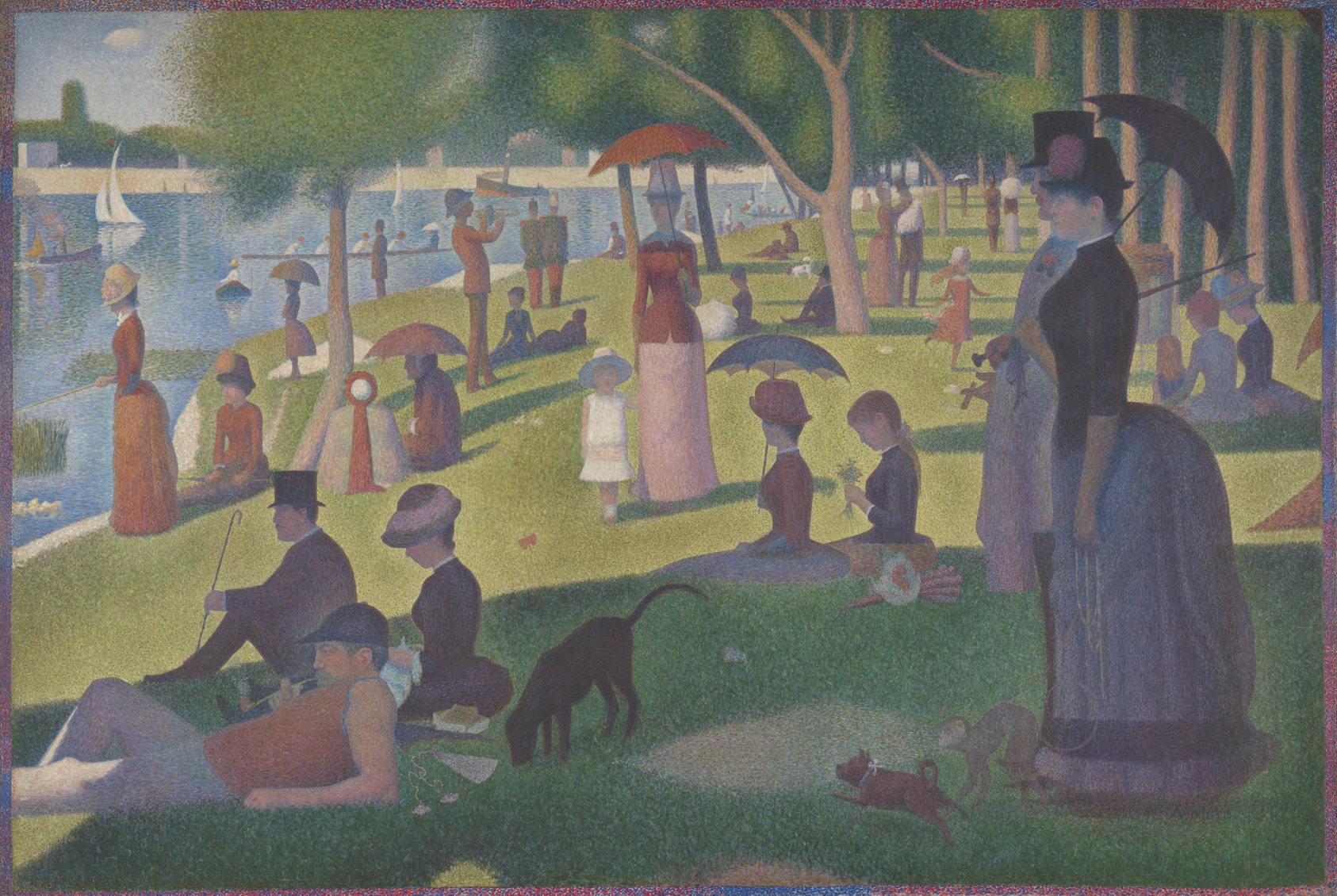
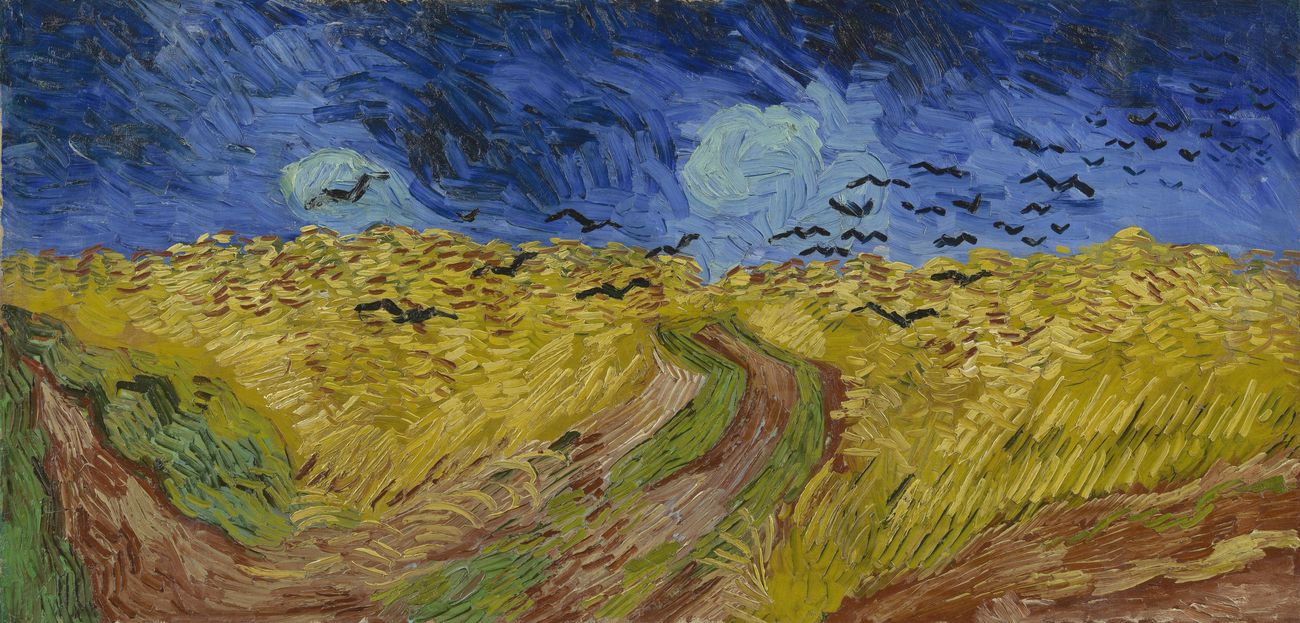
Vincent Van Gogh
