ECO 252 AD & AS Model
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
The most important determinant of consumption is
the current disposable income
(not interest rate,
price level,
nor household wealth)
Which of the following causes saving to increase
an increase in the interest rate
(not increase in consumption,
increase in price level,
increase in unemployment)
Which one of the following is not a determinant of consumption spending
The growth rate in the United States relative to the growth rates in other countries
( not household wealth,
current disposable income,
nor interest rate)
A rise in stock prices and housing prices
increases household wealth which in turn increases consumption and leads to an upwards shift of the consumption function
( not increases household wealth which in turn increases consumption and leads to an upward movement along the consumption function,
does not affect consumption because they do not have any direct impact on disposable income,
reduces consumption due to increase in prices and causes the consumption function to shift downward )
The existence of unemployment insurance makes it _______ that consumption will fluctuate over the business cycle.
less likely
because with unemployment insurance, current disposable income fluctuates less over the business cycle
( not with unemployment insurance, household wealth fluctuates less over the business cycle,
with unemployment insurance, business investment fluctuates less over the business cycle,
with unemployment insurance, interest rates are unlikely to change with the business cycle)
An increase in the price level
decrease consumption
An increase in household wealth
increase consumption
An increase in expected future income
increase consumption
An increase in current disposable income
income consumption
An increase in the interest rate
decrease consumption
What are the four main determinant of investment?
expectation of future profitability
interest rates
taxes
cash flow
How would an increase in interest rates affect investment
Real investment spending declines
The behavior of consumption and investment over time can be describes as follows
Consumption follows a smooth, upward trend, but investment is subject to significant fluctuations
Which of the following statements about investment spending is correct?
The optimism of pessimism of firms is an important determinant of investment spending.
When the economy moves into a recession, many firms will postpone buying investment goods even if the demand for their own product is strong.
A higher real interest rate results in less investment spending.
Which of the following statements is correct?
An increase in the corporate income tax decreases the after-tax profitability of investment spending.
During periods of recession, the ability of firms to finance spending on new factories or machinery and equipment increases.
( not correct: Changes in tax laws have no effect on investment spending.)
Which of the following will increase planned investment spending on the part of firms?
Increased optimism about future demand for its product
A lower real interest rate
(will not increase: Increases in the corporate income tax)
Which of the following is NOT included in the calculation of total government purchases?
Unemployment insurance benefits paid for by the federal government
(things that are included:
The salaries of high school teachers paid for by state government,
A new interstate highway purchased by the federal government,
A local government installs a new stop sign)
Which of the following is not a main determinant of net exports?
Expectations of future profitability in the United States.
( Is a determinant:
The price level in the United States relative to price levels in other countries,
The growth rate of GDP in the United States relative to the growth rates of GDP in other countries,
The exchange rate between the dollar and other currencies.)
How would an increase in the growth rate of GDP in Canada and Mexico affect U.S. net exports?
An increase in the growth rate of GDP in Canada and Mexico will
increase U.S. net exports by increasing exports to these countries
Which of the the following is NOT a determinant of net exports?
The Interest rate
( Is a determinant:
the growth rate if US GDP relative to growth rates of other countries,
The growth rate of the U.S. price level relative to price levels of other countries,
The exchange rate between the dollar and other currencies)
Consider the following four statements.
i. The iPhone is made in China, using Chinese-made parts.
ii. The iPhone is made in the United States, using U.S.-made parts.
iii. The iPhone is made in the United States, using Chinese-made parts.
iv. The iPhone is made China, using parts that are all made outside of China.
Which of the statements above is correct?
What relevance does your answer have to how the Bureau of Economic Analysis calculates data on U.S. imports?
Statement iv is correct. The iPhone is assembled in China using parts shipped to China from many countries.
Relevance: Producers increasingly rely on global supply chains, so there are flaws in accounting for imports and exports.
An increase in the US price level relative to other countries’ price levels
decrease net exports
An increase in the growth rate of US GDP relative to other countries
decrease net exports
An increase in the exchange rate between the dollar and other currencies
decrease net exports
If inflation in the United States is lower than inflation in other countries, then U.S. exports ________ and U.S. imports ________, which _________ net exports.
increase; decrease; increases
When incomes rise faster in the United States than in other countries,
US net export will fall
Which of the following statements is correct if real GDP in the United States had declined by more during the 2020 recession than did real GDP in Canada, China, and other trading partners of the United States?
