Health Services Vocabulary
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What are choices in health care?
In healthcare you choose the best of bad options, based on what’s available to YOU.
What is cost in health care?
What you give up when making a CHOICE.
What is a tradeoff in health care?
The give and the take of a scenario.
What is the Opportunity cost?
the NEXT BEST CHOICE after your BEST CHOICE from the options provided to you.
What are tangible costs?
things that cost money
what are intangible costs?
things that don’t cost money but in the end effect your decision making.
what are direct tangible costs when related to health care?
medical expenses and non medical expenses.
What are indirect tangible costs when related to health care?
opportunity costs, and costs that affect your life indirectly when facing a medical decision.
What is a decision in health care?
Something made over a minimum of 2 choices.
What are domains?
aspects of a DECISION
what are components?
These are associated with choices.
What is a consumption bundle?
Something that includes all of the COMPONENTS for a CHOICE.
What is Utility?
A satisfaction construct associated with a CONSUMPTION BUNDLE. The whole CHOICE.
What is the Optimal Choice? (In regards to utility)
A choice that has the highest UTILITY.
What does it mean when a person is rational?
The individual has the ability to choose the highest UTILITY choice.
What are factor loadings?
these represent the realative importance of components in your choices. NEGATIVE values are COSTS.
What is utility function?
It means individuals value health and COMMODITIES.
Define Commodities.
Everything else you want in life besides health.
What is the concept of Health Production Function?
we produce health
what are inputs of the health production function?
Things that we do to help sustain and improve our health.
Ex. water, medications, exercise, sleep, immunizations, food
What are outputs of the health production function?
What we gain from improved health,
Ex. health, years of life, # of healthy days
Define Endowments
things we can’t change in a short amount of time that still effects our production of health.
What is Marginal Product of Health Care?
change in number of health days caused by change in amount of health care used.
What is a marginal product?
Diminishes in size as you move further along x axis.
What is the law of diminishing marginal returns?
If you put in more and more you get less and less back.
What is a budget constraint?
