STAT 164 - 3RD LE - CHAPTER 6.2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
LOGISTIC REGRESSION
It is used to study the relationship between a categorical dependent variable and independent variables that can either be quantitative and/or categorical.
Binary
Multinomial
Ordinal
Type of logistic regression is based on the nature of the dependent variable:
____________ (ex. dead or alive; success or failure; yes or no)
____________ (ex. Asia, Africa, America, or Europe)
____________ (ex. Life satisfaction level)
BINARY LOGISTIC REGRESSION
It models a binary dependent variable using independent variables (that can either be continuous and/or categorical)
The model computes the probability that the event of interest will occur as a function of the independent variables.
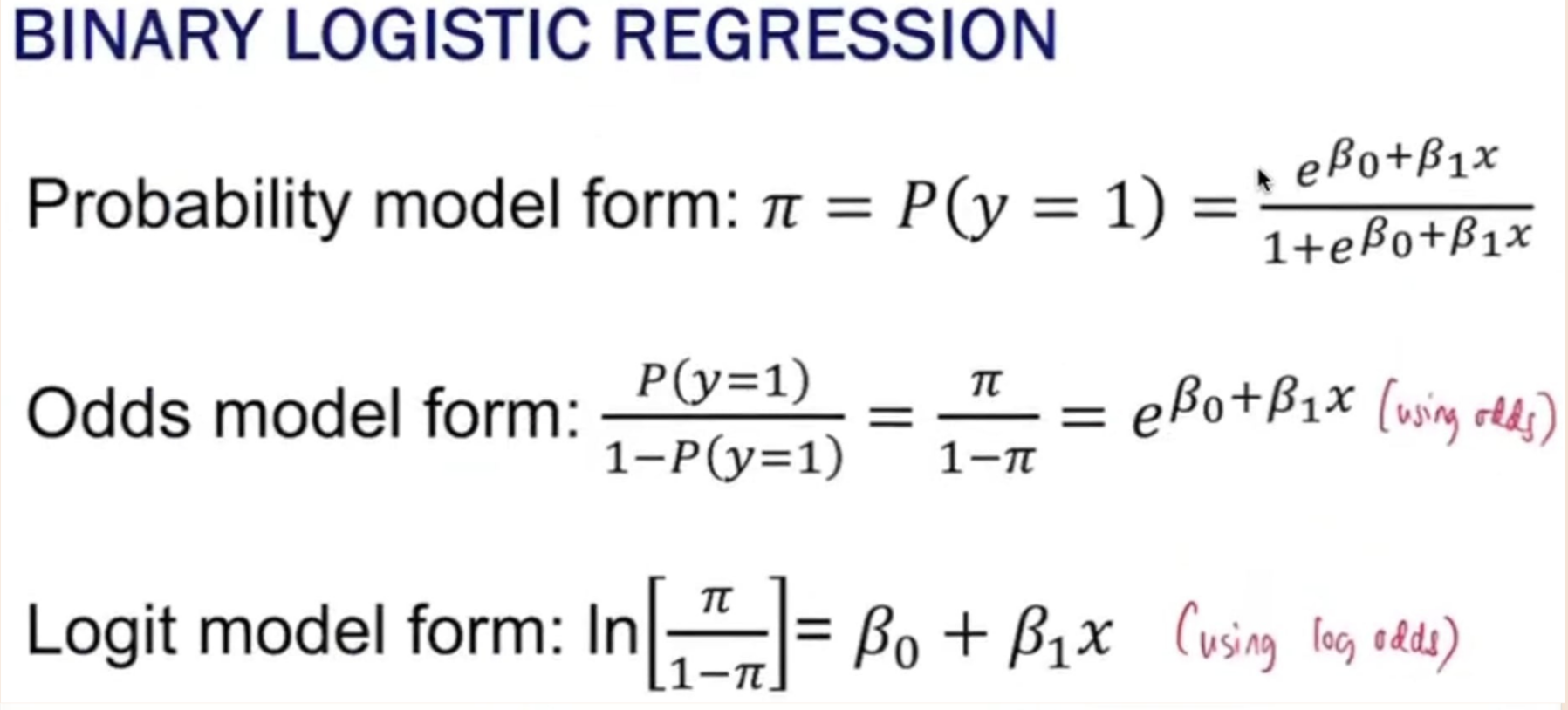

What is the formula for the following:
Probability model form
Odds model form
Logit model form
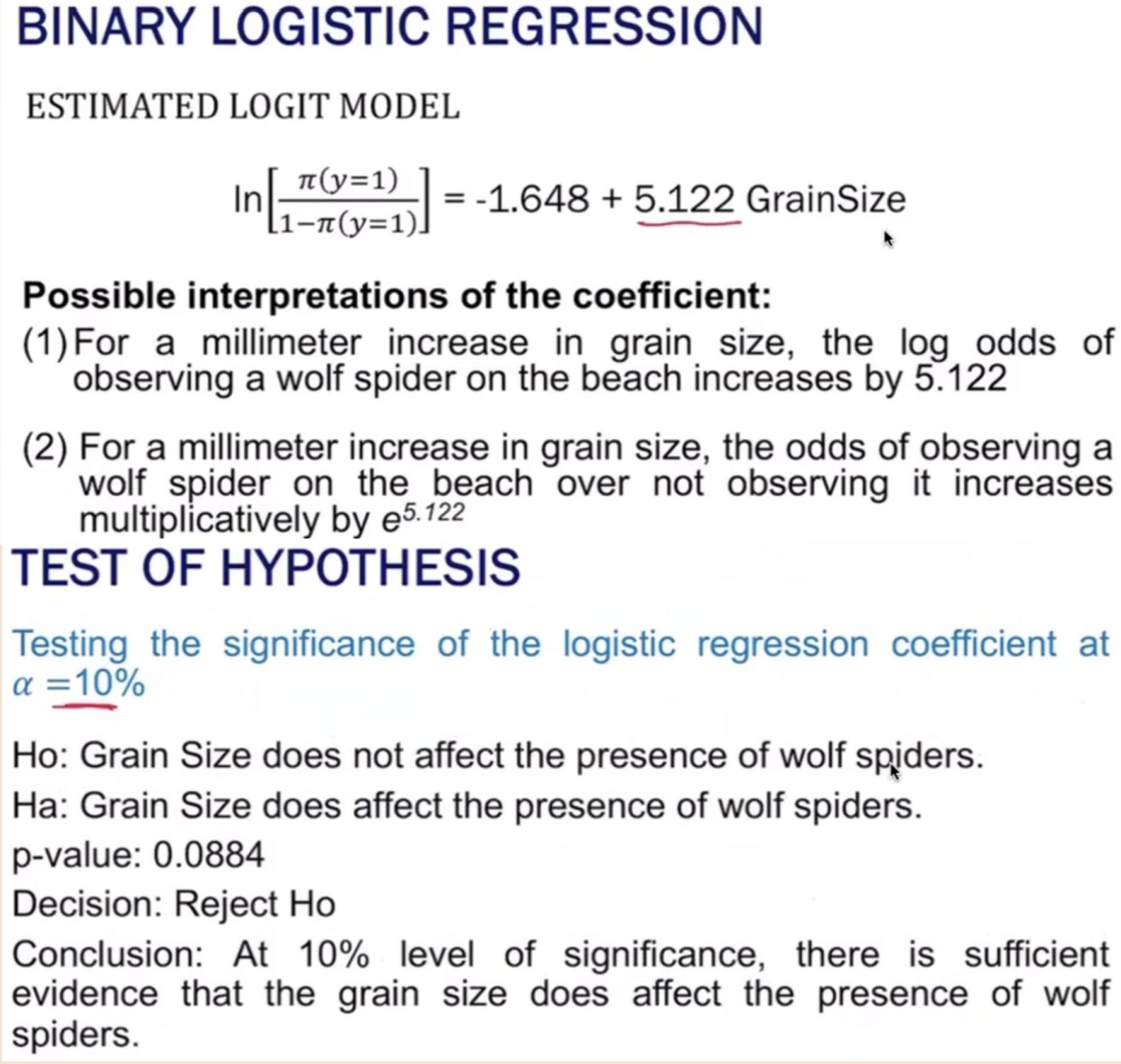


Provide the following:
Estimated LOGIT model
Possible interpretations of the coefficients
Test of Hypothesis, α = 10%, p-value: 0.0884
