BIOL1020 - UQ
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
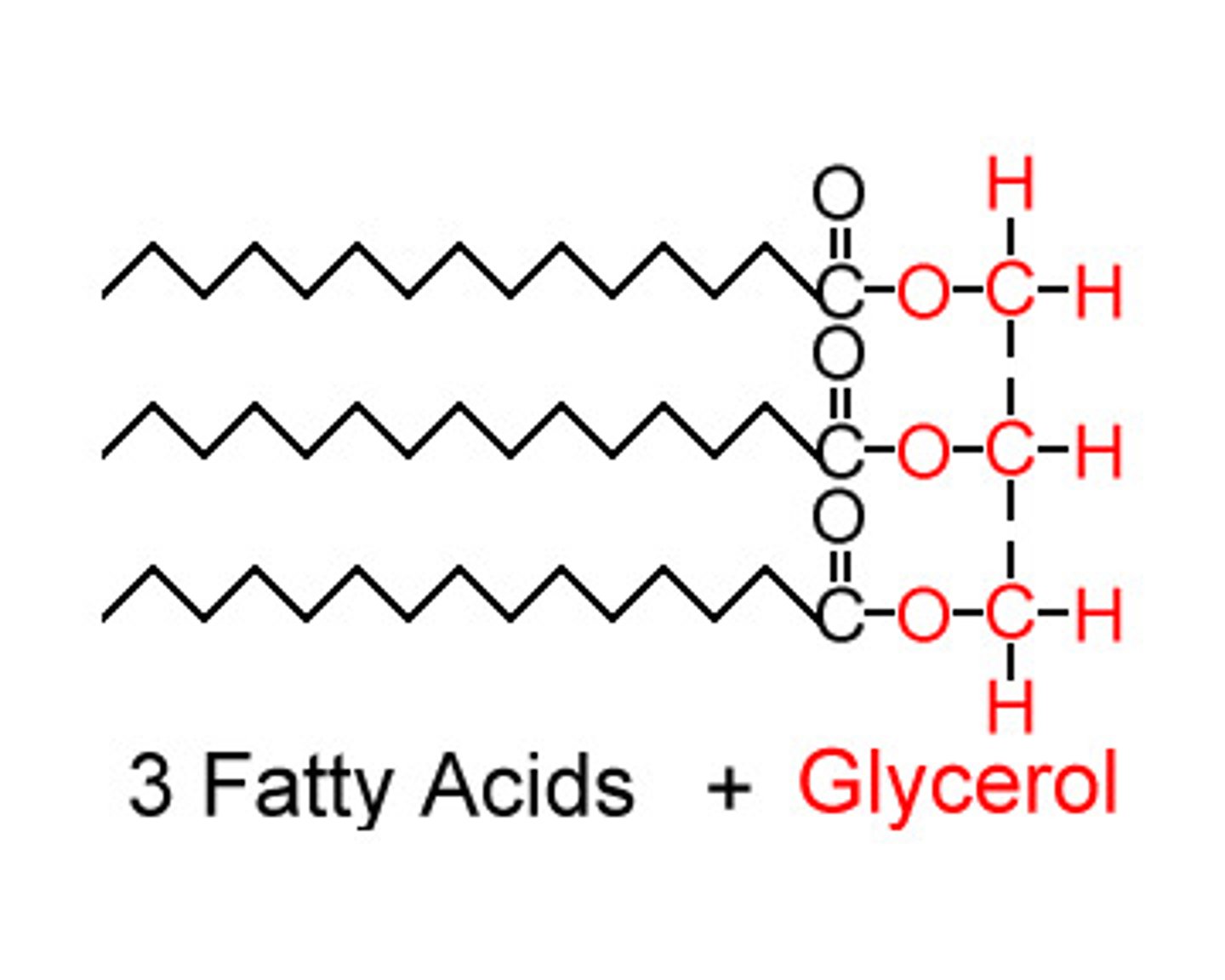
triacylglycerol
Lipid composed of a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids. Joined with an ester linkage.
