The Integument 2 (Hair, glands, hoofs, claws, feathers and scales)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the important functions of hair?
Mechanical protection
Thermoregulation
Sensory perception - specialized tactile hair
What two types of hair follicles are there?
simple and compound
What structures compose a simple hair?
cuticle, cortex, medulla
What portion of the hair projects above the surface of the skin epidermis?
the shaft
What part of the skin is hair embedded?
dermis and hypodermis
What does the root of the hair consist of?
Consist of hair and surrounding root sheaths
Internal root sheath and external root sheath, all surrounded by a connective tissue sheath
What does the bulb of the hair follicle consist of?
dermal papilla and hair matrix cells (stem cells)
Where do cells in the hair follicle become keratinized?
keratogenous zone
Describe how cells in the hair follicle become keratinized, what cells are responsible for this process?
Matrix cells are mitotically active, their activity is dependent on the dermal papilla
Migrating matrix cells pass through the keratogenous zone producing the hard form of keratin and differentiate to form hair and root sheath
What cells associated with the hair bulb provide pigmentation?
melanocytes (Associated with matrix cells)
Keratinization is ___ in hair follicles.
cyclic
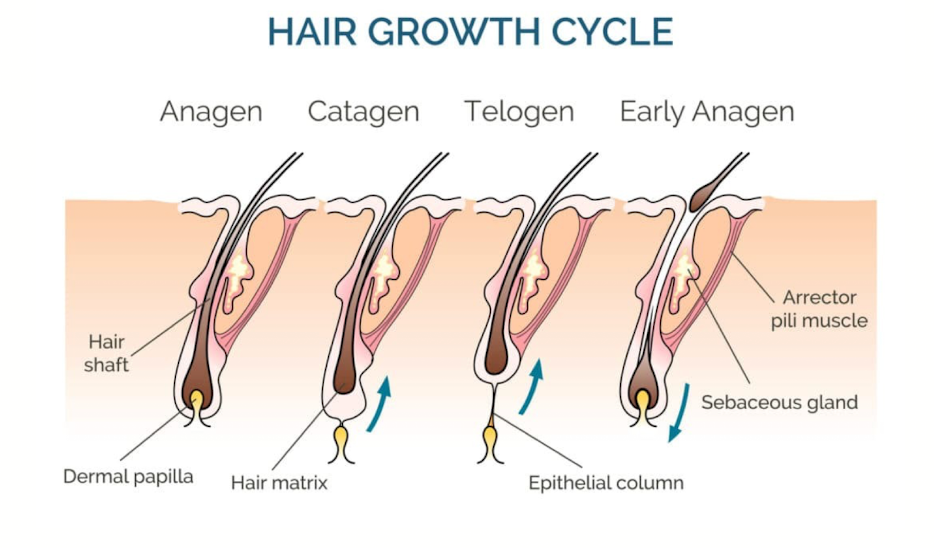
Summarize the hair growth cycle. (4 main steps)
Anagen (growth): Matrix cells divide, hair elongates.
→ DP closely linked, sends growth signals.Catagen (regression): Bulb activity stops, hair shifts upward.
→ DP detaches and withdraws signals.Telogen (resting): Cells quiescent, hair moves toward surface for shedding, anchored but no longer grows
→ DP inactive, little/no contact with matrix.Early Anagen (renewal): New follicle forms below old hair.
→ DP reconnects, reactivates growth.
