LSU MGT 3200
1/117
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What is the most popular definition of Management?
Getting work done through others
What are some of the main concerts of management? Describe balancing them.
Efficiency vs. Effectiveness.
Efficiency: Getting work done with minimum effort, expenses, or waste.
Effectiveness: Accomplishing tasks that help fulfill organizational objectives.
You need too strike a balance. For example, just efficiency would lead to management cutting all costs to maximize profits.
What are the Four Functions of Management? Describe them.
Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling.
Planning: Determining organizational goals, such as determining what business they are in.
Organizing: How these decisions will be made, including optimizing how things get done.
Leading: Inspiring workers to achieve organizational goals.
Controlling: Monitoring progress to goals. Altering the course of the comapny as needed.
What are the four kinds of managers? Know their order/relative status in comparison to each other.
In order of hierarchy,
Top Managers
Middle Managers
First-line Managers
Team Leaders
Describe Top Managers.
Executives who are responsible for the overall direction of an organization. They are in charge of creating context for change, employee buy-in, positive organization cultures. They are important for company branding and defining what the company does/sells.
These include the CEO’s, CFO’s, and COO’s.
Describe Middle Managers.
Middle managers are responsible for setting objectives consistent w/ top managers goals. They plan and allocate resources to meet objectives. They also link and coordinate several divisions within a firm. Also, they monitor and manage subunits and individual managers. Finally, they implement strategies developed by top managers. They are important for putting the top manager’s thoughts into realistic actions for the regions/areas.
Middle managers include Plant, Regional, and divisional managers.
What are First-Line managers?
First-line managers are responsible for managing the performance of entry-level employees (Bottom-level employees who produce a company’s goods/services). They also monitor, teach, and minorly plan projects. They do NOT care about organizational goals, and instead focus on problem solving & day to day.
These are the general “managers” when you think of them. These manage employee’s and are generally worried about completing projects which in turn help the company.
What are Team Leaders?
Team Leaders are the lowest level of management. They facilitate team activities towards goal completion. They direct and lead teams, and even link several teams and departments together (they house external relationships). They help team members plan and schedule work, learn problem-solving methods, and work effectively with workers. They foster internal and external relationships.
The best example of team leaders is Walmart’s Team Leads. They are the head of a group of workers, but not necessarily in charge of the workers’ duties outside of setting up work schedules.
Practice Question:
How would your job differ at a small manufacturing facility if you were a first-line manager compared to a team leader?
First-line manager: You would only take care of your own unit.
Team Leader: You work with other departments and facilitate external relationships between departments.
What are the types of Managerial Interpersonal roles?
Figurehead role, Leader role, Liaison Role
What is a Figurehead role?
Managers form ceremonial duties.
Ex: Steve Jobs would unveil every new iphone.
What is a Leader role?
Managers motivate and encourage workers to accomplish goals.
What is a Liaison role?
Managers deal with people outside their units.
Ex: Elon Musk collaborated with NASA for spaceX and other car companies for Tesla.
What are the types of managerial Informational Roles?
Monitor role, Disseminator role, Spokesperson role
What is a monitor role?
Managers ability to understand and obtain info. They scan their environment, contact others, and receive unsolicited details all for information.
What is a disseminator role?
Managers share collected information with subordinates and the company (Interpreting and informing those around them).
What is a spokesperson role?
Managers share information with people outside their departments or companies.
What are the managerial decisional roles?
Entrepreneur role, Disturbance handler role, Resource allocator role, and Negotiator role.
What is the Entrepreneur role?
Managers adapt themselves, their subordinates, and their units to incoming change. This is an innovative position to keep the company new.
What is the disturbance handler role?
Managers response to pressures and problems that demand immediate attention and actions. This is a crisis management role, for responding to problems.
What is the resource allocator role?
Managers decide who gets what resources and in what amounts. This role decides budgets and helps prioritize certain departments.
What is the negotiator role?
Managers negotiate schedules, projects, resources, goals, outcomes, and employee raises. These fight for the benefit of employees.
