Conservation and Sustainable Development
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EAS 517
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is sustainable development
...development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
what are the three pillars of sustainability
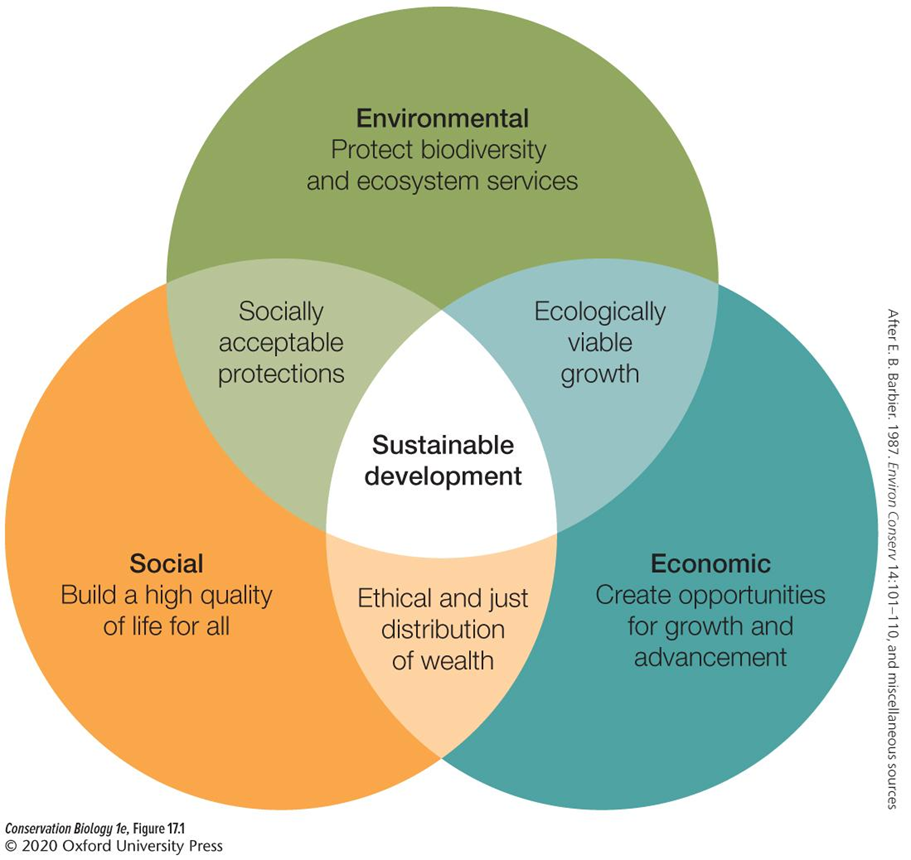
social, economic, and environmental
what are common ecosystem conceptual states or goals
Biodiverse (richness, evenness; genes, species, communities)
High ecological integrity (appropriate composition, structure, function)
Healthy (maintains function, provides ecosystem services)
Stable/Resistant
Resilient
Sustainable
what are international efforts to achieve sustainable development
1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro
2000 Millennium Summit
2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development
2012 UN Conference on Sustainable Development
1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro
Agenda 21 – reduce human impact on the environment
Rio Declaration on Environment and Development
Rio Forest Principles – sustainable forest management
Convention on Biological diversity
(1) biodiversity conservation
(2) sustainable use of biodiversity
(3) fair and equitable sharing of genetic resources.
UN Convention on Climate Change
Convention to combat desertification
what are concerns/critiques in the UN sustainable development goals
Gaps in Biodiversity goals?
Costs/who is funding?
Conflicts within and among goals?
Aichi Biodiversity Targets
Targets set by CBD in 2010 Aichi, Japan
are part of the Convention on Biological Diversity Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011–2020
20 Aichi Biodiversity targets
why did the Aichi targets fail
Lack of clearly defined metrics to gauge progress made the Aichi goals tough to implement.
A mismatch between countries with abundant natural assets and those with the resources to enforce protections.
Insufficient funding to support conservation efforts.
where does funding for sustainable development come from
Global Facility (GEF) Funding
World Bank
NGOs
Individual governments
Global Environment Facility (GEF) Funding
Global Environment Facility (GEF) funding provided by countries in 4-year replenishment cycles
established at the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to help tackle environmental problems
Unites 183 countries in partnership with international institutions, civil society organizations, and private sector enterprises, who provide funding for environmental projects, many of which link to the UN SDGs.
World Bank contributions
provides loans and grants to governments of poorer countries
3 of the agencies contribute to sustainable development projects
require recipients to comply with Environmental and Social Standards (ESSs)
National Environmental Funds (NEFs)
formed by partnership of NGO’s (e.g., WWF, TNC) and international funders (e.g., World Bank)
USAID
helps funding for sustainable development
but funding freeze
options to integrate conservation and development
integrated mix of conservation & development ends
use development means in service of strict conservation ends
explicitly link the project’s conservation ends to broader development ends
option 1: integrated mix of conservation & development ends
most common, worst choice – may not reach both & have to choose; or reach one by a means that conflicts with the other
option 2: use development means in service of strict conservation ends
use resources to meet human needs as a strategy to reduce threats to biodiversity
cannot ignore development concerns. Instead, they need to consider human needs in the context of both the threats at the site and their strategies – to use development means to achieve their desired conservation ends.
option 3: explicitly link the project’s conservation ends to a broader development ends
conservation ends as a means to achieve development ends
Direct limited resources to achieve both goals