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
Decision:
Conclusion:



What is the probability of observing a wolf spider given that the grain size is equal to 0.4?
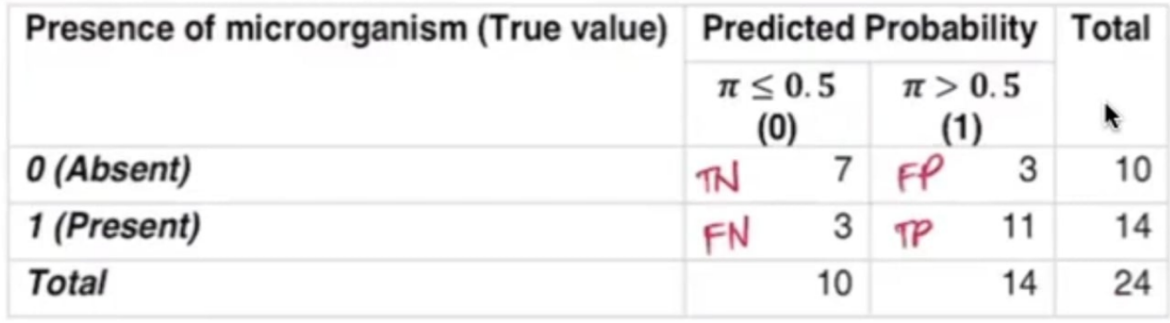
Confusion Matrix
________________ — a cross-tabulation of the actual and the predicted values. It helps us in assessing the accuracy of the model.
Sensitivity

MODEL EVALUATION
_____________ - the proportion of true positives or the proportion of cases correctly identified by the test as meeting a certain condition (e.g. in mammography testing, the proportion of patients with cancer who test positive).
Specificity

