Joints and Muscles
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What type of joint has little to no movement with no space between bones?
Fibrous
Sutures are what type of STRUCTURAL joint?
Fibrous
Teeth are what type of STRUCTURAL joint?
Fibrous
The distal joint between the tibia and fibula is what type of joint?
Fibrous
Joints with hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage between the bones with limited movement are...
Cartilaginous
What STRUCTURAL type of joint is the pubic symphysis?
Cartilaginous
What STRUCTURAL type of joint are the intervertebral joints?
Cartilaginous
What STRUCTURAL joint is the shoulder?
Synovial
Joints that allow no movement are functionally called
Synarthroses
Joints allowing limited movement are functionally called
Amphiarthroses
Joints that allow a large range of movement are functionally called
Diarthroses
The pubic symphysis is what type of functional joint?
Amphiarthrosis
A fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid is a
Bursa
What form the knee joint?
Condyles on the femur and tibia and facets on the patella
ACL stands for
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
What does the ACL prevent?
Hyperextension of the knee and anterior displacement of the tibia
PCL stands for
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
What does the PCL prevent?
Posterior displacement of the tibia
Fibular collateral ligament
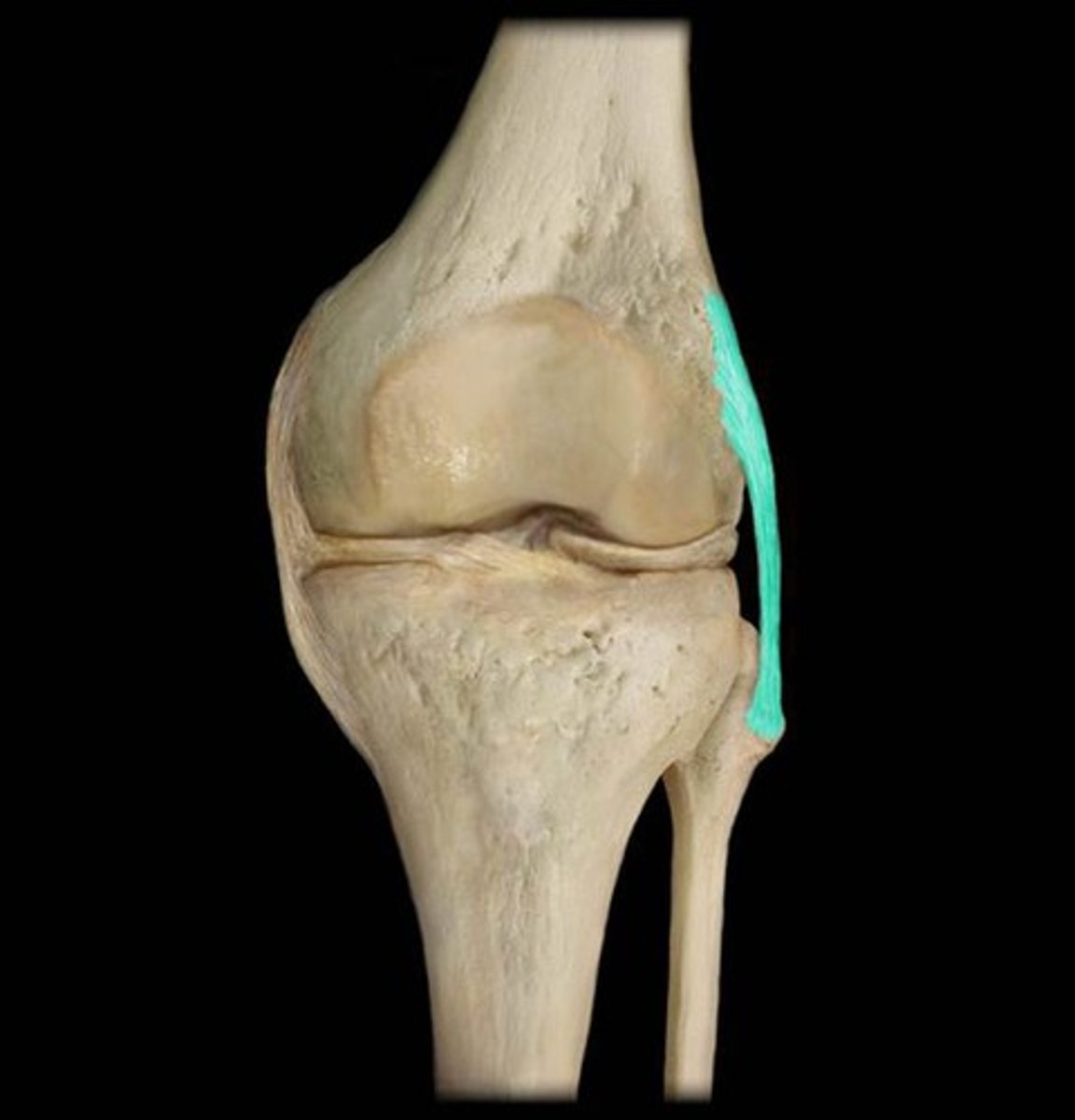
