4.1.1. Part 1 Organic Hydrocarbon Nomenclature: Structural Formulas, Isomers
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the empirical formula of a compound?
The lowest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound.
What does the molecular formula represent?
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound.
What does a full structural formula show?
It shows every bond and atom in the molecule.
What is a Lewis dot diagram?
A representation that shows every atom and all electrons and/or bonds.
What is a condensed structural formula?
A formula that groups atoms and omits most bonds, e.g., CH3CH3.
What is a skeletal formula?
A formula that leaves out hydrogen atoms and shows only the carbon skeleton.
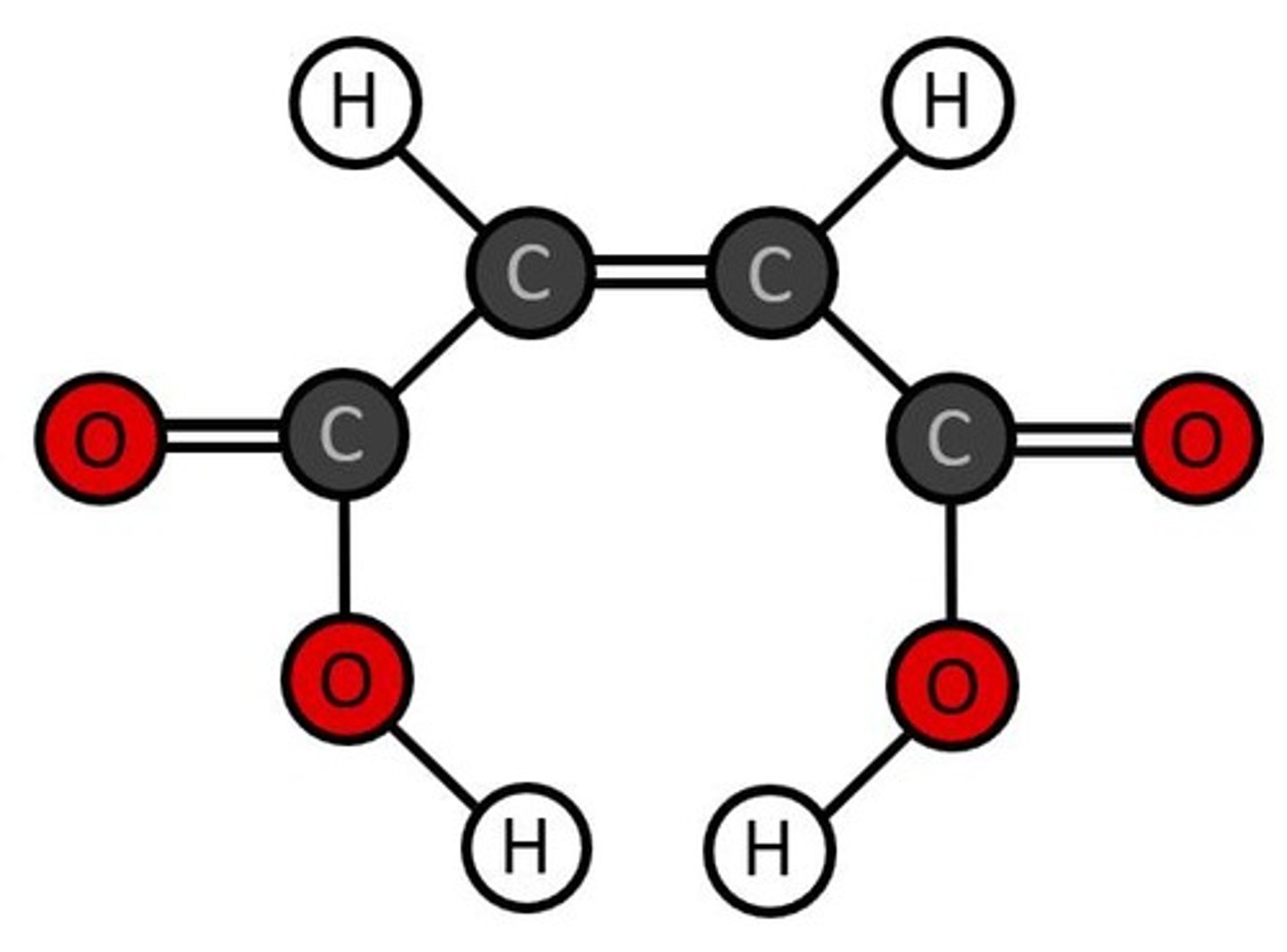
What is the molecular formula for butane?