MODEL EVALUATION
________________ - the proportion of true negatives or the proportion of cases correctly identified by the test as not meeting a certain condition (e.g. in mammography testing, the proportion of patients without cancer who test negative).
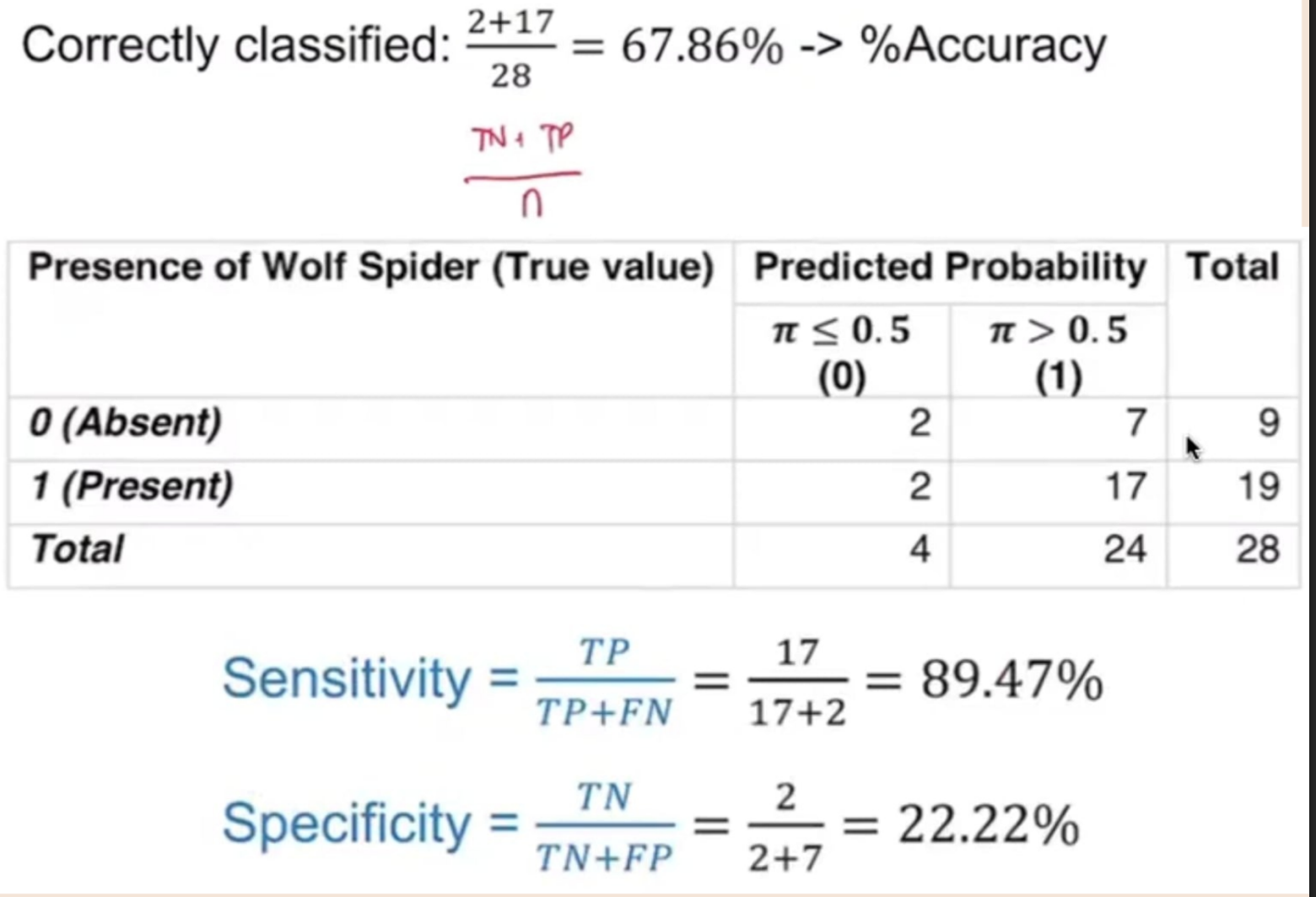

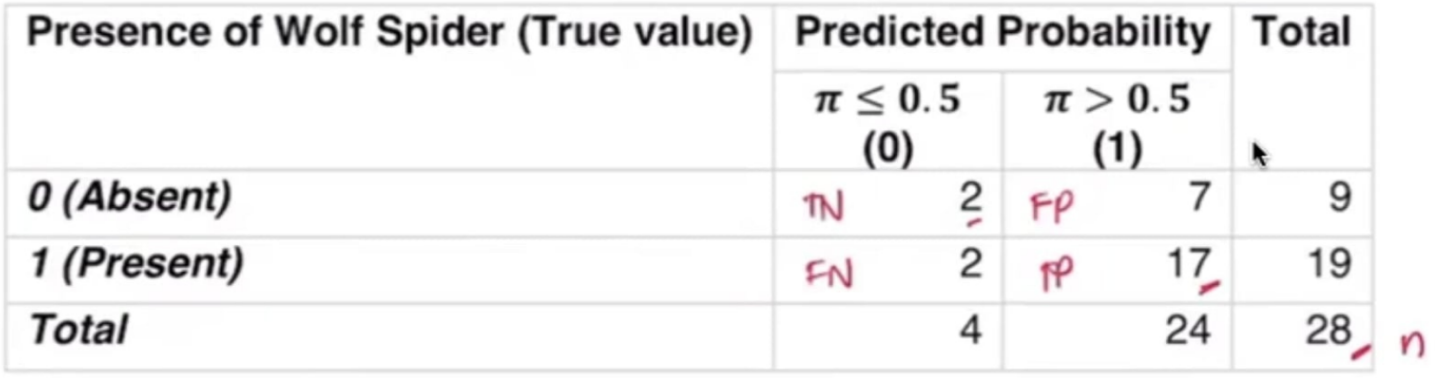
Calculate the following:
Overall Accuracy (%)
Sensitivity (%)
Specificity (%)
False Negative Rate (%)
False Positive Rate (%)
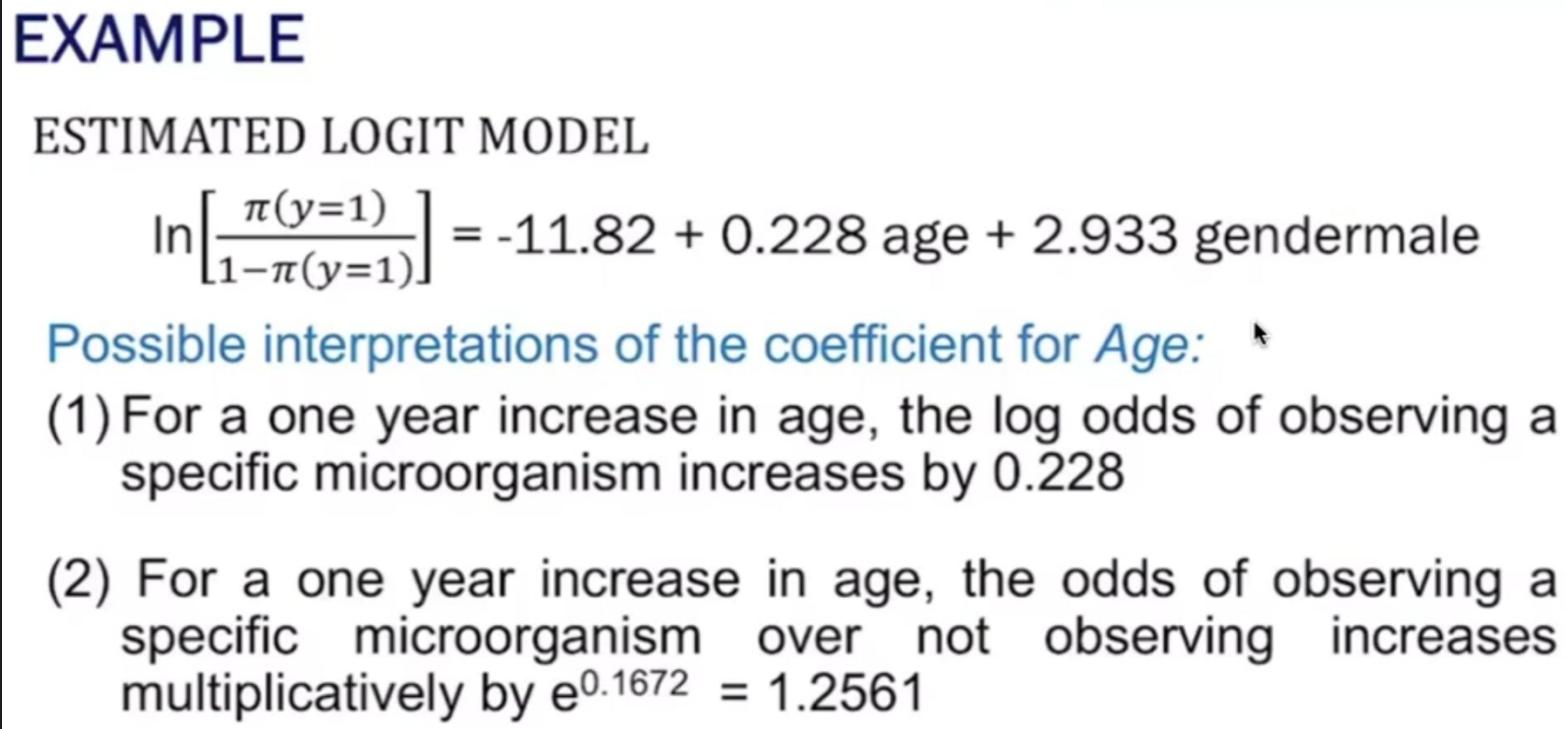