Lateral meniscus
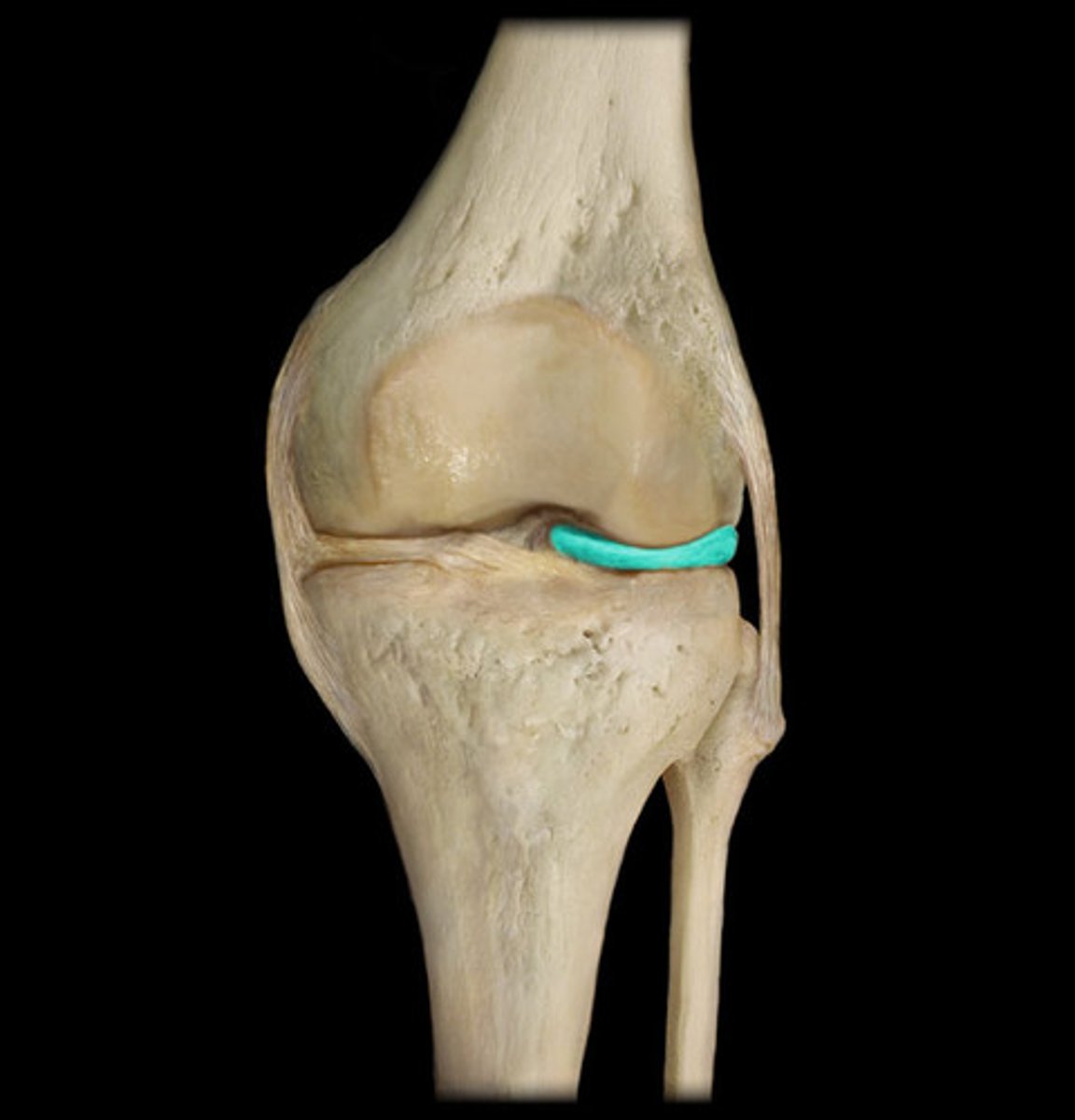
Tibial Collateral Ligament
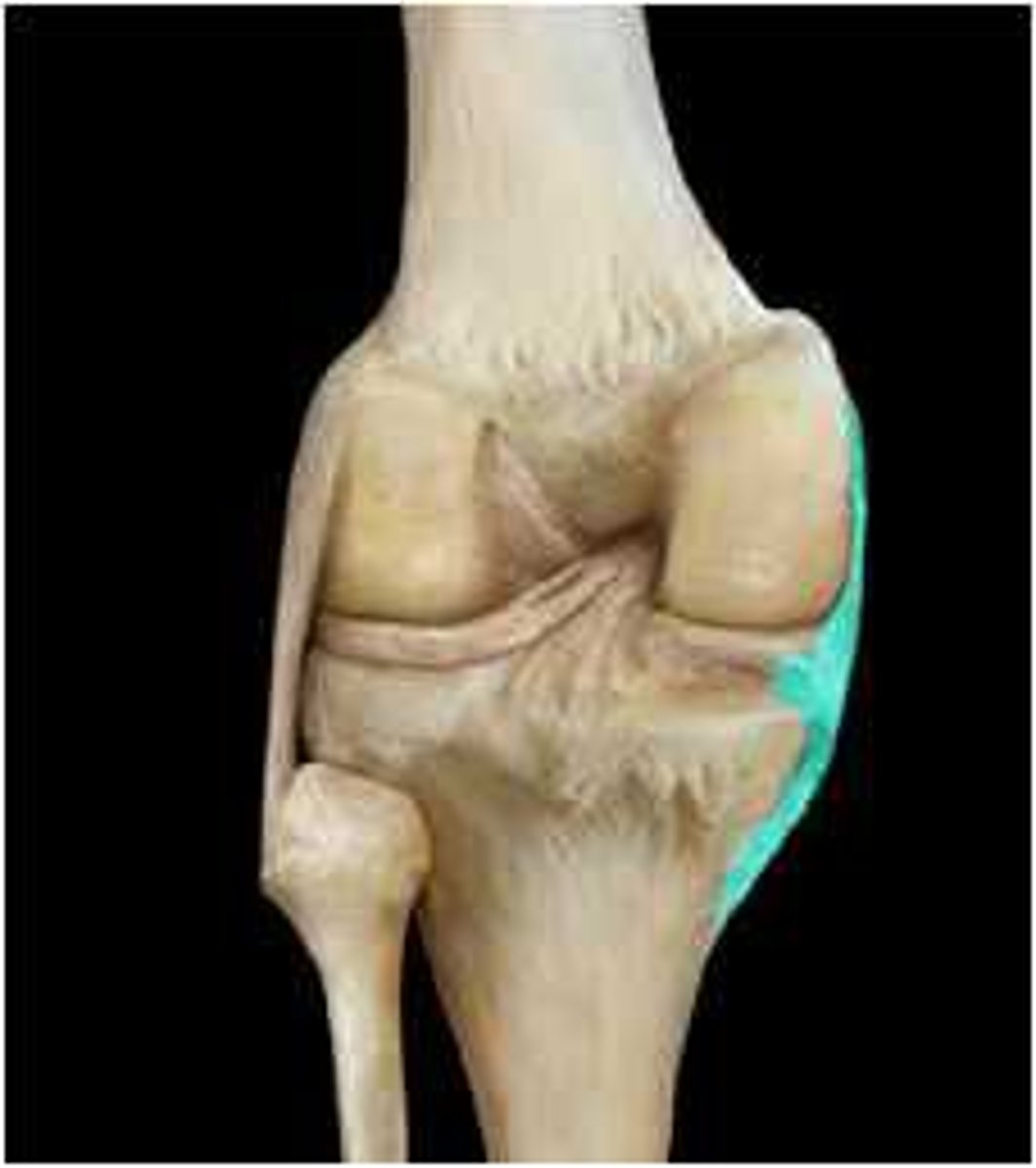
Medial meniscus
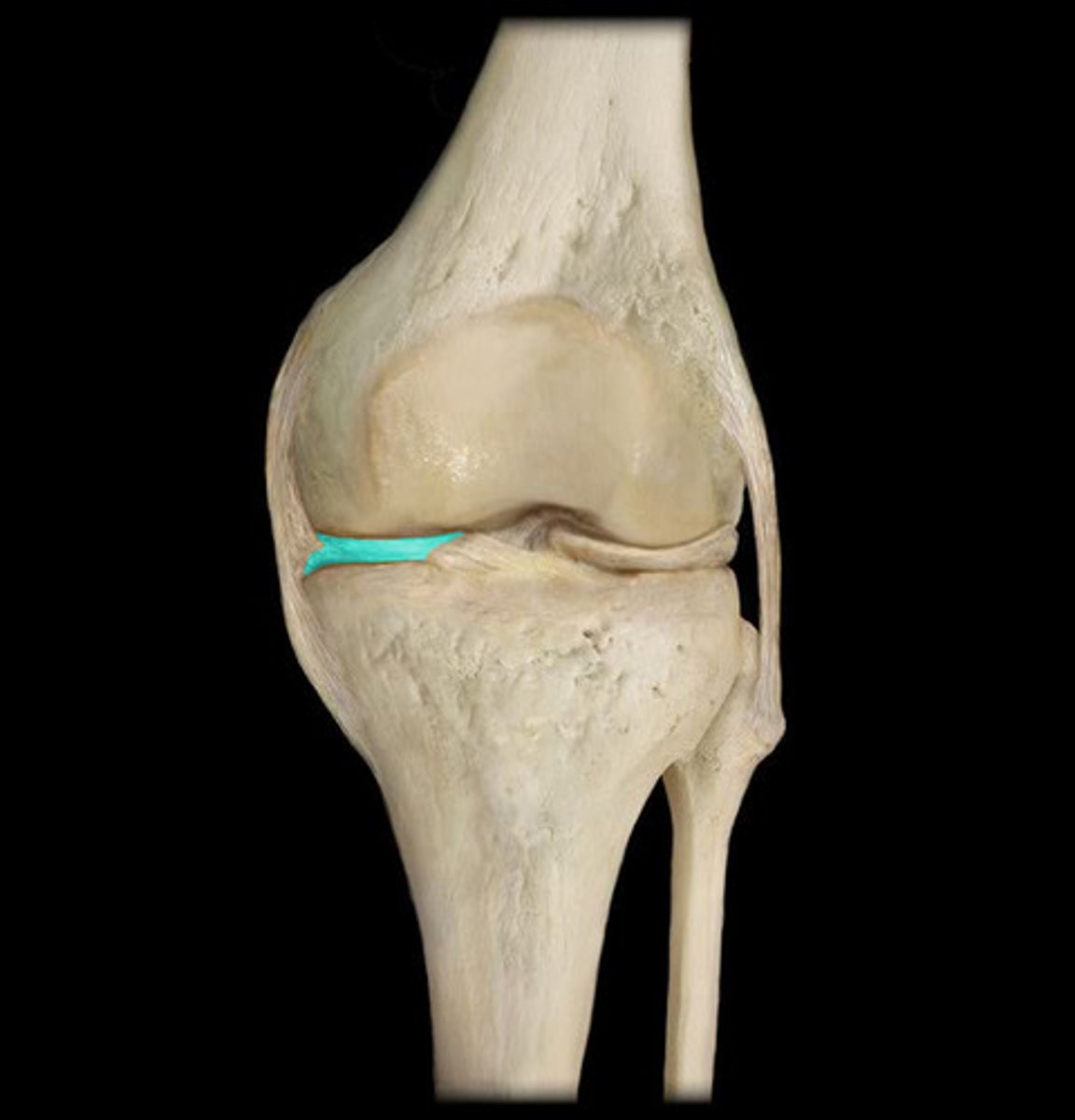
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
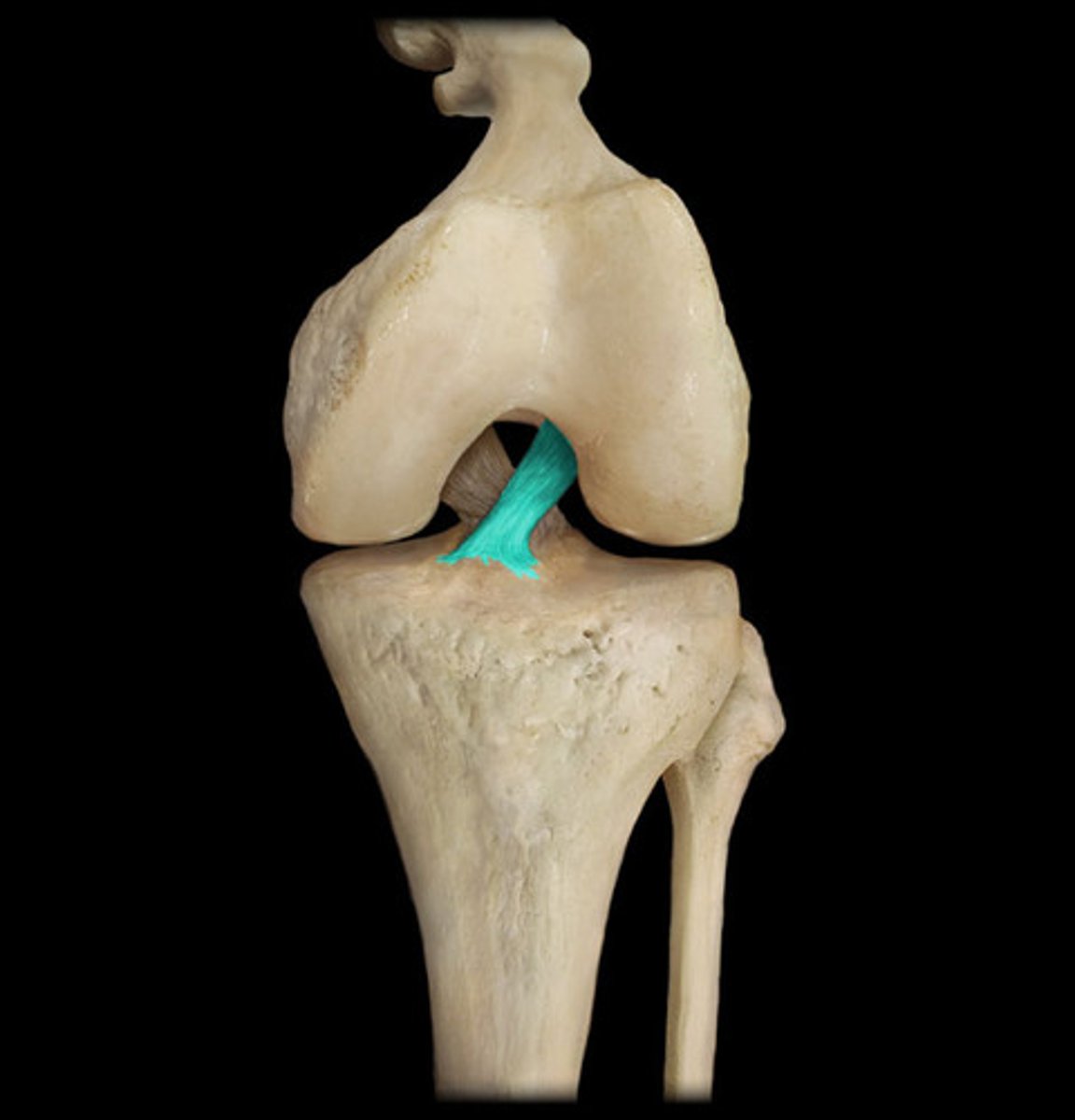
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
