Quiz 2 (Handling and Husbandry)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:50 PM on 10/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
Nutrient
Something essential a plant/animal obtains from its environment for growth and maintenance of life
2
New cards
Digestion
Process of breaking down food stuffs into chemical substances that can utilized by the body to support life
3
New cards
Classification of Diet
Carnivore, Herbivore, and Omnivore
4
New cards
Carnivore
An animal that eats meat only
5
New cards
Omnivore
An animal that eats meat and plants
6
New cards
Herbivore
An animal that eats plants
7
New cards
Malnutrition
Inadequate or unbalanced consumption of nutrients
8
New cards
What can malnutrition cause?
Disease and predisposing to disease
9
New cards
Classification of Nutrients
Water, macronutrients, and micronutrients
10
New cards
What is the most important nutrient?
Water
11
New cards
Essential Nutrients
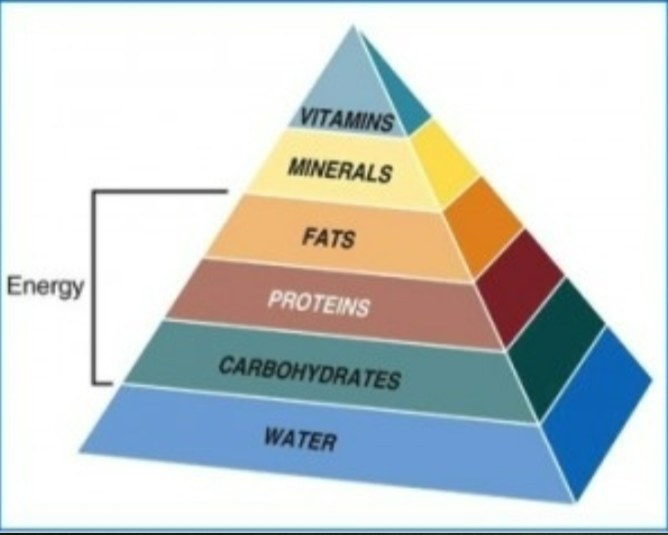
12
New cards
Functions of Water
- Vital role in almost all metabolic processes
- Maintains electrolyte concentrations
- Major component of blood
- Involved in thermoregulation (temp. regulation)
- Transport medium
- Provides shape and structure to organs
- Maintains electrolyte concentrations
- Major component of blood
- Involved in thermoregulation (temp. regulation)
- Transport medium
- Provides shape and structure to organs
13
New cards
What can cause increased water demand?
Critically ill patients, extreme temperatures, and high energy outputs
14
New cards
What are the 2 ways animals source water?
Drinking and food
15
New cards
Dehydration
A negative fluid balance (Body using or losing more water than it is taking in)
16
New cards
Causes of Dehydration
Excessive vomiting/diarrhea, Polyuria (increased urination) due medical conditions, Anorexia, Trauma (blood loss or burns), Neglect
17
New cards
Clinical Signs of Dehydration
Decreased skin elasticity, tacky mucous membranes, prolonged tissue perfusion times, and sunken eyes
18
New cards
What are macronutrients?
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
19
New cards
What is energy?
Property deprived from diet (typically macromolecules) that is used by cells to fuel all body functions
20
New cards
How is energy produced in an animal's body?
Digestion breaks macronutrients down into their structural units that the body absorbs these units into bloodstream to be utilized for ATP production. ATP is produced in cells using Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Electron Transport System.
21
New cards
Carbohydrate Function
Major source of energy that can stored in liver as Glycogen and adipose tissue as fat
22
New cards
What is the structural unit of carbohydrate?
Glucose
23
New cards
Monosaccharide
One sugar unit (ex. Glucose)
24
New cards
Disaccharide
Two sugar units (Sugars, sucrose)
25
New cards
Polysaccharide
Numerous sugar units (Ex. Starches, cellulose)
26
New cards
Soluble Carbohydrates
Carbs that can be dissolved by animals and are broken down by amylase
27
New cards
Insoluble Carbohydrates
Carbs that can not be dissolved by animals and are broken down by cellulose
28
New cards
What is considered a soluble carbohydrate?