total money = amount spent on health care and other goods
What is time constraint?
total time = time spent at work, producing health, producing commodities, and in leisure.
According to Economic Theory, which of the following statements is false?
the cost of a choice is always less than the benefits of a choice
there are tradeoffs to every choice
The opportunity cost is always the second best (or next best) choice.
Economics is the study of how and why people make choices
the cost of a choice is always less than the benefits of a choice
According to the definitions presented in class, a treatment choice is the same as the treatment chose. T/F
False
Which of the following is true (according to Economic Theory and the Taxonomy of Healthcare Costs?
Cost is the amount of money needed to buy something
it is possible for something to have no cost
tangible costs are not measured in terms of money
a negative outcome of a choice is considered a cost of that choice
a negative outcome of a choice is considered a cost of that choice
According to Economic Theory and the Taxonomy of Healthcare Costs, which of the following is false?
Humans have unlimited wants
Resources don’t have to be scarce
indirect costs are opportunity costs
Sometimes humans make choices because they can and sometimes humans make choices because they must
Resources don’t have to be scarce
According to Economic Theory, which of the following is true?
the opportunity cost is an example of a tradeoff
all choices have exactly one tradeoff
tradeoffs are the costs associated with a choice
Only bad choices have tradeoffs
The opportunity cost is an example of tradeoff
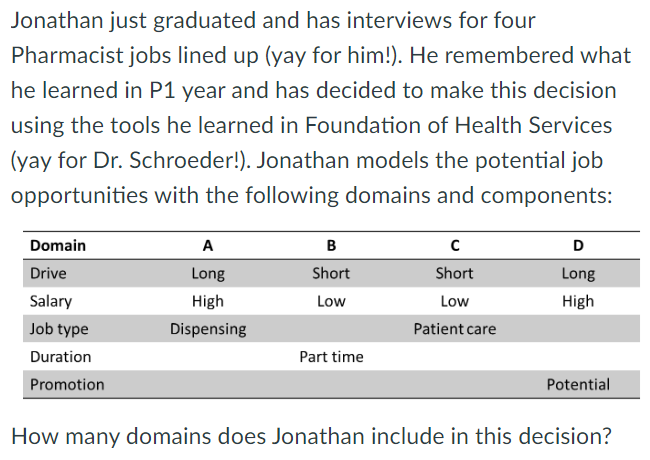
1, 2, 3, 4, or 5
5
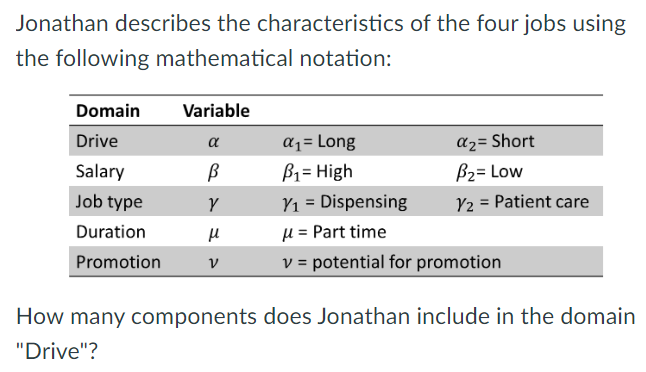
1, 2, 3, 4, or 5
2
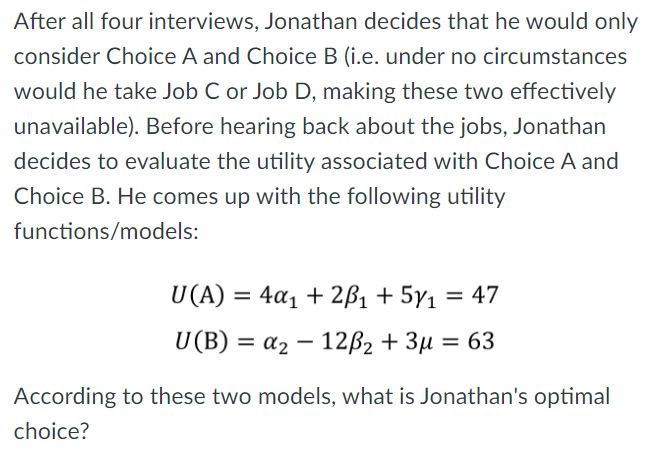
Choice A, Choice B, Neither of them, Either of them
Choice B
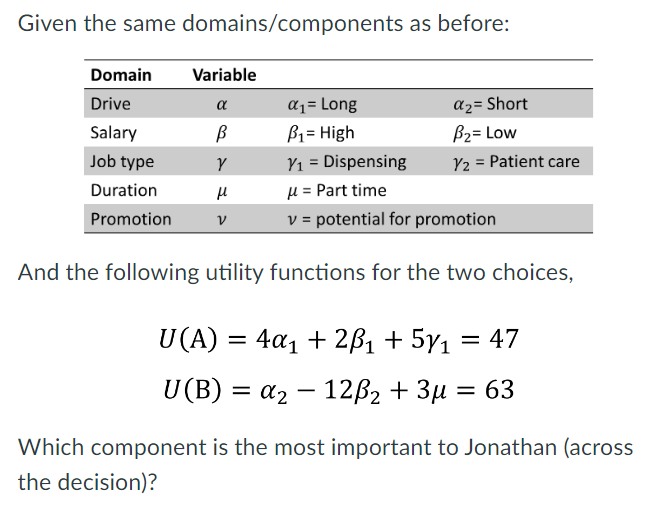
Long drive, short drive, high salary, low salary, mostly dispensing, part time, potential for promotion
Low Salary
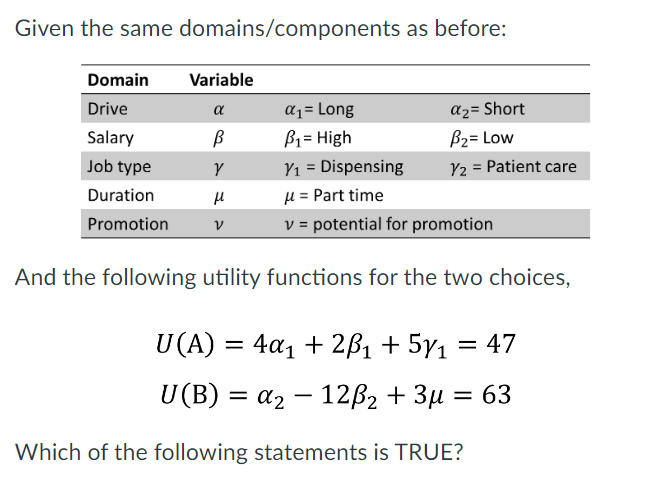
Jonathan views dispensing as a benefit of Choice A (ie something he values/likes)
jonathan views a low salary as a cost of the job in Choice A
Jonathan would prefer the job in Choice A to include patient care
The job in Choice B is part time. This component most impacts the utility of that choice.
Jonathan views dispensing as a benefit of Choice A (ie. something he values/likes)
Which of the following statements is true, according to the Grossman Model?
