Steroid Hormones Biosynthesis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
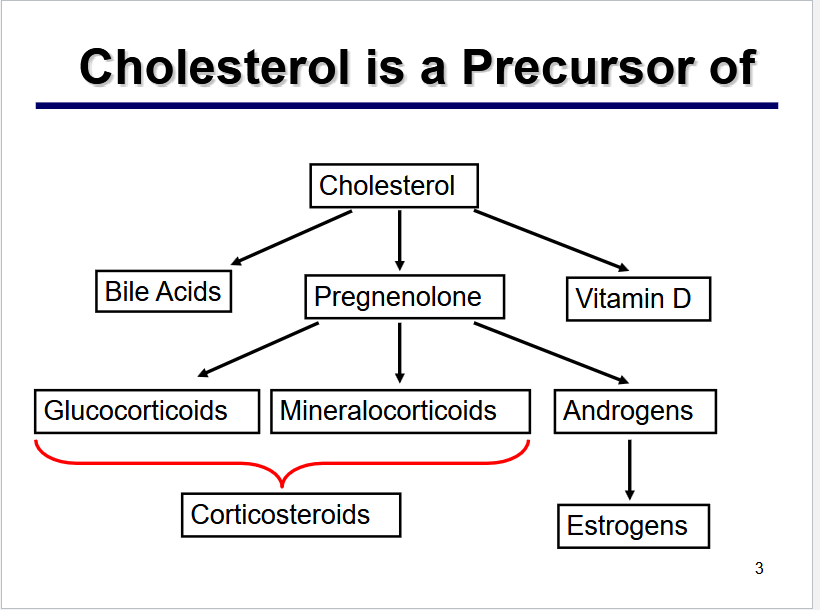
Describe the molecules in which ChL is a precursor of?
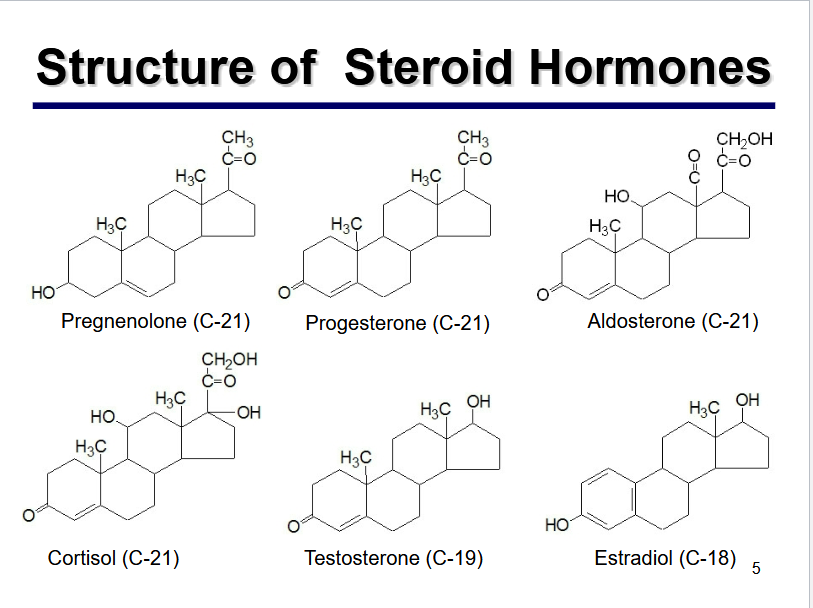
What is the core structural feature of steroid hormones?
Lipid compounds with a carbon skeleton formed by four fused rings.
Describe the unique ability of steroid hormones receptors
A specific Receptor can bind to more than one ligand due to similar structure of steroid hormoes
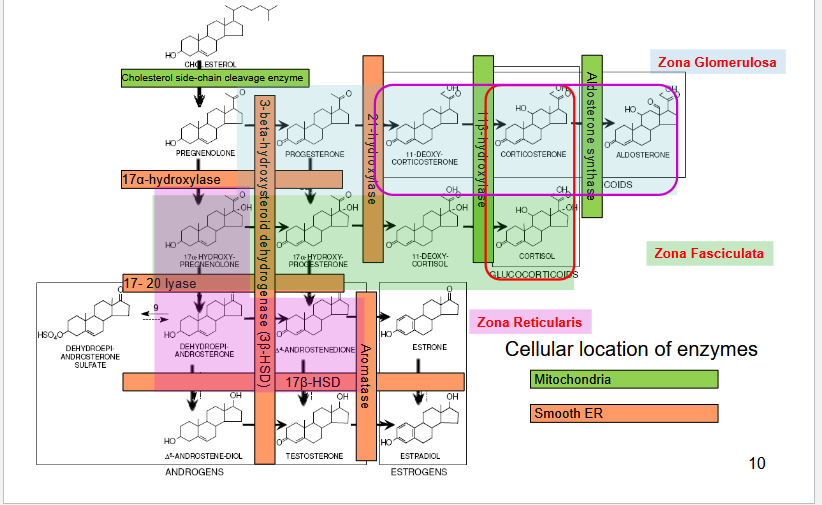
Describe the steps of cortisol synthesis
Cholesteryl esterase (cholesterol ester lipase)
removes ester from cholesterol ester and produces free cholesterol.