Imports to the United States would have fallen more than the U.S. exports, leading to an increase in net exports.
A depreciation in the domestic currency will
increase exports and decrease imports, thereby increasing net exports.
Foreign households and foreign firms demand U.S. dollars in exchange for foreign currency for all of the following, except
when U.S. firms and households want foreign currencies so that they can buy goods and services produced in those foreign countries.
( false:
when foreign firms and households want to invest in the United States either through foreign direct investment or through foreign portfolio investment.,
when currency traders want dollars because they expect that the value of the dollar in the future to be greater than its current value ,
when foreign firms and households want dollars so that they can buy goods and services produced in the United States.)
U.S.households and U.S. firms supply U.S. dollars in exchange for foreign currency
if the interest rate and other conditions in the foreign countries are lucrative for U.S. firms and households to invest dollars.
When the euro was introduced in January 1999, the exchange rate was $1.19 per euro. In December 2024, the exchange rate was $1.05 per euro.
For U.S. firms exporting goods and services to Europe, this change in the value of the euro was
bad news because one euro would buy fewer dollars, making U.S. goods more expensive for European buyers.
On May 01, 2025 (shown as 2025 minus 05 minus 01 in FRED), the pound was trading at $ 1.3358 per pound. On May 01, 2024 (shown as 2024 minus 05 minus 01 in FRED), the pound was trading at $ 1.2636 per pound. This is
an appreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar.
Given the change in the exchange rate between November and December, did U.S. imports from Japan change in a way that economic theory would predict?
It went from $12,077.98286 million to 12,452.25728 million for US Imports from Japan
Yes. Since the dollar appreciated against the yen, economic theory would predict that U.S. imports from Japan would increase.
Given the change in the exchange rate between December and January, did U.S. exports to Japan change in a way that economic theory would predict?
US Exports to Japan went from 6462.36402 million to 6014.23938 million
Yes. Since the dollar appreciated against the yen, economic theory would predict that U.S. exports to Japan would decrease.
The U.S. aggregate demand curve slopes downward due to all of the following reasons
wealth effect, where a change in the price level affects consumption.,
interest-rate effect, where a change in the price level affects investment,
international-trade effect, where a change in the price level affects net exports.
(Not b/c of government-spending effect, where a change in the price level affects government purchases.)
Compared to the U.S. aggregate demand curve, the reason that the demand curve for an individual product, such as bananas, slopes downward is
different, because consumers can substitute between individual products.
An economics student makes the following statement:
"It's easy to understand why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping: When the price level increases, consumers substitute into less expensive products, thereby decreasing total spending in the economy."
This statement is false because the aggregate demand curve is
downward sloping because as prices rise, consumer real wealth declines, interest rates rise, and exports become more expensive.
The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between
the price level and output demanded
The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because
an increase in the price level reduces real money holdings, which reduces the amount of expenditures.
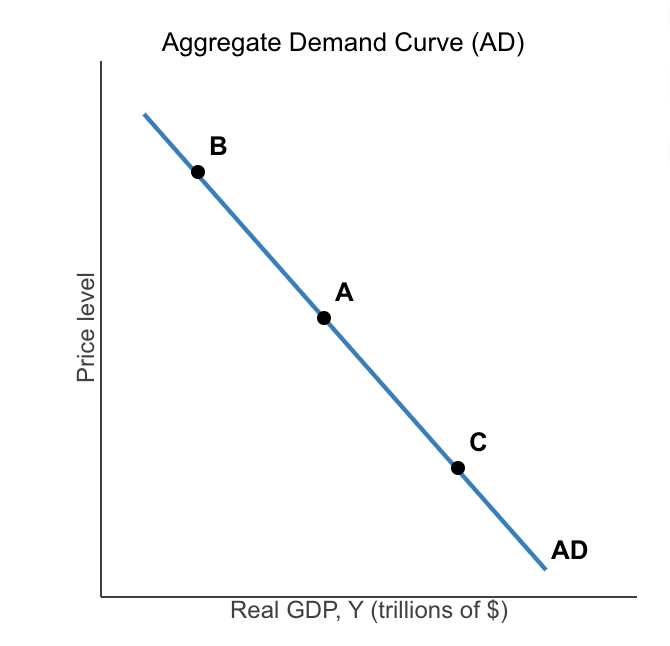
Consider the downward-sloping aggregate demand (AD) curve to the right. Which of the following results in a movement from point A to point B (a movement up along the AD curve) or from point A to point C (a movement down along the AD curve)? (Mark all that apply.)
