Surveying Module 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Surveying
the art and science of determining angular and linear measurements to establish the form, extent, and relative position of points, lines, and areas on or near the surface of the earth or on other extraterrestrial bodies through applied mathematics and the use of specialized equipment and techniques.
Planning and design
are based on the results of surveys, and construction is controlled by surveying.
Surveying
One of the oldest arts practiced by man is __________.
mark and divide
From the earliest times it has always been necessary to ____ boundaries and ______ tracts of land. Through the centuries, the uses of surveying have expanded such that today it is difficult to undertake any type of construction that does not involve some type of surveying.
Egypt
Surveying had its beginning in _____ about 1400 BC.
− Land along the Nile River were divided for taxation.
− Measurements were made with ropes having knots at unit distances.
Nile River
Surveying had its beginning in Egypt about 1400 BC.
− Land along the _______ were divided for taxation.
ropes and knots
Surveying had its beginning in Egypt about 1400 BC.
− Measurements were made with _____ having _____ at unit distances.
Greeks
Expanded Egyptians work and developed Geometry.
Dioptra
is a classical astronomical and surveying instrument. It is used to measure angles.
Romans
Developed surveying into science to create the Roman Roads, aqueducts, and land division systems.
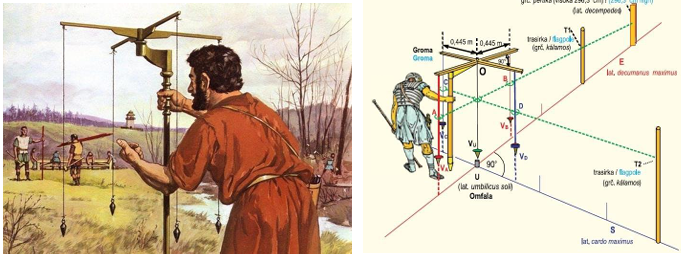
Groma, Libella, and Chorobates
The Romans Developed several instruments such as ________, ________, and ________
Groma
cross instrument used to determine lines and right angles.
Libella
“A” frame with plumb bob used for levelling.
Chorobates
20 feet straight edge with oil or liquid in notch for levelling.
Middle Ages
A period when Land division of Romans continued in Europe.
20th Century and Beyond
As technology advances, population increased, and land value increase caused development of licensure for surveyors in all states.
Educational
20th Century and Beyond
− ____________ requirements for licensure are required.
Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)
20th Century and Beyond
− Development of ___________________, using Global Positioning System (GPS), and lidar or laser radar (scanning) mapping.
Plane and Geodetic
Two general classifications of Surveying
Plane Surveying
Is a type of surveying in which the earth is considered to be a flat surface, and where distances and areas involved are of limited extent that the exact shape of the earth is disregarded. With regard to horizontal distances and directions, a level line is considered as mathematically straight, the direction of the plumb line is assumed to be the same at all points within the limits of the survey, and all angles are considered to be plane angles.
Geodetic Surveying
Are surveys of wide extent which take into account the spheroidal shape of the earth. These surveys employ principles of geodesy, are of high precision, and the related calculations involve the solving of equations derived from advanced mathematics particularly spherical trigonometry, calculus, and some applications of the theory of least squares.
Cadastral Surveys
Usually closed surveys which are undertaken in urban and rural areas for determining property lines and boundaries, corners, and areas. These are also for fixing boundaries of municipalities, towns, and provincial jurisdictions.
City Surveys
Surveys of the areas in and near city for the purpose of planning expansions or improvements, locating property lines, fixing reference monuments, determining the physical features and configuration of the land, and preparing maps.
Construction Surveys
Surveys which are undertaken at a construction site to provide data regarding grades, reference lines, dimensions, ground configuration, and the location and elevation of structures.
Forestry Surveys
Executed in connection with forest management and mensuration, and the production and conservation of forest lands.
Hydrographic Surveys
Refer to surveying streams, lakes, reservoirs, harbors, oceans, and other bodies of water. These are made to map shorelines, chart the shape of areas underlying water surfaces.
Industrial Surveys
Sometimes known as “optical tooling”. It refers to the use of surveying techniques in ship building, construction, and assembly of aircrafts, lay-out and installation of heavy and complex machinery.
Mine Surveys
Surveys which are performed to determine the position of all underground excavations and mining claims, determine geological formations, calculate excavated volumes, and establish lines and grades for other related mining work.
Photogrammetric Surveys
Type of survey that makes use of photographs taken with specially designed cameras either from airplanes or ground stations.
Route Surveys
Involves the determination of alignment, grades, earthwork quantities, location of natural and artificial, objects in connection with the planning, design, and construction of highways, railroads, pipelines, canals, transmission lines, and other linear projects.
Topographic Surveys
Surveys made for determining the shape of the ground, and the location and elevation of natural and artificial features upon it. The features shown include hills, mountains, rivers, lakes, and works of men such as roads, buildings, ports, towns, municipalities, and bridges.
Roman Empire
Development of Surveying Instruments
Surveying instruments were developed gradually. It is believed that an extensive use of surveying instruments came about during the early days of _________. This remarkable engineering ability of their people is clearly demonstrated by their extensive construction of structures and buildings which continue to exist even up to these modern eras.
Astrolabe