C4H10.
What is the molecular formula for heptane?
C7H16.
What is the significance of lone pairs in Lewis structures?
Electrons that aren't in a bond are called lone pairs.
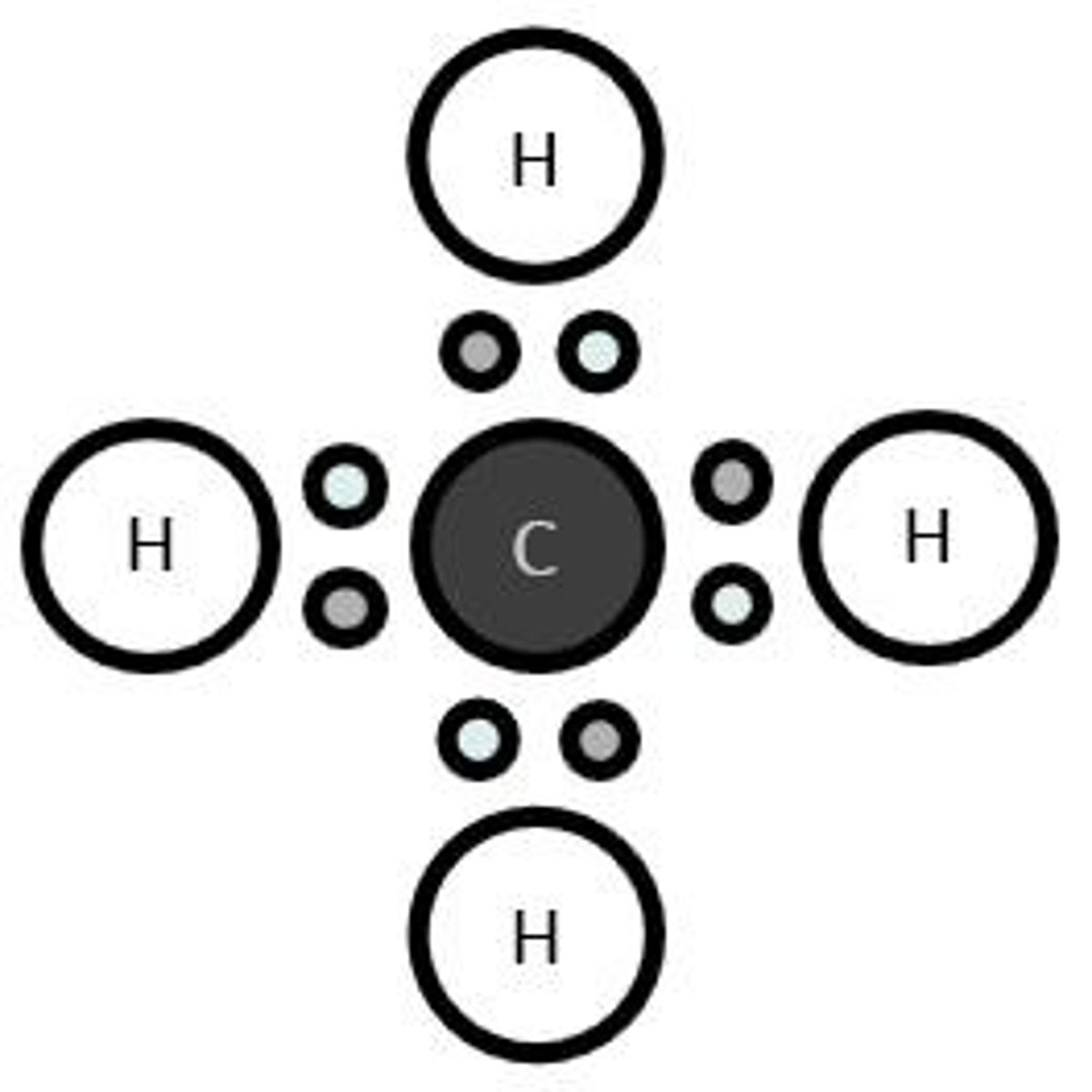
What is the simplest hydrocarbon?
