(4.7.1)(Carbon Compounds as fuels and feedstocks)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is crude oil?
Crude oil is the remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton that was buried in mud.
What is crude oil mostly made up of?
Hydrocarbons.
What are hydrocarbons?
Molecules made of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
What is the formula for alkanes?
CnH2n+2
What are the first 4 members of the alkanes?
Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane (MEPB)(Monkeys Eat Peanut Butter)
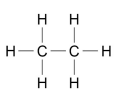
What are the two forms alkanes can be represented as?
Written (C2H6)
OR
DIAGRAM
How can you separate crude oils into usable parts?
Fractional distillation can form smaller usable fractions.
What can smaller usable fractions be used for?
Fuels and feedstocks for petrochemical industry.
What are the all the fuels that we rely on?
Petrol, diesel oil, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquefied petroleum gases. All of which are produced from crude oil.
What are useful materials made by the petrochemical industry?
Solvents, lubricants, polymers, detergents.
What do the properties of hydrocarbons depend on?
Size of their molecules, including boiling point, viscosity (thickness) and flammability.
The ________ of hydrocarbon fuels releases energy. During _______ , the carbon and hydrogen in the fuels are _______ . The complete _________ of a hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide and ________ .
The combustion of hydrocarbon fuels releases energy. During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen in the fuels are oxidised. The complete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide and water.
How does boiling point, viscosity and flammability change with increasing hydrocarbon chain?
As the hydrocarbon chain length increases, boiling point increases, viscosity increases, flammability decreases.
What is the name of breaking down hydrocarbons to produce smaller useful molecules?
Cracking.
What are the two methods for cracking?
Catalytic cracking and steam cracking.
What is the conditions for steam cracking?
800 degrees Celsius and no catalyst.
What are the conditions for catalytic cracking?
A slight pressure, high temperature and in the presence of a zeolite catalyst.
What are the products of cracking?
Alkanes and Alkenes.
Are alkanes less or more reactive than alkenes?
Alkenes are more reactive.
How to test for alkenes?
Bromine water.
What happens to the colour of bromine when it reacts with alkenes?
Becomes colourless.
What bond do alkenes have?
Double carbon carbon bond.
What is the equation for alkenes?
CnH2n
Why are alkenes unsaturated?
Alkene molecules are unsaturated because they contain two fewer hydrogen atoms than the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
What are the first 4 alkenes?
Ethene, Propene, Butene, Pentene. ( EPBP )
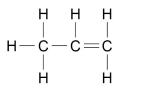
What are the two ways alkenes can be represented as?
WRITTEN C3H6
OR
DIAGRAM
What is the functional group of alkenes?
C=C
Why is alkenes reaction with oxygen different?
They tend to burn in the air with smoky flames due to incomplete combustion.
What happens to the their bonds when alkenes react with hydrogen, water and the halogens?
The double carbon bond becomes single carbon bond.