Ap human unit one vocabulary review
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
absolute location
Exact location of a place on the earth described by global coordinates
Accesibility
the relative ease with which a destination may be reached from some other place
Activity Space
the space within which daily activity occurs
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Cartography
science or art of making maps
Connectivity
The degree of economic, social, cultural, or political connection between two places
Contagious Diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
context
The circumstances, atmosphere, attitudes, and events surrounding a text.
Cultural Ecology
the geographic study of human-environment relationships and how human cultures adapt to and interact with their environments
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity on the landscape
cultural trait
The specific customs that are part of the everyday life of a particular culture, such as language, religion, ethnicity, social institutions, and aspects of popular culture.
Distance Decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction
enviromental determinism
A doctrine that claims that cultural traits are formed and controlled by environmental conditions.
epidemic
regional outbreak of a disease.
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process.
Fieldwork
the study of geographic phenomena by visiting places and observing how people interact with and thereby change those places.
formal region
An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics.
friction of distance
the increase in time and cost that usually comes with increasing distance.
region
Area of Earth identified as sharing a formal, functional, or perceptual commonality that makes it different from regions around it.
Reference Map
provides a general overview of a location, displaying geographical information like boundaries, features (mountains, rivers), and political data (cities, roads).
Cartogram
A special kind of map that distorts the shapes and sizes of countries or other political regions to present economic or other kinds of data for comparison.