Who is the artist of Wheatfield with Crows?

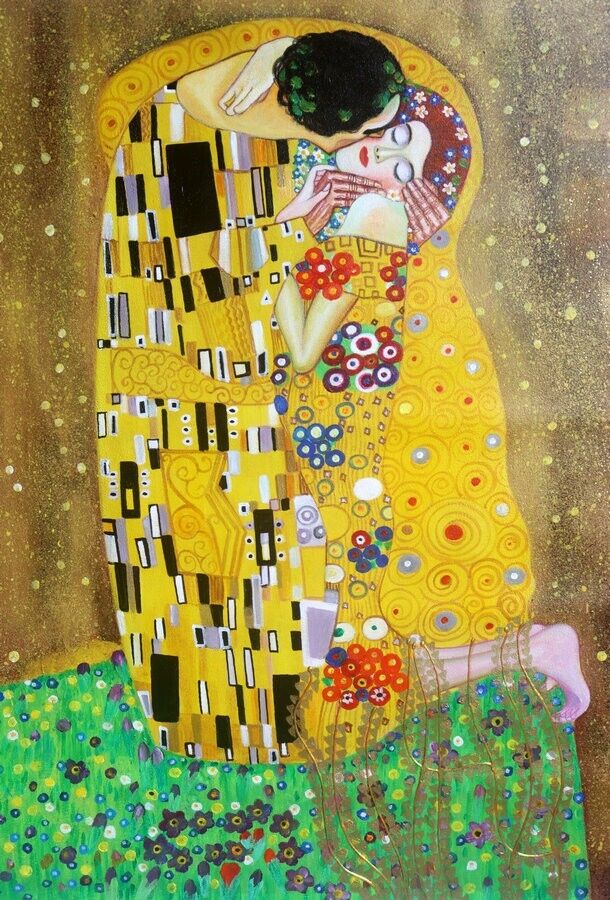
Gustav Klimt
Who is the artist of The Kiss?