Amphipathic molecules
have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties
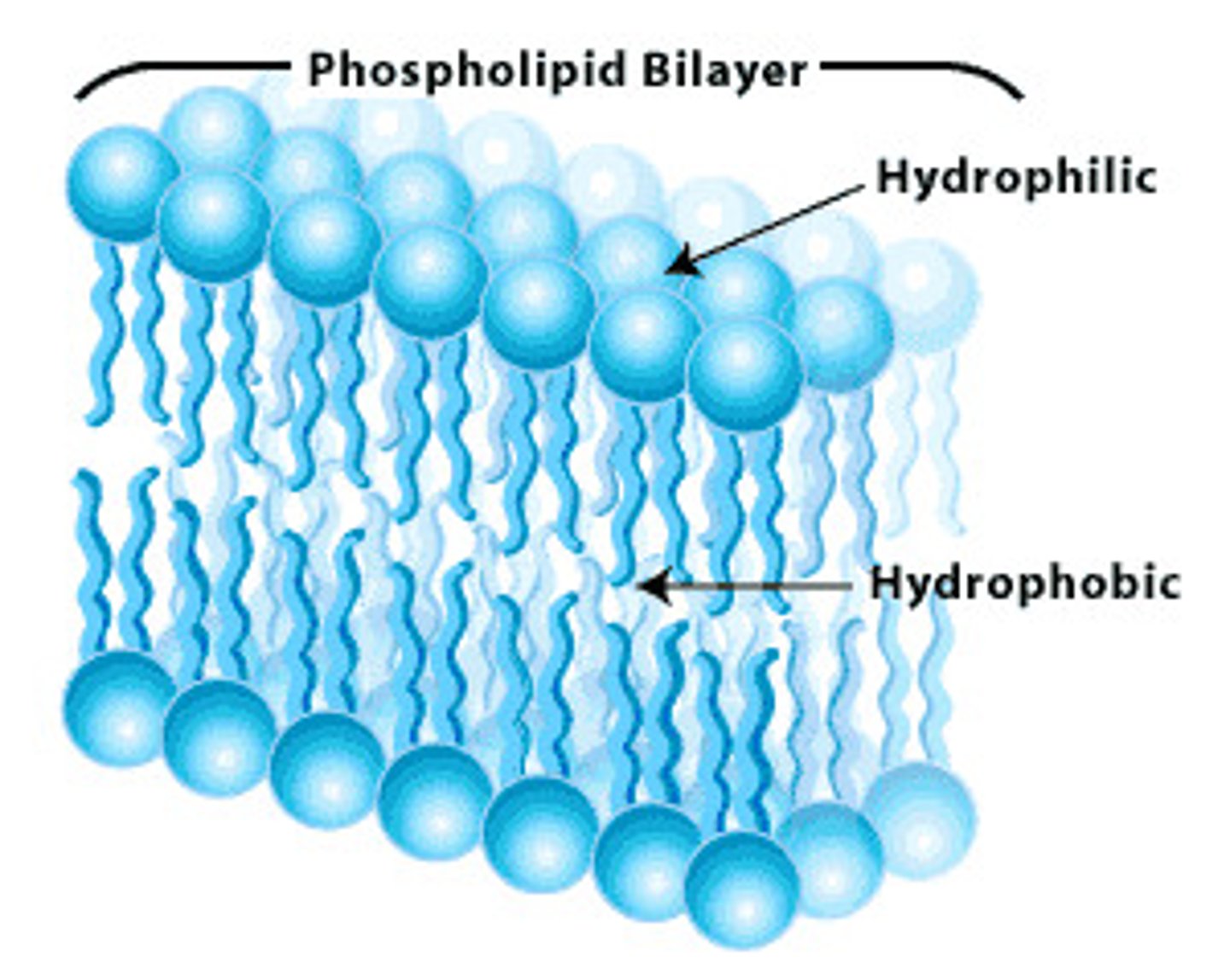