Health only depreciates (i.e. decreases) over time if you continue to invest in your health
individuals actively choose how much health to buy in the next time period
money and time are both scarce resources (i.e. they are finite)
endowments are modifiable (i.e. can be changed)
money and time are both scarce resources (i.e. they are finite)
According to the Grossman Model, ____________________________________________. Select a phrase that is ALWAYS true.
people value their health as well as other commodities
people value their health over other commodities
people value their health less than other commodities
people value their health equally with other commodities
people value their health as well as other commodities
In the Grossman’s model, a person’s health can increase or decrease in the next time period (i.e. the future). T/F
True
Which of the following statements about the Marginal Product of Health (MPH) is true?
A person with a lower MPH (i.e. smaller number) requires more inputs to produce the same amount of health as a person with a higher MPH
MPH is a way to measure how healthy a person is today
A person’s MPH remains constant throughout their life
MPH is an example of an unlimited want
A person with a lower MPH (i.e. smaller number) requires more inputs to produce the same amount of health as a person with a higher MPH
Which of the following is true, according to the Grossman Model?
individuals choose the price of goods (e.g. how much a surgery would cost).
People never make rational choices when it comes to health
there are tradeoffs to every choice: investing in more M (healthcare) means giving up some X (all other goods)
Choices are only constrained by time, not money
there are tradeoffs to every choice: investing in more M (healthcare) means giving up some X (all other goods)
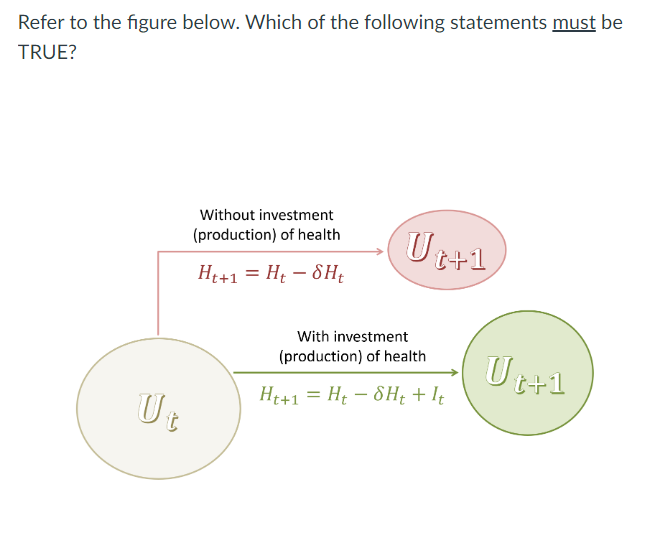
utility in the next period Ut+1 with investment in health (the green circle) is always greater than utility in the next period Ut+1 without investment (the pink circle)
Ut can never be equal to Ut+1
Producing utility today will result in greater utility tomorrow
It is always larger then sHt
utility in the next period Ut+1 with investment in health (the green circle) is always greater than utility in the next period Ut+1 without investment (the pink circle)
According to the Grossman model, which of the following do individuals actively choose (or have direct influence over)?
How much money to spend on goods
How much health they have tomorrow
How good they are at making health (the magnitude of their marginal product of health, MPH)
How long they live
how much money they spend on goods
The grossman model would predict that a person with a lower marginal product of health (MPH) would be __________ to invest in their health, compared to a person with a higher MPH (all else equal).
less likely
more likely
equally likely
Less likely
According to the Grossman model, all else equal, if the cost of goods used to produce health (i.e. Pm) were to increase, then people would become more likely to invest in their health. (T/F)
False
According to the Grossman model, for which of the following cases/scenarios would it be optimal to stop investing in health?
when the depreciation in health is very small compared to the potential investment
when the marginal product of healthcare is very small
when the cost of all goods is low
when the person values their health more than other commodities
when the marginal product of healthcare is very small

U2 > U1 and U2 > U3
U2 > 0
U3 > U2 and U1>U2
U1>U2>U3
U3>U2>U1
Shannon would never select this treatment
U2>U1 and U2>U3
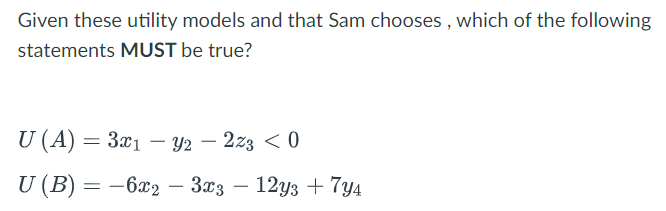
U(B)<0
Sam likes y2
Sam is irrational
The costs of Choice A outweigh the benefits of Choice A
None of the above
The costs of Choice A outweigh the benefits of Choice A

Which component has the greatest value (ie is the most imporant) to the individual"?