Cartographic Scale
refers to the way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents.
Chloropleth Map
a map that uses differences in shading, coloring, or the placing of symbols within predefined areas to indicate the average values of a property or quantity in those areas.
clustered
Gathered closely together in a group.
Concentration
The spread of something over a given area.
data or variable scale
Equal interval, Equal frequency, Natural breaks, Percentage or Ratio vs Total Numbers
Density
the degree of compactness of a substance.
dispersed
distributed or spread over a considerable extent.
Distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
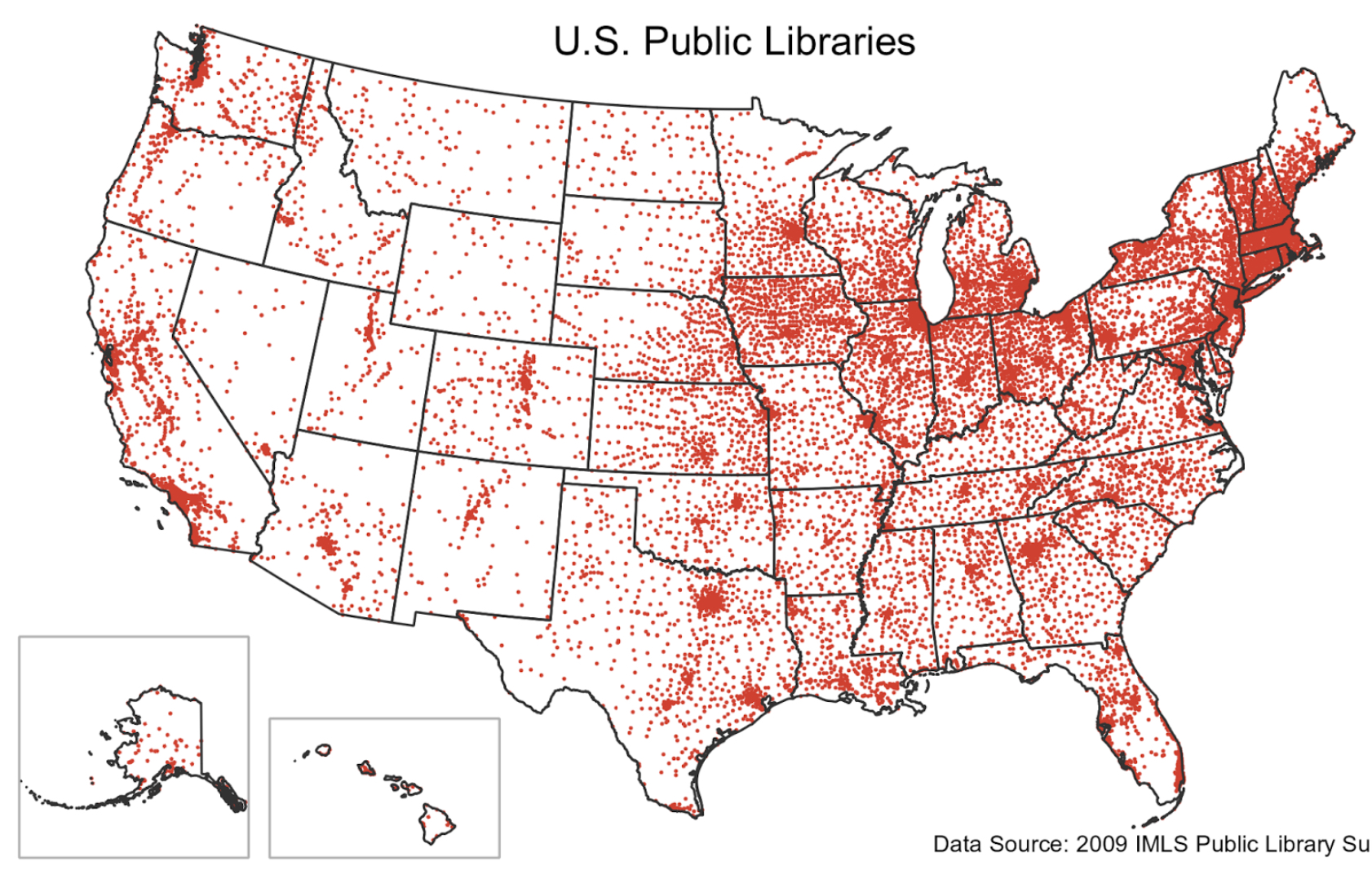
Dot Distribution Map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena.
Example of formal region
Corn Belt.
Functional Region
An area organized around a node or focal point.
Geographic Infromation System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Geographic Scale
The scale at which a geographer analyzes a particular phenomenon, for example: global, national, census tract, neighborhood, etc. Generally, the finer the scale of analysis, the richer the level of detail in the findings.
Globalization
the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.
Global Grid System
1 degree =60 min
1 min=60 sec
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Satellite-based system for determining the absolute location of places or geographic features.
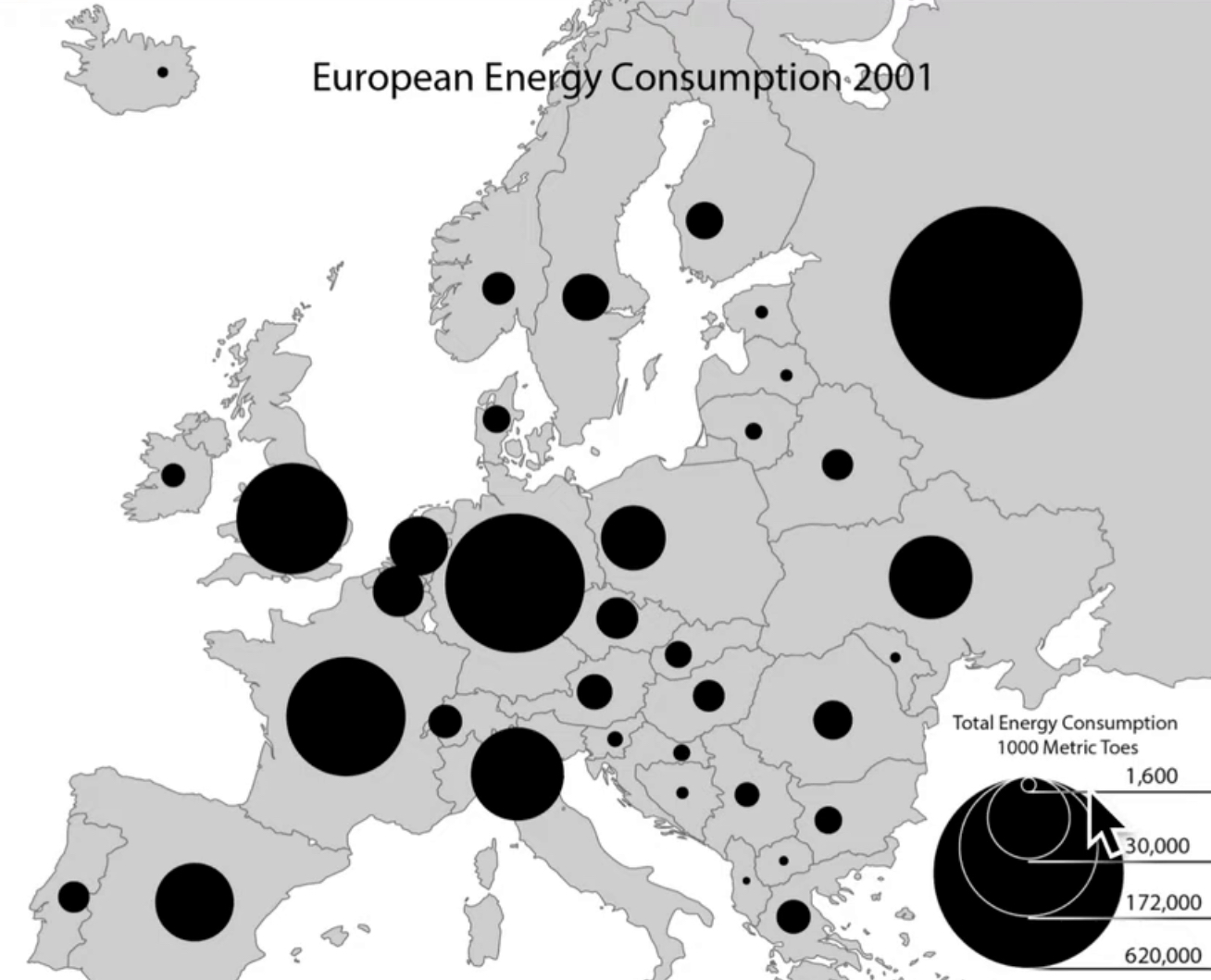
graduated symbol map
uses symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something.
grid pattern
Also called a rectilinear pattern, reflects a rectangular system of land survey adopted in much of the country under the Ordinance of 1785. Streets form grids and are sometimes labeled "1st", "2nd", "3rd" streets and so on.
Hearth
The region from which innovative ideas originate.
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places.
Human Environment Interaction
the study of the interrelationship between people and their physical environment.
Human Geography
