(2.4) Biology - Transport Across Cell Membranes
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Why is it called the ‘fluid mosaic model’
fluid → phospholipid molecules can move around layers via diffusion
mosaic → the membrane has protein molecules and their arrangement varies
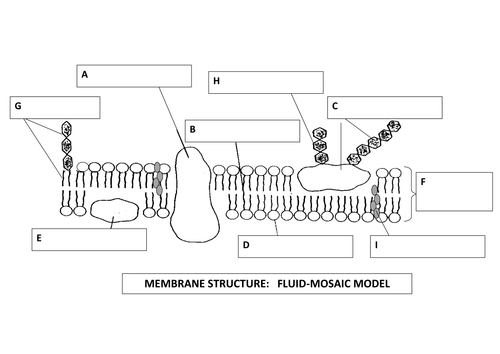
label ts
A → intrinsic protein
B → fatty acid tail
C → glycoprotein
D → phospholipid head
E → peripheral protein (support)
F → phospholipid bilayer
G → glycolipid
H → carbohydrate
I → cholesterol
function of membranes?
provide support for cell
controls what enters and exits
function of phospholipids ?
allow lipid soluble substances to enter and exit cell
prevent water soluble molecules from entering and exiting cell
make membrane flexible
function of glycoprotein and glycolipids
act as recognition sites
help cells attach to eachother to form tissues
function of cholesterol
decreases fluidity at high temps which decreases water loss
binds to hydrophobic fatty acid tails making them close together, decreasing fluidity
function of channel protein
allows specific water soluble ions and water molecules to diffuse through
used for facilitated diffusion
function of carrier protein
changes shape when molecules or ions bind to active site and transports them across membrane
used for active transport
what is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion
diffusion is the net movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
simple diffusion → allows direct transport of non-polar molecules across cell membrane
facilitated diffusion → hydrophilic substances diffuse across membrane via channel proteins / carrier proteins
describe the process of active transport
movement of molecules from low conc. to high conc. using ATP and carrier proteins
Molecule binds to receptor on carrier protein
ATP binds to carrier protein and is hydrolysed into ADP + Pi
Carrier protein changes shape and releases molecule on other side
Phosphate ion is released and carrier protein returns to original shape
ADP and Pi reform ATP during respiration
describe the process of cotransport
Sodium ions enter bloodstream from the epithelial cell via active transport
This creates a concentration gradient for facilitated diffusion of Na+ to enter epithelial cell from ileum
Glucose enters epithelial cell from ileum via cotransport with sodium
(Glucose exits epithelial cell into bloodstream via facilitated diffusion)
what is an advantage of cell membrane fluidity
membrane proteins can diffuse to where they are needed
explain 3 factors that affect the fluidity of the cell membrane
higher temperature → increases fluidity because there is more kinetic energy
higher conc. of saturated acids decrease fluidity as there are more intermolecular forces
cholesterol decreases fluidity at high temperatures
( + unsaturated acids increase fluidity since phospholipids are further apart)