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR)
Moves ChL from outer → inner mitochondrial membrane.
rate-limiting step
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage (P450scc) enzyme
Produces pregnenolone
From there, pregnenolone is transformed to specific steroid hormones dictated by the cell
What regulates:
Cholesteryl esterase
StAR
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage (P450scc)
Cholesteryl esterase: posttranslational modification:
cAMP → PKA → Phosphoylation of cholesteryl esterase → active state
StAR- stimulated by:
LH
ACTH
Angiotensin II
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage (P450scc)- transcription
Gene contains CRE (cAMP regulatory element)
cAMP binding → increases expression
What cells make testosterone?
What cells make DHT?
Describe the potentency of DHT vs Testosterone
Leydig cells:
main site of testosterone synthesis
Sertoli cells:
Prduces Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) via (5α-reductase),
***However, most of the conversion of testosterone to DHT occurs outside the testes.***
DHT= 10 times more potent than testosterone.
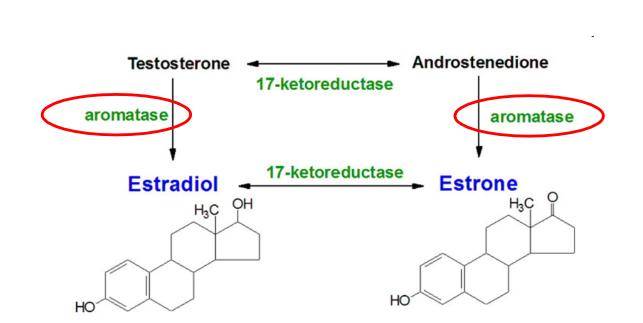
What are estrogens formed by?
Where is this enzyme found?
Estrogens are formed by aromatization of androgens
Aromatase = complex ER enzyme found in ovary and numerous other tissues
Block Out Later
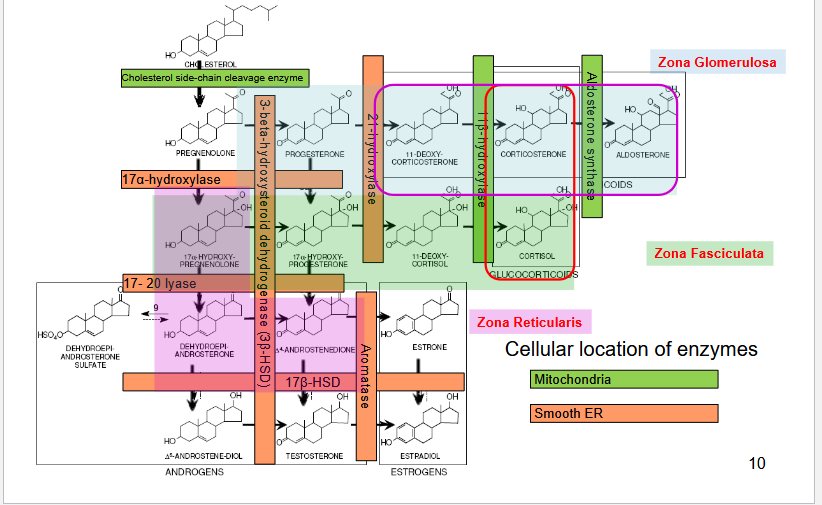
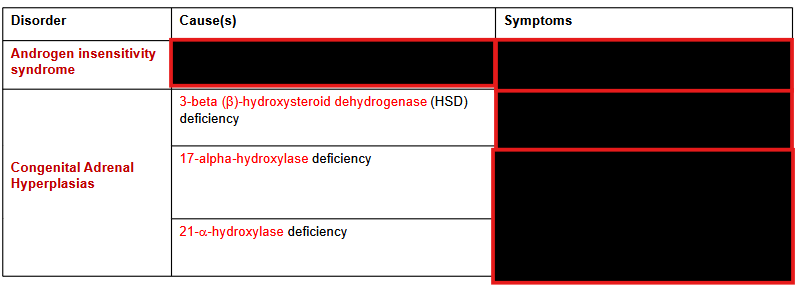
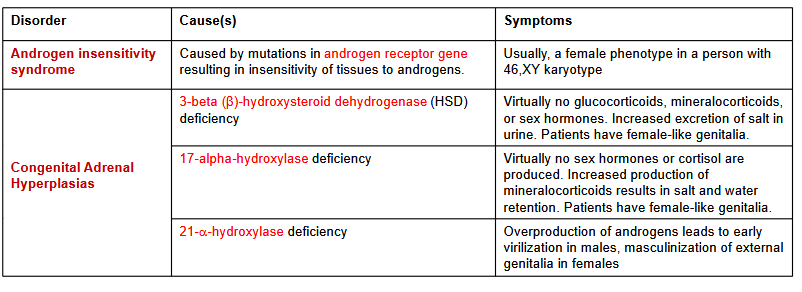
What does 3-beta-hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency affect? Hereditary?