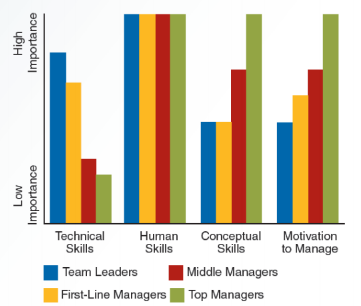
What are the four Managerial skills?
Technical, Human, Conceptual skills, and Motivation to manage.
What are technical skills?
Technical skills are specialized procedures, techniques, and knowledge required to get jobs done. These are your applied skills such as knowing HOW to perform company actions (such as accountants knowing how to fill out and file documents right).
These are essential for lower level managers and are less important the higher up the corporate ladder.
What are human skills?
Human skills are just interpersonal skills and the ability to work well with others. These are communication skills, professionalism, etc.
These are essential for all levels of management.
What are conceptual skills?
These are the ability to “understand the bigger picture”. You see the organization as a whole, understand how different parts interact with each other, and how the company fits into its environment.
What is the motivation to manage?
This is the assessment of how enthusiastic employees are about managing the work of others.
Know the importance of management skills across all 4 levels of mangement.
(Picture on back).
Out of the top 10 mistakes managers make, what are the “Fatal Flaws”?
There are 6:
Insensitivity to others: abrasive, intimidating, bullying style
Cold, aloof, arrogant
Betrays trust
Overly ambitious: thinking of next job, playing politics
Specific performance problems with the business
Overmanaging: unable to delegate/build a team
Out of the top 10 mistakes managers make, what are the NOT fatal flaws?
There are 4
Unable to staff effectively
Unable to think strategically
Unable to adapt to boss with different style
Overdependent on advocate or mentor
What are the stages in transitioning to management?
Initial Expectations:
Be the boss
Formal authority
Manage tasks
Job is NOT managing people
After 6 months:
Fast paced
Heavy workload
Job is to be the problem solver and troubleshooter
After 1 year:
No longer a doer
Communication, listening,e tc.
Learning to adapt & control stress
Job is people development
What are the competitive advantages gained through people? Know what they mean
Employment security
-You will not be fired over little things. Establishes trust.
Selective Hiring
-Only top notch employees are initially hired.
Self-managed Teams & Decentralization
-Teams are responsible for their own hiring, purchasing, etc. Employees close to the problems make the decisions.
High wages contingent on organizational performance
-Encourages talented workers to apply to the job and retain their positions. Financial stakes in the company mean they have stuff to lose if they leave or if the company performs poorly.
Training and skill development
-Cares about employees growth.
Reduction of status differences
-The company treats everyone as equals, which improves communication and values employees.
Sharing information
-Employees are knowledgeable about the company itself. There is transparency in information sharing.
What is the staffing process?
Staffing outcomes determines who works for the firm. It influences the success of future training, performance management, and compensation.
Defining requirements of competitive resources:
Valuable, Rare, Imperfectly imitable, Non-substitutable
What are the effects of competitive advantages through people?
Helps develop smarter, better trained, more motivated workforces.
Produces advantages in revenue, profits, stock market returns, and employee/customer satisfaction.
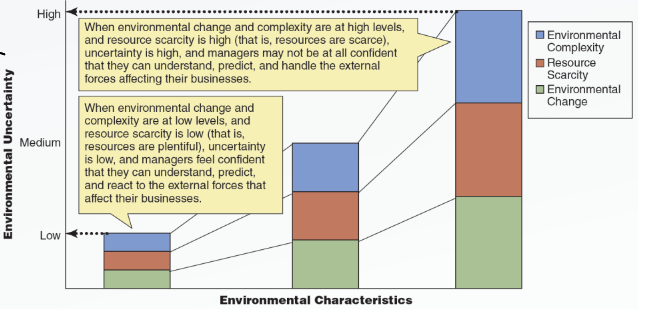
What is a companies external environment and its basic characteristics?
All events outside a company that can influence or affect it.
Environmental change, environmental complexity, and resource scarcity are all basic characteristics.
What is environmental change?
The rate at which a company’s general and specific environments change.
Stable environment: Slow rate of change
Dynamic environment: High rate of change
What is Punctuated Equilibrium theory?
