A&P Test 3
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
what is blood
fluid component of cardiovascular system
functions of blood
transport (gases, nutrients, wastes, and hormones)
regulates pH and ion composition of interstitial fluids
restricting fluid loss at injury site (clotting)
defense (white blood cells provide immune function)
temperature (redistribute heat)
erythrocytes
red blood cells
carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
leukocytes
white blood cells
immune response
platelets
cell fragments that help with clotting
hemocytoblast
immature blood cell that can become a RBC or WBC
blood sampling
powerful diagnostic tool
can collect blood from any vessel for analysis
veins are preferred - low pressure
arterial puncture needed to examine blood gasses
whole blood composition
plasma (46-63 %)
formed elements (38-54 %)
plasma composition
water (92%)
plasma proteins (7%)
other solutes (1%)
hemopoiesis
production of blood
1. pluripotent stem cell (hemocytoblast)
2. colony forming units
3. precursor cells
4. mature cells
erythropoiesis
red blood cell production
~3-5 days
requires iron, B12, folic acid
nucleus is ejected for function
high turn over rate
life span ~120
erythropoiesis steps
stem cell - hematopoietic stem cell
committed cell - proerythroblast
ribosome synthesis
hemoglobin accumulation
ejection of nucleus
red blood cells
most abundant formed element
shaped like bi-concave disc
high surface area/volume (lots of area for gas exchange)
slightly flexible (squeeze thru capillaries)
no organelles
obtains coloration from hemoglobin
hemoglobin
contains heme
folded protein with 4 subunits
site that holds oxygen
oxyhemoglobin
bound to oxygen
bright red
deoxyhemoglobin
after oxygen has been delivered
dark red
anemia
low number of RBCs
low Hb content
symptoms: lethargy, weakness
reduces O2 transport - body weakens
polycythemia
too many RBCs
blood is too thick and cannot move through vessels easily
blood loss anemia
loss of RBCs due to hemorrhage
can be caused by NSAIDS
cause stomach and GI bleeding
inhibits clotting
RBC production is hampered
iron deficiency anemia
most common
not enough iron to make heme molecules
body can’t make Hb
no way to carry O2
pernicious anemia
vitamin B12 deficiency
B12 is needed for erythropoiesis
either low B12 in diet or not able to absorb B12 in digestive system
sickle cell anemia
caused by point mutation
defective beta chain in Hb molecules
Hb molecules stick together after releasing O2
causes RBCs to become rigid, fragile, and sickle shaped
RBCs get hooked and stuck together causing blockage of blood vessels
die faster than normal RBCs
what is erythropoiesis stimulated by
erythropoietin
increases when environmental O2 is low (hypoxemia)
androgens (ie. testosterone)
blood doping
enhancing athletic performance due to increased O2 supply to muscles
taking EPO/testosterone can increase blood viscosity and hematocrit up to 65%
removing blood while training then reinfusing RBCs before a competition
order of abundance for leukocytes
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
have granules
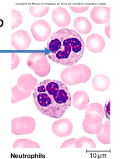
neutrophils
most abundant
phagocytosis of bacteria
release antimicrobial chemicals
have 2-3 lobes in nucleus
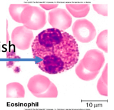
eosinophils
phagocytosis of antigen-antibody complex and allergens
release chemicals to kill parasitic worms
stain reddish
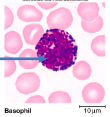
basinophils
rare
secrete histamine (vasodilator)
secrete heparin (anticoagulant)
important for immune response to work
stain bluish
agranulocytes
lymphocytes
monocytes
absence of granules
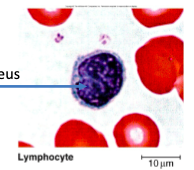
lymphocytes
second most abundant WBC
role in specific immunity
secrete antibodies
coordinate other immune cells
immune memory
seen a lot in viral infections
big nucleus
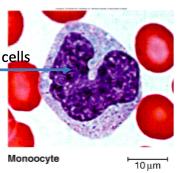
monocytes
differentiate into macrophages
phagocytosis
slow but numerous
very large cells
platelets
fragments of megakaryocytes
function in clotting
create a plug
initiate a signaling cascade
