bio exam yr11
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
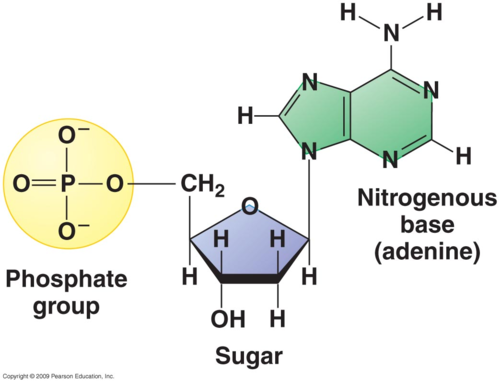
nucleotide and three parts
hemizygous
on the x sex chromosome of the male
pure breeding
homozygous
complementary base pairing
base in one strand can from a specific hydrogen bonds with another base in the opposite strand across from it
rna
ribonucleic acid
single stranded sugar phosphate
uracil
dna
deoxyribonucleic acid
thymine
double stranded sugar phosphate
transcription
DNA is copied onto a strand of mRNA
RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an RNA strand
initiation, elongation, and termination
translation
The code on mRNA is "read" and used to create a protein
tRNAs bind to mRNAs inside of a protein-and-RNA structure called the ribosome
initiation
RNA polymerase binds to a sequence of DNA called the promoter
RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands
elongation
strand of DNA, the template strand, acts as a template for RNA polymerase
polymerase builds an RNA molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'
contains the base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)
termination
signal that the RNA transcript is complete
Once transcribed, the transcript to be released from the RNA polymerase
translation steps
small ribosomal sub-unit attaches to a specific nucleotide sequence on the mRNA strand
‘upstream’ the initiation codon (AUG) where translation will start.
initiator tRNA, carrying methionine, attaches to the initiator codon.
large ribosomal sub-unit binds to complete the protein-synthesizing complex.
amino acids are added one by one by tRNAs as the ribosome moves along the mRNA.
release factor binds to the stop
codon and hydrolyzes the completed
polypeptide from the tRNA, releasing
the polypeptide from the ribosome.
mrna
is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis. mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription.
trna
responsible for matching amino acids with the appropriate codons in mRNA. molecule has two distinct ends, one of which binds to a specific amino acid, and the other which binds to the corresponding mRNA codon.
triplets
a three-nucleotide sequence that is unique to an amino acid
codons
DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides that forms a unit of genomic information encoding a particular amino acid or signaling the termination of protein synthesis (stop signals)
anti codons
a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule
rna processing
5' cap is added to the beginning of the RNA transcript, and a 3' poly-A tail is added to the end.
splicing, some sections of the RNA transcript (introns) are removed, and the remaining sections (exons) are stuck back together
Capping at the 5' end
Addition of a polyA tail at the 3' end. and
Splicing to remove introns
alternative splicing
one pre-mRNA may be spliced in either of two (or sometimes many more than two!) different ways
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
a double-stranded nucleic acid chain made up of nucleotides.
Nucleic acid
macromolecules that includes DNA and RNA
Nucleotide
the monomer unit of nucleic acids.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific protein
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
Allele
An alternative form of a gene.
Locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome
Phenotype
observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
somatic cells
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
Telomeres
DNA at the tips of chromosomes
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes, that have the same structure, and that pair during meiosis.
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
sex chromosomes
One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human, contains genes that will determine the sex of the individual.
Aneuploidy
the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell
Polyploidy
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
Monosomy
Chromosomal abnormality consisting of the absence of one chromosome from the normal diploid number
Trisomy
a condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nuclei, causing developmental abnormalities.
Meiosis
a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores.
Gametes
reproductive cells
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
independent assortment
the random distribution of the pairs of genes on different chromosomes to the gametes
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a particular gene
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
Carrier
A person whose genotype includes a gene that is not expressed in the phenotype.
Codominance
situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism
incomplete dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits.
Codominance example
AB blood type
incomplete dominance example
red flower + white flower = pink flower
sex-linked gene
gene located on a sex chromosome
X-linked
referring to a gene located on the X chromosome
monohybrid cross
A cross between two individuals, concentrating on only one trait
Punnet Square
a method of predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in genetic crosses
test cross
the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
gene pool
All the genes, including all the different alleles for each gene, that are present in a population at any one time
genetic diversity
a measure of the genetic variation among individuals in a population
sexual reprodcution
reproduction in which two parents have offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the gametes of the two parents.
asexual reproduction
involves one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which one cell divides to form two identical cells.
Budding
Asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism
Fragmentation
A means of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.
parthenogenesis
Asexual reproduction in which females produce offspring from unfertilized eggs.
Advantages of asexual reproduction
1. no need mate; can live isolate
2. numerous offspring quickly
3. no energy needed for maintenance of reproductive structures
4. good with stable enviroment
somatic cell nuclear transfer
a cloning technique that involves substituting genetic material from an adult's cell for the nucleus of an egg
embryo splitting
a form of cloning that is accomplished by dividing a growing embryo into equal parts using a surgical procedure performed with the aid of a microscope
plant cuttings
in plant cloning, a leaf and stem are cut off a plane and then dipped in hormone powder to encourage rooting, and a new plant grows
plant grafting
the attachment of two individual plant stems together
structural adaptation
a physical feature of an organism's body having a specific function that contributes to the survival of the organism
physiological adaptation
a physical or chemical event that occurs within the body of an organism and enables survival
Ecosystem
A community of organisms and their abiotic environment
population size
the total number of individuals within a defined area at a given time
population density
Number of individuals per unit area
population distribution
how population is spread out in an area
Immingration
Moving into a population
carrying capacity
the largest population that an environment can support at any given time
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites.
integrity
encourages a full commitment to knowledge and understanding as well as the honest reporting of all sources of information and results
Justice
encourages fair consideration of competing claims, and ensures that there is no unfair burden on a particular group from an action
Beneficence
encourages the maximisation of benefits while minimising the risks and harms involved in taking a particular position or course of action
Non-maleficence
discourages causing harm - or when harm is unavoidable, ensuring that the harm is not disproportionate to the benefits from any position or course of action
respect
encourages the acknowledgment of the intrinsic value of living things, and considers the welfare, beliefs, customs, and cultural heritage of both the individual and the collective
cell
The basic unit of life (living things)
Cell Theory
all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of life and new cells are produced from existing cells
Prokaryote
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
small and simple
cell walls
unicellular
bacteria
linear dna
eukaryote
nucleus
membrane bound organelles
cilia
uni or multicellular
Cytoskeleton
helps cell keep its shape
involved in movement
cytoplasm
jelly fluid in cell which organelles sit in
cytosol
fluid of cytoplasm
chloroplast
photosynthesis
plants only
chlorophyll