Companies go through long period of stability during which incremental changes occur, followed by short periods of dynamic, fundamental change. This is then followed by a new equilibrium.
What is environmental complexity?
The number and intensity of external factors in the environment that affect organizations.
Simple environment: Few factors
Complex environment: Many factors
What is Resource Scarcity?
The abundance or shortage of critical organizational resources in an organization’s external environment. This is like the balance of supply vs demand.
What is Resource Uncertainty?
This is the extend to which managers can understand or predict which environmental changes and trends will affect their businesses. This is a byproduct of environmental complexity, resource scarcity, and environmental change.
What is a company’s General Environment?
The economy, technological, sociocultural, political/legal trends that all INDIRECTLY affect ALL organizations.
These general environment trends are vague & conceptual.
What does the Economy say about a company’s General environment?
Growing economy’s are favorable for business growth, as consumers have more money to spend.
What is the Business Confidence Indices?
It is the statistic from ACTUAL managers’ opinions of the confidence about future business growth. This is different from GDP, LPI, etc. because it is about general opinions and is NOT a calculated statistic.
What is the Technological component of a company’s General Environment?
Technology helps change companies to provide better produce and to produce them more efficiently. It must be used effectively to improve products or decrease costs.
Companies must maintain advancements or become outdated.
What is the Sociocultural component of a company’s General Environment.
It consists of demographic characteristics, general behavior, attitudes, and beliefs of people in society.
Changes in demographic characteristics affects how companies staff.
Ex: How would various industries be affected if Christmas was no longer celebrated? How would companies such as TJ Max or Best Buy be affected?
What is the Political/Legal component of a company’s General Environment.
This will include legislation, regulations, and court decisions that govern and regulate business behavior. Managers must be aware of these.
What is a company’s Specific Environment?
These are elements unique to an industry and DIRECTLY affecting how a company does business.
What is the Customer Component of a company’s Specific Environment?
Customers purchase products and services. Companies cannot exist without them. There are two strategies for monitoring customers.
Reactive: Identifies and addresses customer trends and problems AFTER they occur (such as listening to feedback) (Passive, responsive).
Proactive: Identifies and addresses customers needs trends and issues BEFORE they occur (Active sometimes inaccurate though).
What is Competitive Analysis?
It is the process for monitoring the competition that involves indentifying competitors, anticipating their moves, and determining their strengths/weaknesses.
What are Suppliers?
Suppliers are companies that provide material, human, financial, and informational resources to companies.
What is Buyer/Supplier Dependence?
Supplier dependence: The degree to which a company relies on a supplier because of the importance of the suppliers product to the company and the difficult of finding other sources.
Buyer dependence: The degree to which a supplier relies on a buyer because of the importance of that buyer to the supplier and the difficulty of finding other buyers.
What is Opportunistic vs Relationship behaviors for suppliers?
Opportunistic behavior is where one party benefits at the expense of the other.
Relationship behavior is the establishment of a mutually beneficial, long-term exchange between a set buyer and supplier.
What is Industry Regulation?
Regulations and rules that govern business practices and procedures of specific industries. Industry standards then push innovative standards.
What are Advocacy Groups?
Concerned citizens who group up to influence business practices.
What are the techniques used by Advocacy Groups?
Public Communications: Relies on voluntary participation by news and the advertising industry to send a message out.
Media advocacy: Involves framing issues as public issues, and exposing questionable practices.
Product boycott: Protests company’s actions by persuading consumers to not purchase from the company.
What is Environmental Scanning?
Searching the environment for important events or issues that may affect an organization. This helps managers stay up-to-date, affects the development of organizational strategies, and contributes to business performance.
What are Cognitive maps?
Graphic depictions of how managers believing environmental factors relate to organizational actions.
What is a Company’s Internal Environment?
Events and trends inside of an organization that affect management, employees, and organizational culture.
What is Organizational Culture?
Values, beliefs, and attitudes shared by organizational members.
Contains:
Organizational Stories: Stories told by organizational members to make sense of organizational events and changes and to emphasize culturally consistent assumptions, decisions, and actions.
Organizational heroes: People celebrated for their qualities and achievements within an organization.