One of the two major divisions of Geography the spatial analysis of human population, its cultures, activities, and landscapes.It examines how human activities shape and are shaped by the environment.
independent invention
a trait that many cultural hearths that develop independent of each other
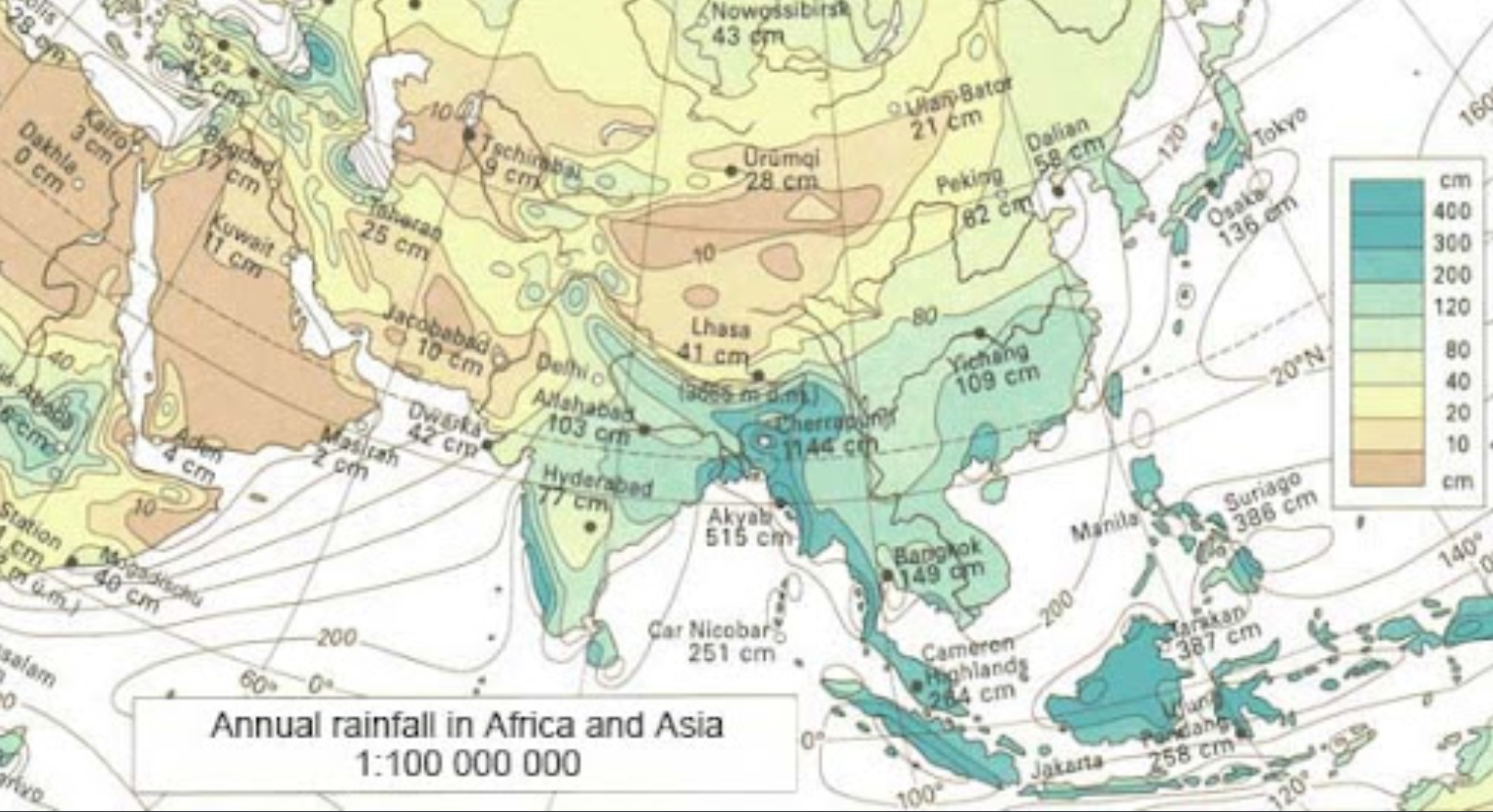
Isoline Map
Map displaying lines that connect points of equal value, for example, a map showing elevation levels.
Landscape Analysis
the task of defining and describing landscapes.
land use
the ways in which people use a particular area of Earth's surface; for example, for farming, development, or preservation.
large-scale
A relatively small ratio between map units and ground units. Large-scale maps usually have higher resolution and cover much smaller regions than small-scale maps.
Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees.
Location
the position that something occupies on Earth's surface.
Longitude
Distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees.
Mash Up Maps
practice of overlaying data from one source on top of one of the mapping services(ie google) to come up with a mix of both. ie. locate businesses near a particular street in a particular city.
Mental Maps
Maps in our minds of places we have been and places we have only heard of.
Movement
the mobility of people, goods, and ideas across the surface of the planet.
Networks
defined by Manuel Castells as a set of interconnected nodes without a center.
Node
Connection point in a network, where goods and ideas flow in, out, and through the network.
Pandemic
Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population.
pattern
The geometric or regular arrangement of something in a study area.
perception of place
Belief or "understanding" about a place developed through books, movies, stories or pictures.
perceptual region (vernacular region)
These are not as rigorously structured as formal and functional regions. It is where people believe they are part of some cultural identity.
Physical Geography
One of the two major divisions of systematic geography; the spatial analysis of the structure, processes, and location of Earth's natural phenomena such as climate, soil, plants, animals, and topography.