Telescope
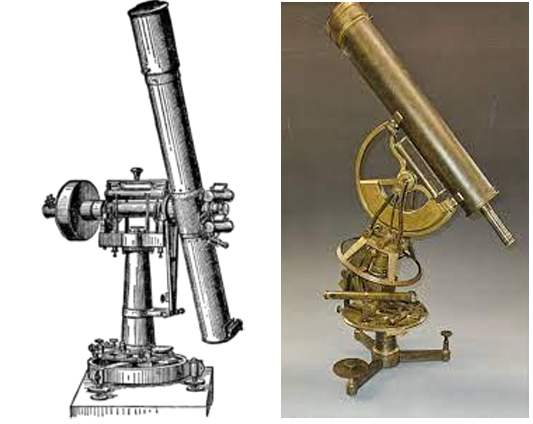
Transit

Semicircumferentor

Plane Table
Dioptra

Roman Groma
Libella

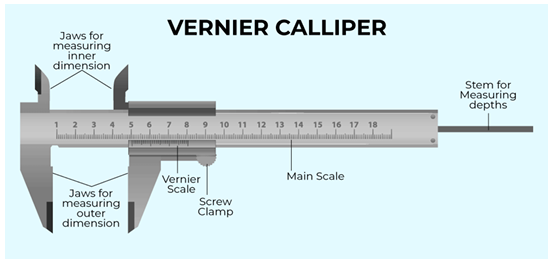
Vernier
Compass

Gunter’s Chain
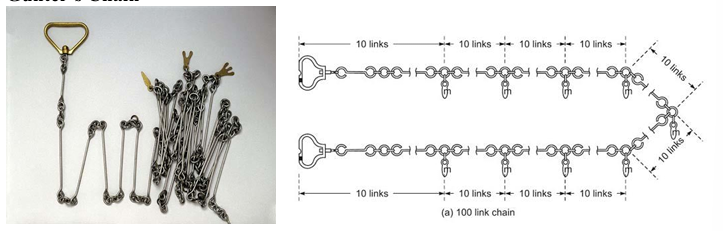
Chorobates

Merchet

Measurement
the process of determining the extent, size, or dimensions of a particular quantity in comparison to a given standard.
Direct and Indirect
Types of Measurement
Direct Measurement
is a comparison of the measured quantity with a standard measuring unit employed for measuring quantity of that kind.
Indirect Measurement
is used when it is not possible to apply a measuring instrument directly to a quantity to be measured
Meter
The international unit of linear measure
French scientists
The international unit of linear measure is the meter. This was proposed sometime in 1789 by _________ who hoped to establish a system suitable for all times and all people, and which could be based upon permanent natural standards.
Significant Figures
In recording results from values obtained by measurements and in making computations, it is important to determine which should be retained as significant figures. By definition, the number of __________ in any value includes the number of certain digits plus one digit that is estimated.
Rounding Off
the process of dropping one or more of the final digits so that the value contains only the significant figures required for further computation or for portraying the final results.