Human Food Poisoning (disease control in animals to benefit public health)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is foodbourne infection?
Infection with an agent (usually bacterial or viral) that results in often diarrhoeal disease
Frequently zoonotic
What are some examples of foodbourne infection?
Salmonella, E.coli, Norovirus
What is food poisoning?
Exposure to toxins (microbial or other) that results in disease
What is food poinsoning frequently caused by?
Contamination, poor storage or poor handling
What are some examples of food poisoning?
Staphylococcus toxin, bacillus enterotoxin, afalotoxins from fungi
What is food security
Exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food which meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
What are the UK’s major foodbourne diseases?
Salmonella enterica
Escherichia coli
Compylobacter
Listeria monocytogenes
Clostridium perfringes
Hepatitis E
Norovirus
What is the main cause of human bacterial gastroenteritis?
Campylobacter
caused by c.jejuni & c.coli
What type of bacteria are campylobacter?
Gram negative spiral rods
What are the human symptoms of campylobacteriosis?
D+ (frequently with blood in faeces)
Abdo pain
Fever
Headache
Nausea and/or vomitting
Who are at main risk of campylobacteriosis
Under 5s
Over 65s
Bowel cancer patients
Those taking proton pump inhibitor drugs
What are the main sources of campylobacter?
Poultry meat
Red meat
Water
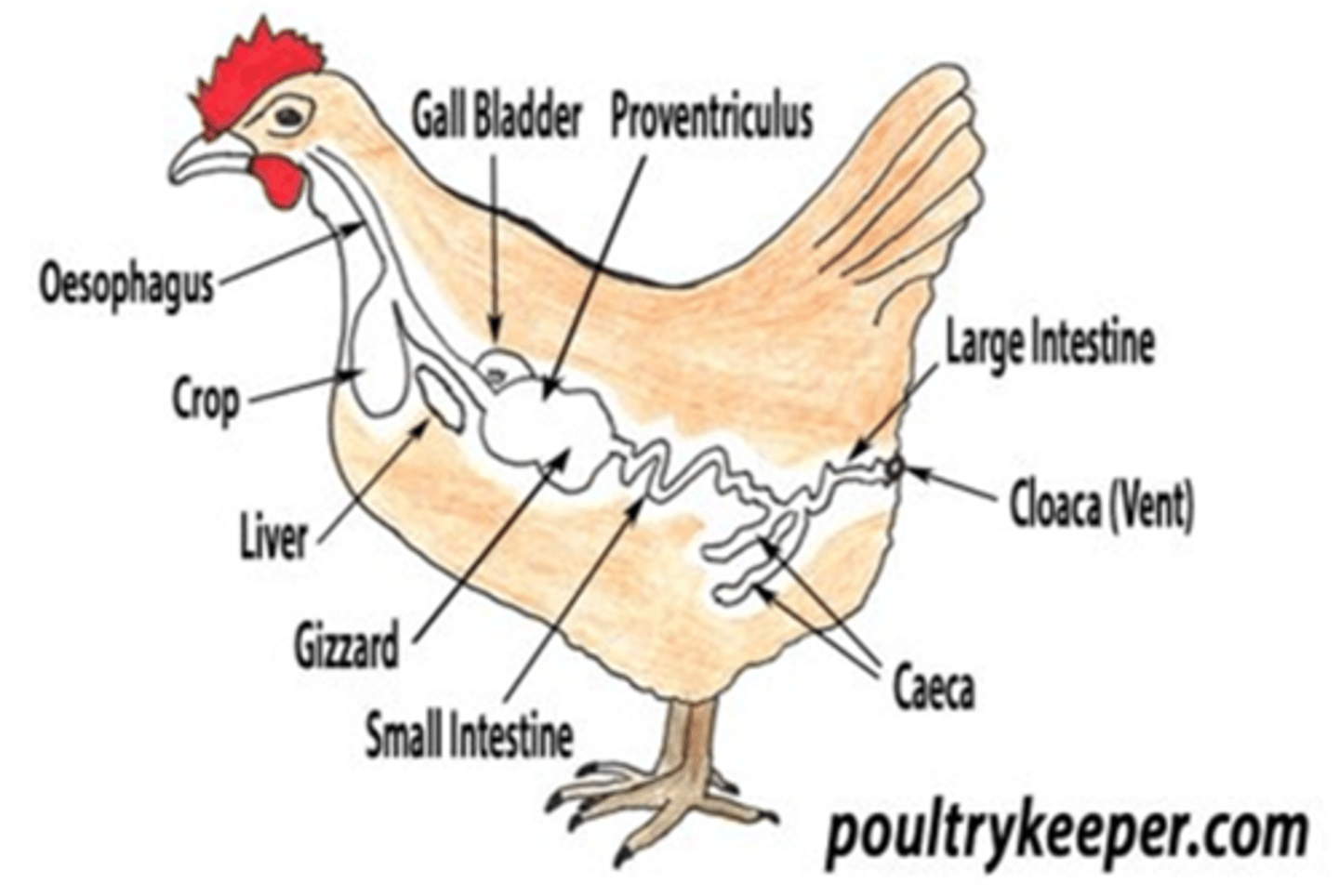
Why are broiler chickens associated with campylobacter?
