Topic 8 - forces doing work
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
state the law of energy conservation
energy cannot be created or destroyed (it can only be transferred into different forms)
describe the energy changes involved when a ball is thrown upwards and then returns to its starting position. (ignore air resistance)
upwards: KE is converted to GPE
peak: maximum GPE, zero KE
downwards: GPE is converted to KE
energy in a system
when a system changes, energy is transferred from one form to another
electrical energy changes into kinetic energy in a motor
what is a closed system
a closed system is a system which experiences no external forces
eg. a circuit, or a skydiver
in a closed system, the total energy remains the same at all times
equation for change in gravitational potential energy
change in gravitational potential energy (joule, J) = mass (kilogram, kg) x gravitational field strength (newton per kilogram, N/kg) x change in vertical height (metre)
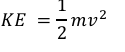
formula for kinetic energy
kinetic energy (joule, J) = ½ x mass (kilogram, kg) x (speed)²((metre/second²),m/s)²)
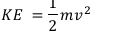
changes
work done
this is when an external force transfers energy to a system
eg. a human doing work to push a ball up a hill
electric
chemical potential energy (stored in batteries) forms electirc
heating
electric transfers to thermal energy, as work is done against the heating coils causing it to heat up
equation for work done
work done (joule, J) = force (newton, N) x distance moved in the direction of the force (metre, m)
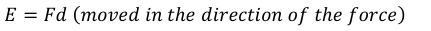
waste
energy is rarely 100% transferred into the desired form
some energy is dissipated so it is stored in less useful ways
mechanical processes are wasteful when they get hot (usually due to friction)
energy is dissipated as heat, causing a rise in temperature
so the energy is lost to the surroundings
what is power and equation for it
the rate at which energy is transferred
power (watt, W) = energy transferred or work done (joule, J)/time taken (second, s), where 1 watt is equal to 1 joule per second
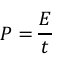
what is efficiency
measure of how much energy is not lost as waste
efficiency equation
efficiency = useful output energy/total input energy
one watt in joule per second
1 watt = 1 J/s