Interest rate effect and wealth effect
(Not Inflation effect , nor multiplier effect)
Milovia is a small open economy. The general price level in the economy has been increasing at a rate of about 7.5 percent each year. Jane Wilson, an industry analyst, is of the opinion that such high inflation is adversely affecting aggregate demand in the economy and therefore its ability to grow. Her colleague, Harry Gomes, however, disagrees. According to Harry, some amount of inflation is unavoidable in a growing economy. Higher prices for products help to increase the level of corporate profits and induce firms to increase aggregate output.
Jane's argument is based on which of the following assumptions?
The purchasing power of nominal assets declines with an increase in the price level.
The wealth effect refers to the fact that
when the price level falls, the real value of household wealth rises, and so will consumption.
The interest rate effect refers to the fact that a higher price level results in
higher interest rates and lower investment.
The international-trade effect refers to the fact that an increase in the price level will result in
a decrease in exports and an increase in imports.
Which of the following would cause a decrease in aggregate demand?
a decrease in government spending
(Not a depreciation in the U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies,
a decrease in interest rates through monetary policy,
a decrease in taxes)
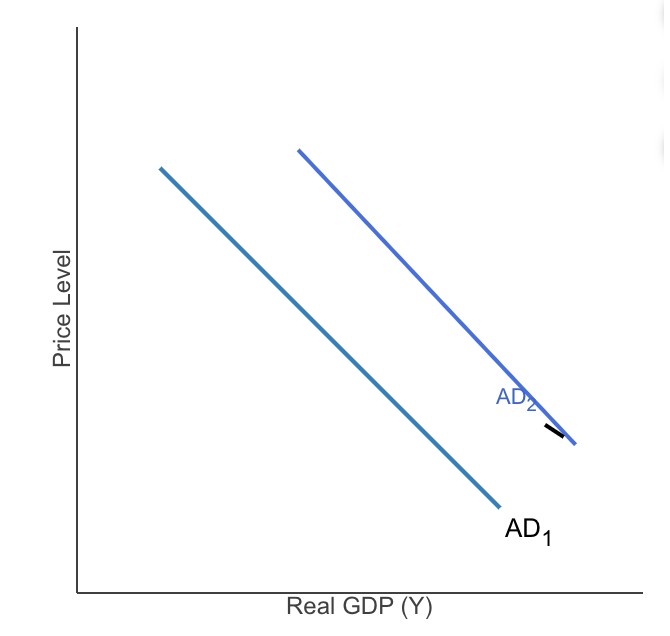
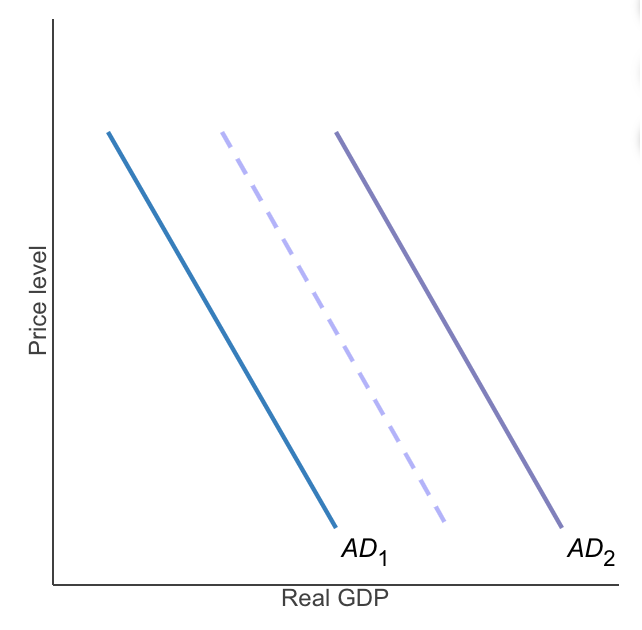
The graph to the right shows the aggregate demand curve for an economy AD1
The effect of a monetary policy change that causes a decrease in interest rates AD2
