metabolism 2/fermentation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
explain the problem with anaerobic metabolism that fermentation adresses
-without oxygen, cells can’t regenerate NAD+ through the electorn transport chain
-fermentation solves this by converting NADH back into NAD+ for ATP production
recall the two types of fermentation discusses + products
alcohol fermentation/yeast: produces ethanol, co2 and NAD+
Lactic acid fermentation: produces lactic acid and NAD+
what are the 4 main tissue classes
epithelial
connective
muscle
nervous
recall the 3 types of muscle
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle
describe skeletal muscle: voluntary or not, striated or not, multinucleated or not or other
voluntary, striated, and multinucleated
describe cardiac muscle: voluntary or not, striated or not, multinucleated or not or other
involuntary, striated, single nucles so not multinucleated, interacalated discs
describe smooth muscle: voluntary or not, striated or not, multinucleated or not and what kind of shaped cells
involuntary, not striated, single nucleus, spindle shaped cells
recall the path of blood flow thorugh the heart
right atrium
right ventricle
pulmonary arteries
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atrium
left ventricle
aorta
body
what is the pulmonary circuit
carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and brinds oxygenated blood back to the heart
define systemic circuit
carries oxygenated blood fromt he heart ot the body and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart
descibe the physical movments that correlate to heartbreat: atrial contraction, ventricular contraction, and relaxation
(just keep in mind don’t memorize)
Atrial contraction/systole: pushes blood into ventricles
ventricular contraction/systole: sends blood to lungs/body
relaxation/diastole: allows chambers to refill with blood
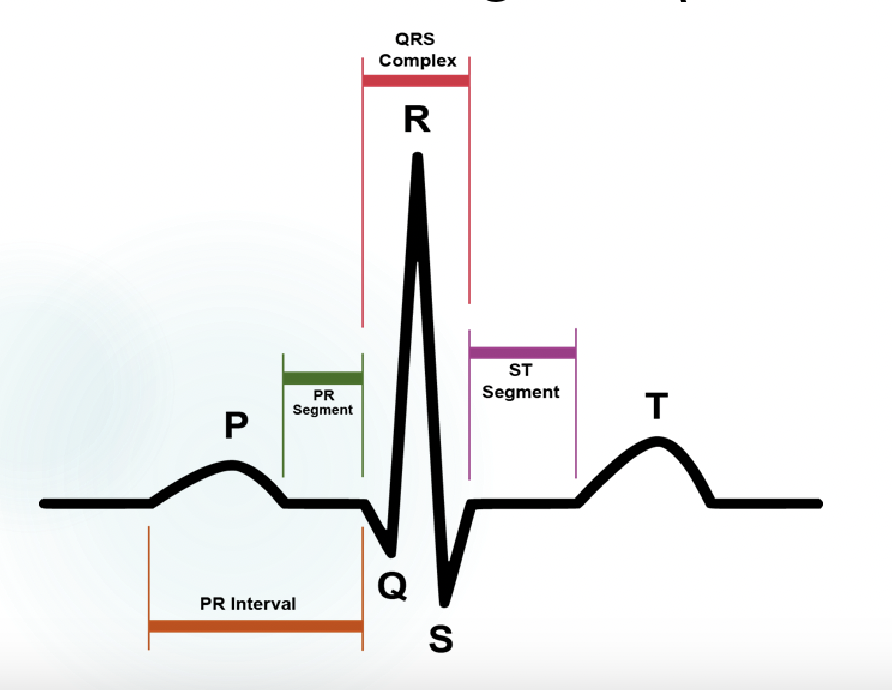
explain what is happening at P, QRS, and T
-p wave: atrial contraction
-QRS complex: ventricular contraction
T wave: ventricular relaxation
what is the optimaal temperature for fermentation by yeast
around 37 C
describe the effects of temperate on feremntation by yeast
too cold, yeast metabolism slows down, less CO2 production
too hot: enzymes denature, yeast can die, stoppinc CO2 production
optimal: speeds up fermentation and produces the most CO2 w
which sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharide
mon:glucose, fructose, galactose
di:sucrose, and lactose, maltose
describe the differences in how yeast ferments monosaccharides and disaccharides
yeast ferments monosaccharides more easily bc they don’t require extra breakdown into monosacharides
