DENT 1111 Test 1 Review Ch. 6-12
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Tissues
-millions of the same type of cell join together to perform a specific function for the body
Types of tissues
1. Epithelial
2. Muscle
3. Nerve
4. Connective
Function of muscle tissue
-ability to lengthen and shorten thus moving body parts
-voluntary
-involuntary
Function of nerve tissue
-coordinates and controls many body activities
-stimulates muscle contraction
-plays role in emotions, memory and reasoning
-caries messages from all of body to brain
-found in spinal cord, brain and nerves
Function of connective tissue
-major support materials of the body
-provides support for the body, connects its organs + tissues
-stores fat
-destroys bacteria
-produce blood cells
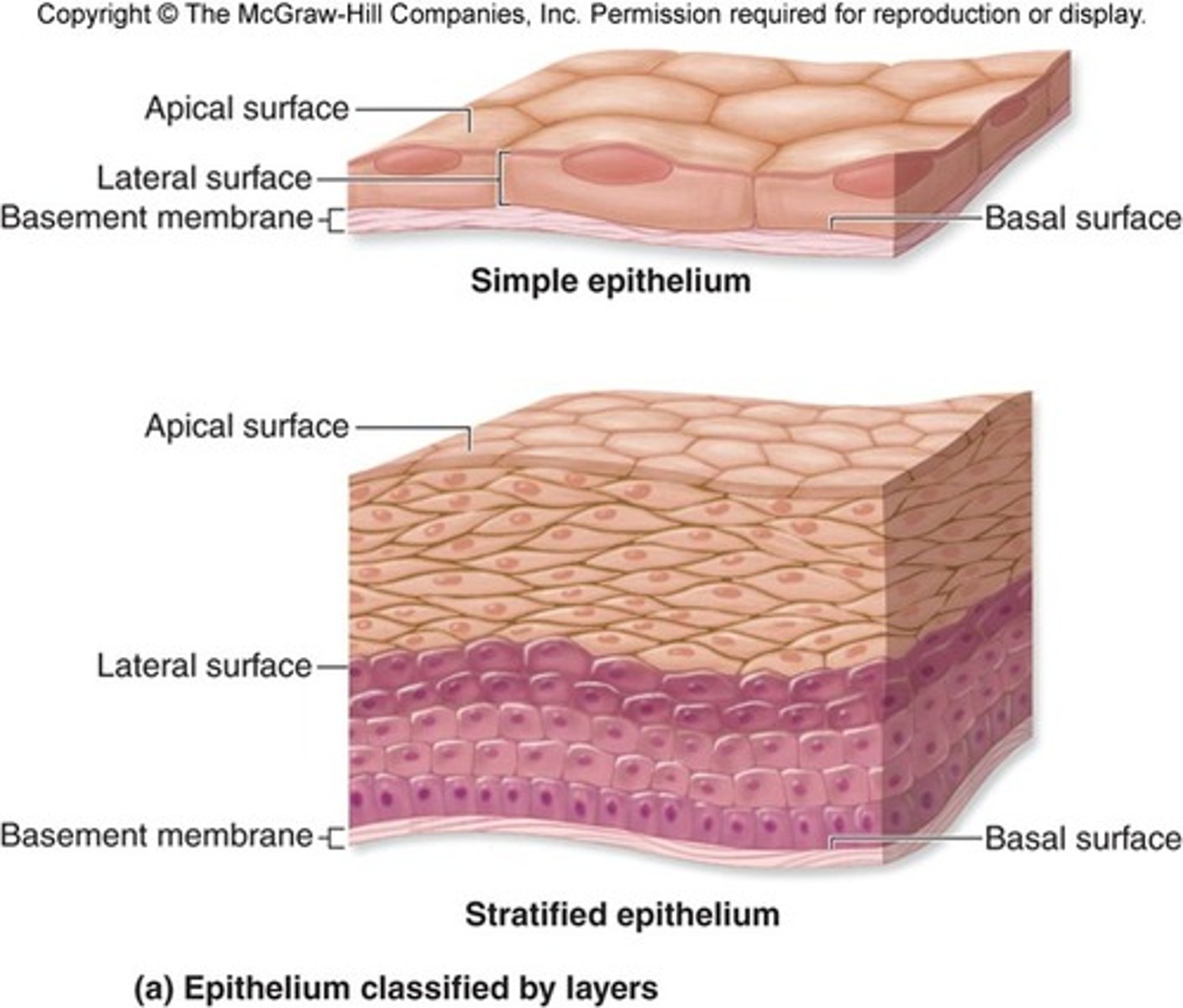
Epithelium
-type of tissue that forms the covering of all body surfaces
Function of epithelial tissue
1. provide protection
2. produce secretions
3. regulate the passage of materials across them
Specialized epithelial cells
-some epithelial cells are specialized meaning they have special functions associated with skin color, hair, nails, mucus production and sweat regulation
Epithelial tissue covering and lining function
-skin protects the body fro exposure to disease causing organisms
-lines internal organs and body cavities
ex. nose, mouth, lungs and stomach
What are the 11 body systems
1. Skeletal system
2. Muscular system
3. Cardiovascular system
4. Lymphatic and immune system
5. Nervous system
6. Respiratory system
7. Digestive system
8. Urinary system
9. Integumentary system
10. Endocrine system
11. Reproductive system
Function of body systems
Skeletal system
Subdivides into:
-Axial skeleton
-Appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton
-accounts for 80 bones in the human body
-consists of the skull, spinal column, ribs and sternum
Function:
-protect major organs of the nervous, respiratory and circulatory systems
Appendicular skeleton
-126 bones
-consists of upper extremities and lower + pelvic area
Function:
-protects organs of digestion and reproduction
Skeletal system- function
-protection
-support
-shape
-hematopoietic: storage of certain minerals
206 bones
Disorders of the skeletal system
-Arthritis-fracture-gout-osteomyelitis-osteoporosis-sprain
Arthritis
-inflammation of a joint
-swelling and pain
-mobility impairment
-difficulty performing daily tasks
Gout
-inflammatory joint reaction
-caused by accumulation of uric acid crystals
-usually affects big toe-swelling + redness
-intense pain
-sensitive to touch
Sprain
-injury to a joint when stretched beyond its normal range of movement
-pain
-swelling
-brusing
-abnormal movement
-joint weakness
Periosteum
"surrounding the bone"
-dense membrane made up of thin layer or whitish connective tissue containing nerves and blood vessels
-covers all surfaces of bone
-contributes to bone production and remodelling
-necessary for bone growth, repair, nutritive and carrying away waste
What is in the inner layer of the periosteum?