Core temp (41-42 degrees) suits campylobacter
Ceca supports high levels of growth
High shedding levels in faecal and caecal droppings
How can production and processing of chicken lead to campylobacter spread?
biosecurity breakdowns
transport increases stress = more shedding
cross contamination on production lines
low infective dose - can cause disease in low doses
2017 regulations to reduce campylobacter
Food Standards Agency introduced targets for reducing risk
Reduce campylobacter levels to less than 1000 Colony Forming Units (CFU)
Is it possible to rear campylobacter-free chickens?
Yes
Would cost £20-£50 per bird though
What is the main pathotype of concern for E.coli?
EHEC - Entero Haemorrhagic (STEC/VTEC)
Where does E.coli live in animal host?
Distal rectum
Even if not shed, bacteria from the GI tract may contaminate meat at time of slaughter
Yersinia & Shigella
Both similar to salmonella and E.coli
Causes human dysyntery
Describe Listeria monocytogenes
Gram positive rod-shaped intramacrophage pathogen
May be zoonotic (including foodborne)
What is Literia Monocytogenes associated with?
Cooked meats
Pate
Soft cheese
Smoked fish
Pre-prepared sandwiches
Cook-chill meals
can grow well at low temperatures
What are the human symptoms of listeriosis?
Either gastroenteritis or flu-like symptoms (mild)
Who is at risk of listeriosis?
Pregnant, elderly & immunocompromised
What do enterotoxins usually induce?
D+
V+

Bacillus food poisoning is associated with which foods?
Pulses and rice
Why shouldn't you reheat cooked rice?
Cooking kills vegetative bacteria but not spores
When left and not chilled more spores form which produce toxins
When re-heated and consumed, spores are eaten
Which two species of clostridia may cause severe food poisoning?
Clostridium perfringens & Clostridium botulinum
C.botulinum poisoning is associated with which foods?
Poorly canned or bottled foods
Honey
less of a problem now
C.perfringens germinates in which conditions?
Poorly stored meat or reheating meat in mass catering
Type A toxins is biggest concern
Vibrio parahaemolyticus poisoning is associated with which foods
Salt
Undercooked shellfish
The main viral cause of diarrhoea in UK
Norovirus
How is hepatitis A transmitted?
Through person-to-person contact (poor hygiene)
Anal intercourse
Faecal contamination of food & water
What is the main source of foodbourne hepatitis A?
Contaminated shellfish (oysters in particular)
What are symptoms of hepatitis A?
Nausea, D+, V+, jaundice & flu-like illness
What are symptoms of Hepatitis E? In which food products is it commonly found?
Short lived hepatitis but can be severe & cause death
Pork and pork products
How can bugs survive on food so well?
biofilms - attaching to surfaces of food and prep areas
listeria - resistant to cold and grow well
salmonella persists well in chilled foods
Why vegetables and other foods may be a source of foodborne infection?
manure/fertiliser can contain pathogens
livestock carriers can contaminate the environment
rodent and wild bird contamination
continuous, warm system with water re-use = contamination of water