Genetics exam 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
conditional expression of phenotype
phenotype only expressed under restrictive conditions
unconditional expression of phenotype
phenotype expressed under any conditions
Null mutation
mutation that eliminates normal function or expression (loss of function)
Hypomorphic mutation
mutation that reduces normal function (loss of function)
hypermorphic mutation
mutation that opposes normal activity (gain of function)
pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine, one ring
spontaneous mutations
occurs in the absence of a known mutagen (occurs without the mutagen needing to be there)
induced mutation
mutation that occurs in the presence of a known mutagen ex.radiation
somatic cell mutations
mutations that occur in non-reproductive cells
germ-line cell mutations
mutations that occur in reproductive cells (ex. X-linked cells)
Purines
Adenine and Guanine, two rings
Base Analogs
Mimics one of the base pairs with wrong complementary base and causes GC-> AT or AT-> GC transitions. Causes point mutations
ex. 5-bromouracil - can mimic T or C
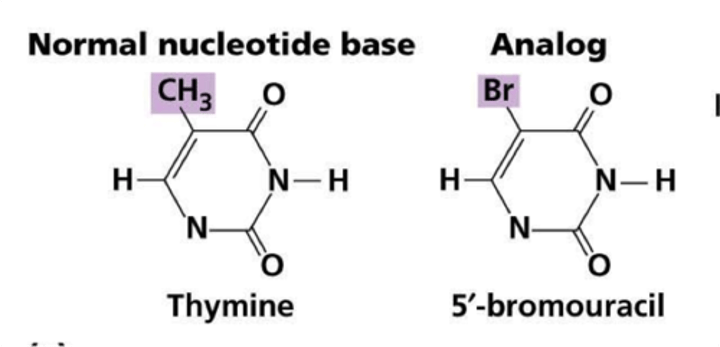
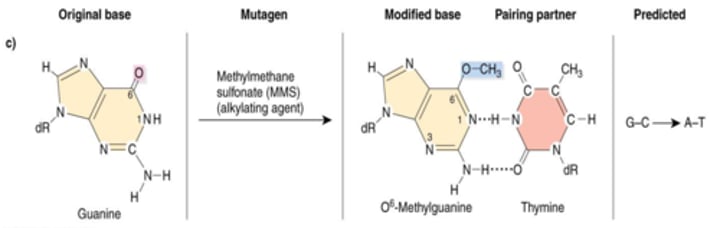
Alkylating Agents
methyl groups added to oxygens on bases, which changes base pairing and causes GC->AT or AT-> GC transition. Causes point mutations
ex. EMS (ethyl methane sulfonate) mutagenesis
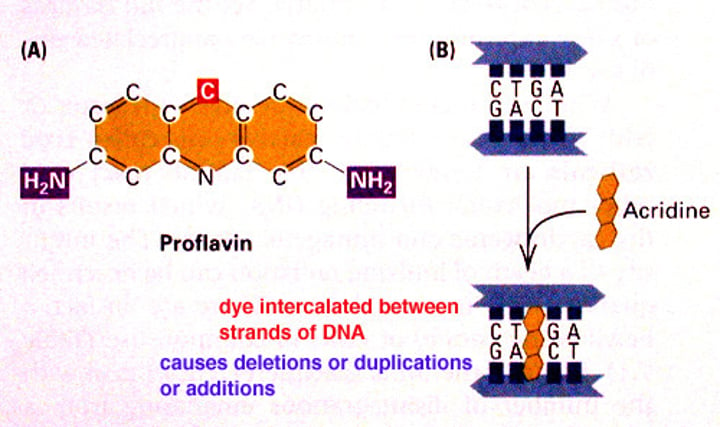
Intercalating Agents
Aromatic rings that are similar to bases, and fit in between bases in the DNA helix and trick DNA polymerase into adding an extra nucleotide. Causes frameshift mutations
ex. Proflavin, Ethidium Bromide, acridine orange
UV radiation
Irradiation causes thymine dimers to form, which blocks DNA replications. Ex. UV light
Ionizing Radiation
Irradiation causes double and single stranded breaks in DNA, which lead to errors during DNA repair and base damage via Reactive Oxygen Radicals ex. x-rays, gamma rays
cystosine deamination
cytosine loses an amine group and becomes uracil, 5-methylcytosine would become thymine
Trinucleotide repeat extension
strand slippage - when highly repetitive sequences on a DNA strand either bind themselves instead of the parent strand, or bind upstream from where they are supposed to. Slip-back results in insertion (expansion), and slip-forward results in deletion.
Transposons
mobile DNA sequences that integrate into various sites in the genome via non-homologous recombination
non-homologous recombination
recombination of double strand break of DNA but with no sticky ends, so no need for the two strands to match
Why is deamination of 5-methylcytosine worse than if it happened to normal cytosine
because a deaminated of 5-methylcytosine will turn into thymine, which naturally occurs in DNA, whereas cytosine would turn into Uracil, which only occurs in RNA. Uracil is easily detected as a mistake in DNA and will be quickly found and fixed by the cell.