-loose connective tissue containing osteoblasts
What is the periosteum anchored to bone by?
Sharpey's fibers
What kinds of bone are below the periosteum?
1. Compact bone
2. Cancellous bone
Compact bone
aka cortical bone
-hard, dense bone
-forms the outer layer of bone (needed for strength)
Cancellous bone
aka trabecular or spongy bone
-found inside the bone
-light in weight, not as strong
-spongy, bony spicules that form a honeycomb pattern of spaces filled with BONE MARROW
Bone marrow
-gelatinous materials that produces white blood cells (fight infection) and red blood cells (carry oxygen) and platelets (help stop bleeding)
Cartilage
-strong flexible tissue
-covers the ends of your bones at the joint
-tough
-NONvascular CT
-gives shape and support to your nose, ears and trachea
-helps in movement (bones glide over each other)
Joints
-where 2 bones come together to allow movement
Fibrous joints
-do not move
Cartilaginous joints
-move slightly
-made of connective tissue cartilage
Synovial joints
-move in many directions
ex.
Ball and socket- movement in hips and shoulders
Hinge joints- knee and elbows
Gliding joints- wrist bones to slide
Saddle joint- touching thumb to the fingers
Pivot joint- rotating or twisting motion like head
Gomphoses- attaching tooth to a socket
*Muscular system- function
-holding body erect
-locomotion
-movement of body fluids
-production of body heat
-communication
Muscular system- components
Striated, smooth, and cardiac muscle
Disorders of the muscular system
-contusions -strain muscular dystrophy -sprain
Strain (NO TEAR)
-injury of a muscle that has been stretched beyond its capacity
-rupture of small blood vessels (swelling)
-area becomes tender
-painful muscle spasm
Sprain (TEAR)
-injury to a joint stretched beyond its normal range of motion, resulting in a tear
-pain
-swelling
-bruising
-abnormal motion
-joint weakness
Nervous system- function
-reception of stimuli
-transmission of messages
-coordinating mechanism
Includes:
-cns
-pns
-special sense organs
*Respiratory system- function
-transport of oxygen to cells
-excretion of carbon dioxide and some water wastes
Includes:
-nose
-paranasal sinuses
-pharynx
-epiglottis
-larynx
-trachea
-bronchi
-lungs
*Digestive system- function
-digestion of food
-absorption of nutrients
-elimination of solid wastes
Includes:
-mouth
-pharynx
-esophagus
-stomach
-intestines
-accessory organs
Structures of the digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas, large intestine, gallbladder
Digestive process
1. Ingestion
2. Digestion
3. Movement- peristalsis
4. Absorption
5. Elimination
Stomach
-saclike organ that lies in the abdominal cavity just under the diaphragm
-glands produce gastric juices that aid in digestion and the mucus that forms the protective coating of the stomach lining
Small intestine
-extends from the stomach to the first part of the large intestine
3 parts: duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Large intestine