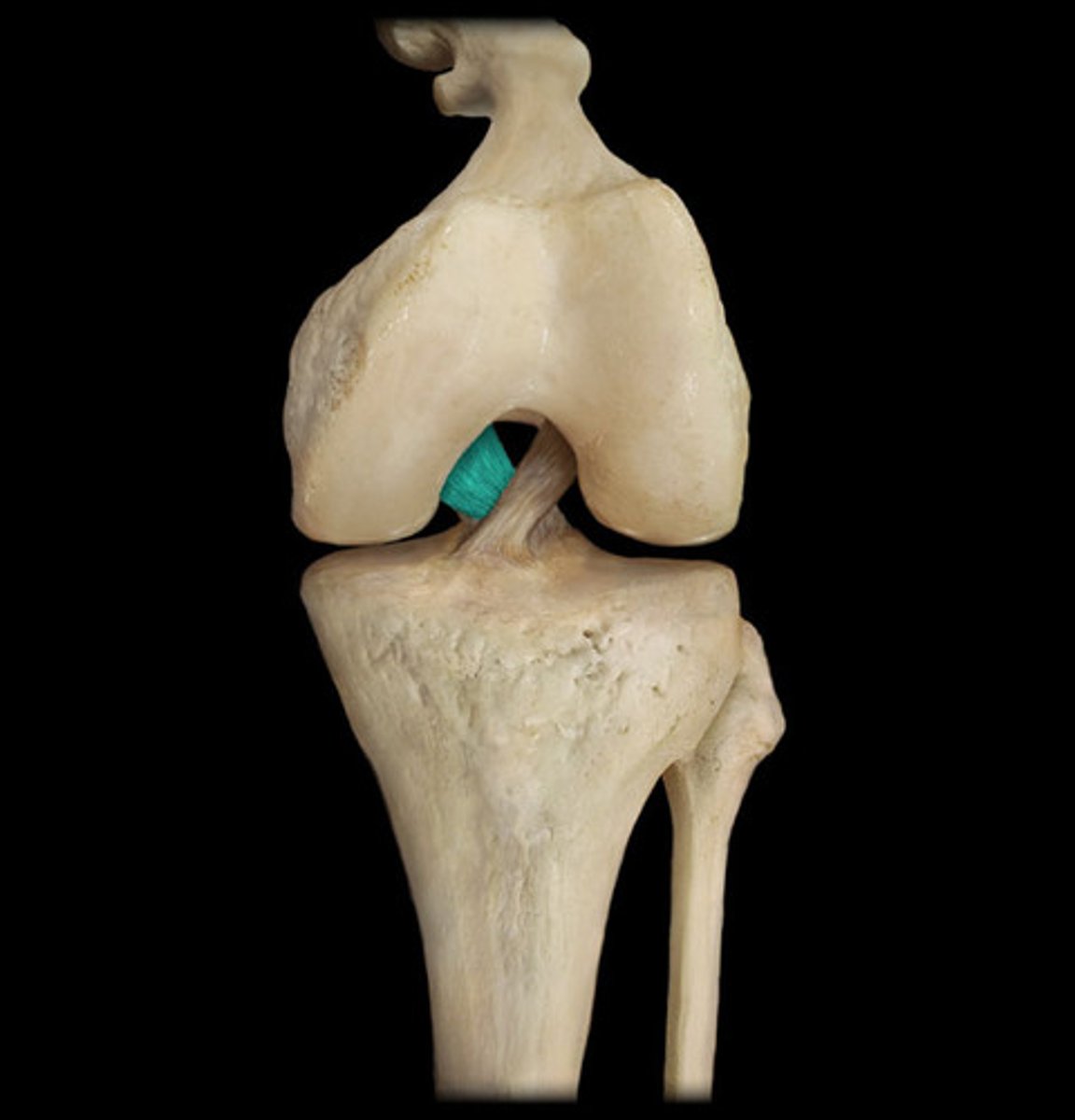
Muscles are attached to bones through structures called
Tendons
The sliding of one bone surface across the surface of another is...
Gliding
What type of movement alters the angle between bones?
Angular
Sticking out your jaw is an example of what type of movement?
Protraction
Pulling your jaw in is an example of what type of movement?