place
uniqueness of a location.
Possilbilism
A theory in geography that argues the environment may set certain constraints or limits, but human ingenuity can adapt and overcome those limitations.
relative location
where a place is located in relation to another place.
relocation diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another.
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
Rescale
To take an idea or movement and reframe it in the context of a different scale. (jumping scale).
scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole. Small number means large scale. Large number means small scale.
sense of place
State of mind derived through the infusion of a place with meaning and emotion by remembering important events that occurred in that place or by labeling a place with a certain character.
sequent occupance
the notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape.
site
The physical characteristics of a place.
Examples of site
climate, water sources, topography, soil, vegetation, latitude, and elevation.
situation
the location of a place relative to other places.
Examples of situation
situation of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia is roughly center of the Arabian Peninsula; situation of Arabian Peninsula is between the continents of Asia and Africa.
small scale map
Map showing a large area of land but not much detail.
Spatial Approach
the arrangement of the phenomena being studied across the surface of the earth.
Spatial Data
All of the information that can be tied to a specific locations.
spatial distribution
The arrangement of phenomenon across the Earth's surface.
spatial interaction
the movement of peoples, ideas, and commodities between different places.
Spatial Perspective
a way of looking at the human and physical patterns on Earth and their relationships to one another.
spatial scale
the different sized "containers" or ways to group places together to organize investigations into human activities.
Stimulus Diffusion
a form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place.
terra incognita
unknown or unexplored territory.