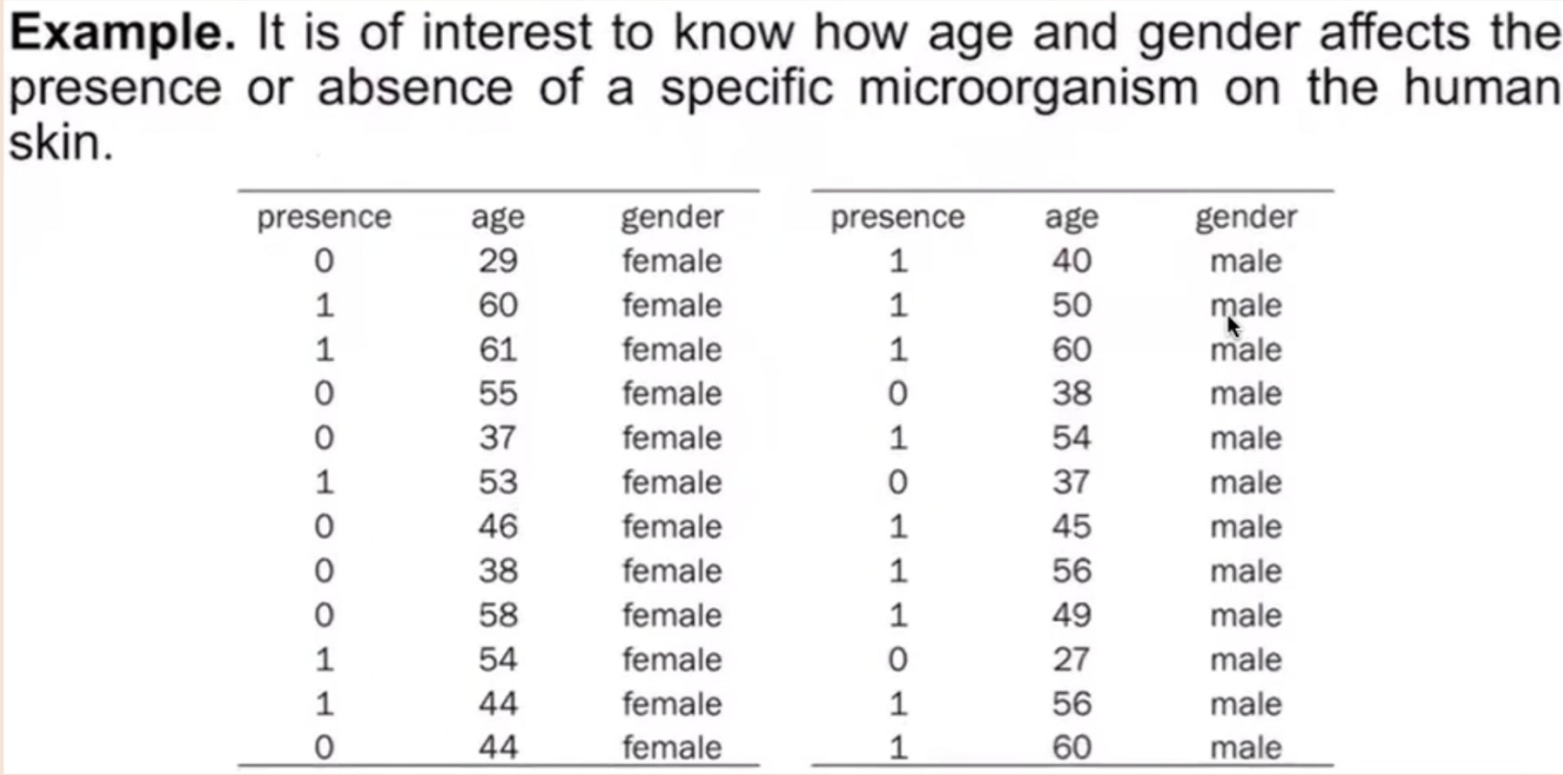
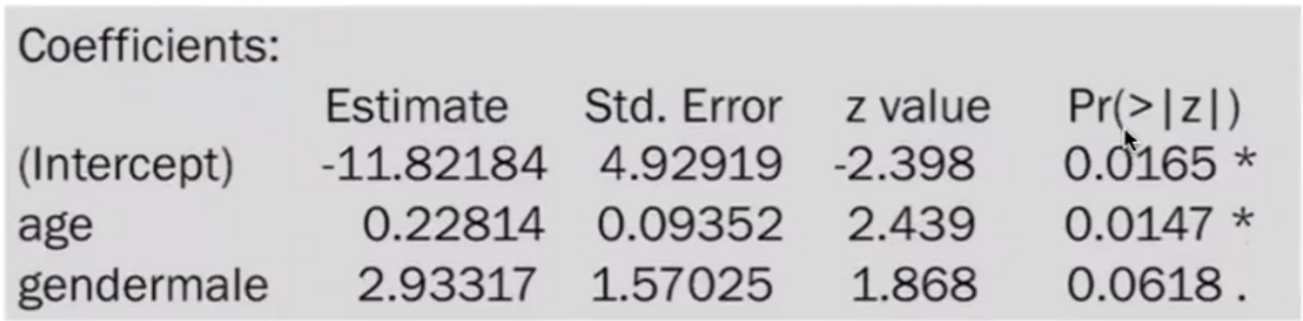
Provide the following:
Estimated LOGIT model
Possible interpretations of the coefficients
Test of Hypothesis - α = 5%
Age, p-value: 0.0147
Conclusion:
Gender, p-value: 0.0618
Conclusion:
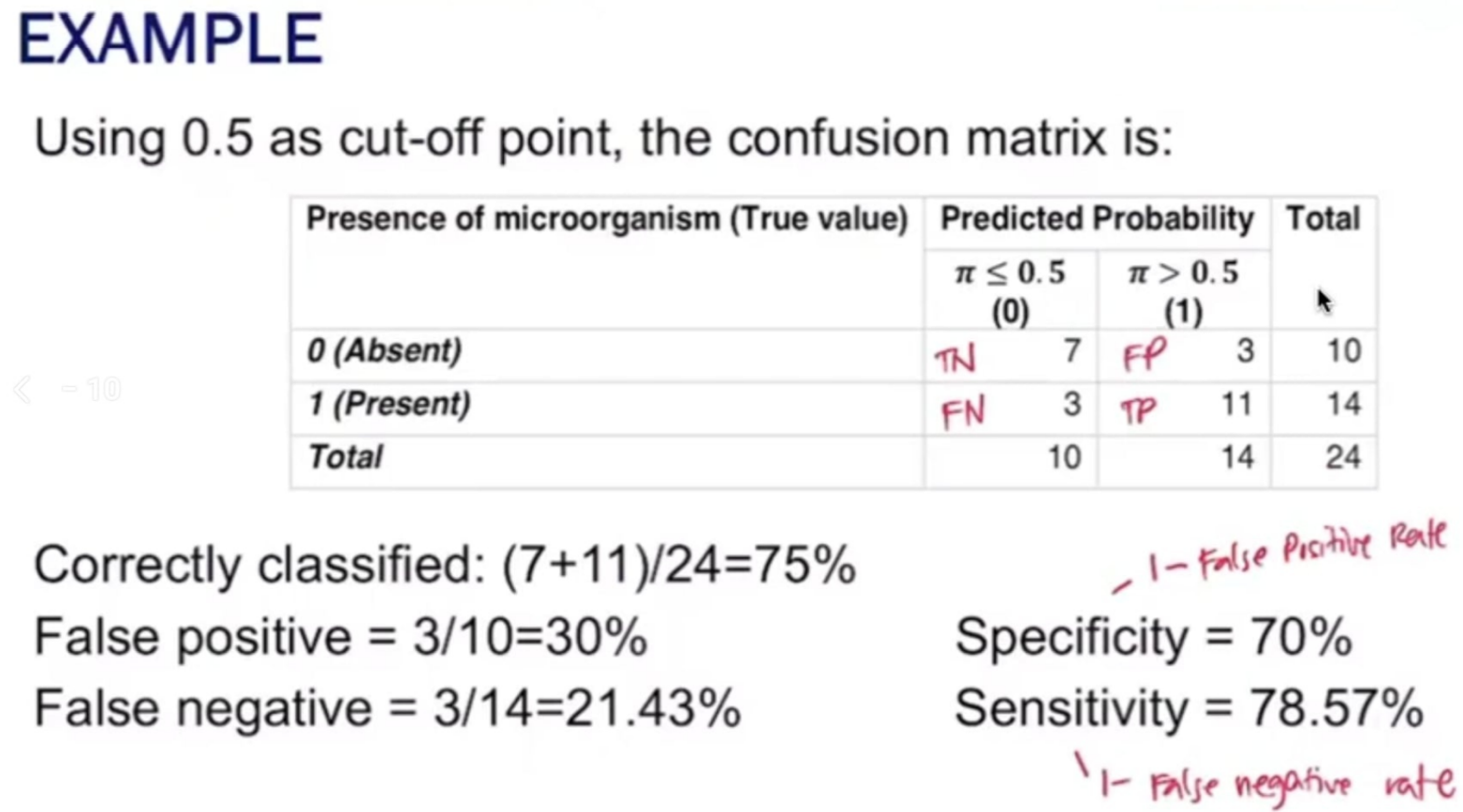
Calculate the following:
Overall Accuracy (%)
Sensitivity (%)
Specificity (%)
False Negative (%)
False Positive (%)
PROBIT REGRESSION MODEL
Another model that has S-shaped curve
The model transforms the probabilities to Z-scores from the standard normal distribution.