What is the consequence of 3-beta-hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency in males/females?
Deficiency: affects gonads/ adrenal glands; autosomal recessive
Males:
abnormalities of the external genitalia.
Females:
slight abnormalities of the external genitalia at birth
What does 17-alpha-hydroxylase Deficiency affect? Heredity?
Effect on Males/Females?
17-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency affect the gonads and the adrenal
glands; Heredity: autosomal recessive
Effects:
Female: internal reproductive organs are underdeveloped
Males: Infertility
Increased production of aldosterone
What does 21-hydroxylase Deficiency affect? Symptoms? Hereditary?
affects the adrenal glands; autosomal recessive
most common form of adrenal congenital hyperplasia.
Symptoms:
low fertility rate.
hypotension
Females:
hirsutism (excessive body hair)
male pattern baldness
Differentiate between the two forms of vitamin D
Vitamin D2 is largely human-made and added to foods.
Vitamin D3 is produced from 7-dehydrocholesterol by exposure to ultraviolet light.
Describe the steps of Vitamin D synthesis
@ Epidermis:
UV light cleaves 7- dehydrocholesterol, → vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D3 binds vitamin D binding protein (DBP) → into liver
@ liver:
vitamin D3 → 25(OH)D3
@ Kidney:
25(OH)D3 → calcitriol
What four things can cause Vit. D deficiency?
Risk Factors?
associated diseases?
Correlation?
Vit. D Deficiency:
Inadequate sunlight exposure
Disorders of vitamin D absorption
Certain disorders of the liver and kidney
Deficiency of parathyroid hormone
Risk factors:
Age
Darker skin color
Malnutrition
Obesity: Vitamin D is extracted from the blood by fat cells, altering its release into the circulation.
Sunscreens and excessive clothing
Geographic location (high latitude)
Associated Diseases:
Rickets; impeded growth, bone deformities
Osteomalacia; a bone thinning disorder
Osteoporosis; reduced bone mineral density
Muscle ache and weakness
CVD: LVH, atherosclerosis, vascular calcification, and renin/angiotensin system
Inverse correlation with incidence of certain types of cancer
What occurs to 90% of steroid hormones?
90% steroid hormones in plasma are bound to plasma proteins
Specialized – high affinity for particular hormone
Nonspecific - binds a variety of hydrophobic hormones (albumin)
What type of protein structure are prevalent on steroid receptors?
Zn fingers
Describe how steroid hormones affect protein transcription
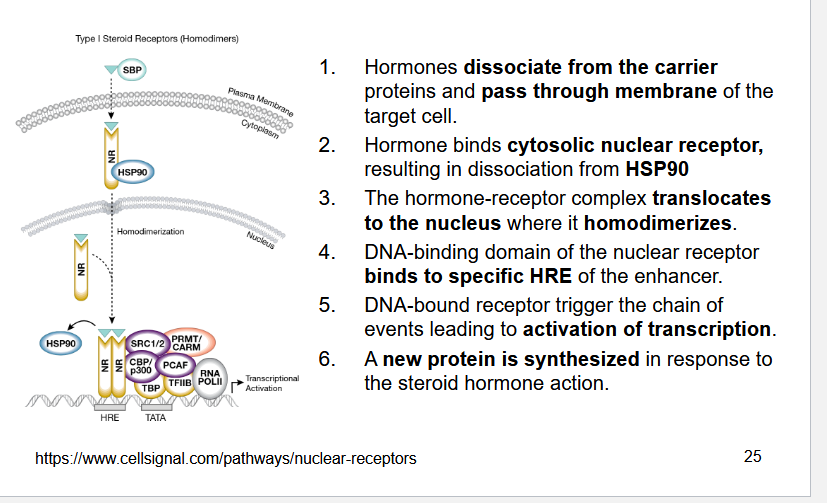
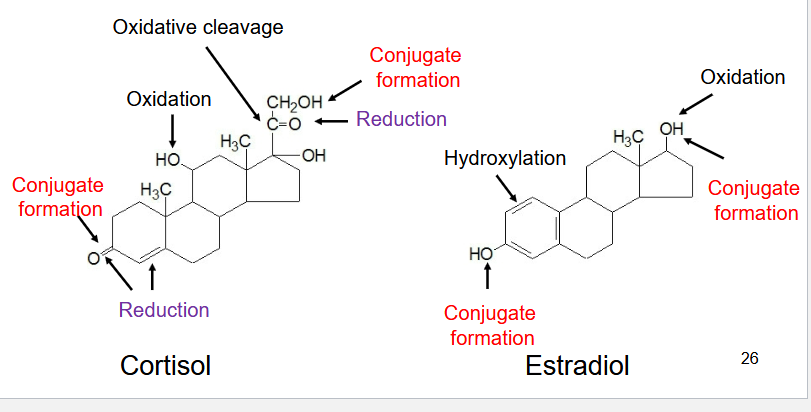
Describe how steroid hormones are inactivated
@ Liver; excreted as urine (and some as bile)
Mechanism:
Reduction/Conjugation formation