-extends from the end of the small intestine to the anus
4 parts: cecum, colon, sigmoid colon and rectum and anus
Liver
-located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
-removes excess glucose from the blood stream stores it as glycogen
-when blood sugar is low the liver converts glycogen back into glucose and releases it for use of the body
-destroys old erythrocytes, removes poison from blood, manufactures blood proteins
-manufactures bile, a digestive juice
Gallbladder
-pear shapes sac located under the liver
-stores and concentrates bile for later
-bile is emptied into the duodenum of the small intestine
Pancreas
-produces pancreatic juices which contains digestive enzymes
-these juices are emptied into the duodenum of the small intestine
Esophagus
-tubelike structure approximately 10 inches in length
-transports food from the pharynx to the stomach
Disorders of the digestive system
-gastroesphageal reflux
-peptic ulcer
-ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease
-hemorrhoids
-peritonitis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
-backward flow of gastric juices into the esophagus
-heartburn
-difficulty swallowing
Peptic ulcer
-erosion of the gastric mucosa that exposes it to gastric juice and pepsin
-feeling of pressure, burning, heaviness or hunger, change in appetite and weight loss
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease
-chronic inflammatory process of bowel that results in poor absorption of nutrients
-abdominal pain
-cramping
-diarrhea with weight loss
-anemia
-fatigue
*Integumentary system- function
-protection of body
-regulation of body temperature
Includes:
-skin
-hair
-nails
-sweat and sebaceous glands
3 different layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous fat
Epidermis
-outer layer of skin
-nonvascular
-receive nutrients from vessels in underlying tissue
-new cells are pushed into the surface, older cells die ad are sloughed off
Dermis
-thick connective tissue
-gives bulk of the skin
-many free nerve endings and receptors which allow for detection of touch, temp and pain
-with age, CT becomes less elasticized and wrinkles form
Subcutaneous fat
-loose connective tissue
-anchors skin to underlying organs
-insulates body against heat loss
-cushions underlying organs
-distribution of fat is responsible for differences of in body contours between men and women
Disorders of the integumentary system
Abscess, acne, eczema, basal cell carcinoma
Abscess
-result of a wound that allows bacteria to invade the dermis
-red
-tender nodule that enlarges and becomes more painful as it grows
3 different types of muscles
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Skeletal muscle
-also referred to as striated muscles attach to the bones of the skeleton and make voluntary movement possible
ex. you decide when to move your leg
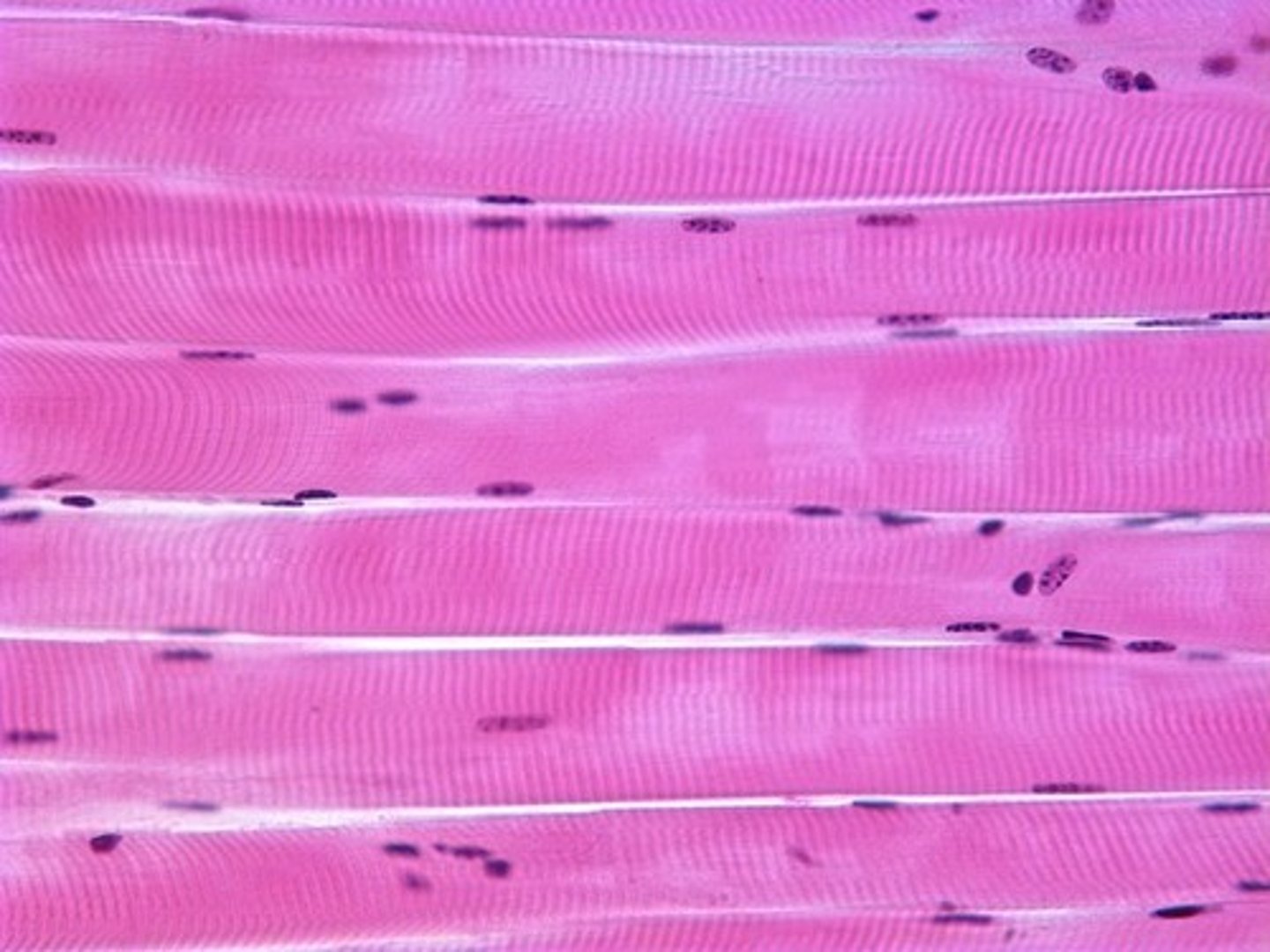
Where does the name striated come from?