z1
z3
z5
z8
z5
The treatment chosen is the one that is assigned the highest utility value
always true
could be true
never true
always true
The treatment chosen is associated with positive utility (ie is a number greater than zero)
always true
could be true
never true
could be true
According to the Grossman Model, if the cost of all goods is constant (ie Pm=Px) everyone will choose to buy the same amount of M and X. T/F
False
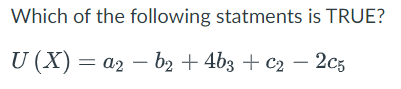
the utility of Choice A must be positive
The utility of Choice A must be negative
Choice A is the optimal choice of this decision if no other options are available
choice A is not optimal
None of the other statements are true
none of the other statements are true
3. is not the correct choice because if there were no other options available it is NOT considered a CHOICE.
What are the 3 P’s of public health?
Preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical health
What are the 3 levels of prevention in public health?
Primary - Prevent the disease from happening, identifying Risk Factors
Secondary - disease has started but there are no symptoms = no medication or treatment
Tertiary - stop complications of the disease through medical intervention once it has taken root
Classify the following as one of the three prevention types:
A policy that increases tax on sweetened beverages
Aspirin use for patients who have coronary artery disease
primary
tertiary
What is public health’s approach to a community’s health problem?
Assessment
assess the problem
Policy Development
design an intervention
Assurance
does it work? monitor the changes in the intervention and make changes as needed.
What is System level intervention in public health?
HIGH level, government run
entire population affected
policies and laws are made
What is Community level intervention in public health?
Middle level
group of people affected
local community groups involved
change community norms, attitudes and awareness
social marketing
What is individual level intervention in public health?
Low level
the individual members at risk
change individual behaviors, knowledge, and skills
What was the healthcare like Pre-1875? (system, hospitals, health outcomes, providers)
Pure market system - paid for with cash, money = care and quality = $$$
Some options for the destitute - Charity hospitals
Poor health outcomes
SO many different types of doctors, no licensures b/c doctors aren’t better than us
Medical school was so easy, pumping out doctors
What was healthcare like post civil war? (system, hospitals, health outcomes, providers)
Better system improvements
licensing for providers - required education
Better quality medical schools - increased students
what happened in healthcare between 1900-1915?
Minimum standards for med schools
Access to medical care falls due to lack of doctors
Raised prices for medical care
What happened to the healthcare system because of WWII?
INSURANCE YAY, employer-sponsored health care.
What are the positives and negatives of Britian’s Healthcare?
Positive
lower costs for patietns
everyone is covered
low overall spending
good outcomes (health wise)
good preventative care
Negative
NO choices
gatekeepers
government control
higher taxes
moral hazard - no cost → more appointments scheduled
What is Britain’s healthcare system (basic)?
No average family premiums - Except for dental, drugs, and glasses
government pays for hospitals, doctors, etc.
What is Germany’s Healthcare? (basic)
Everyone has insurance, Rich pay for the poor.
Rich can opt out for private
They bargain with doctors - set prices based on the state
What are the positives and negatives of German healthcare?
Positive
no copays for pregancy
school is free for healthcare providers
short wait times
copays are small + known in advance
keep insurance if lost job
OPTIONS
Negative
Poor provider compensation
let rich opt out - costs will overall increase for poor
What is Tiawan’s healthcare system? (Basic)
one government run insurance company
copays for drugs
What are the positives and negatives of Taiwan’s healthcare?
Positives
smartcards - keeps track of medical history
NO opting out
NO wait times
choices
Negatives
government is borrowing from banks to fund healthcare
usage is monitored
Moral hazard
What is japan’s healthcare system? (basic)
Insurance provided by employers OR community based insurance companies
government negotiates prices with providers
What are the positives and negatives of Japan’s healthcare?
Positive
No appointments
Transparency
CHOICES
good outcomes
low costs
lose job → community insurance
low prices → innovation
Negative
low pay for providers
hospitals are in debt
government sets all the prices (1 price for whole country)
Compare a Pure market system vs a pure government system.
Pure-Market
No government intervention
no waiting
no moral hazard
choices
POOR have less choices
Skimp preventative care
Pure - Government
Government intervention
think like Britain