platelets form when cytoplasm of megakaryocytes break
thrombopoiesis
production of platelets
process of stopping blood or bleeding (hemostasis)
vascular spasm/phase
platelet phase
coagulation phase
vascular phase
vessel spasms
endothelial cells contract and release endothelin
endothelin signals for smooth muscle to contract and for endothelial cells to divide and repair
endothelial cells become sticky
platelet phase
form platelet plug
1. adhesion - platelets stick to endothelial cells
2. aggregation - platelets stick to eachother (15 seconds after injury)
platelets release chemical signals to stimulate clotting process
ADP - low energy, not enough phosphate
PDGF - platelet derived growth factor
coagulation phase
requires clotting factors
Ca2+
13 proteins working in a cascade
vitamin K
end result is fibrin
seals injury site
begins 30 seconds after injury
can take 8-18 minutes to complete
bleeding usually stops in 1-4 minutes
functions of respiratory system
gas exchange
oxygen to blood
CO2 from blood to atmosphere
moving air
protection
guards respiratory membranes from dry/cold air and inhaled pathogens or debris
communication
olfaction (smells)
ventilation
air transport
respiration
gas exchange
conducting zone of respiratory system
site of ventilation
cleanse, humidify, warm air
nose to terminal bronchioles
respiratory zone of respiratory system
site of respiration
exchange CO2 and O2
respiratory bronchioles to alveoli
nasal cavity
superior portion
ethmoid and sphenoid bones
inferior portion
hard bone and soft palates (muscle)
midline nasal septum
inside of nostrils are covered with hair to filter debris
nasal conchae
circulates air to warm and humidify
paranasal sinuses
in frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary bones
lighten skull
secrete mucus
help to warm and moisten air
pharynx
muscular tube
connects nasal cavity and mouth to larynx and esophogus
three regions
nasopharynx
uvula closes off and provides passage for air only
first section of pharynx
oropharynx
second section of pharynx
for air and food
laryngopharynx
third section of pharynx
epiglottis closes off and provides passage for air only
glottis
opening connecting pharynx to larynx
epiglottis
covers glottis
prevents food from entering airway
larynx
attaches to hyoid bone
continuous with trachea
airway
routes air and food into proper channels
voice production
what are the 9 cartilages of the larynx
thyroid cartilage (hyaline)
cricoid cartilage (hyaline)
paired arytenoid (hyaline)
paired cuneiform and corniculate cartilages (elastic)
epiglottis (elastic cartilage)
vocal ligaments
contain elastic fibers
form core of vocal folds (true vocal cords)
glottis is opening between vocal folds
folds vibrate to produce sound as air moves from lungs to external environment
vestibular folds
superior to vocal folds
no part in sound production
help to close glottis during swallowing
trachea
within mediastinum
wall with 3 layers
mucosa
ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
submucosa
connective tissue with seromucous glands
adventitia
connective tissue
encasing C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
mucus escalator
respiratory mucosa lines conducting zones
cells produce mucus to catch particles
cilia sweep particles toward pharynx
found in trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles
alveolar defense
alveolar macrophages
aka dust cells
eat dust
nasal filtration
nasal cavity lined with hairs
filters out large particles
nasal conchae
boney ridges that stir air
primary bronchi
trachea bifurcates into right and left primary bronchi
primary bronchi enter lungs and branch profusely
enter hilum of one lung
right bronchus is wider, shorter, more vertical
lobar bronchi (secondary)
primary bronchus branch into secondary bronchus
3 on right
2 on left
each lobar bronchus supplies one lobe of the lungs
segmental bronchi (tertiary)
lobar bronchi branch into tertiary bronchi
cartilage rings becomes plates
divide repeatedly
bronchioles
tertiary bronchi branch into bronchioles
little bronchi
smaller than 1 mm in diameter
terminal and respiratory bronchioles
terminal bronchioles