Retraction
What type of movement decreases the angle between two bones, usually in the sagittal plane?
Flexion
What type of movement increases the angle between two bones, usually in the sagittal plane?
Extension
What type of movement increases the angle between bones beyond the anatomical position in the sagittal plane?
Hyperextension
Movement of a body part away from the midline along the frontal plane is...
Abduction
Movement of a body part toward the midline along the frontal plane is...
Adduction
Movement of a distal body part in a circular motion is...
Circumduction
Circular movement of a bone along its longitudinal axis is
Rotation
Pulling your arm or leg back past your side is
Hyperextension
Raising your arm forward along the sagittal plane is
Flexion
Bending the lower half of your leg back at the knee along the sagittal plane is
Flexion
Palms facing up (like holding a cup of soup) is
Supination
Palms down or lying face down is
Pronation
Movement of the sole of the foot toward midline is
Inversion
Movement of the sole of the foot away from midline is
Eversion
What movement allows the thumb to touch other fingertips?
Opposition
The movement of the thumb back to anatomical position would be...
Reposition
Shrugging your shoulders is
Elevation
Opposite of shrugging your shoulders is
Depression
Pointing your toes downward is described as which type of movement?
Plantar flexion
Raising your toes and ankle toward your knee would be
Dorsiflexion
Your chin touching your chest would be
Flexion
Bringing the back of your head backward would be
Extension
What are the 6 types of synovial joints?
-Plane
-Hinge
-Pivot
-Condylar
-Saddle
-Ball and socket
A joint that exhibits movement in 2 planes is...
Biaxial
A joint that exhibits movement in 1 plane is...
Monoaxial
A joint that exhibits movement in multiple planes is...
Multiaxial
The elbow joint is what type of synovial joint
Hinge
The shoulder joint is what type of synovial joint
Ball and socket
The metacarpophalangeal joint (knuckles) is what type of synovial joint?
Condylar
The intercarpal joint is what type of synovial joint?
Plane
What type of movement does a pivot joint allow?
Rotation
What type of movement does a ball and socket joint allow?
All angular movements and rotation
What type of movement does a saddle joint allow?
All angular movements
What type of movement does a condylar joint allow?
All angular movements
What type of movement does a hinge joint allow?
Flexion and extension
What type of movement does a plane joint allow?
Back-and-forth and side-to-side gliding
Which joint is multiaxial?
Ball and socket
Pivot and hinge joints are... (axial)
Monoaxial
Masseter origin
Zygomatic arch
Buccinator origin
alveolar processes of maxilla and mandible
sternocleidomastoid origin
sternum and clavicle
pectoralis major origin
Clavicle/rib cartilages
latissimus dorsi origin
Vertebrae
Rectus abdominis origin
pubic symphysis and superior pubis
Deltoid origin
Acromion process and scapular spine
Trapezius origin
Occipital bone/spinous process of C7-T4
Biceps brachii origin
Coronoid process of scapula/margin of glenoid cavity
Triceps brachii origin
Glenoid margin and shoulder capsule/humerus
Rectus femoris origin
ilium and acetabulum
Biceps femoris origin
ischial tuberosity and linea aspera
Gastrocnemius origin
Femur
gastrocnemius insertion
calcaneus
Biceps femoris insertion
head of fibula
Rectus femoris insertion
tibial tuberosity and patella
Triceps brachii insertion
olecranon process of ulna
Biceps brachii insertion
radial tuberosity
Trapezius insertion
Scapular spine and lateral part of clavicle
Deltoid insertion
deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Rectus abdominis insertion
xiphoid process
latissimus dorsi insertion
intertubercular sulcus of humerus
pectoralis major insertion
intertubercular sulcus of humerus
Sternocleidomastoid insertion
mastoid process
Buccinator insertion
Orbicularis oris/ cheeks, and lips
Masseter insertion
mandibular ramus and angle
Triceps brachii action
Extends forearm
Rectus femoris action
Extends knee
Biceps femoris action
Flexes knee
Biceps brachii action
Aids in forearm flexion and supinates forearm
Rectus abdominis action
compresses and flexes abdomen
Buccinator action
compresses cheeks (blowing)
Trapezius action
Elevates, depresses, and rotates scapula