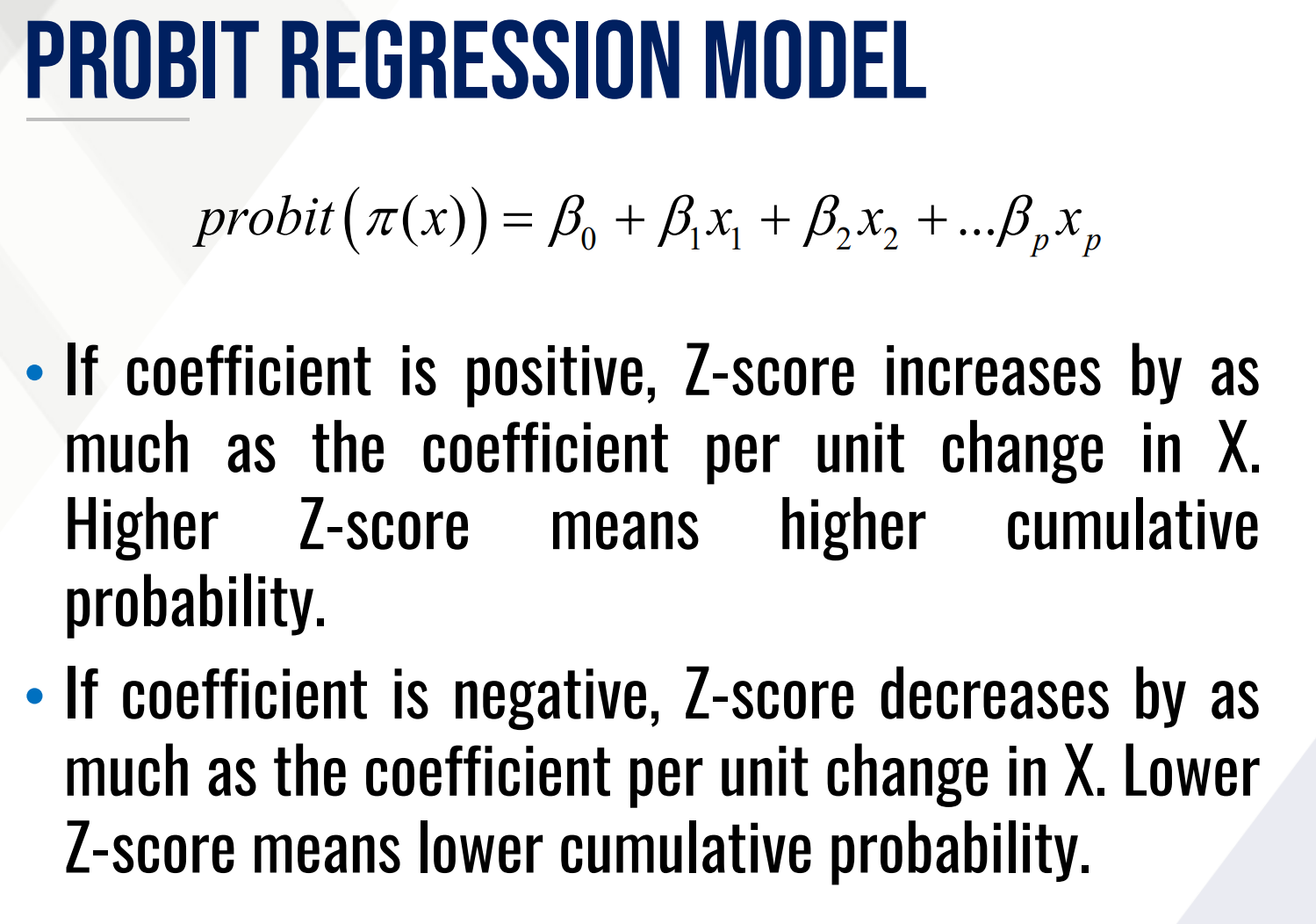
Probit Regression Model formula.
PROBIT REGRESSION MODEL
The model outputs left-tailed Z-scores which is then converted