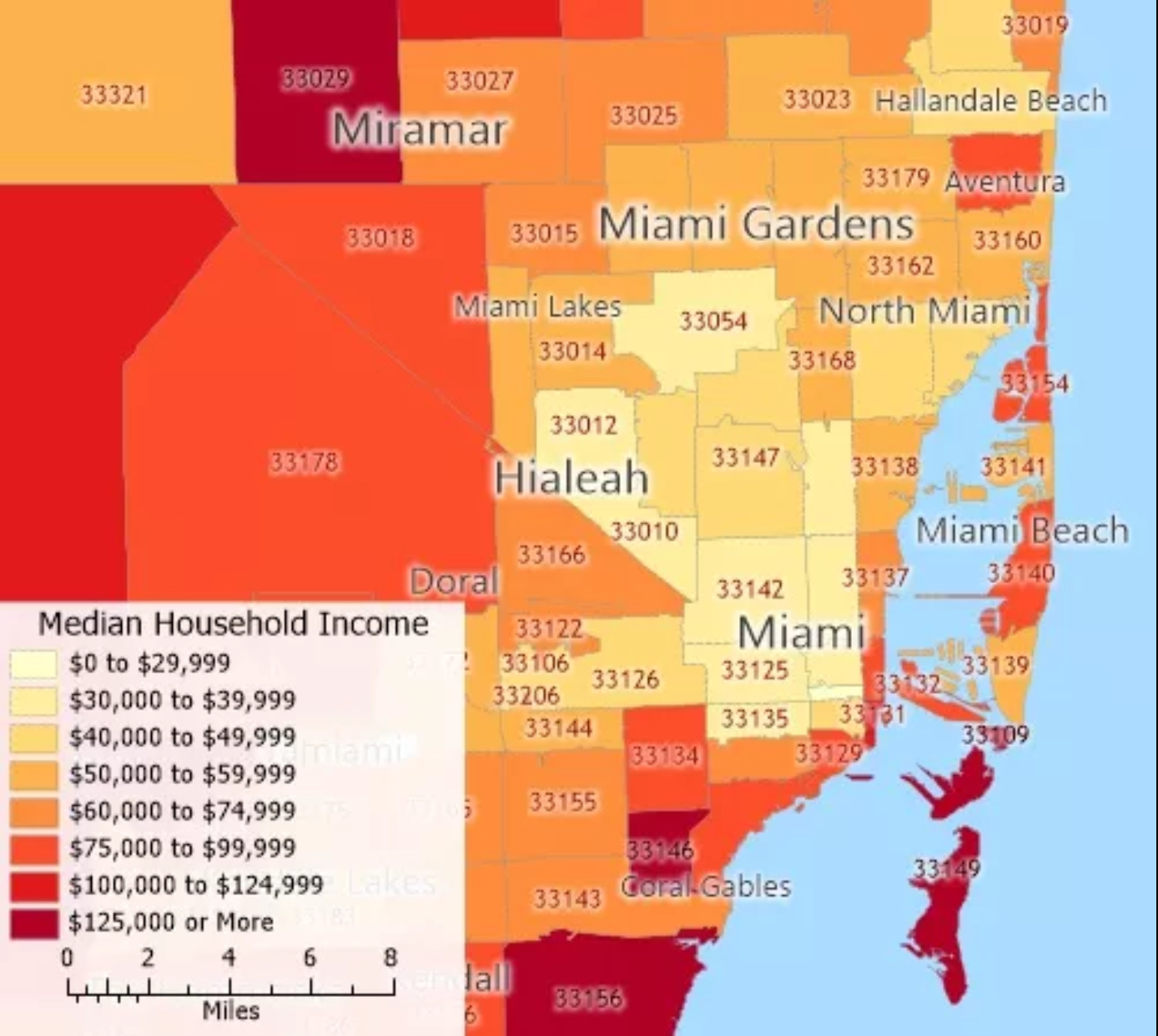
thematic map
a map that shows a particular theme, or topic
time-distance decay
the idea that the farther away from its hearth a culture trait gets, the less likely it is to be adopted or have an impact.
time-space compression
the rapid innovation of communication and transportation technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time.