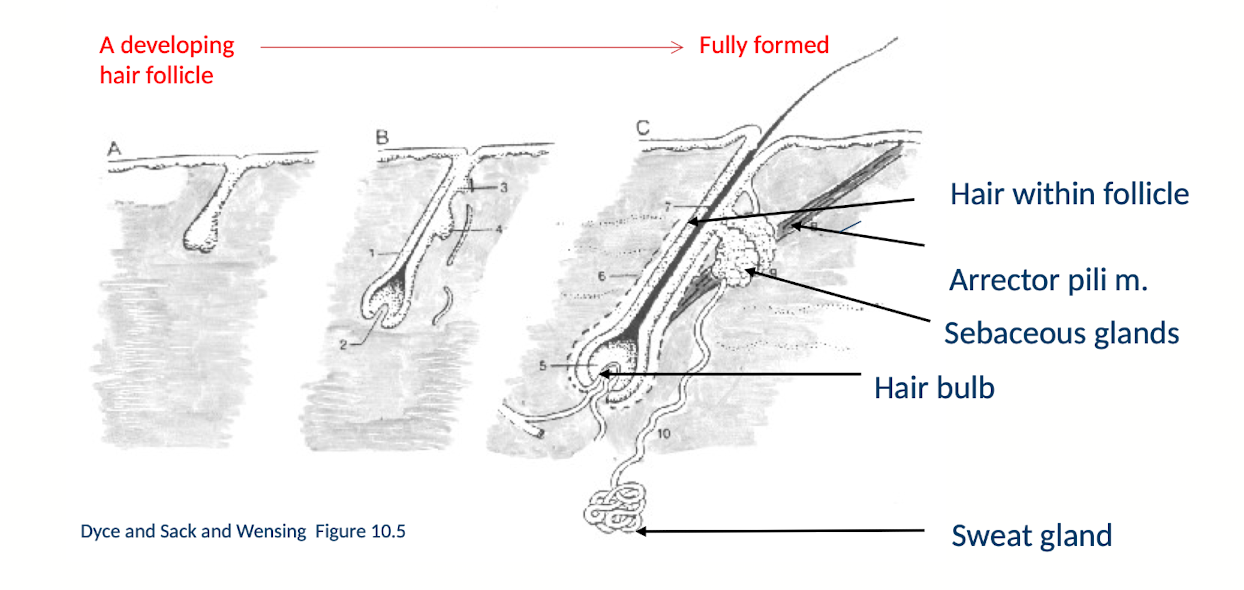
How does the embryological development of a simple hair follicle and associated skin gland begin?
Begins with a localised thickening of epidermis (ectodermal bud) which grows down into underlying mesenchyme
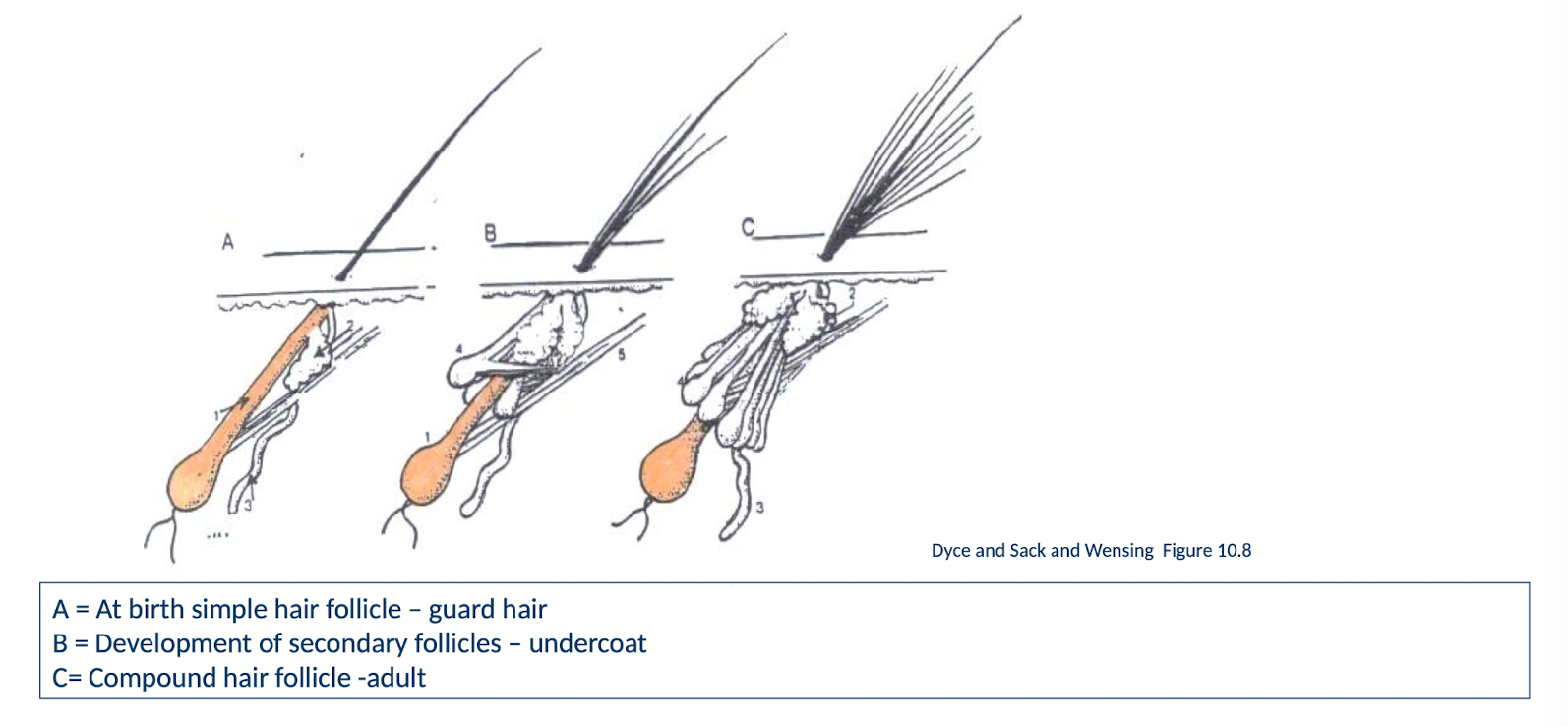
Describe how the development of compound hair follicles in carnivores occurs and their subsequent terminology by stage.
Compound hair follicles contain a primary, long hair with a deep root called a guard hair and several more shallowly rooted and short hairs known as the undercoat
At birth, there are only guard hairs
In about 6 months there are development of secondary follicles giving rise to the undercoat, to allow for compound hair follicles as adults
What are some features of sinus or tactile hairs (vibrissae)?
• Limited facial distribution
• Extremely large
• Specialised for tactile sense - blood filled sinus, innervated, which is sensitive to movement and external stimuli, is vibrated and amplified by the sinus which is sensed by nerve endings
What is sweat composed of?
ultra-filtrate of blood plasma
What are the functions of sweat glands?
• Thermoregulation (some species)
• Excretion
• Scent signalling (some species)
Histology
What cells makeup the secretory portion of sweat glands and aid secretion?
What cells makeup the excretory portion / duct of sweat glands?
Secretory
• Simple cuboidal epithelium
• Myoepithelial or 'basket' cells surround aid secretion
Excretory
• 2 layers cuboidal epithelium
• Exit = Hair follicle or sweat pore
What are the differences between apocrine sweat glands and eccrine sweat glands?