Sugars and starches
29
New cards
What is considered an insoluble carbohydrate?
Anything that contains cellulose (Hay, grasses, gums, pectin)
30
New cards
How are insoluble carbs get digested?
Digested in small intestine through microbial fermentation (Microbes create cellulase enzymes)
31
New cards
Importance of fiber for non-herbivore
- Stabilizes gut motility
- Supports colon health
- Increased bulk + water content in large intestine
- Dilutes other macronutrients to induce weight loss
- Supports colon health
- Increased bulk + water content in large intestine
- Dilutes other macronutrients to induce weight loss
32
New cards
What is the structural unit for fats?
Fatty acids and glycerol
33
New cards
Fats/Lipids Function
Provides energy, increases palatability and adds texture, provides essential fatty acids, transports and distribute fat soluble vitamins, used to create cell membranes and sex hormones
34
New cards
What makes up a fat?
One glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains (Triglyceride)
35
New cards
How are lipids digested?
Using Lipase enzyme in pancreas, lipids are broken into components (1G and 3FAs) used to create ATP
36
New cards
Where is excess lipids stored?
Adipose tissue
37
New cards
2 Categories of Lipids
Saturated and Unsaturated
38
New cards
2 Categories of Unsaturated fats (Where and how many double bonds are present)
Monounsaturated: One double bond
Polyunsaturated: Multiple double bonds
Polyunsaturated: Multiple double bonds
39
New cards
Saturated fats
Solid at room temperature, referred as fats, typically animal based with no double bonds
40
New cards
Unsaturated fats
Liquid at room temperature, referred as oils, typically plant based with some double bonds present
41
New cards
Fatty Acid Families
Omega 3, Omega 6, Omega 9 fatty acids
42
New cards
What are Omega 3, 6, 9 fatty acids good for?
Skin, hair, hooves, horns
43
New cards
What are the function of essential fatty acids?
Essential for normal body functions (like Kidney + Reproductive functions, membrane formation, and prostaglandin production)
44
New cards
What deficiencies happen without the proper amount of fatty acids?
Dull hair coat, hair loss, susceptibility to infection or poor wound healing
45
New cards
What is the structural unit for proteins?
Amino acids
46
New cards
What is the function of proteins?
Used in tissue growth and repair; serves enzymes, hormones, and antibodies; used to make hemoglobin, used as energy
47
New cards
How are proteins made?
Amino acids linked together with peptide bonds
48
New cards
What determines type and function of protein?
Type and order of amino acid
49
New cards
How are proteins digested?
Proteins are broken down into amino acids in the small intestine. Amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream and sent to liver for reconstruction into the body.
50
New cards
Can amino acids be produced by the body?
Typically, no. If so, they are not produced fast enough to meet requirements for the body. They must be provided by the animal's diet.
51
New cards
How many amino acids are considered essential?
10 (11 for cats!)
52
New cards
Is protein be used for energy?
If the body can't meet energy requirements with carbs and fats, the body will use protein for energy. Protein is NOT a good source of energy.
53
New cards
Anabolic Pathway
Proteins are broken down in to amino acids and are circulated throughout the body to build new body tissues. Any unused amino acids are utilized as energy and stored as glycogen
54
New cards
Catabolic Pathway
Energy demands are not met by diet, and body will break down body proteins into amino acids and use it for energy
55
New cards
What are the two types of micronutrients?
Vitamins and minerals
56
New cards
What are macrominerals expressed as? (What units does it use?)
%
57
New cards
What are microminerals expressed as? (What units does it use?)
Ppm
58
New cards
What are minerals?
Inorganic substances essential to life
59
New cards
How many minerals are essential to mammals?
At least 18
60
New cards
Macrominerals Examples
Sodium + Chloride, Potassium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Calcium, Sulfur
61
New cards
Microminerals Examples
Zinc, Selenium, Manganese, Iodine, Fluorine, Chromium, Copper, Iron, Boron, Molybdenum, Cobalt
62
New cards
What minerals are required for skeletal structure maintenance?
Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium
63
New cards
What minerals are required for acid base balance or fluid balance?