_________ would cause a similar shift in the aggregate demand curve.
A decrease in taxes
An increase in the price level will cause a
movement up along the aggregate demand curve
An increase in government purchases will cause a
rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
An increase in state income taxes will cause a
leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
An increase in interest rates will cause a
leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
A faster income growth in other countries will cause a
rightward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
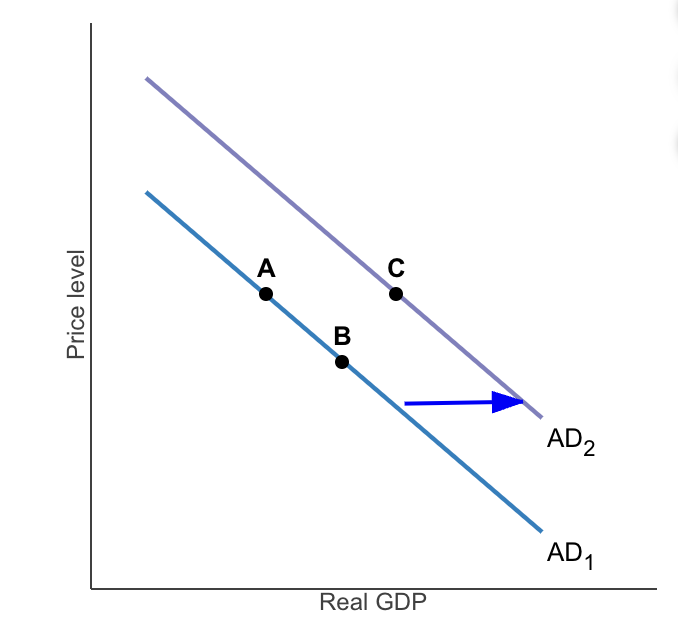
A movement from point A to point B on AD Subscript 1 could be the result of a
change in the price level
(NOT natural disaster, change in the cost of production, nor change in government policies)

A movement from point A to point C could be the result of a
change in the expectation of households
(Not change in the cost production, natural disaster, nor change in the price level)
Firms become more optimistic and increase their spending on machinery and equipment. Because this is a change in
investment, it will cause a shift to the right in the aggregate demand curve.
The federal government increases taxes in an attempt to reduce a budget deficit. Because this is a change in
consumption, it will cause a shift to the left in the aggregate demand curve.
The U.S. economy experiences 4 percent inflation. Because this is a change in
the price level, it will cause a movement along the aggregate demand curve
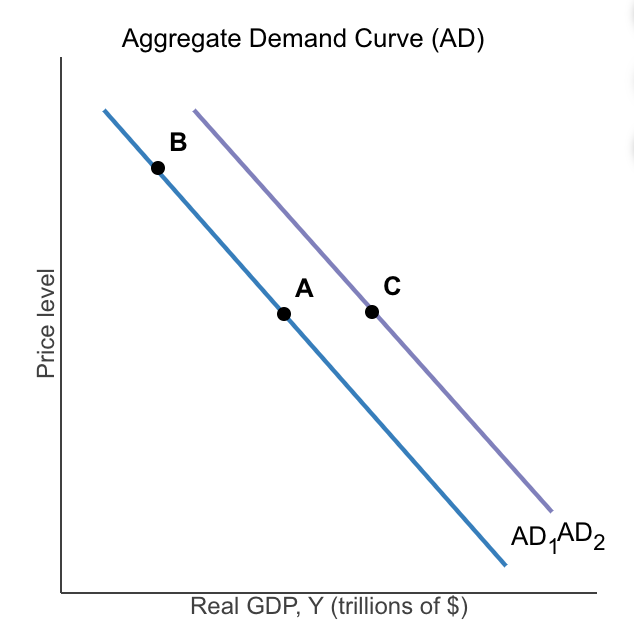
In the diagram to the right, moving from point A to point B is called a
movement along the AD curve.
