Musculoskeletal System
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the 3 types of muscle?
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
muscle fiber
long cylindrical cell in muscle
What are the components/features of muscle fiber?
multinucleate
myofibrils
sarcolemma
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
T-tubules
filaments
What is the storage location for Ca2+?
sarcoplasmic reticulum
What are myofibrils composed of?
thick & thin filaments
What are two features of thick and thin filaments?
highly organized proteins
striated
What are the two kinds of filaments?
thick filament
thin filament
What makes up thick filament?
~ 350 myosins
head
flexible hinge region
tail
What makes up thin filament?
2 strands of actin + 2 regulatory proteins
tropomyosin
troposin
actin subunit
Where is the binding site for myosin?
actin subunit
What is the basic unit of contraction?
sarcomere
sarcomere
overlapping thin & thick filaments
100s of sarcomeres end-to-end =
myofibril
In a sarcomere, thin filaments are attached to…
Z line
In a sarcomere, thick filaments are anchored to…
M line
draw a sarcomere
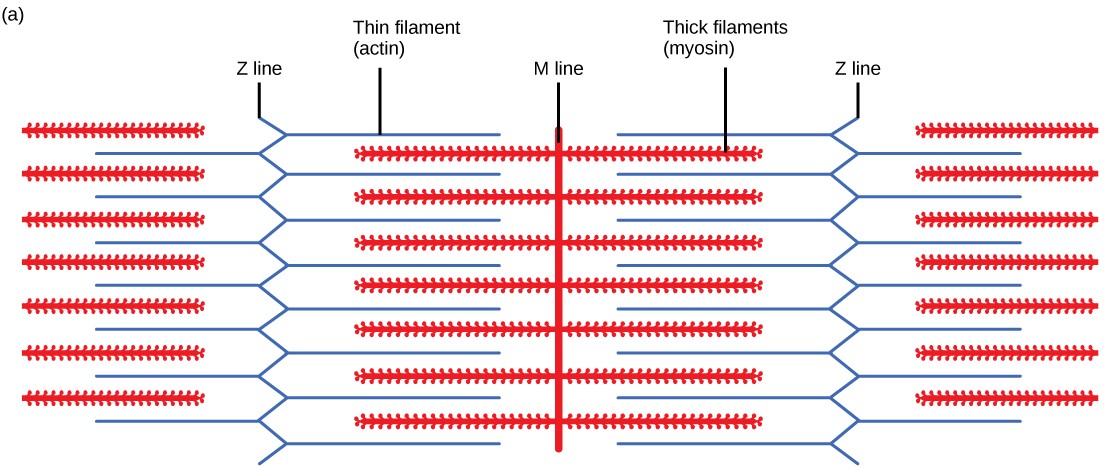
What do thin and thick filaments do during contraction?
make & break connections;
“slide” past each other and increase overlap
What shortens during contractions?
the sarcomere NOT the length of filaments
How does the sarcomere shorten during contractions?
the distance between the Z lines shorten
Does the sarcomere shorten during contractions?
yes
Does the overlap increase during contractions?
yes
Do the thin filaments shorten during contractions?
no
Do the thick filaments shorten during contractions?
no
When the muscle fiber is at rest, myosin binding sites are blocked by…
tropomyosin
SEQ the process of a motor neuron transmitting a message
AP arrives at junction
acetylcholine released into synaptic cleft
acetylcholine binds to receptors on muscle fiber
Na+ channels open
AP in sarcolemma of muscle fiber
AP down T-tubules
Ca2+ channels in SR open
Ca2+ released into cytoplasm
SEQ muscle contraction
myosin head is bound to ADP +Pi = high energy state
Ca2+ binds to troponin
changes shape
tropomyosin moves away from myosin-binding sites
myosin binds & forms cross-bridge
ADP + Pi released
myosin head goes to low energy state
pulls thin filament toward center of sarcomere = “power stroke”
ATP attaches to myosin & myosin head detaches
breaks cross-bridge
head in low energy state
myosin is a ATPase
ATP → ADP + Pi
myosin head changes shape → now in high energy state
What is needed to break cross-bridges?
ATP
What is the difference between ATP and creatine phosphate?
ATP = not stockpiled
creatine phosphate = stockpiled → contractions for ~ 15 seconds
What are the two kinds of glucose metabolism?
aerobic = cellular respiration
anaerobic = lactic acid fermentation
cardiac muscle
walls of the heart
striated & branched
autorhythmic
intercalated disks
What makes cardiac muscle autorhythmic?
pacemaker cells respond to autonomic nervous system to control rate
What do intercalated disks do?
allow ions to pass between cells
AP can pass quickly to all cells
contract simultaneously
smooth muscle
not attached
not striated
no T-tubules
SR less developed
less efficient
long, slow contractions
walls of digestive tract, bladder, uterus, & blood vessels
What are the functions of skeletons?
support
protect organs
movement (force from muscle contractions)
What are the 3 types of skeletons?
hydrostatic skeleton
exoskeleton
endoskeleton
hydrostatic skeleton
coelom
muscle contracts → force on fluid → shape change
soft-bodied invertebrates
cnidarians, nematodes, annelids
exoskeleton
external, non-living tissue → protection
mollusks
CaCO3 shell secreted by mantle
enlarges at outer edge
arthropods
chitin
ecdysis
endoskeleton
internal, living tissue → growth
echinoderms & chordates
What are the two kinds of endoskeletons that chordates can have?
cartilage
chondrocytes → collagen
bone
osteoblasts → collagen
hydroxyapatite (Ca & P)
ligaments
connects bone to bone
joints
junctions between 2 or more bones;
flexibility & movement