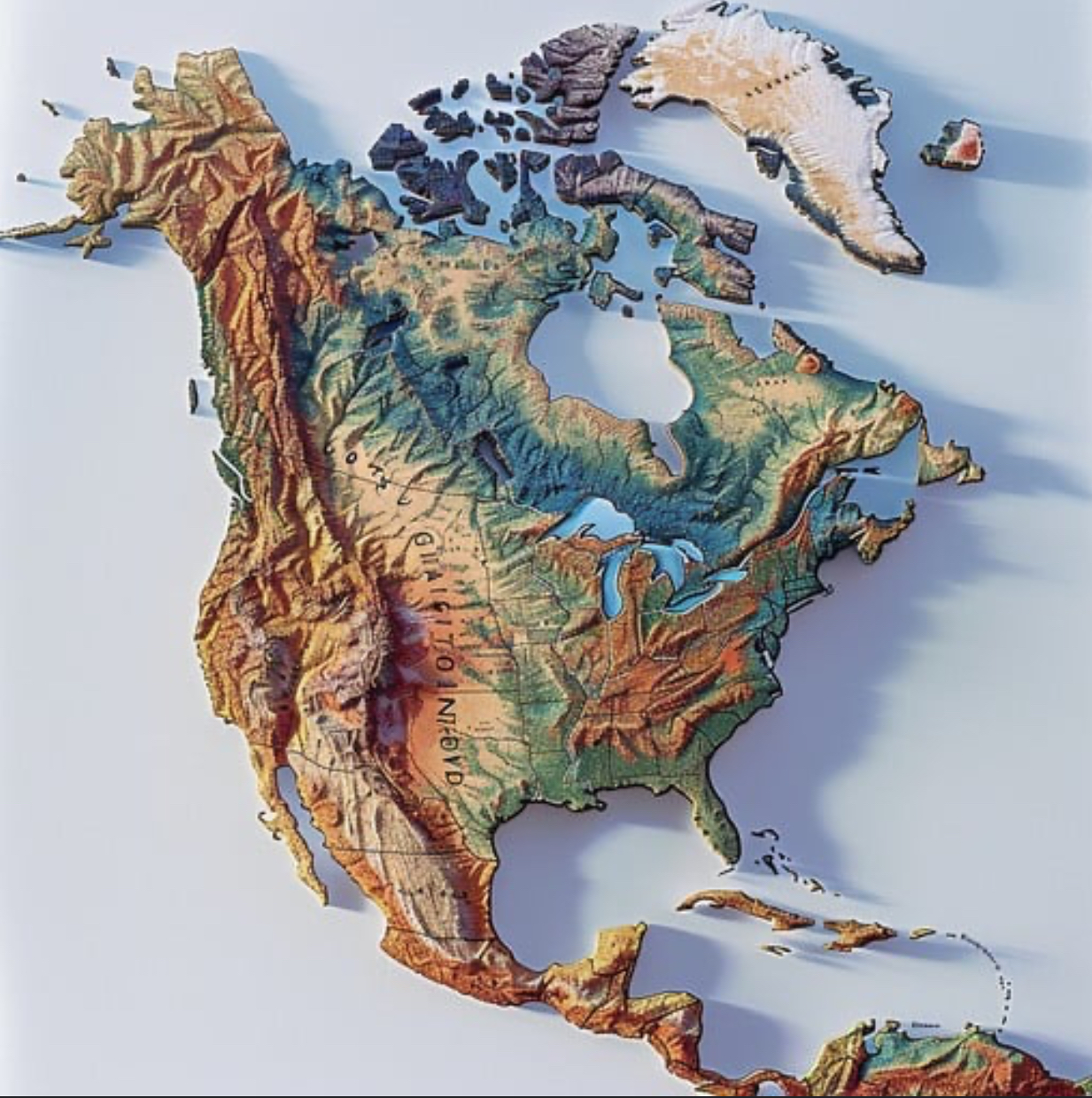
topographic map
a map that shows the surface features of Earth.
Toponym
place name.
Two main features of human behavior
culture and economy.
Two questions geographers ask
Where are things located? Why are they there?
spatial thinking
a way of thinking about space on Earth's surface, including where places are located and why they are there.
multinational corporation
a large business that operates in many countries.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
the time in the zone encompassing the prime meridian, or 0 degrees longitude.
International Date Line
the line of longitude that marks where each new day begins, centered on the 180th meridian.
Isotherm
Line drawn on a weather map that connects points having equal temperature.
location theory
A logical attempt to explain the locational pattern of an economic activity and the manner in which its producing areas are interrelated.
Political Ecology
the study of the relationships between political, economic and social factors with environmental issues and changes.