3.5 Labour Markets
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What does the demand curve for labour represent?
The quantity of labour that employers would wish to hire at each possible wage rate
What determines the demand for labour?
The Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
What is the MRP?
The extra revenue generated by an individual worker
What does a higher MRP mean?
A higher demand for workers
How does the law of diminishing marginal productivity affect the demand for labour?
Increasing number of workers means MRP rises at first, then causes it to decline
Why is the demand for labour downward sloping? 2
In the long run, all factors of productions vary, so high wage rates will encourage businesses to use machinery instead of workers
In the SR, firms have fixed levels of capital, and so diminishing marginal productivity means that adding extra workers gives a lower return so to employ these workers, the wage rate has to fall
How to calculate the MRP?
Marginal output X price
or
Marginal output X difference in total revenue
What factors influence the demand for labour? 6
Wage rates (The price of labour, as wage rates increase, demand for labour contracts)
Demand for the product (Labour is a derived demand, if there is no demand for the product, there is no demand for the labour)
Prices of other FOP (if machinery and equipment become cheap, firms switch to that)
Wages abroad (if wages are lower abroad, demand will contract domestically)
Technology (Tech improvements mean jobs may be lost due to innovations)
Regulation (Regulation may discourage firms from hiring, as it may be expensive and time consuming)
What is the price elasticity of demand (PED) of labour?
The responsiveness of the quantity demanded of labour to the wage rate
What factors effect the PED of labour? 4
The PED of labour is directly tied to the PED of the product the labour produces
The proportion of wages to the total cost of production (if wages are a huge proportion of costs, then an increase in wages will increase costs massively, so there will be a fall in demand for labour)
If there are many substitutes
Time (in the long run, PED of labour is more elastic as machinery can be developed and jobs can be moved)
What are the factors influencing the supply of labour? 7
Wages (higher wages make people work more)
Population and age distribution (high population means many workers, people of high working age)
Non-monetary benefits (free healthcare, holiday, flexibility, hours)
Education/training/qualification (more educated workers means there is a higher supply of workers)
Trade unions and entry barriers (Trade unions may be able to restrict the supply of labour by introducing barriers to entry)
Wages and conditions of other jobs (If many jobs in a local area are considered to be unpleasant, then supply for alternatives will be higher)
Legislation (School leaving age, retirement age)
What does a perfectly competitive wage market look like
just a supply and demand graph mate
What is on the x and y axis in a labour market diagram
X = Quantity of labour
Y - Wage Rate
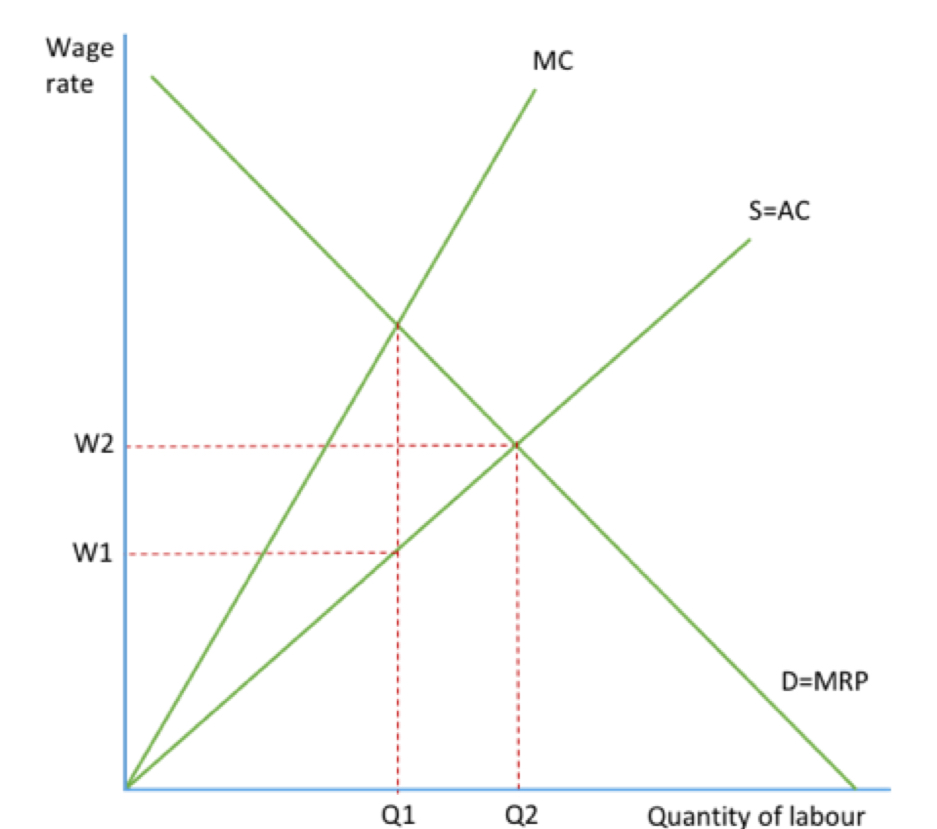
What does monopsony in a labour market entail?
There is only one buyer of labour
Why is MC above AC in a monopsony labour market?
In order to increase their labour force
businesses must increase their wage for each new worker they hire
which means that the marginal cost of hiring new workers increases for each new worker they hire
What does a monopoly in a labour market entail?