into cumulative probabilities using the Z-table.
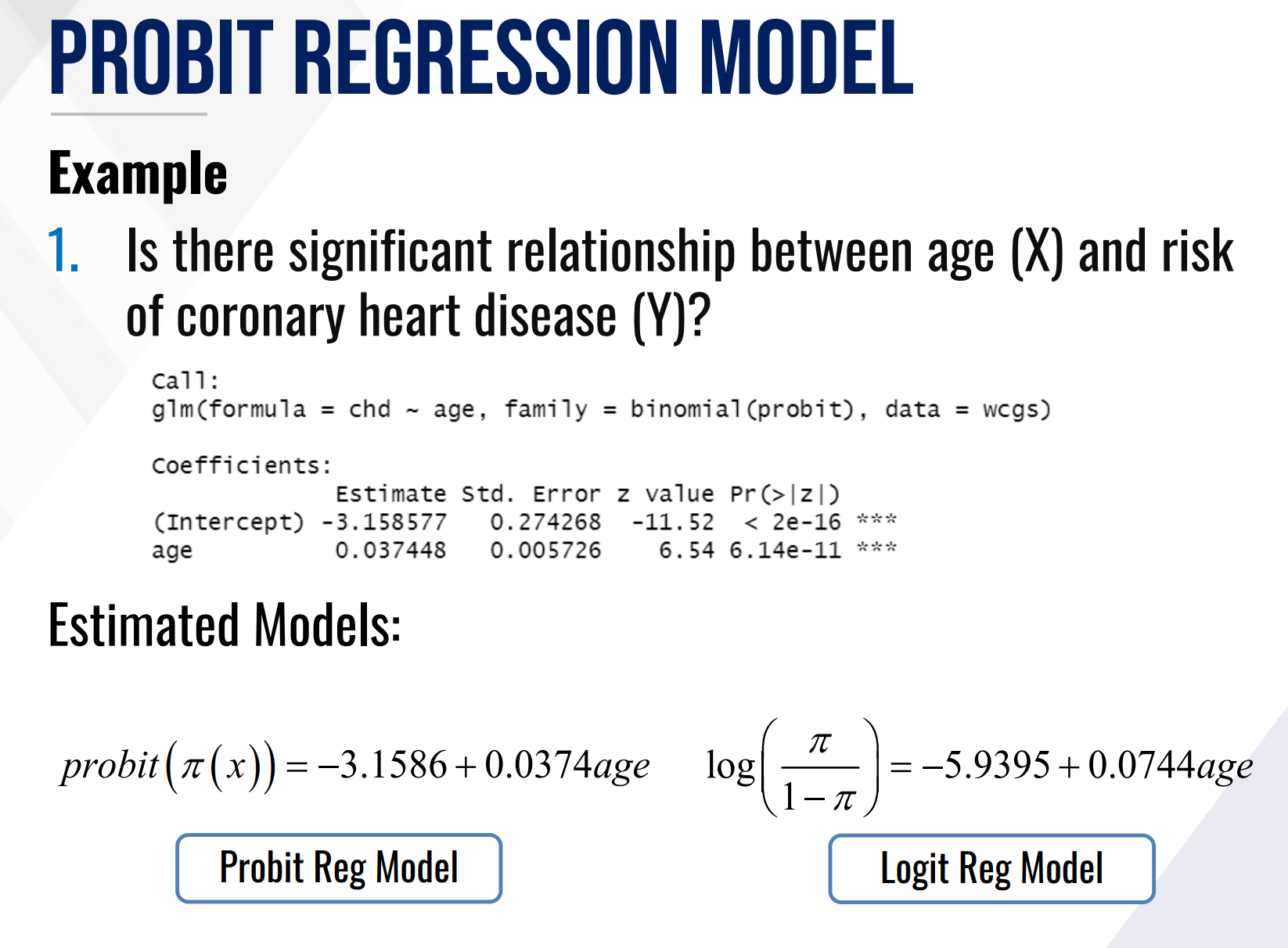
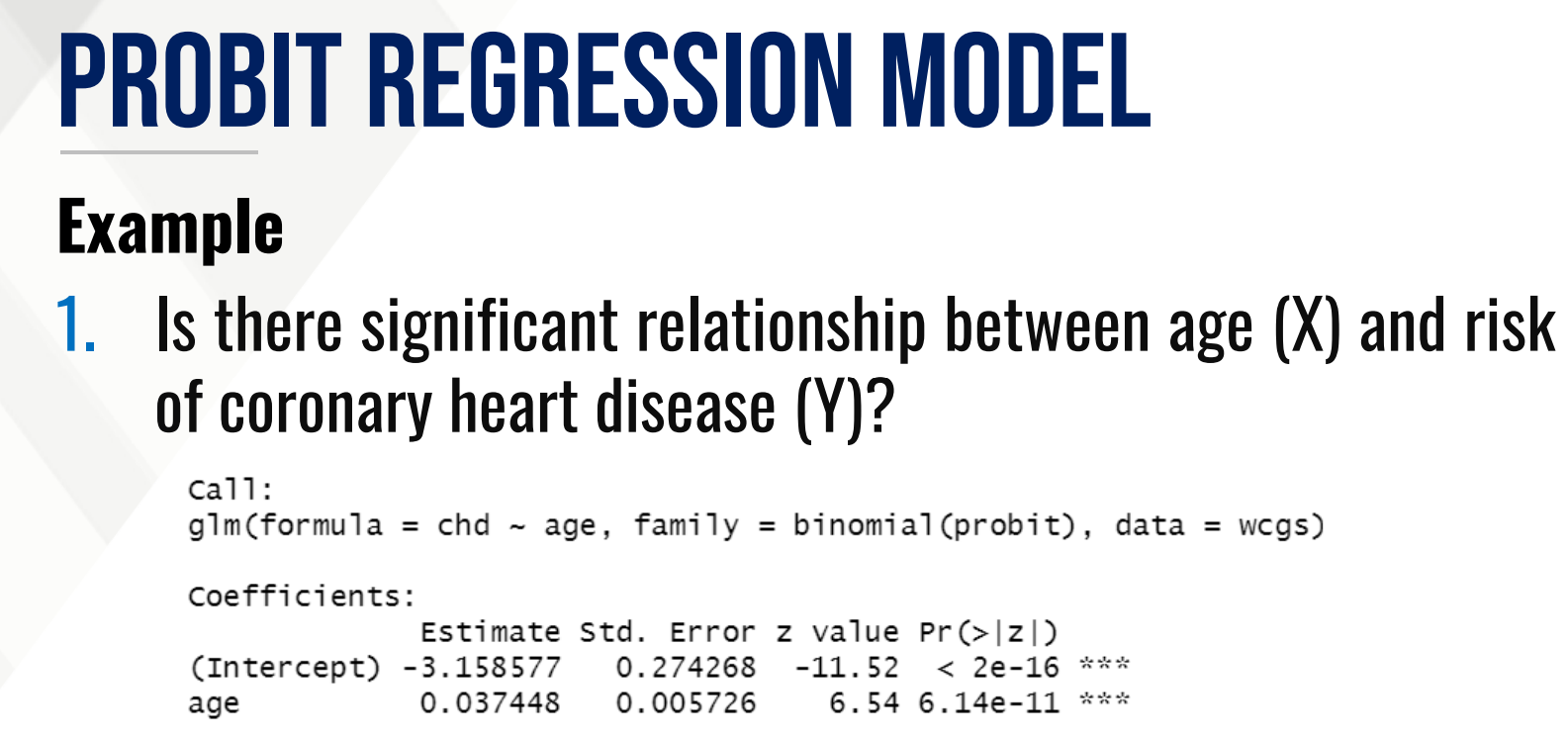