-dark and light bands within the muscle fibers create a striped or striated appearance
Smooth muscle
-produce slow contractions
-visceral
-nonstriated
-involuntary bc under control of ANS
ex. (digestion)
-found in visceral (internal) organs as well as in hollow body cavities
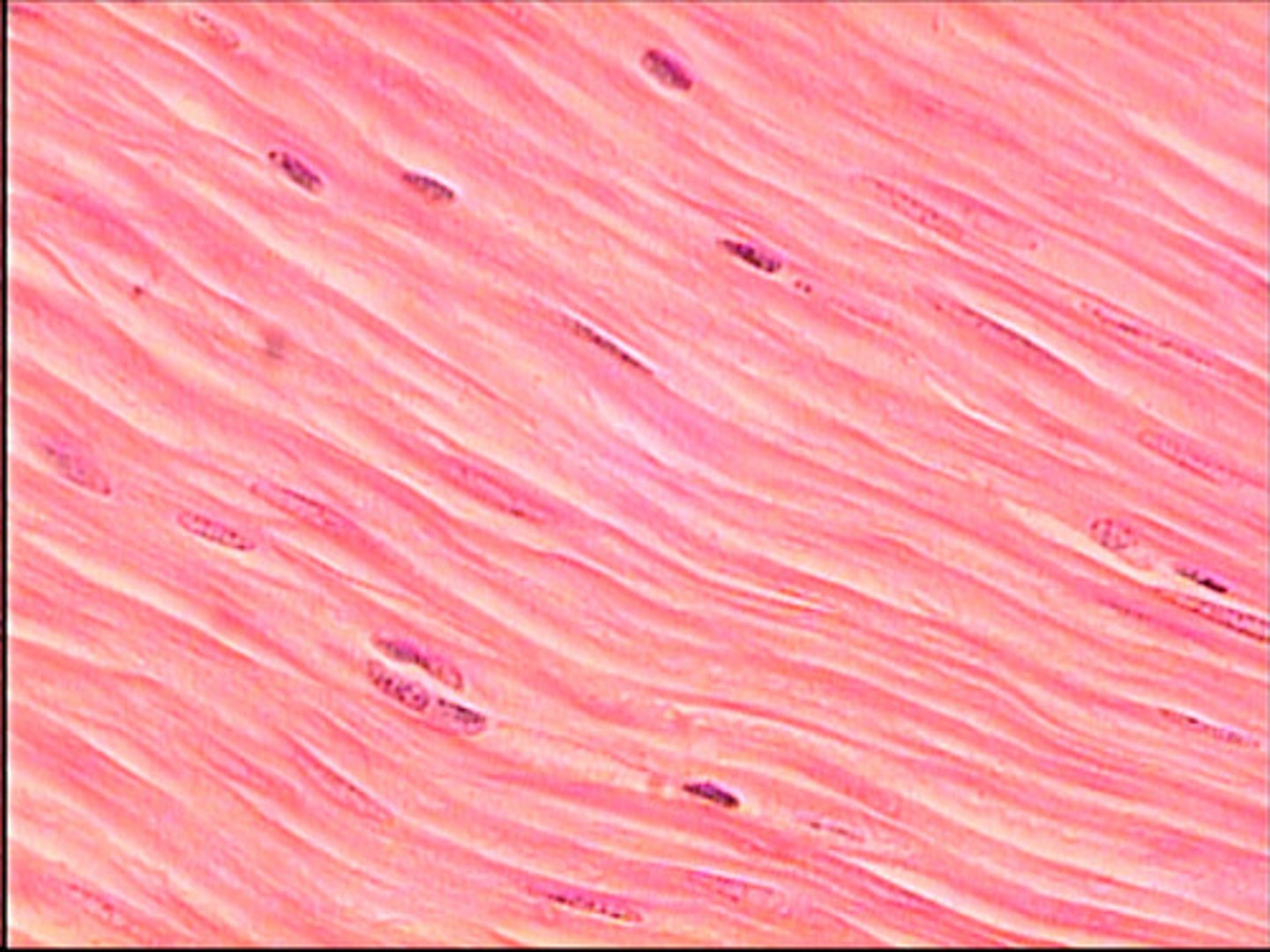
Cardiac muscle
-striated in appearance
-involuntary
-tissue makes up the walls of the heart
-contraction of this muscle results in the heartbeat
-muscles help pump blood out of the heart
Alveolar process (bone)
-thick ridge of bone
-contains the tooth sockets that hold the teeth
-develops in response to the growth of developing teeth
-bone resembles a sponge in appearance with irregular spaces
What happens to the alveolar process after teeth have been lost?
-bone resorbs and the ridge decreases in size and changes in shape
Osteoblasts
-responsible for the formation of bone
Osetoclasts
-responsible for the resorption and remodelling of bone
Cortical bone- alveolar process
-dense outer covering of the spongy bone that makes up the central part of the alveolar bone
-provides strength and protection
-place where skeletal muscle attach
-cortical plate on mandible is denser than the maxilla and has fewer openings for vessels and nerves
Alveolar crest- alveolar process
-highest point of the alveolar ridge
-alveolar bone fuses with cortical plates on the facial and lingual sides of the crest of the alveolar process
-distance between CEJ and alveolar crest is fairly constant
Alveolar socket- alveolar process
-cavity within the alveolar bone that surrounds the root of the tooth
-tooth doesn't contact bone at this point, it is suspended in place within the socket by the PDL
Interdental septum
-bony projection that separates each socket
Interradicular septum
-bone that separates the roots of a multirooted tooth
Lamina dura- alveolar process
aka cribriform plate
-thin compact bone that lines the alveolar socket
-pierced by many small openings, which allows blood vessels and nerves to communicate with the PDL
-thin white line on a dental radiograph
What is the oral mucosa composed of?
