Unit 3 Electricity, Magnetism, and Electromagnetism
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is Electrostatics?
The study of electric charges in their stationary form.
What is Electrodynamics?
too few or too many electrons (protons do not move)
What are the three methods of electrification?
Friction, contact, and induction.
How does friction electrify an object?
By rubbing one material against another (e.g., fur against a rod).
How does contact electrification occur?
When a charged object physically touches another object, transferring charge.
What is induction in electrification?
The rearrangement of electrons in an uncharged object due to the presence of a charged object.
What are the laws of electricity?
Unlike charges attract; like charges repel.
Electrons travel on the outside of a conductor.
Charges concentrate on the sharpest curvature.
Electrostatic force is proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
What is Coulomb’s Law formula?
EF = k (Q₁Q₂ / d²)
What is voltage?
The potential energy possessed by a charged object; measured in volts (V). It represents potential difference in a circuit.
What is a conductor?
A material that allows electrons to flow through it, like copper or silver.
What is an insulator?
A material that hinders electron flow, like rubber or wood.
What is a superconductor?
A material that allows electrons to flow with zero resistance (e.g., titanium).
What is Ohm’s Law?
V = IR (Voltage = Current × Resistance)
In Ohm’s Law, what does I = V/R represent?
Current = Voltage divided by Resistance
In Ohm’s Law, what does R = V/I represent?
Resistance = Voltage divided by Current
What is a series circuit?
A circuit with only one path for current to flow; current is constant throughout.
What happens if one part of a series circuit breaks?
The current stops flowing.
What is a parallel circuit?
A circuit with two or more paths for current; voltage is the same across all branches.
What happens if one branch in a parallel circuit breaks?
Current can still flow through the other branches.
What is electrical power?
Work done per unit of time; measured in watts (W).
What are the formulas for electrical power?
P = IV and P = I²R
What is the difference between AC and DC?
DC flows in one direction (e.g., batteries). AC reverses direction (e.g., wall outlets).
What is the frequency of AC in the U.S.?
60 Hz
What factors influence resistance?
Wire length, cross-section, material, and temperature.
How does wire length affect resistance?
Longer wire = more resistance.
How does cross-sectional area affect resistance?
Smaller cross-section = more resistance.
How does temperature affect resistance?
Higher temperature = more resistance.
What is magnetism?
The ability of a material to attract iron.
What is a magnetic domain?
A group of aligned atomic magnets within a material.
What is the SI unit of magnetism?
Tesla (T)
What are the 3 types of magnets?
Permanent, temporary, and electromagnets.
What are the magnetic laws?
Every magnet has North and South poles.
Like poles repel; unlike poles attract.
Magnetic force is proportional to pole strength and inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
What are the magnetic classifications of materials?
Ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, and diamagnetic.
What is susceptibility?
The ability of a material to be magnetized.
Which has high susceptibility: wood or iron?
Iron.
What is retentivity?
The ability of a material to remain magnetized.
Which has higher retentivity: hard iron or soft iron?
Hard iron.
What are magnetic lines of force?
Invisible lines representing the magnetic field; flow from one pole to another.
What is an electromagnet?
A magnet created and controlled by electricity.
What did Oersted discover?
A magnetic field surrounds a moving electric current.
What is Faraday's First Law?
A current is induced by a moving magnetic field.
What factors affect the magnitude of induced current?
Speed, magnetic strength, angle, and number of coil turns.
What is mutual induction?
When a magnetic field induces current in a nearby coil.
What is a generator?
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
What is a motor?
A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
What is an induction motor used for?
Rotating the anode in x-ray tubes.
What are the parts of an induction motor?
Rotor and stator.
What is a transformer?
A device that changes voltage/current using AC.
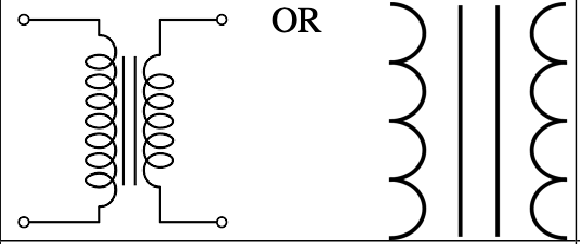
What are the parts of a transformer?
Primary coil, secondary coil, and core.
What is a mutual induction transformer?
One that induces voltage/current in the secondary coil via a changing magnetic field in the primary coil.
What is a self-induction transformer (autotransformer)?
A single coil acting as both primary and secondary.
What is the transformer voltage law formula?
VS / VP = NS / NP
What is the transformer current law formula?
IP / IS = NS / NP
What is a step-up transformer?
A transformer with more turns in the secondary coil to increase voltage.
What is a step-down transformer?
A transformer with fewer turns in the secondary coil to decrease voltage.
What are the 3 types of transformer construction?
Open core, closed core, and shell core.
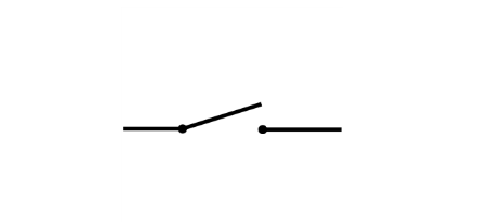
Open Switch
The circuit is switched OFF
Open (break) the circuit without disconnecting the wires
Closed Switch
The circuit is switched ON
Closed (complete) the circuit
Transformer
A device used to change the voltage and current in an electric circuit
Resistor
Electrical component use to reduce or resist the flow of electricity

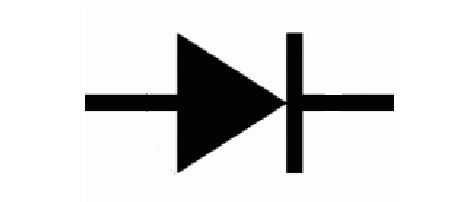
Diode
Electronic device allow current to flow in one direction only
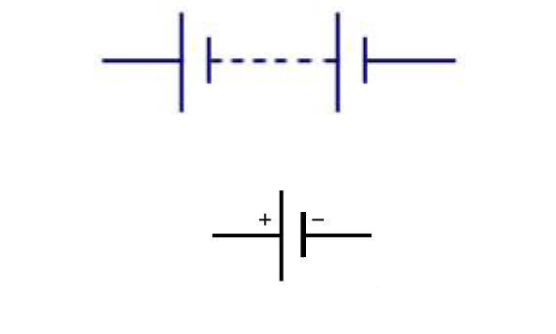
Battery
DC supply of voltage and current, usually made of many cells
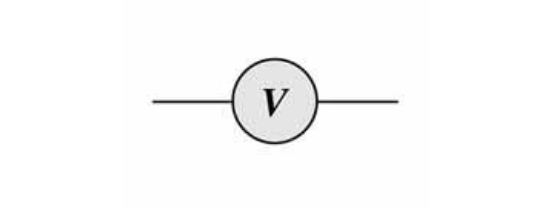
Voltmeter
A device used to measure potential difference, must be put in parallel
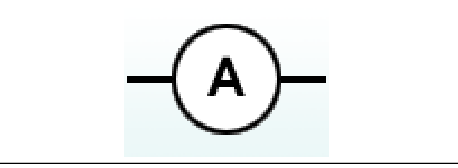
Ammeter
A device used to measure the current flowing through a circuit, must be in series