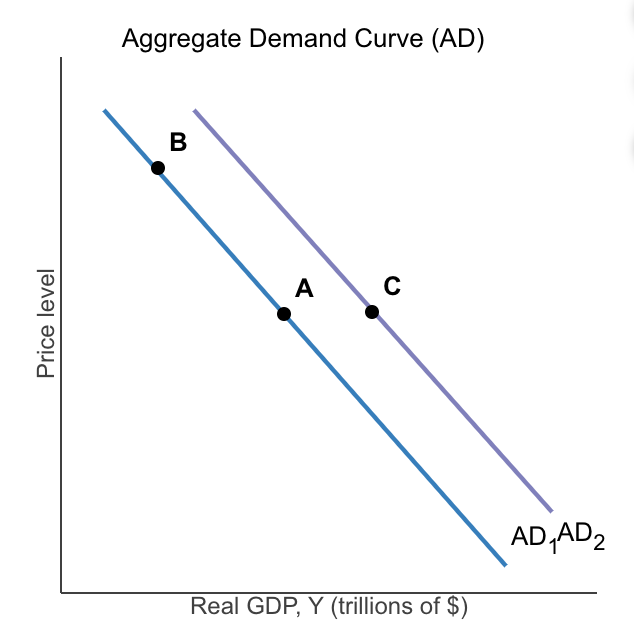
Moving from point A to point C is referred to as a
shift in the AD curve.
Which of the following would cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve from point A to point C
Lower interest rates, decrease in the US exchange rate relative to other currencies, lower taxes, increased consumer optimism
(Not Inflation, nor decrease in the price level)
Which of the following factors does not cause the aggregate demand curve to shift?
a change in price level
(Does cause a shift:
a change in foreign variables, a change in government monetary or fiscal policies, a change in the expectations of households and firms)
How can government policies shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
by increasing government purchases
(Not by increasing business taxes, nor by increasing personal income taxes)
The country of Cubania was adversely affected by the global recession of 2008. David Oster, a sociology professor at the University of Cubania, is of the opinion that tax rates on wealthy individuals should be lowered. Since the wealthy have a higher level of income, a tax cut would significantly increase consumption and aggregate demand.
Which of the following would weaken David's argument that tax cuts for the wealthy would increase consumption and aggregate demand?
Economic research shows that wealthy individuals have a high marginal propensity to save.
The multiplier represents the
total amount of additional increases in consumption spending induced by an initial change in aggregate expenditure.
According to the multiplier effect, an initial increase in government purchases increases real GDP by
more than the initial increase in government purchases.
The formula for the multiplier is
1/ (1 - MPC)
The value of the multiplier is larger when
the value of the MPC is larger.
If there is an increase in the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), then
the value of the expenditure multiplier will increase.
Indicate which of the following is correct about the multiplier effect.
A decrease in autonomous spending decreases real GDP by a multiple of the change.
The multiplier ignores the effect on real GDP of imports, inflation, and interest rates.
The larger the MPC, the more additional consumption that occurs.
An MPC equal to 0 implies a multiplier of 1, meaning that a $1 increase in autonomous expenditures would increase real GDP by only $1.
Why does an MPC of 0 result in no multiplier effect? Explain your answer using the logic of the multiplier process.
When the MPC is 0, any additional income does not induce any additional consumption spending.
Conversely, an MPC equal to 1 implies an infinite multiplier, meaning that a $1 increase in autonomous expenditures would increase real GDP by an infinite amount.
Why does an MPC of 1 result in an infinite multiplier? Explain your answer using the logic of the multiplier process.
An MPC of 1 means that any additional income induces a matching increase in consumption spending, which leads to a matching increase in income, and so on.
Why does a $1 increase in government purchases lead to more than a $1 increase in income and spending?
Through the government purchases multiplier, the $1 increase in government spending will lead to
an increase in aggregate demand and national income, which will lead to an increase in induced spending.
Another infrastructure project in northern California funded in part by ARRA funds involved expanding the Caldecott Tunnel between the cities of Oakland and Orinda.
A spokesperson for the California state agency in charge of the project mentioned that the Caldecott tunnel project would have a "ripple effect" on employment. The ripple effect meant that
the job creation would spread to other industries and eventually to the whole economy due to the consumption of the construction workers.
An opinion column in the New York Times quotes an economist's analysis of the effect of government infrastructure spending on new bridges and highways in the United States: "The investment multiplier would give a further kick to the U.S. economy."
The "investment multiplier" referred to by the economist is the
larger change in equilibrium real GDP resulting from a change in investment.
By saying that the investment multiplier would "give a further kick to the U.S. economy," the economist means
the multiplied effect of the increased infrastructure spending will increase real GDP and employment.