Provide the estimated probit regression model and
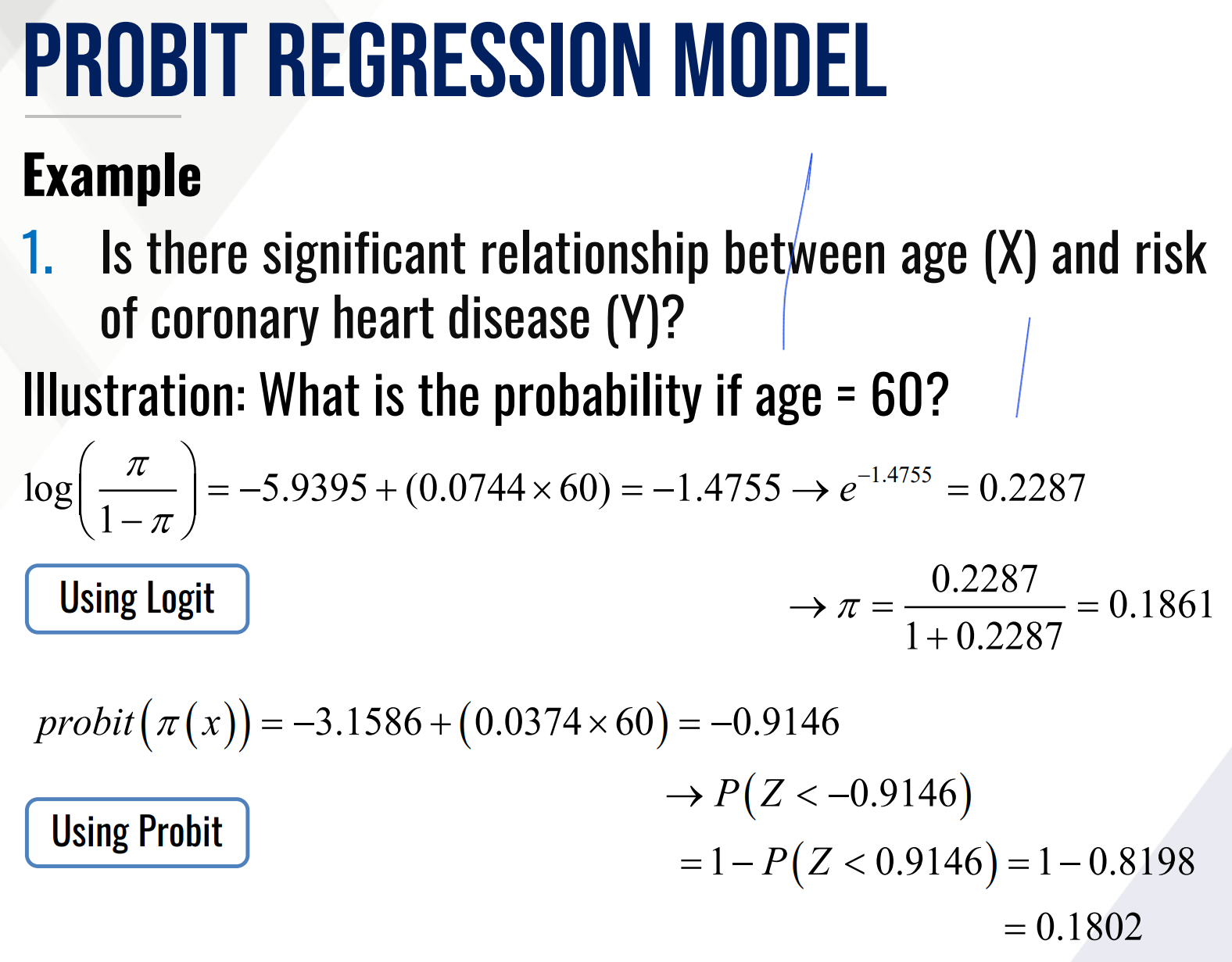
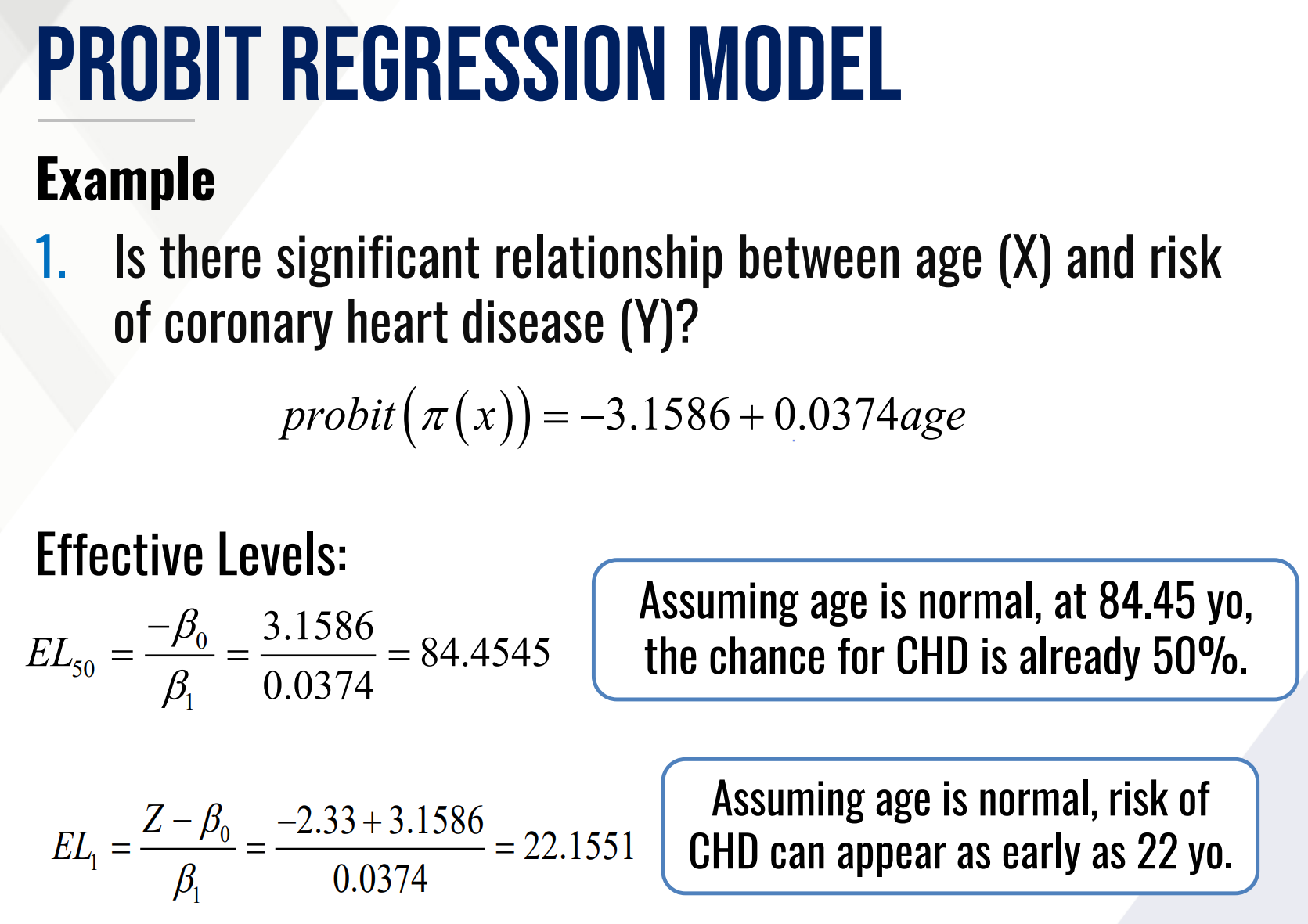


Also what solve for the effective level EL50.