stratified squamous epithelium overlying a connective tissue proper (lamina propria)
Types of oral mucosa present in the mouth
-lining
-masticatory
-specialized
Lining mucosa
-non keratinized
-soft texture
-moist surface
-ability to stretch and compress
-act as a cushion for underlying structures
-covers inside of the cheeks, vestibule, lips, soft palate and ventral surface of the tongue
-not attached to bone so it moves freely
Masticatory mucosa
-keratinized
-rubbery surface, texture and resilience
-light pink
-firmly affixed to bone and does not move
Specialized mucosa
-on dorsal of the tongue
-present in from of lingual papilla
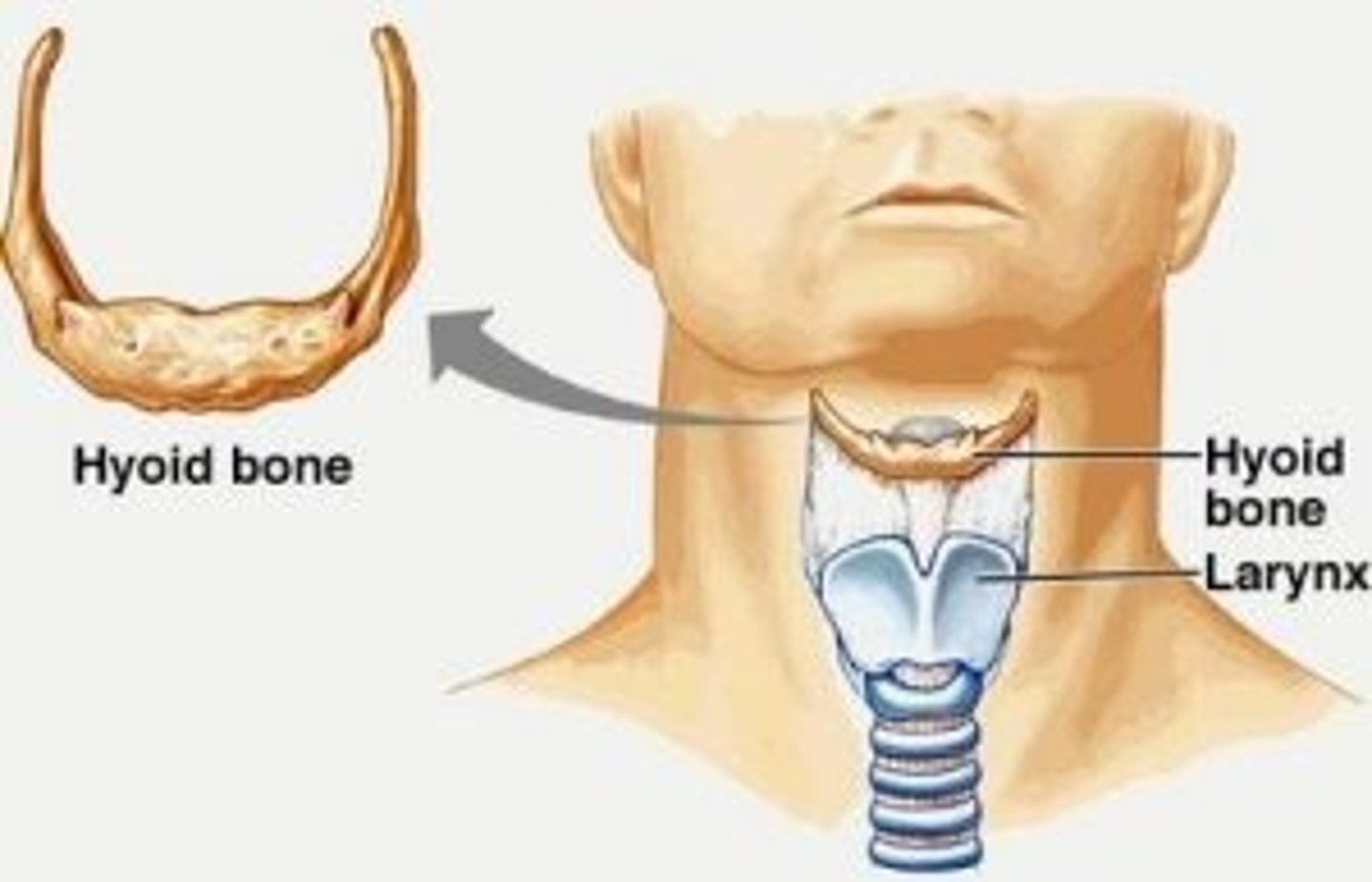
Hyoid bone
-shaped like a horseshoe, central body with 2 lateral projections
-does not articulate with any other bone
-suspended between mandible and larynx
-primary support for tongue and other muscles
Movement of the lower jaw
-TMJ performs 2 basic movements
1. Hinge (open + closes jaw)
2. Gliding (allows jaw to shift side to side)
Hinge movement
-first phase
-only lower compartment of joint used
-condylar head rotates around a point on the undersurface of the articular disc
-body of the mandible drops downward and backward
How does the jaw open?
Combined actions of the:
-external pterygoid
-digastric
-mylohyoid
-geniohyoid
How does the jaw close?
Combined actions of the:
-temporal
-masseter
-internal pterygoid
Gliding movement
-allows lower jaw to move forward or backward
-involves both lower and upper compartments of the joint
-condyle and articular disc glide forward and downward along the articular eminence
When does the gliding movement happen?