end conducting zone
smallest bronchiole
respiratory bronchioles
begin respiratory zone
connect to alveoli
alveoli
tiny air sacs
site of respiration (gas exchange)
collectively make up respiratory membrane (150 million/lung)
1 capillary wraps around each alveolus
alveolar sacs
clusters of alveoli
respiratory membrane/surfactant
2 cells thick
alveolar surfaces are thin and moist
surfactant prevents sticking
detergent breaks surface tension of water
allows alveoli to inflate
produced by pneumocyte II
reduce surface tension
gas exchange
right lung
3 lobes
superior
inferior
middle
2 fissures
horizontal
oblique
left lung
2 lobes
superior
inferior
1 fissure
oblique
cardiac notch
pleurae
thin, double layered serosa
encases pleural cavity
parietal pleura
on thoracic wall, diaphragm, and between lungs
wraps body wall
visceral pleura
external lung surface
wraps lungs
pleural cavity
potential space
filled with pleural fluid
lubrication and surface tension - assist with expansion and recoil
boyle’s law
inverse relationship between pressure and volume
increase in volume, decrease in pressure
decrease in volume, increase in pressure
chest volume increases, alveolar pressure falls, air flows in
chest volume decreases, alveolar pressure rises, air flows out
inhalation
diaphragm contracts and rib cage elevates
volume of thoracic cavity increases
pressure of thoracic cavity decreases
air flows into lungs
exhalation
rib cage returns to original position and diaphragm relaxes
volume of thoracic cavity decreases
pressure of thoracic cavity increases
air moves out of lungs
normal quiet breathing (tidal) muscles
inspiration (active)
diaphragm and external intercostals contract
expiration (passive)
diaphragm and external intercostals relax
forced inspiration muscles
accessory muscles - scalene, sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis minor contrat
diaphragm and intercostals contract
forced expiration muscles
active process
abdominal muscles and internal intercostals contract
tidal volume (TV)
~500 mL
inspiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inspiration
~3100 - 1900 mL
expiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume expiration
~1200-700 mL
residual volume
amount of air left in lungs after a forced expiration
~1200 - 1100 mL
pneumothorax
collapsed lung
hole in parietal pleura allows pleural cavity to fill with air
no longer potential space
air flows in
lung recoils and collapses
alveoli can’t open
pressure in pleural cavity is too great
dalton’s law
sum of all partial pressures of gasses gives us the total pressure
high altitudes, partial pressure decreases
low altitudes, partial pressure increases
pressure gradient of gas movement
inspired air moves into alveoli; PO2 decreases as it mixes with air and water vapor
alveoli diffuse O2 into blood
pulmonary veins bring oxygenated blood back to heart and into body
O2 diffuses into the tissues
blood leaves tissues, returns back to heart, and is pumped to lungs to be oxygenated
inspired air
PO2 - 160 mmHg
PCO2 - 0.3 mmHg
alveoli
PO2- 104 mmHg
PCO2 - 40 mmHg
blood leaving lungs and entering tissue capillaries
PO2- 100 mmHg
PCO2 - 40 mmHg
tissues
PO2 - less than 40 mmHg
PCO2 - higher than 45 mmHg
blood leaving tissues and entering lungs
PO2 - 40 mmHg
PCO2 - 45 mmHg
ventilation-perfusion coupling
match of ventilation and perfusion is necessary for optimal gas exchange
ventilation (V)
amount of gas reaching alveoli that can participate in gas exchange
need to make sure airways are wide enough to allow right amount of air flow in and out
perfusion (Q)
blood flow reaching alveoli that can participate in gas exchange
need to make sure capillary beds have blood flowing through them quickly enough to pick up oxygen and unload carbon dioxide
PO2 controls
perfusion
changes arteriolar diameter
alveolar O2 is high, arterioles dilate
alveolar O2 is low, arterioles constrict
direct blood to go to alveoli to get O2
PCO2 controls
ventilation
changes bronchiolar diameter
alveolar CO2 is high, bronchioles dilate
alveolar CO2 is low, bronchioles constrict
allows for more rapid elimination of CO2