In a closed economy, the MPC is 0.50. Government spending changes by 400 The change in equilibrium GDP is
800 b/c 1/(1- 0.5) = 2 × 400
What is the effect on real GDP of a $150 billion change in planned investment if the MPC is 0.65?
429 billion b/c 1/ (1-0.65) * 150
Suppose booming economies in the BRIC nations (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) causes net exports (NX) to rise by $150 billion in the United States.
If the MPC is 0.5, the change in equilibrium GDP will be $
300 billion b/c 1/(1-0.5)*150
Suppose the marginal propensity to consume increases from 0.68 to
0.95. The value of the expenditure multiplier will increase from
3.13 to 20.00 b/c 1/(1-0.68) = 3.125 and 1/(1-0.95) = 20
When the value of the multiplier increases, all else equal, a change in expenditure will raise aggregate expenditure by a larger amount.
Would a larger multiplier lead to more severe recessions or less severe recessions?
A larger multiplier means that small changes in spending lead to large changes in GDP, and thus recessions would be more severe.
The table below provides expenditure and unemployment data for the years 1929 and
1933 — transition points of the Great Depression.
Year | Consumption | Investment | Exports | Real GDP | Unemployment Rate |
1929 | $781 billion | $124 billion | $40 billion | $1,056 billion | 2.9% |
1933 | $638 billion | $27 billion | $22 billion | $778 billion | 20.9% |
If the multiplier had a value of 4 in 1929, then how large must the change in autonomous expenditure
Ao have been to cause the decline in real GDP between 1929 and 1933 shown in the table?
ΔAo = $ -69.5 billion b/c 778 - 1056 = -278 and -278/4 = -69.5
An article published in an economics journal found the following: "For the poorest households, the marginal propensity to consume was close to 70%. For the richest households, the MPC was only 35%."
Source: Atif Mian and Amir Sufi, "Who Spends Extra Cash?," House of Debt,
April 13, 2014.
Assume that the macroeconomy can be divided into three sections.
Section A consists of the poorest households.
Section B consists of the richest households.
Section C consists of all other households.
The value of the multiplier for Section A is
3.33 b/c 1/(1-0.7)
The value of the multiplier for Section B is
1.54 b/c 1/(1-0.35)
Assume there was an increase in planned investment of $4 billion.
If the MPC for the economy was 70 percent (or 0.70), the change in equilibrium real GDP would be $
If the MPC for the economy was 35 percent (or 0.35), the change in equilibrium real GDP would be $
13.3 b/c 1/(1-0.7) * 4
6.2 b/c 1/(1-0.35) * 4
A study by the management consulting company McKinsey & Company recommended that the U.S. increase spending on infrastructure, such as bridges and highways, by between $150 and $180 billion per year. The study estimated that the result would be an increase in GDP of between $270 billion and $320 billion per year.
Source: David Harrison, "Nation's Crumbling Roads Put a Dent in Drivers' Wallets," Wall Street Journal, July 31, 2015.
If the McKinsey study's estimate of the effect of infrastructure spending on GDP is correct, the implied value of the multiplier is between
1.78 and 1.80 b/c 270/150 = 1.8 and 320/180 = 1.78
What component of aggregate expenditure would a decline in consumer confidence be likely to affect?
Consumption, as consumers cut spending over concerns about the future.
What component of aggregate expenditure would a decline in business confidence likely effect?
Investment, as decreasing business optimism would decrease investment expenditures.
Holding constant other factors affecting the U.S. economy, can you be certain whether these changes will cause real GDP to increase or to decrease?
Autonomous expenditure and real GDP will unambiguously decrease.
The position of the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is determined by
the number of workers, the amount of capital, and the available technology.
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run,
changes in the price level do not affect potential GDP, as potential GDP depends on the size of the labor force, capital stock, and technology.
The price level increases.
Because this is a change in the price level
the LRAS curve will not change
The labor force increases.
Because this is a change in the productive capacity of the economy
the LRAS will shift to the right
There is an increase in the quantity of capital goods.
Because this is a change in the productive capacity of the economy
the LRAS will shift to the right.
Technological change occurs.
Because this is a change in the productive capacity of the economy
the LRAS will shift to the right
An article in the Economist magazine noted that:
"the economy's potential to supply goods and services [is] determined by such things as labour force and capital stock, as well as inflation expectations."
Source:"Money's Muddled Message" Economist, May 19, 2009.