Potassium, Sodium, Chloride
64
New cards
What minerals are required for cellular function?
All Minerals
65
New cards
What minerals are required for nerve conduction?
Potassium, Magnesium
66
New cards
What minerals are required for muscle contraction?
Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium
67
New cards
Which amino acid is essential for only cats?
Taurine
68
New cards
What can calcium toxicity cause?
Problems with iron absorption and kidney function, reduction of copper absorption, may cause magnesium deficiency
69
New cards
What can iron toxicity cause?
Alimentary disturbances, reduced growth, phosphorus deficiency, reduction of copper absorption
70
New cards
What can copper toxicity cause?
As accumulation happens in liver, can cause necrosis of liver walls, jaundice, loss of appetite
71
New cards
What can iodine toxicity cause?
Reduction in weight gain, reduction in feed intake, reduced egg production in chickens
72
New cards
What can manganese phosphorus toxicity cause?
Depressed appetite, retarded growth
73
New cards
What can zinc toxicity cause?
Depressed food consumption, induced copper deficiency
74
New cards
What can selenium toxicity cause?
Dullness, stiffness in joints, reduced food intake, loss of hair, acute poisoning (leads to death)
75
New cards
What can phosphorus toxicity cause?
Calcium deficiency, bone malformation, fractures
76
New cards
What can sodium chloride toxicity cause?
Nervousness, weakness, seizure, and death usually associated with low intake of water
77
New cards
What are vitamins?
Organic substances that come from the diet
78
New cards
What are the 2 categories that vitamins are sorted in?
Fat and water soluble (based on absorption in intestinal tract)
79
New cards
How do fat soluble vitamins work?
They bind to lipids in the small intestine and are absorbed in lipids
80
New cards
What are examples of fat soluble vitamins?
Vitamin A, D, K
81
New cards
Where are excess fat soluble vitamins stored?
Adipose tissue
82
New cards
How do water soluble vitamins work?
They are dissolved in water in small intestine and absorbed when water is absorbed
83
New cards
What are examples of water soluble vitamins?
Vitamin B, C
84
New cards
Where are excess water soluble vitamins stored?
They are exerted in urine within a few hours of ingestion
85
New cards
What is Vitamin A?
Coming from animal and plant forms (animal tissues and colorful veggies), this vitamin helps immune health, bone resorption, spermatogenesis, eye health, and epithelial cell differentiation
86
New cards
What is Vitamin D?
Coming from animal and plant forms, this vitamin helps with calcium and phosphorus balance, bone mineralization and resorption, and insulin synthesis
87
New cards
What vitamin needs sunlight to be activated for animals?
Vitamin D
88
New cards
What is Vitamin E?
Coming from plant based sources, it helps with antioxidation and maintaining cell membrane integrity
89
New cards
What is Vitamin K?
Coming from animal and plant based sources, it helps with blood clotting and regulation of bone growth
90
New cards
How many B vitamins are there?
8
91
New cards
What is Vitamin B?
Coming from animal and plant based sources, it helps with multiple metabolic functions and is components in glycolysis and Krebs's cycle.
92
New cards
What is Vitamin C?
Coming from citrus fruits, leafy green plants, and vegetables, it helps as an antioxidant, creation of collagen, immunity, and wound healing
93
New cards
What can Vitamin A toxicity cause?
Hair loss and blurred vision
94
New cards
What can Vitamin D toxicity cause?
Nausea, weakness, irritability, brain or liver damage, jaundice, and destruction of red blood cells
95
New cards
What can Vitamin E toxicity cause?
Problems with absorption of other fat soluble vitamins
96
New cards
What can Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) toxicity cause?
Permanent nerve damages
97
New cards
What can Vitamin B3 (Niacin) toxicity cause?
Itching, skin flushing, and gastrointestinal distress
98
New cards
How do you perform a nutritional assessment?
Medical evaluation on animal's current nutritional health (Physical exam and nutritional history)
99
New cards
What is the parts of the physical exam when checking for nutrition issues?
Body Condition Score (BCS), Weight, Coat and skin health, Oral health
100
New cards
What is the parts of the nutritional history?
Current diet, current feeding method, current energy output