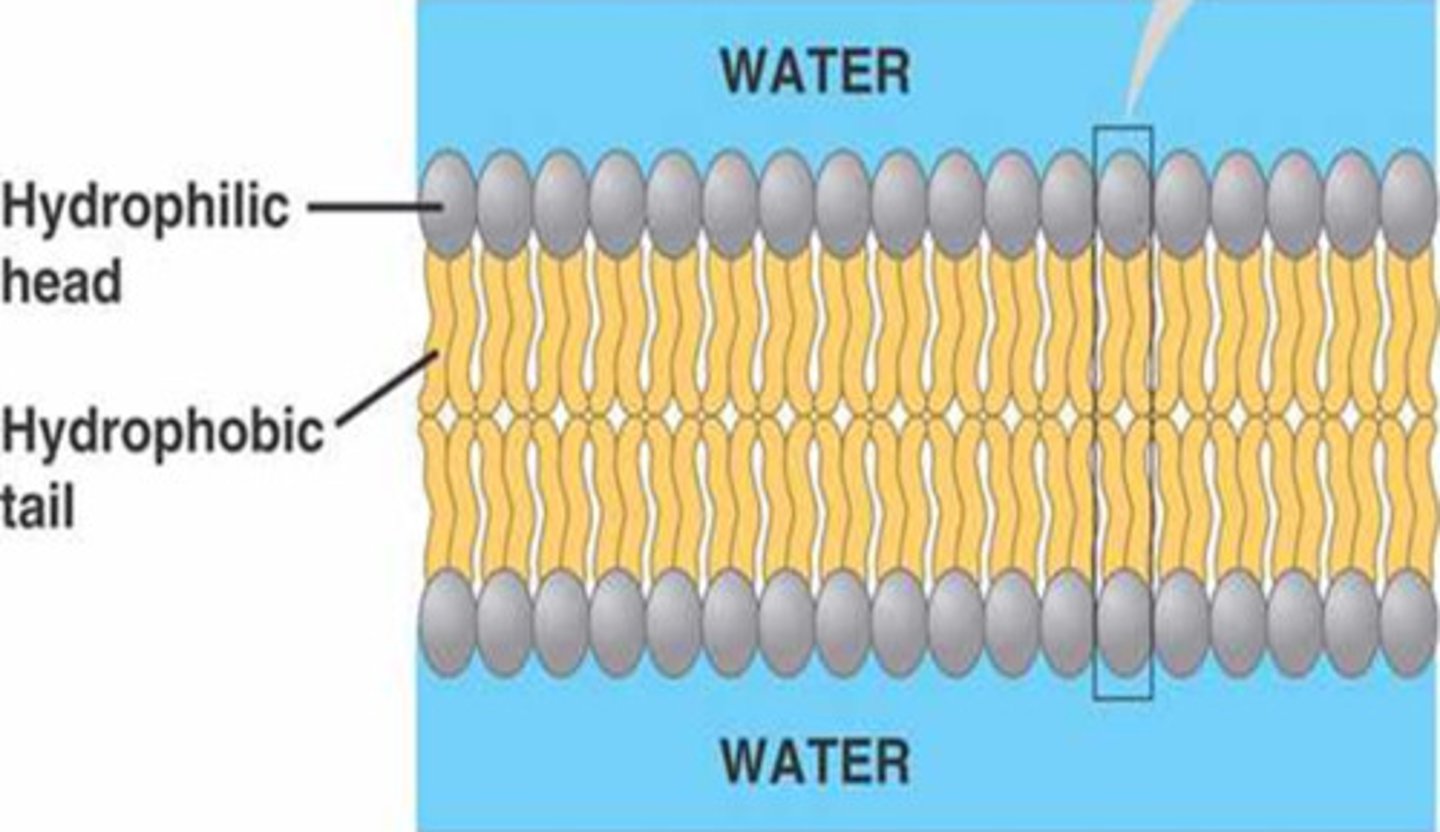
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