That there is only one seller of labour
Give an example of a monopoly in a labour market
A trade union
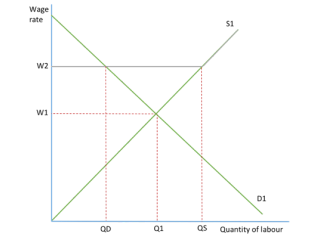
What does a trade union look like in a wage market diagram
What does a monopsony in a labour market look lie?
just draw a monopsony diagram bro
When drawing a monopoly diagram, (labour market) remember! 3
wage 2 line is SOLID, wage 1 is dotted
remember Qd, Q1 and Qs
W1 hits the equilibrium, W2 is above it x
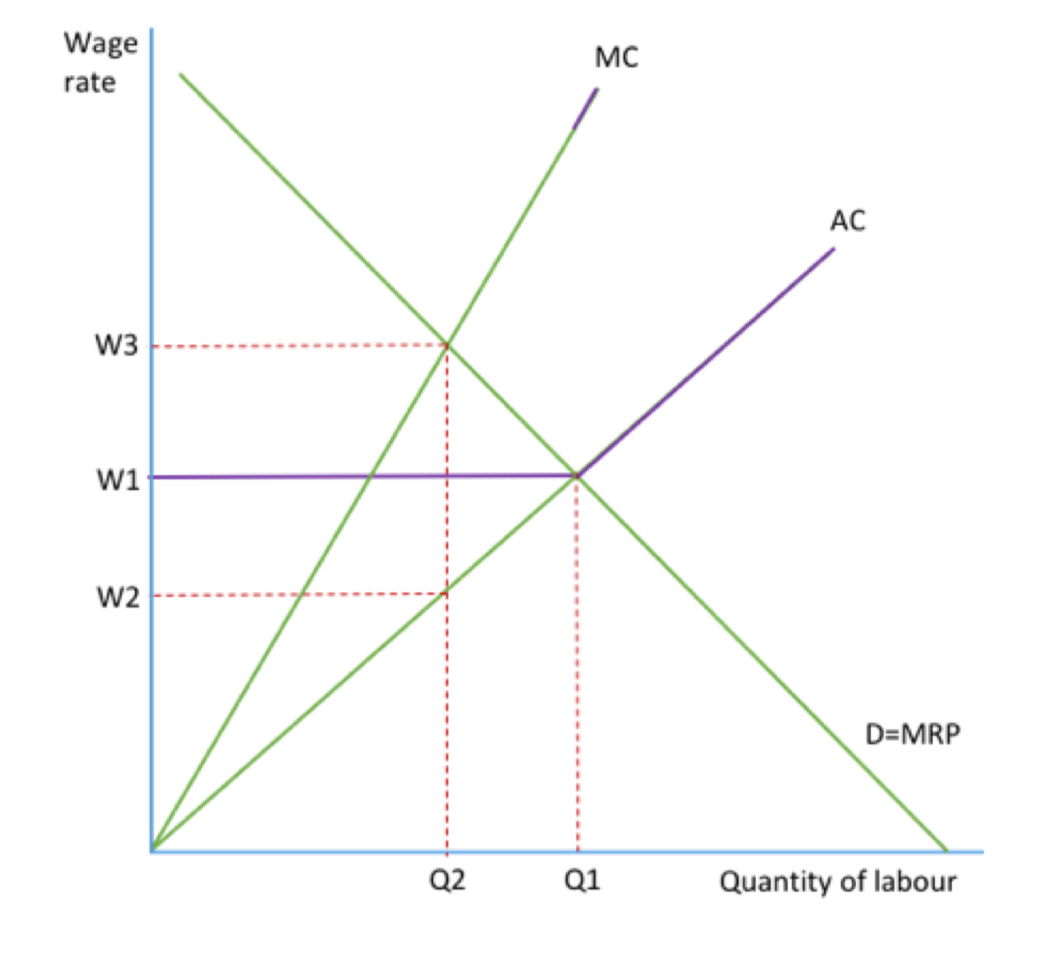
Draw a bilateral monopoly diagram please
What are 7 issues with the labour market?
Skills shortage
Young workers (lower lifetime earnings)
Retirement (rising life expectancy, pensioners over 50% welfare spending)
Wage inequality (over time those on highest wages have had disproportionate growth)
Zero-hour contracts (there has been a rise in these, makes it harder for people to know what they need)
The ‘Gig economy’ (concerns over the rights of these workers)
Migration (Suggests this causes a fall in wages, allows workers to recruit from a large pool)
What ways can the government intervene in a labour market? 4
National minimum wage
Maximum wages
Public sector wage setting
Tackling immobility
What are arguments for national minimum wage? 4
the wage is able to reduce poverty as it mainly impacts the lowest paid
Can reduce male/female wage differentials (Women more likely to take up lower paid job)
More content workforce (higher productivity)
Ensure everyone receives a fair wage
What are the arguments against national minimum wage? 3
loss of jobs in the industry
Raises costs for companies
Regional differences are not accounted for
How can geographical immobility be tackled? 4
improve the supply of houses 9reducing price)
Improving transport links
National advertising
Subsidies in areas where there are labour shortages
How can occupational immobility be tackled? 3
vocational training increased
Encouragement of further study
Spending on training within work