Solutions
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Binary Solution
A solution made up of one solute and one solvent
Factors affecting solubility
Nature of Solute
Temperature
Pressure
Nature of Solute
Polar solutes and soluble in polar solvents
Non-polar solutes are soluble in non polar solvents
Temperature
Follows Le Chateliers Principle
Increase in temperature favours dissolution if the process is endothermic (ΔsolH > 0), the solubility should increase with temperature
Decrease in temperature favours dissolution if the process is exothermic
The process of dissolving gas in liquid is always exothermic
Aquatic animals feel more comfortable in cold water because at colder temperatures, the water has more dissolved oxygen
Pressure
Solubility of a solid or liquid in liquid is not affected by pressure as solid and liquid are not compressible
Solubility of a gas increases with increase in pressure of the gas over the liquid
Henry’s Law
In terms of solubility:
Solubility of a gas in liquid is directly proportional to partial pressure of the gas over the liquid
s = KHp
In terms of partial pressure:
The partial pressure of vapour phase of a gas over the surface of the liquid is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the gas inside the liquid
p = KHx
Note: The value of Henry's constant KH is greater for gases with lower solubility
Application of Henry’s Law
Preparation of carbonated drinks - To increase the solubility of CO2 in soft drinks and soda water, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
Scuba divers face high dissolved gas levels due to increased pressure underwater, raising gas solubility in the blood. As they ascend, pressure drops, releasing nitrogen bubbles that block capillaries, causing a painful, dangerous condition called bends.
To avoid bends, as well as, the toxic effects of high concentrations of nitrogen in the blood, the tanks used by scuba divers are filled with air diluted with helium (11.7% helium, 56.2% nitrogen and 32.1% oxygen).
At high altitudes due to low pressure, solubility of oxygen decreases and causes climbers to become weak and unable to think clearly, symptoms of a condition known as anoxia.
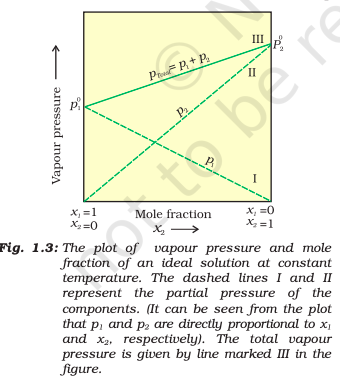
Raoult’s Law
For a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
p1 = po1x1
Raoult’s Law as a special case of Henry’s Law
p = KHx
p1 = po1x1
Thus, Raoult’s law becomes equivalent to Henry’s law in which KH becomes equal to po1
Ideal and Non Ideal Solutions
Name the type of deviation shown by this system from raoult's law
By graphic inspection, answer the following questions:
i) Predict the sign of ΔmixH and ΔmixV for this system.
ii) Give an example of such a system
iii) What type of azeotrope will this system form, if possible?
The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
When a solution does not obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration, then it is called non-ideal solution

A:
i) Both negative
ii) Phenol and aniline or Chloroform and acetone
iii) Maximum boiling point azeotrope
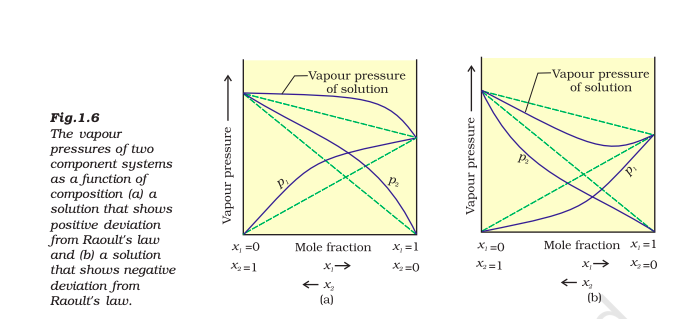
What role does the molecular interaction play in solution of alcohol in water?
There are strong hydrogen bonding in atoms and molecules as well as water molecules
On mixing alcohols and water, the molecular interactions become weak
Therefore, they show positive deviation from ideal behaviour
As a result, the solution will have higher vapour pressure and lower boiling point than that of alcohol and water
Why do gases always tend to be less soluble in liquids as the temperature is raised?
When gases are dissolved in water, it is accompanied by a release of heat energy, i.e., process is exothermic. When the temperature is increased, according to Lechatlier’s Principle, the equilibrium shifts in backward direction, and thus gases becomes less soluble in liquids.
Osmosis
Movement of solvent molecules from pure solvent in a solution through a semi permeable membrane
or
Osmosis is a process of movement of solvents through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration
Osmotic Pressure
Which one of the following solution show higher osmotic pressure and give the reason 1M KCI or 1M Urea solution?
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure required to be applied on the solution side to stop the naturally occuring osmosis
A: 1M KCl solution has higher osmotic pressure than 1M urea solution because KCl dissociates into 2 ions (K⁺ and Cl⁻), doubling the number of particles (i = 2), while urea does not dissociate because it is not an electrolyte (i = 1).
Reverse Osmosis
If pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied then, flow of solvent molecules is reversed, i.e. from a higher concentration solution to lower concentrated solution.
This phenomenon is called “Reverse Osmosis”.
It is used in water purification and desalination of water.
Advantages of Osmotic Pressure
Why the measurement of osmotic pressure is more widely used for determining molar masses of macromolecules than the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point of their solutions?
The magnitude of osmotic pressure is very high even for a very dilute solution
Osmotic pressure depends on molality of a solution and hence can be calculated at room temperature
It can be used to determine molar mass of macro molecules like polymers or biomolecules like hormones and enzymes which may be unstable at a variable temperature or pH
A: The same points as above (https://www.doubtnut.com/pcmb-questions/166297)
Isotonic Solutions
Two solutions with same osmotic pressure
Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
Blood cells are isotonic with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. What happens if we place blood cells in a solution containing:
a) 1.2% sodium chloride solution?
b) 0.4% sodium chloride solution ?
Hypertonic solution is a type of solution that has a higher concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell than on the inside of the cell
A hypotonic solution is a solution that has a lower concentration of solute compared to the cell
Eg:
Osmotic pressure associated with fluid inside blood is cell is 0.9% (mass/volume) sodium chloride solution
If we place the cell in a solution more than 0.9% NaCl (hypertonic solution), water will flow out of the cell and the cell would shrink
If we place the solution less than 0.9% NaCl (hypotonic solution), water will flow into the cell and the cell would swell up
People taking a lot of salt or salty food experience water retention tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis. The resulting puffiness or swelling is called edema
Define conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss its variation with concentration.
Conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of a solution of 1 cm in length and area of cross-section 1 sq. cm. The inverse of resistivity is called conductivity or specific conductance
Conductivity always decreases with a decrease in concentration, both for weak and strong electrolytes.
This is because the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases with a decrease in concentration.
Define molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss its variation with concentration.
Molar conducitivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of volume V of a solution containing 1 mole of the electrolyte kept between two electrodes with the area of cross-section A and distance of unit length.
Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration as the total volume of a solution containing one mole of electrolyte also increases