How does water deaminate DNA?
Water would create a carbonyl (or ketone) group on the cytosine where there was originally an amine group. This occurs via hydrolysis with water
DNA-excision repair steps
1. Damaged DNA recognized by enzymes
2. Nicks created on ends of damaged segment
3. Segment is removed and degraded
4. DNA polymerase re-synthesizes DNA based on un-damaged strand
5. Ligase repairs remaining nicks
base excision repair
removes a mismatch by eating away one base, and then removing the backbone. DNA polymerase then fills the gap and DNA ligase repairs the nicks left over
How is deamination repaired?
by base-excision repair
Which strand is repair biased towards and why?
repair is biased towards the original strand, because the parent strand is recognized through methylation in prokaryotes. In eukaryotes, the parent strand is recognized because the daughter strand has nicks.
barr body
a disabled X chromosome
a quadruplex
a single strand structure folded in on itself
Drosophila X-linked test
the most sensitive test for mutation is the number of genes that can show that mutation. ex. look at relationship between x-ray dose and frequency of X-linked recessive lethal mutations
Microbial dosimetry
treat yeast with mutagens and see how many survive. aka survival test
Methods for detection of Environmental mutagens
Microbial dosimetry, Drosophila X-linked lethals, Ames Test
Ames test
assay for mutations using base substitution and frame shift mutation - input yeast with a frameshift mutation, and then treat the yeast with mutagens until there is a mutagen that undoes the original mutation (pseudo reversion). This creates a revertant population. This test is a sensitivity assay for mutation induction on bacteria, to see how mutagenetic difference compounds are (like cigarette smoke). Produces a linear dose response, so compounds can be compared
Why is liver extract important in Ames Test
because many carcinogens cannot do damage until metabolized in the body, liver extract is important in the ames test to activate carcinogens to allow mutation to occur
1st division segregation (Neurospora)
genes separated in meiosis 1 - pattern will be half and half
2nd division segregation (Neurospora)
genes separated in meiosis 2 - will looked like striped patter
What is evidence of gene conversion
When the ratio of phenotypes in neurospora spores is not 1:1
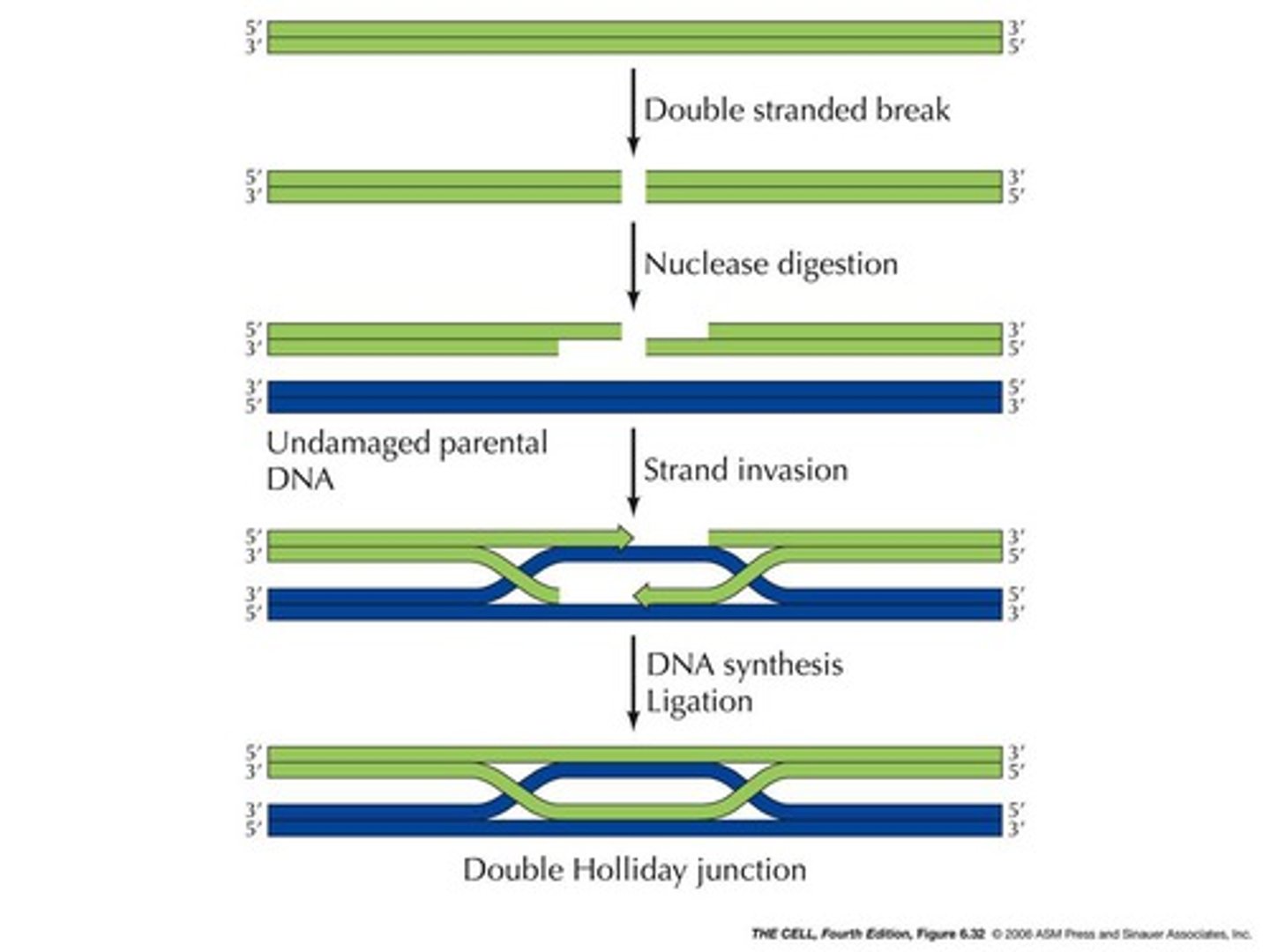
5' resection
when a double stranded break is made in a holliday junction, the 5' ends are eaten
strand invasion
the entry of the 3' end of a displaced DNA into an intact sister chromatid
Spo11
makes the double stranded break in holliday junction
asymmetrical cleavage
if you cleave a holliday junction on the inside, and twice on the outside, it will make a crossover event, and there will be recombination
Holliday junction
cross-shaped structure that forms during the process of genetic recombination, when two double-stranded DNA molecules become separated into four strands in order to exchange segments of genetic information.
suppressor
a mutation that reverses the phenotype causes by another mutation
intragenic suppressor
a suppressor that lies in the same gene as the initial mutation
extragenic suppressor
a suppressor that lies in a different gene from the initial mutation
psuedorevertant protein
a protein that has two mutations: one mutant and the other a suppressor, so they cancel out and the protein acts normally despite having two mutations
Where does Ames Test sensitivity come from