Methane (CH4).
What are the three basic parts of the name of a hydrocarbon?
Prefix, stem, and suffix.
What does the prefix in a hydrocarbon name indicate?
The position, number, and name of substituents.
What does the stem in a hydrocarbon name indicate?
The number of carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain.
What does the suffix in a hydrocarbon name indicate?
The type of bonds that join the atoms together (single, double, or triple).
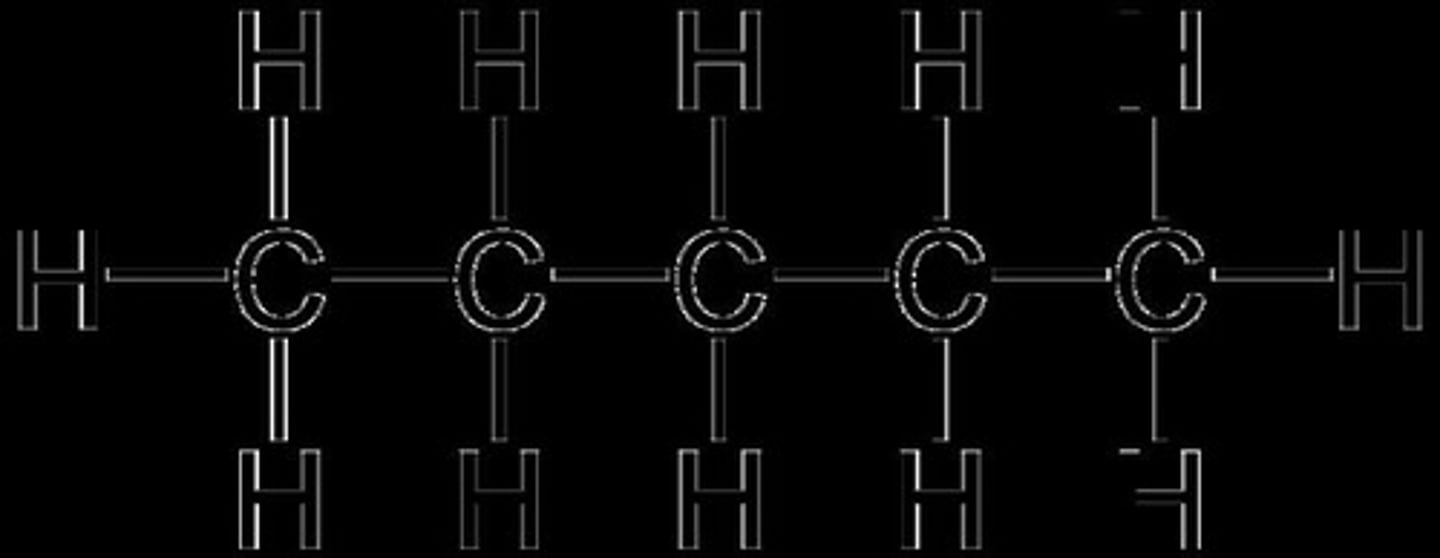
What is the general formula for alkanes?
CnH2n+2.
What is the general formula for alkenes?
CnH2n.