Organizational ceremonies: Gatherings in which symbolic acts commemorate or celebrate notable achievements or changes.
What are aspects of a Successful Organizational Culture?
Company mission: A company’s purpose or reason for existing
Consistent organizational culture: A culture in which the company actively defines and teaches organizational values, beliefs, and attitudes.
What are the aspects of organizational culture that managers can control?
Behavioral addition: The process of having managers and employees preforming new behaviors that are central and symbolic to new organizational cultures that a company wants to create.
Behavioral substitution: The process of having managers and employees preforming new behaviors that are central and symbolic to new organizational cultures in place of behaviors central to old cultures.
Visible artifacts: Visible signs of an organization’s culture, such as office design, company dress code, etc.
What is Planning? What are its benefits and pitfalls?
Choosing a goal and developing a strategy to reach the goal.
Benefits: People work harder to reach goals. They are more persistent & have direction. It also encourages the development of task strategies.
Pitfalls: Impedes change, as it prevents/slows any needed changes. It also creates a false sense of certainty. Finally, it leads to detachment of planners (planners may not think of everything).
What are the steps to making a plan that works?
Set goals
Develop commitment
Develop effective action plans
Track progress towards goal
Maintain flexibility
What are SMART goals?
Goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely.
What is goal commitment and its techniques?
The determination to achieving a goal. It includes setting goals participatory, making the goal public, and obtaining top management’s support.
What are the methods to track progress?
Setting both Proximal and Distal goals.
Proximal is short term goals, or sub-goals (think close PROXIMity to the goals).
Distal goals are long-term or primary goals (think there is a large DISTAnce from the goal).
How do you Maintain Flexibility when planning?
Options-based planning: Constantly make small changes to the plan throughout development.
Slack resources: Add a cushion of extra resources that can be used for options-based planning to account for any unanticipated changes, problems, or opportunities.
What are the levels of planning, and what level of management do they apply to?
Top management : Mission
Middle Managers: Tactical plans, management by objectives
First-level managers: Operational plans, Standing plans, single-use plans
What are Strategic plans?
Plans made by top management. They clarify how the company serves customers and positions itself for the next 2-5 years.
Includes a purpose statement for a company’s purpose/reason to exist.
Includes a strategic objective, which is a more specific goal to unify the company’s efforts, challenge the organization, and give the company a finish line.
What is the difference between a purpose statement and a strategic objective?
Purpose statements are vague and loosely describe the company’s goals.
Strategic Objectives will be very specific, often with numbers and a short time frame. These are REALISTIC goals such as “Raise the average amount of product sold by x% in the next 6 months”
What are Tactical Plans?
Plans created and implemented by middle managers that direct behavior, efforts, and attention over the next 6 months to 2 years.W
What is management by objectives?
A four step process in which managers/employees:
Discuss possible goals
Collectively select goals
Develop tactical plans
Meet regularly to review progress
What are Operational plans?
There are three types:
Single-use, Standing, and Budgets
They are day-to-day plans that are developed and implemented by lower-level managers for producing or delivering organization’s products and services over 30-day to 6-moth period.
Describe the types of Operational Plans.
Single-use plans: Plans that cover unique, one-time only events (like Buffalo Wild wings giving free wings to people since the Superbowl went into overtime).
Standing plans: Plans used to repeatedly handle frequently recurring events (like tornado plans).
Budgeting: Quantitative planning to which managers decide how to allocate available money.
What are the types of Standing Plans?
Policies: Standing plans that indicate the general course of action.
Procedures: Standing plans that indicate specific steps to be taken in response to a particular event
Rules and Regulations: Standing plans that describe how a particular action should be performed or what must not happen in response to a particular event.
What is decision-making vs rational decision making?
Decision-making: Choosing a solution from a list of available alternatives.
Rational decision-making: A systematic process of defining problems, evaluating alternatives, and choosing optimal solutions.
What are the steps of the Rational Decision-making process?
Define the problem (Gap between a desired state and existing state). Managers must be aware of the problem, be motivated, and be capable of fixing it.
Identify decision criteria (the standards used to gu ide judgements/decisions)
Weigh the criteria (Absolute or Relative comparisons)
Generate alternative courses of action
Evaluate each alternative against each criterion systematically
Compute the optimal decision (weighted average of each criterion x weight, sum the scores).