disacchardies must be broken down into monosaccharides before fermentation, which slows down the process
what ar ethe 4 chambers of hte heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle
waht are the vessels in the heart
pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, aorta, and vena cava
what are the two types of anaerobic respiration
lactic and alcohol
alcohol fermentaiton produces ___ molecules of ATP, ____ moleculs of CO2 and ___ molecules of ethanol per glucose
2, 2, 2,
lactic acid fermentation will produce ____ molecules of ATP and ____ molecules of lactic per glucose
2, 2
In lactic acid fermentaiton, what enzyme produces pyruvate
lactate dehydrogenase
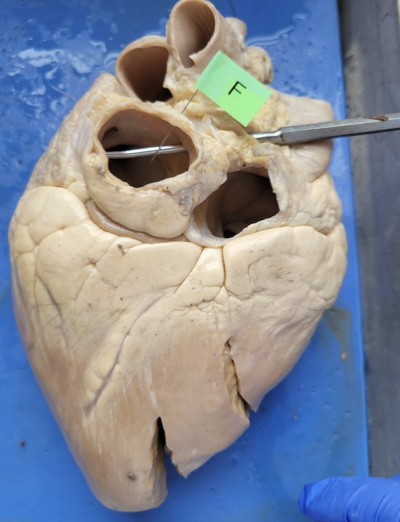
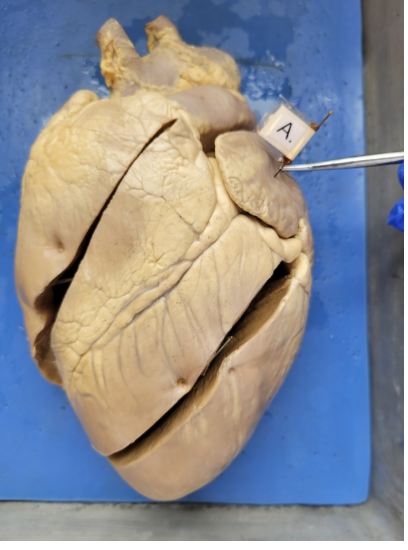
what is this
the left atrium
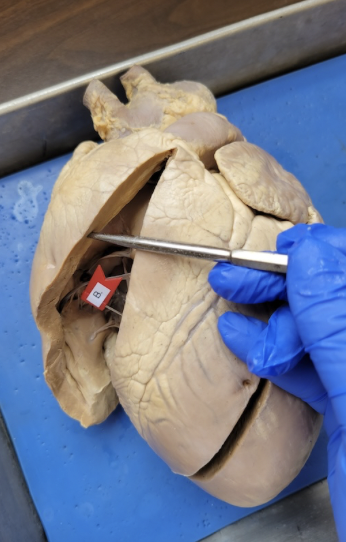
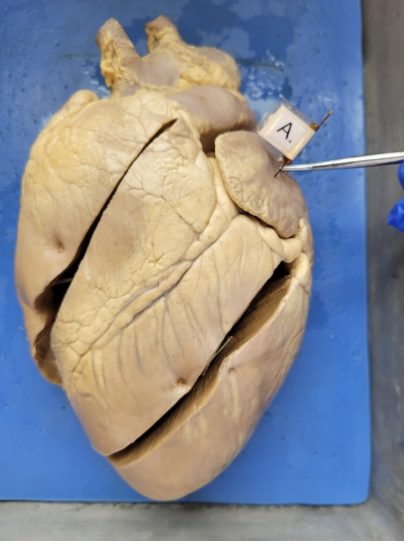
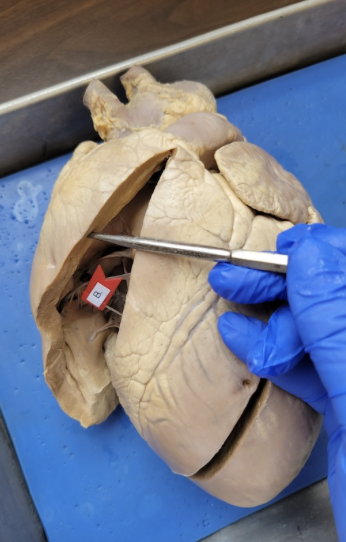
what is this
right ventricle
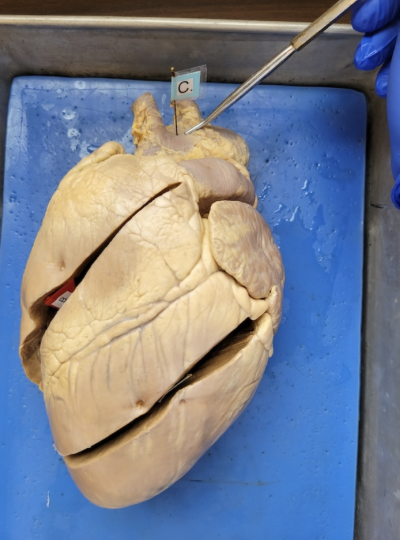
what is this
Aorta
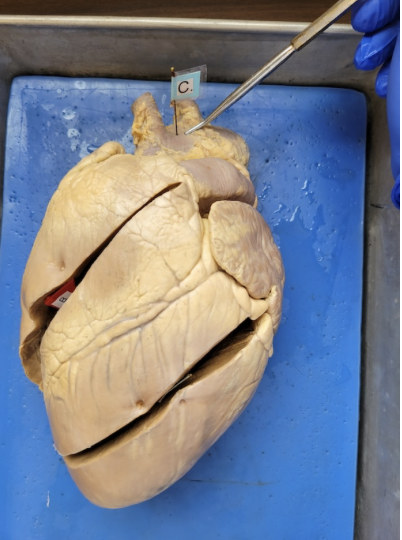
what is this
the left ventricle
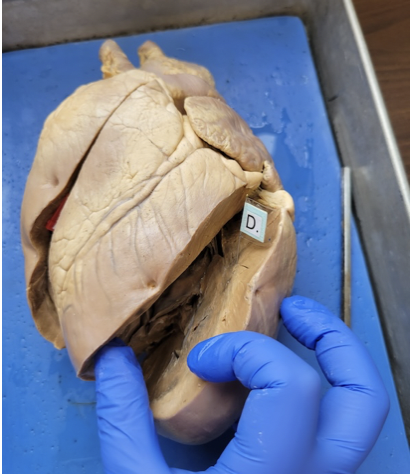
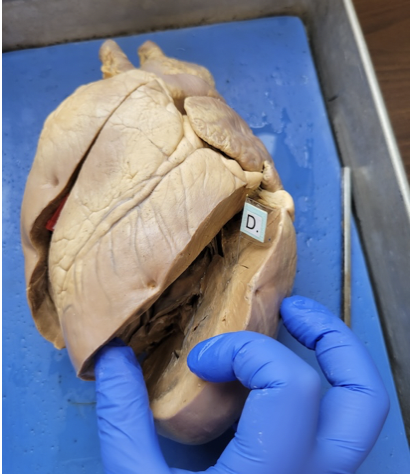
what is this
pulmonary artery
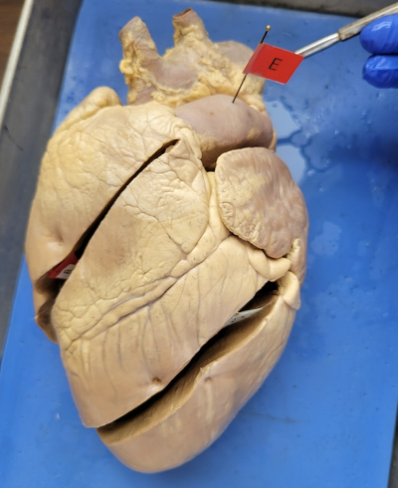
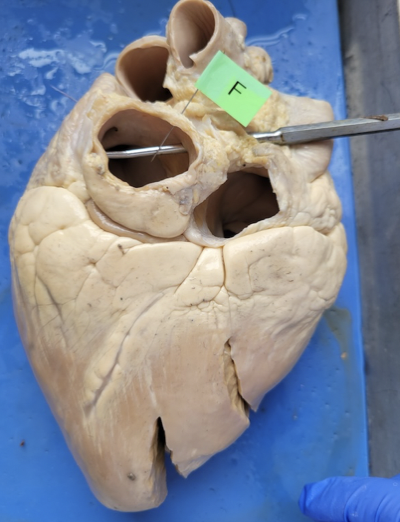
what is this
pulmonary vein