Ancient times (30,000 BCE - 3,500 BCE). "Paleo" meaning old and "lithic" meaning stone.
What is the Paleolithic period?
Paleolithic Period
It is the period where crude tools of man became more shaped, thinner and sharper — which became conducive to the development of art
Representation; paved the way to the development of art
What was the stone man's most important contribution, and how did it influence the future of art?
Man became wholly human; Imagination, Concepts of Identity, and Meaning
What significant development occurred after the ice age ended that contributed to man's full humanity?
Early Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic
What are the sub-periods in Paleolithic?
Later Stone Age
What is the other name for Early Paleolithic?
Poses captured were fleeting or indicating movement.
Representation of animals was descriptive rather than optical (twisted perspective).
Purpose was often ritualistic, religious, or magical in nature.
What are characteristics of art in the Early Paleolithic period?
Ritualistic, Religious, Magical Nature
What was the purpose of art in the Early Paleolithic period?
Altamira Cave
What was the first cave art in Northern Spain during the Early Paleolithic period?
Hunters left caves to make rock shelters, and man became gatherers as well as hunters.
What is the Mesolithic period?
Middle
What does “meso” mean from the period Mesolithic?
Animals
They are far more common than humans in the Old Stone Age art. They always appear in profile.
Abstract Signs and Handprints
What were always included in Paleolithic paintings?
Pech-Merle painted hands
Some scholars think the ___________ are signatures of cult or community members or less likely, of individual painters
Human themes, often pictorial records of memorable events.
Art became more abstract and symbolic rather than pictorial.
What are characteristics of art in the Mesolithic period?
Mesolithic Period
In what period where hunters left their caves to make rock shelters, semi-nomadic existence. They didn’t have permanent shelters but were able to make dwellings of light wooden materials or in rock shelters
Light wooden materials or Rock shelters
Where did man dwell during the Mesolithic period?
Pictorial records of memorable events
What could have been the purpose of early human themes in art?
Human themes, Styles became more abstract
What were the characteristics of art during the Mesolithic period?
Culminated in the invention of writing
What major development occurred in the East as a result of the abstract evolution of art styles?
Rock shelter paintings, Microliths, Petroglyphs
What are examples of artwork during the Mesolithic period?
Microliths
These are the small stones, small blades of various shapes; made of stone; also used as tools and ornamentation
Petroglyph
These are images on rock made by carving and exposing a lighter color underneath
The new stone age, where man settled into fixed abodes, domesticated animals, and started farming.
What is the Neolithic period?
Great stones used in the Neolithic period.
What is a megalith?
Horus, Seth, Thoth, Anubis, Isis, Ra, Osiris
What are the Egyptian Gods?
Head in profile, body from the front (Frontalism).
Figures stand or sit in formal, stiff posture.
Slaves and animals depicted more naturally and on a smaller scale.
What are key features of Egyptian painting?
Raw materials
Where did the artists made colors from?
Men - red, Women - yellow
What were the colors used for the skin color for men and women?
Conventional postures, frozen gestures, and size reflecting rank.
Canopic jars for the safekeeping of particular human organs for the afterlife.
What are characteristics of Egyptian sculptures?
Canopic Jars
It is for safekeeping of particular human organs for the afterlife
Stomach, Intestines, Lungs, and Liver
What were the particular human organs stored in the Canopic jars?
Post and lintel construction, thick sloping walls, closely spaced stone columns, flat roofs, small openings, and use of hieroglyphs and religious symbols.
What are characteristics of Egyptian architecture?
Walls immensely thick and sloping
It is a structural requirement for balancing (vertical walls of stone are unstable)
Stone columns closely spaced
Large spans were not possible. Buildings had no mortar so stones or pieces had to be cut precisely so they fit together.
Cut precisely
How did ancient Egyptian builders ensure stones fit together without mortar?
Flat roofs
Domes and vaults were unknown in Egypt, what type of roof did they use?
Small openings
This also secured privacy for religious structures, which were inaccessible to the public.
Hieroglyphs
What were used for recording historic events on stone obelisks, columns, and walls?
Religious Symbols
These were essential components for decorating all architectural elements such as scarabs and the solar disk.