BIOL 2020: Lecture 5 (movement against the gradient)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level
movement against the concentration gradient requires ATP
structure:
nitrogenous base (adenine)
ribose sugar
3 bonded phosphate groups
ATP → ADP
releases energy
ADP → ATP
requires energy
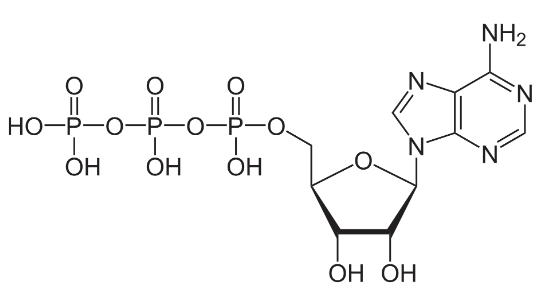
Indirect active transport
involves the transport of a solute in the direction of its increasing electrochemical potential coipled to the facilitated diffusion of a second solute
ex. symporters and antiporters
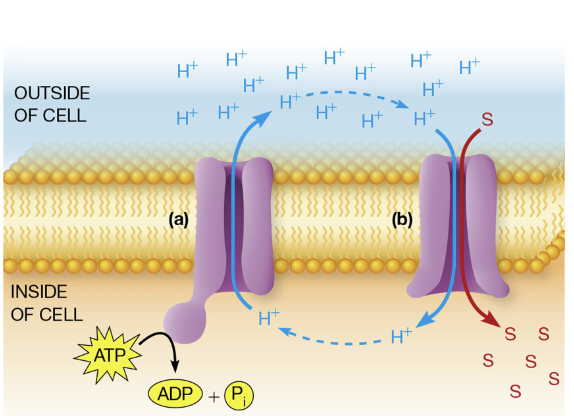
Direct active transport
involves using ATP to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient
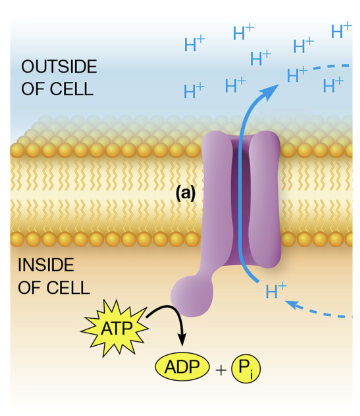
transport ATPases
ATP-driven pumps
hydrolyze ATP to ADP and single phosphate
use the energy released to pump ions or other solutes across a membrane
P-type pump
p-ATPases (ATP-driven pump) which phosphorylates itself during the pumping cycle
4 types:
P1: tranport heavy metals
P2: maintain electrochemical gradients
Ca2+/H+
Na+/K+
H+/K+
P3: membrane potential for plants and fungi
P4: moves phospholipids (flippase)
Ca2+/H+ P2-ATPases
occurs within eukaryote muscles
sarcoplasmic reticulum, or plasma membrane
keeps [Ca2+] low in cytosol

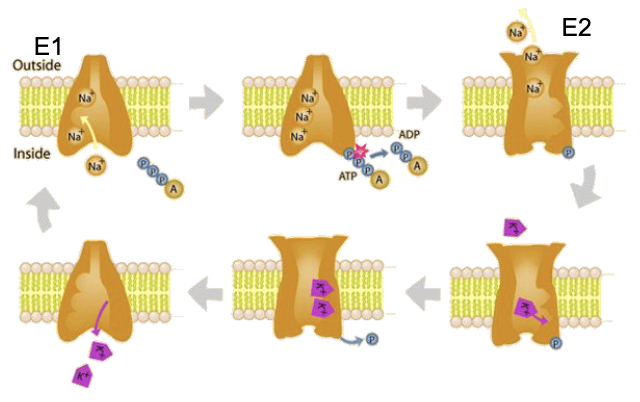
Na+/K+ P2-ATPases
occurs within animals
plasma membrane
maintains membrane potential (via electrochemical ion gradients in all cells)
-60mV
continuously pumps Na+ ions out of the cell, and K+ ions into the cell
cycles between two conformations
E1: open inside
E2: open outside
H+/K+ P2-ATPases
occurs in animals
plasma membrane
pumps H+ to acidify stomach
Vacuolar-ATPase
two rotary motors
ATP driven motor turns an axle, which turns a second motor that pumps protons across the membrane
the linkers hold the complex together
pumps H+ ions to increase acidity in specific organelles
vacuoles
lysosomes
not phosphorylated
regulated by separating the ATP-powered motor form the proton pumping motor

F-type ATPases
ATP synthases
moves ions with the concentration gradient to produce ATP
F stands for “factor”
H+ F-type ATPases
occurs in eukaryotes
inner mitochondrial membrane
uses H+ gradient to drive ATP synthesis
2 motors connected together via stator
F0: electric motor powered by flow of H+
F1: chemical motor powered by ATP
joins ADP and phosphate together by force to create ATP

ABC-type ATPases
ATP-binding cassette transporters mediate ATP-powered translocation of big molecules
2 conformational states
importers and exporters
some need a binding protein
conserved protein domain
all ABC-type ATPases have a shared amino acid sequence in the ABC domain