What are the limits to the rational decision-making process?
Managers don’t operate in a perfect world.
Managers face resource constraints as well as human restraints.
Maximization: Choosing the best alternative.
Satisficing: Choosing a “good-enough” alternative.
What is the advantage of group decision-making?
Groups perform better as individuals in defining the problem and generating alternative solutions.
What are the pitfalls of group decision-making?
Groupthink: a barrier to good decision-making caused by pressure within the group for agreement
Takes Time
Individuals can dominate discussion
Equality bias
When is groupthink likely to occur?
When the group is insulated from those with different perspectives
The group leader provides a strong preference towards one decision
The group has no procedure for defining problems
Group members are too similar
What are the two types of structured conflict?
C-type conflict (Cognitive/Constructive): Disagreement that focuses on PROBLEM and ISSUE related differences.
A-type conflict (Affective): Disagreement focused on INDIVIDUALS or PERSONAL issues.
What are the methods of creating C-Type conflict?
Devil’s advocate: A decision making method where an individuals assigned role is to disagree with others. (The role of a critic).
Dialectical inquiry: A method where the decision makers state the assumptions of a proposed solution and generate a solution that is the opposite of the solution (thesis vs antithesis).
What is the Nominal Group Technique?
A method that begins and ends by having group members separately write down and evaluate ideas to share with the group.
What is the Delphi technique?
A method in which members of a panel of experts respond to questions and to each other until agreement is reached.
What is Brainstorming vs Electronic Brainstorming?
Brainstorming: Group members build on each others’ ideas to generate alternative solutions
Electronic Brainstorming: A method in which group members use computers to brainstorm ideas.
What are the pros/cons of Electronic brainstorming?
Electronic Brainstorming: A method in which group members use computers to brainstorm ideas.
Pros: Helps overcome production blocking (waiting to share an idea due to lack of face-to-face) and evaluation apprehension (fear of others’ opinions on your ideas). It is anonymous and is more productive as well.
Cons: Expense of computers, network, software. Also has the challenge of writing rather than speaking ideas.
What are resources?
The assets, capabilities, processes, employee time, information, and knowledge used by an organization to improve effectiveness/efficiency and create and sustain competitive advantages.
What is a competitive advantage?
Providing greater value for customers than competitors can (Malleable - can change over time)
What is a sustainable competitive advantage?
A competitive advantage that other companies have tried to unsuccessfully duplicate and have, for the moment, stopped trying to duplicate. PROTECTED COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE! LENGTH OF TIME DOES NOT MATTER.
What are the aspects of a sustainable advantage?
Valuable resources: Allows companies to improve effectiveness/efficiency (But this may degrade over time)
Rare resources: Not controlled/owned by many firms
Imperfectly imitable resource: Impossible or costly or difficult for other firms to duplicate.
Nonsubstitutable resource: Produces value or competitive advantage and has no equivalent substitutes/replacements.
What are the three steps of the Strategy-Making Process?
Assess need for Strategic Change (Avoid competitive interia, look for strategic dissonance)
Conduct Situational Analysis (SWOT Anal.)
Choose Strategic Alternatives (Risk avoiding/Risk seeking)
What is Competitive Intertia?
A reluctance to change strategies or competitive practices that have been successful in the past (market resistance to change).W
What is Strategic Dissonance?
A discrepancy between a company’s intended strategy and the actual steps taken by managers to implement the strategy.
What is a SWOT analysis?
Two parts:
Internal:
Stengths
Weaknesses
External:
Opportunities
Threats
What is a company’s distinctive competence?
What a company can do that is better than its competitors (what makes it unique?)
What is a company’s core capabilities?
The internal decision-making routines, problem-solving processes, and organizational cultures that determine how efficiently inputs can become outputs. (What makes it run efficiently)
What is a stragetic group?
A group of companies within an industry against which top managers compare, evaluate, and benchmark strategic threats and opoprtunities.
What are core firms?
The central companies within a strategic group (essential companies)
What are secondary firms?
The non-central companies within a strategic group (quirky firms)