Endocrine System - Glands and Hormones
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quite literally the same thing that Friem had posted, but its free and it has the locations of the anatomy that we need to know
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
pineal gland
time keeper and regulator of day/night cycle
melatonin
sleep inducing hormone, may also contribute to fertility
posterior pituitary
store and release ACTH, ADH, and Oxytocin
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids (cortisol)
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
produced by posterior lobe of pituitary gland. targets kidneys for water conservation. inhibits urine production. altered by alcohol
oxytocin
a hormone released by the posterior pituitary that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and sexual relations, and milk ejection during breastfeeding
anterior pituitary
stimulates the development of gametes in men and women
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
stimulates the secretion of ovarian sex hormones, development of ovarian follicles, and sperm production
prolactin
promotes milk secretion
growth hormone (GH)
influences growth of skeletal muscles and long bones. can be used as a “steroid”
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
thyroid
regulates metabolism
thyroxine
controls rate of metabolism/oxidation of glucose and all chemical reactions
calcitonin
hormone that the thyroid gland makes and releases to help regulate calcium levels in your blood by decreasing it
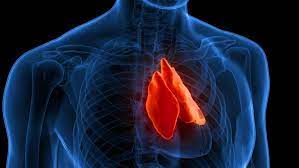
thymus
gland in thoracic cavity above the heart where T lymphocytes mature
thymosin
stimulates the maturation of lymphocytes into T cells of the immune system
adrenal cortex (outer adrenal gland)
outer section of each adrenal gland, secretes sex hormones
aldosterone
“salt-retaining hormone” which promotes the retention of nat by the kidneys. Nat retention promotes water retention, which promotes a higher blood volume and pressure
cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex, alters immune response, digestive system, and reproductive system
adrenal medulla (inner adrenal gland)
middle portion of adrenal glands, secretes norepinephrine
epinephrine (adrenaline)
fight or flight response, can be used to treat anaphylaxis
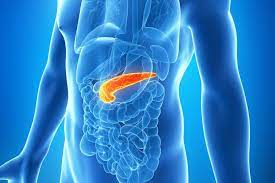
pancreas
produced digestive enzymes and secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream and help regulate blood glucose levels
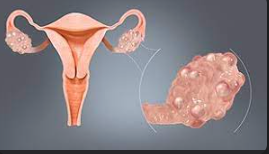
ovaries
female gonad
estrogen
helps develop second characteristics and mature female reproductive organs
progesterone
acts with estrogen to bring out the menstrual cycle assist in implanting the embryo
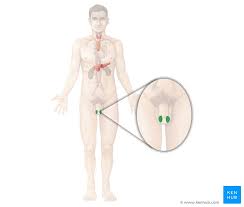
testes
male gonads
testosterone
both males and females have it, it’s just more present in males. stimulates the growth of males sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty and sperm production
parathyroid
ridges piggy back on thyroid gland
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
peptide hormone that increase blood calcium concentrations by removing CA from the bones, imbalances can lead to kidney stones
placenta
a structure that allows an embryo to be nourished with mothers blood supply, is responsible for multiple pregnancy hormones
human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
stimulates corpus luteum to produce estrogen and progesterone…the pregnancy hormone. detected in pregnancy tests
placental lactogen (hPL)
preps breasts for lactation, antagonist of insulin. makes sure baby gets enough glucose, minerals, and protein
relaxin
the hormone that creates the flexibility in the pubic symphysis and ligaments during pregnancy and birth
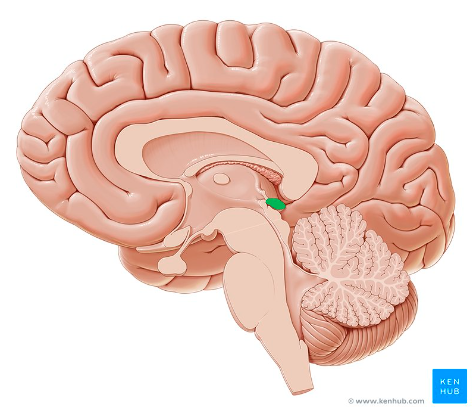
pineal gland
name this part
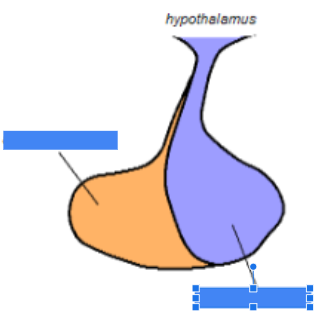
posterior pituitary
name the purple region
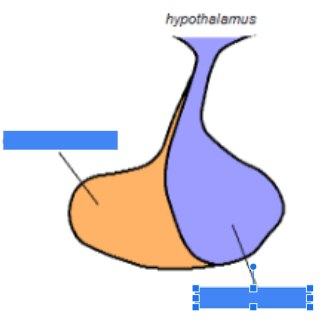
anterior pituitary
name the orange region
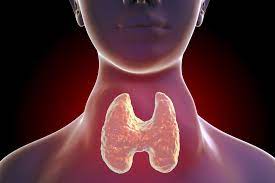
thyroid
name the part
thymus
name the part
pancreas
name this part
testes
name this part
ovaries
name this part
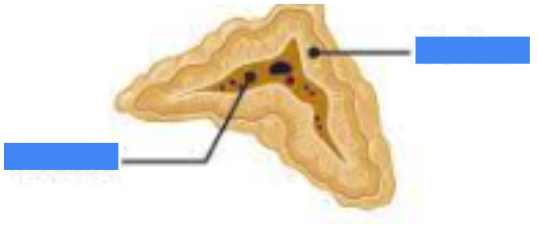
adrenal medulla
name the inner part
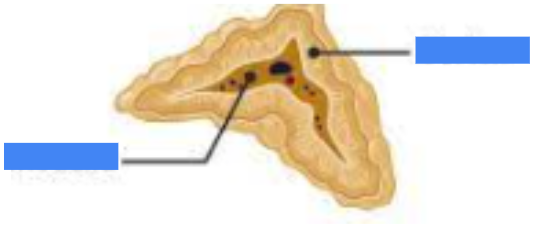
adrenal cortex
name the outer part
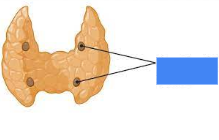
parathyroid
name this part (horseback ridges)
placenta
name this part