Ames test sensitivity comes from pseudo reversion - start with a gene that has a lethal frame shift, and treat the yeast with mutagens until there is a mutation that reverses the frameshift, either through true revertant (reverse the original damage in the same spot)(back mutation), or pseudo revertant (add a mutation later in the gene that restores the frameshift, but will leave a section of the genome out of shift)(suppressor mutation)
CpG cluster
where we can find an abundance of 5-methyl cytosine - eukaryotes methylate CpG dinucleotides that are congregated together for the purpose of gene regulation
nucleotide excision repair
A repair system that removes and then correctly replaces a damaged segment of DNA using the undamaged strand as a guide.
How are thymine dimers repaired
by nucleotide excision repair
aneuploidy
abnormal chromosomal ratio
trisomy
one extra chromosome
monosomy
one less chromosome
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 - 23 from mom, 23 from dad
mosaicism
one X is turned into a Barr body and other is used and expressed, leads to mosaic of parental X chromosome across the body
dosage compensation
an organism shuts off gene expression in one or more copies of a gene so the gene is expressed at the appropriate time. Ex. Barr body
transition mutation
pyrimidine to pyrimidine, or purine to purine
transversion mutation
pyrimidine to purine, or purine to pyrimidine
missense mutation
change in amino acid
nonsense mutation
an amino acid turned into a stop codon
How is a deletion mutation be inherited with cross over
two genes many have a lower frequency of recombination, if there was a section of the genome deleted from the middle of them
How is a duplication mutation inherited with cross over
can mediate unequal crossing over which can change chromosome structure
paracentric inversion
crossing over that does not include the centromere - if crossing over does occur, then a dicentric chromosome forms and an acentric fragment is lost.
Only have 2 viable products, and two inviable
pericentric inversion
inversion where the centromere is included
makes two unbalanced products which may yield inviable or non-productive gametes
protanomaly
a defective hybrid gene, for ex a gene that is half red and half green, means the person is color blind
deuteranomaly
a protanomaly gene with both intact genes, but also a hybrid gene in the middle
interchromatid crossover
When a gene crosses over itself, making a protanomaly of gene, and a loop with the hybrid gene on it that just gets digested
what are the two different methods to analyze the encoding function of genes
forward genetics and reverse genetics
Forward genetics
conducted by observing effects of genetic mutations, then try to trace back where the mutation occurred
Reverse genetics
conducted by inserting a mutation at a specific spot in the genome and seeing how it affects the genotype of the cell
genetic selection
only let progeny of specific genotype survive
genetic screening
let some cells survive, but then screen them for mutations and desired phenotype
concatemer
a series of repeating DNA sequences ligated together with non-homologous end joining - ex. if you try to insert a drug marker, it may accidentally insert itself multiple times in a row in one gene
Translocation
Without crossover, either 4 viable or inviable, with crossover 2 viable, 2 inviable
Differences in how the chromosomes separate in the cell may cause crossing over - segregate in + formation vs x formation
If two offspring viable, 2 inviable, what mutation likely occurred?
Inversion mutation