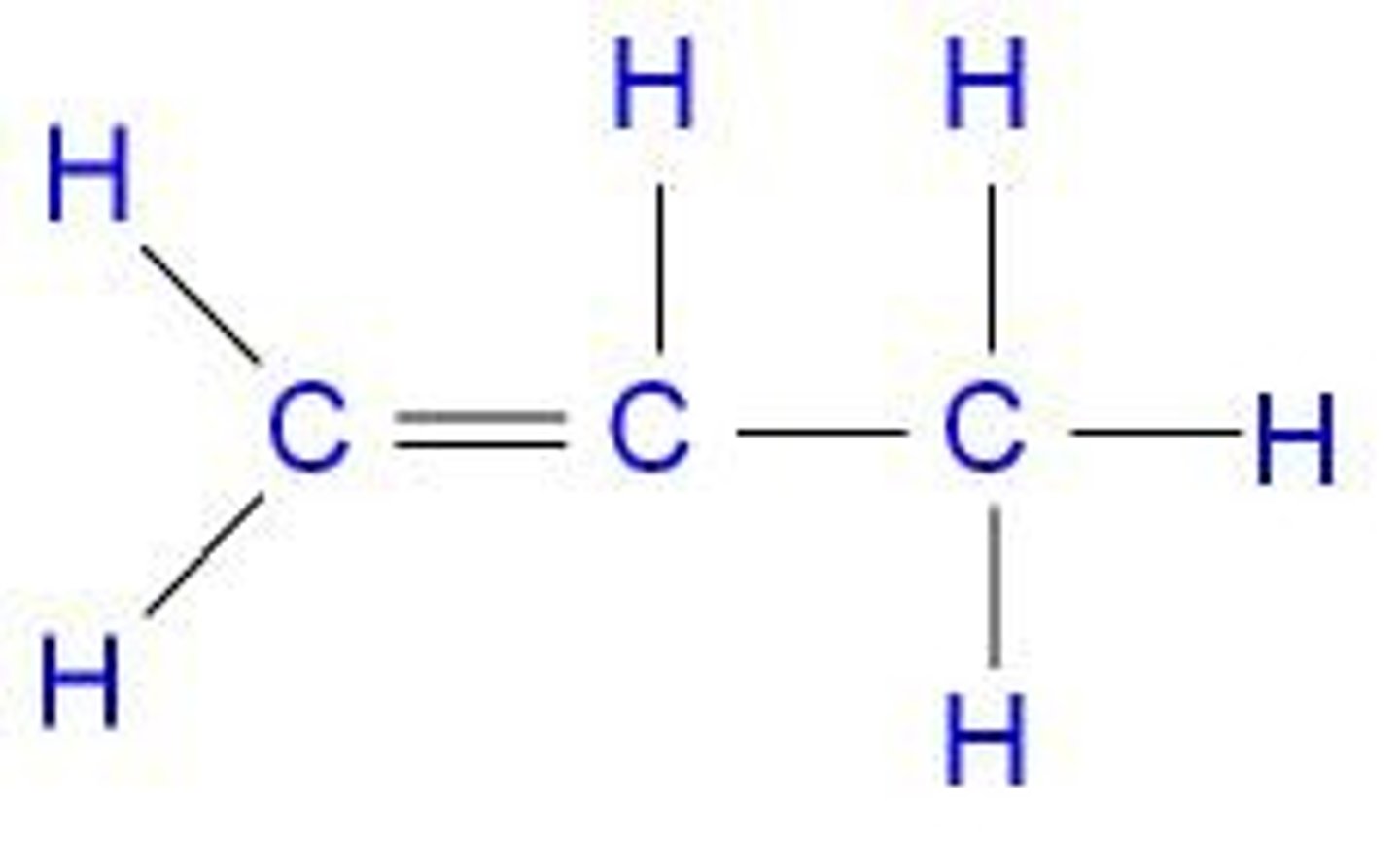
What is the general formula for alkynes?
CnH2n−2.
What is a structural isomer?
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
How many structural isomers does pentane have?
Three: pentane, 2-methylbutane, and 2,2-dimethylpropane.
How many structural isomers does hexane have?
Five: hexane, 2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, 2,2-dimethylbutane, and 2,3-dimethylbutane.
What is the priority in naming hydrocarbons with multiple bonds?
The multiple bond gets the lowest number.
What is the naming convention for multiple substituents?
Use di-, tri-, tetra-, etc., and separate numbers with commas.
What is the correct way to write the name of a compound with multiple substituents?
Alphabetize the substituents, ignoring di-, tri-, tetra-, etc.
What is the formula for determining the number of hydrogens in alkenes?
CnH2n.
What is the formula for determining the number of hydrogens in alkynes?
CnH2n−2.
What is the significance of the longest carbon chain in naming hydrocarbons?
The name of the compound is derived from the longest chain.
What do side chains in hydrocarbons refer to?
Substituents that branch off the main carbon chain.
What is the importance of numbering in hydrocarbon naming?
To give the substituents the lowest possible numbers.