• Apocrine sweat glands- hair follicle
• Eccrine sweat glands - empty directly onto skin surtace via sweat pore
REMINDER: mammary glands are modified _____ glands!
sweat
What is the secretory product of sebaceous glands?
sebum
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
waterproofing, suppleness, spread sweat via sebum
Describe the cells and features of the secretory portion and excretory duct of sebaceous glands.
Secretory Portion
Pale staining, flask shaped, holocrine secretion
Excretory Duct
Empties into hair follicle
What are specialized skin glands and name an example.
Localized accumulations of sweat or sebaceous glands in some domestic animals such as:
Supra caudal or tail gland in the dog (Concentration of sebaceous glands on dorsum of tail)
Do claws, hoofs and horns contain all layers of the normal integument?
Yes, retain structural organisation of epidermal, dermal and subcutis equivalent layers albeit in modified form
What are the functions of claws, hoofs and horns?
protection of underlying tissues but also scratching, digging and as weapons
What muscle is responsible for erecting the hair in animal which is cold or alert?
Arrector pili muscle, by raising the hair, air can be trapped which cain raise body temperature
What is different about the keratin in hair compared to the keratin found in the skin epidermis?
“hard keratin” has a lower lipid content, and higher sulfur content
How do sweat glands eject their contents to the surface of the skin?
Myoepithelial cells act a bit like smooth muscle to propel substance to the surface, much like mammary glands