-protrusion
-lateral movements of the mandible in combination with hinge action when mouth is opened wide
Protrusion
-forward movement of mandible
-internal and external pterygoid muscles on both sides contract together
Origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
Insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone or the end opposite the origin
Muscles of head and neck
1) muscles of the neck
2) muscles of facial expression
3) muscles of mastication
4) muscles of the floor of the mouth
5) muscles of the tongue
6) muscles of the soft palate
7) muscles of the pharynx
1) Muscles of neck
sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
Muscles of facial expression
-orbicularis oris
-buccinator
-mentalis
-zygomatic major
*Muscles of mastication
"Don't choke, take your TIME chewing"
T- Temporalis
I- Internal pterygoid
M- Masseter
E- External pterygoid
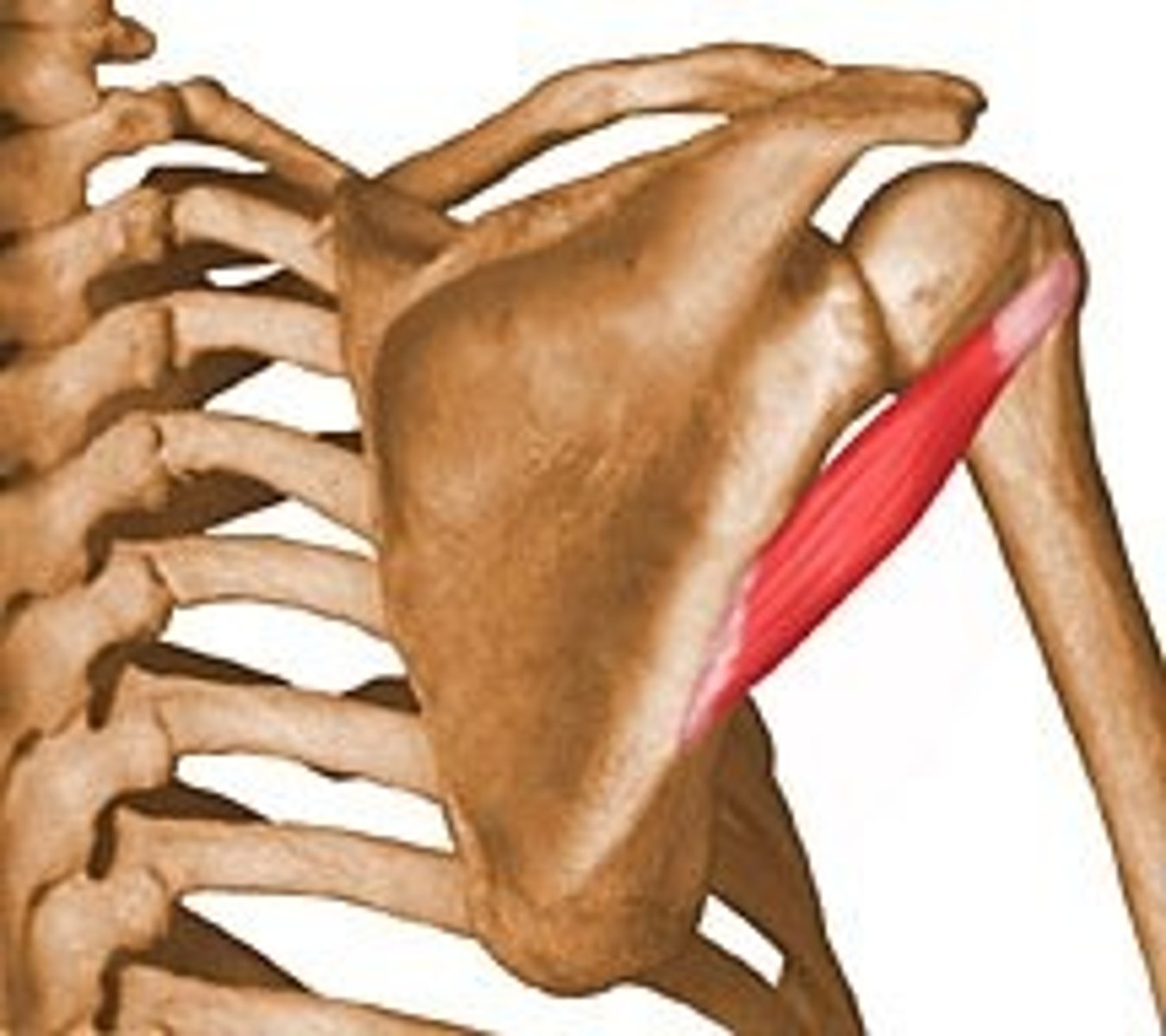
Temporalis muscle
Origin:
-temporal fossa
Insertion:
-coronoid process and anterior border of mandibular ramus
Temporalis muscle function
-raises mandible and closes jaw
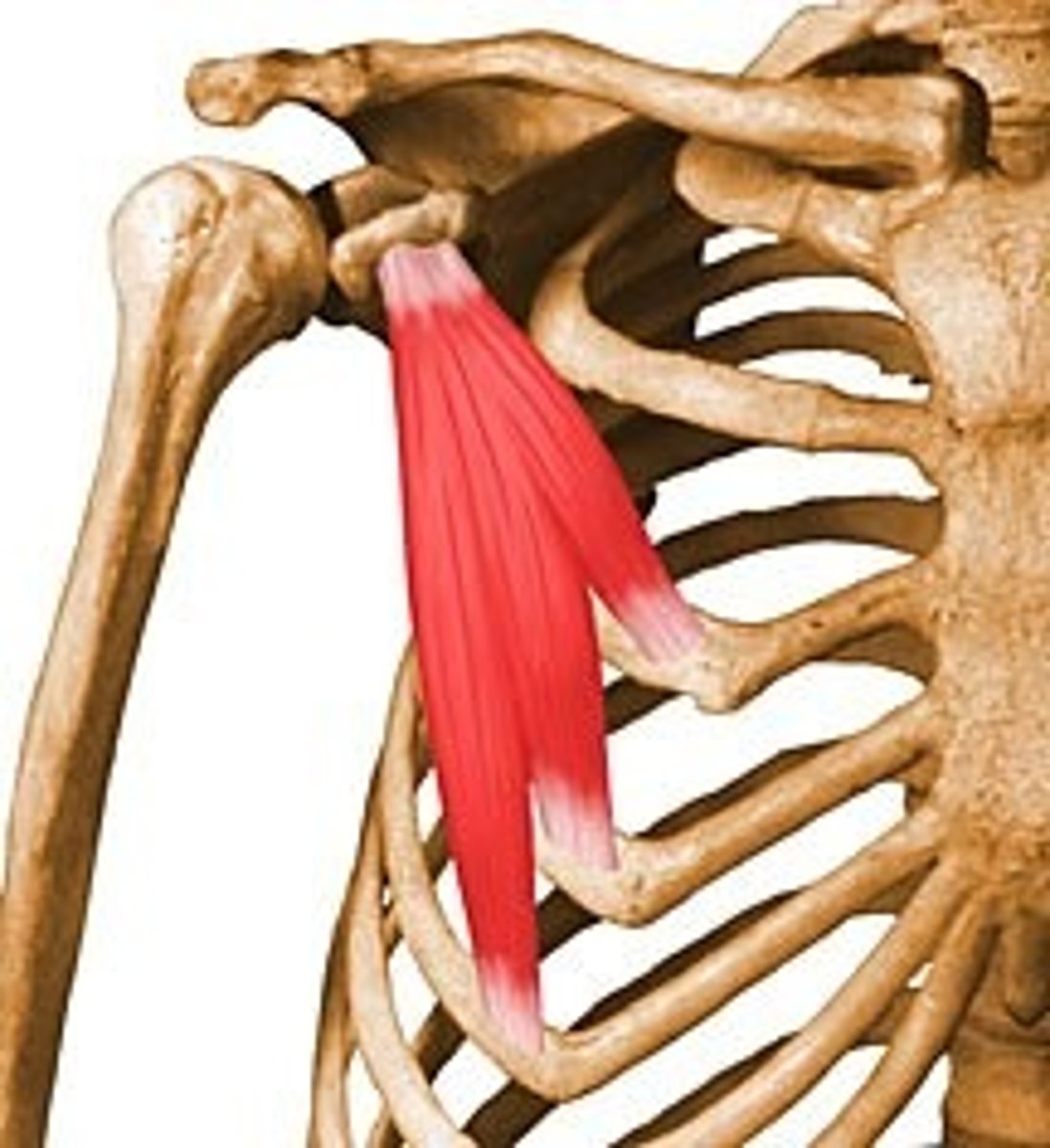
Internal pterygoid muscle
Origin:
-medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone, palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity
Insertion:
-into inner (medial) surface of ramus and angle of mandible
Internal pterygoid function
-closes jaw
-acts with lateral pterygoid on the same side, pulls mandible to one side; medial and lateral pterygoids on both sides act together to bring lower jaw forward
Masseter muscle (superficial)
Origin:
-lower border of zygomatic arch
Insertion:
-angle and lower lateral side of mandibular ramus
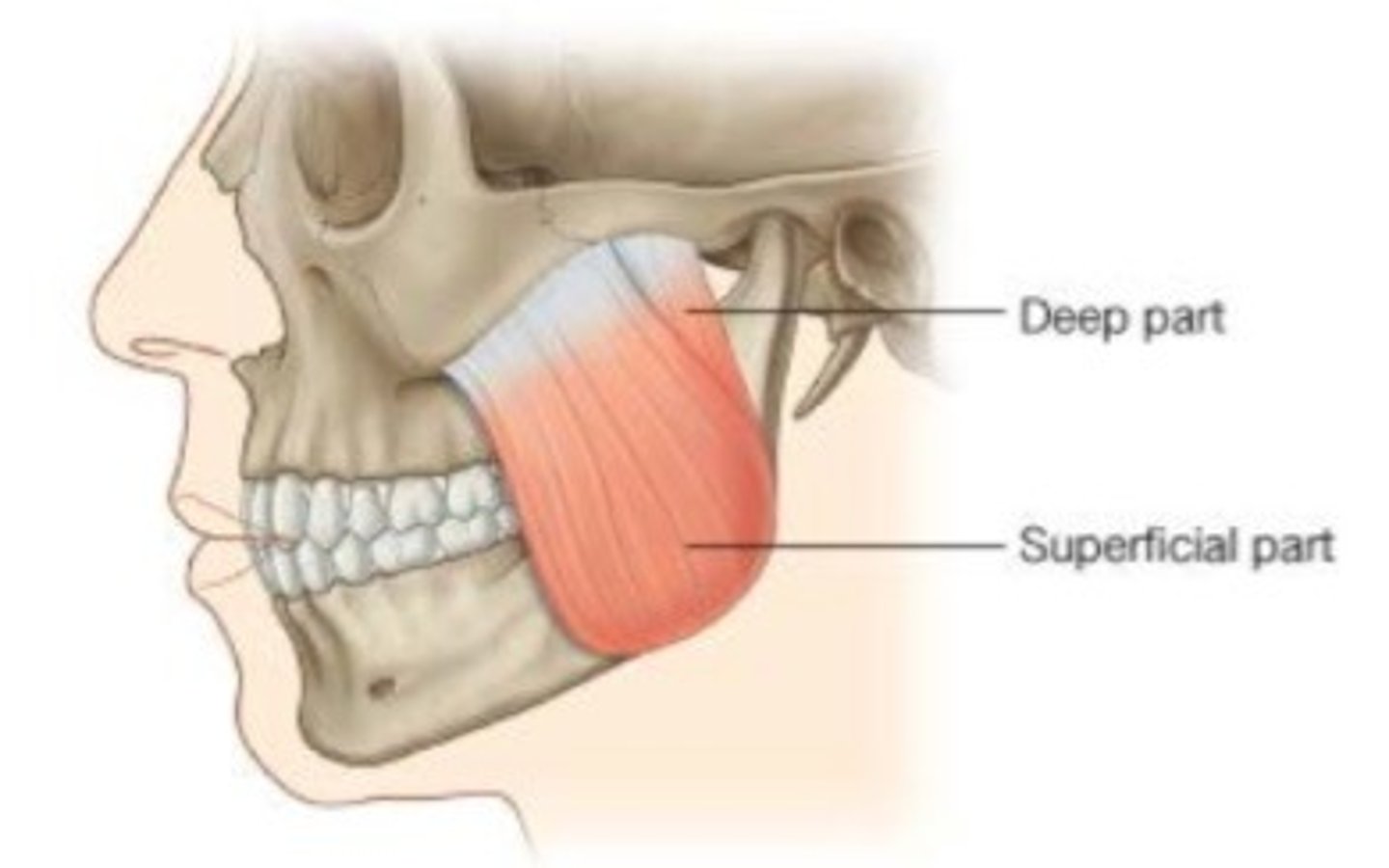
Masseter muscle (deep)
Origin:
-posterior and medial side of zygomatic arch
Insertion:
-upper lateral ramus and mandibular coronoid process
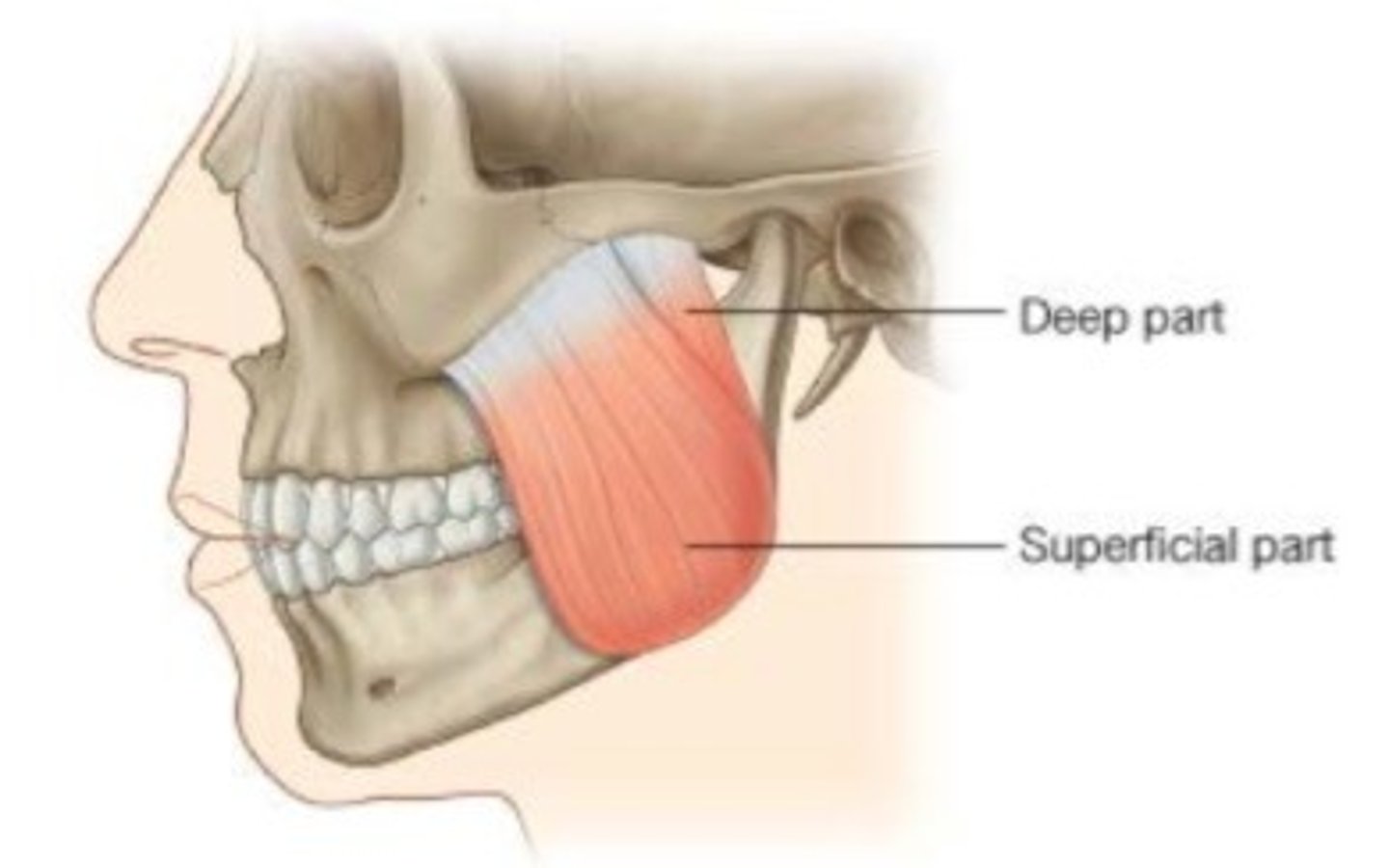
Masseter muscle function
-raises mandible and closes jaw