This list of the determinants of potential GDP is
incorrect since changes in the expected price level affect short run aggregate supply but not the long run aggregate supply.
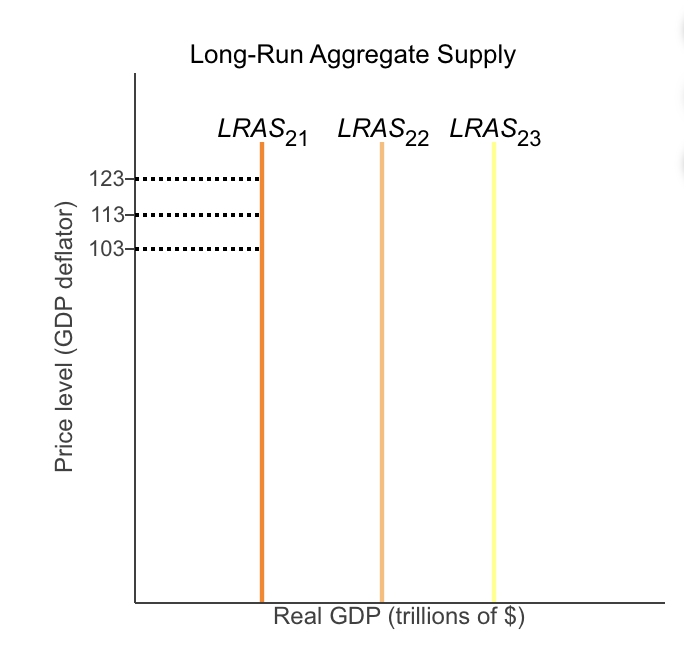
How does an increase in the price level affect the quantity of real GDP supplied in the long run?
Changes in the price level do not affect the level of GDP in the long run.
Which of the following factors will cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the right?
an increase in the number of workers in the economy
the accumulation of more machinery and equipment
technological change
In the long run, changes in the price level
do not affect the level of real GDP.
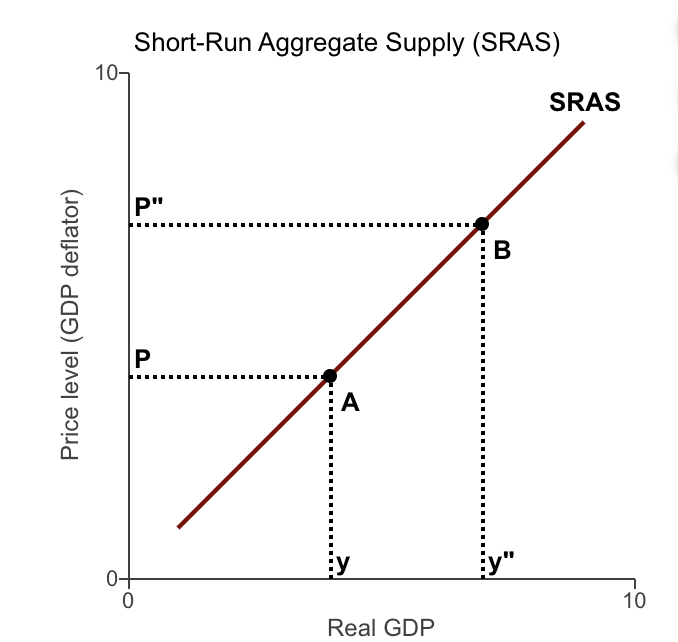
Consider the figure to the right. Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) slope upward?
Prices of final goods rise more quickly than the prices of inputs.
Contracts keep wages "sticky".
Firms and workers fail to predict changes in the price level.
The short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward because of all of the following reasons
in the short run, as prices of final goods and services increase, input prices react more slowly.
in the short run, as prices of final goods and services increase, some firms are very slow to adjust their prices, thus their sales increase.
in the short run, prices of final goods and services adjust slowly due to the existence of menu costs.
(Not in the short run, an unexpected change in the price of an important resource can change the cost to firms.)
Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve slope upward?
Profits rise when the prices of the goods and services firms sell rise more rapidly than the prices they pay for inputs.
Why does the failure of workers and firms to accurately predict the price level result in an upward-sloping aggregate supply curve?
because menu costs make some prices "sticky"
because contracts between workers and firms make some wages and prices "sticky"
because firms are often slow to adjust wages