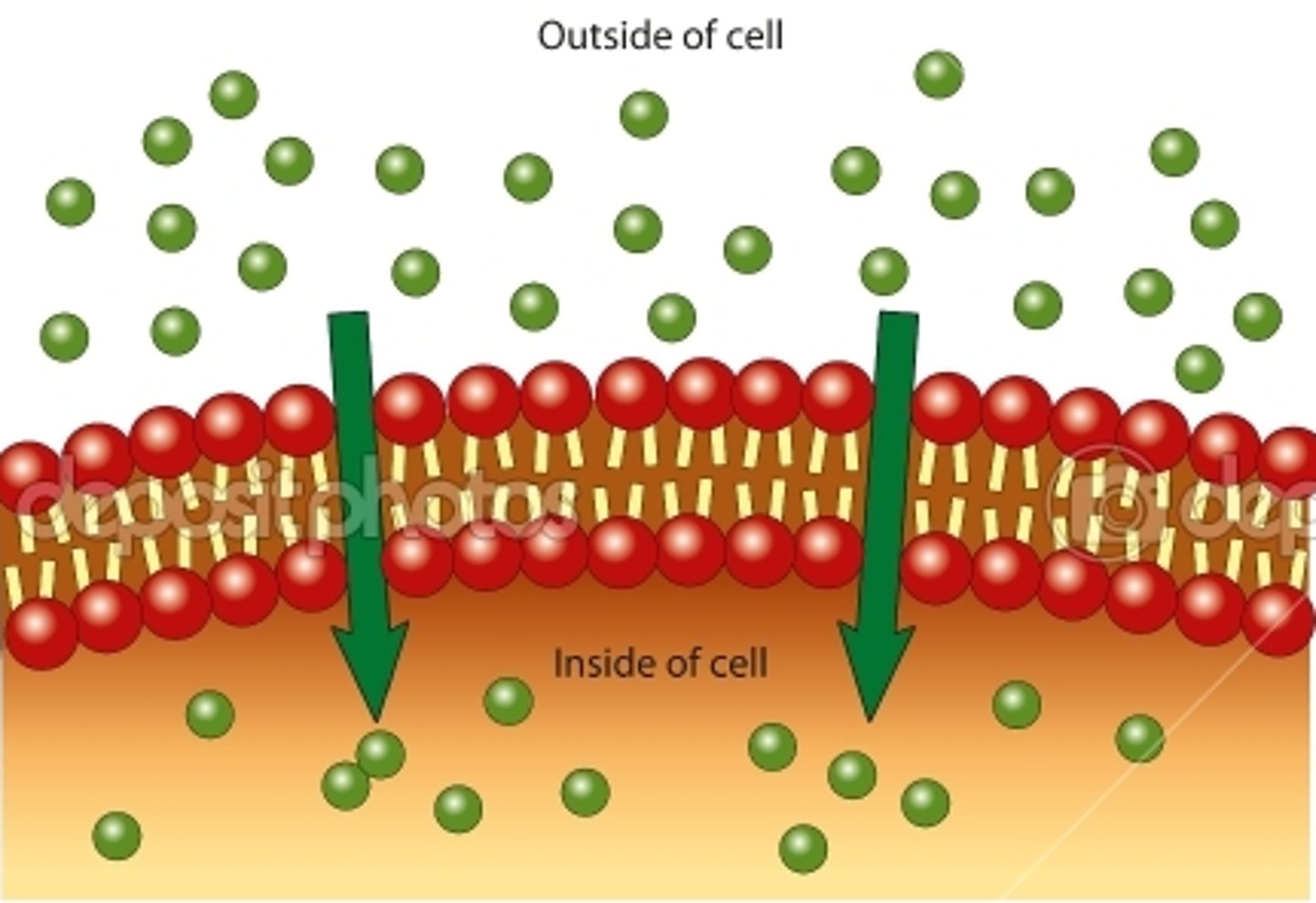
passive transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient
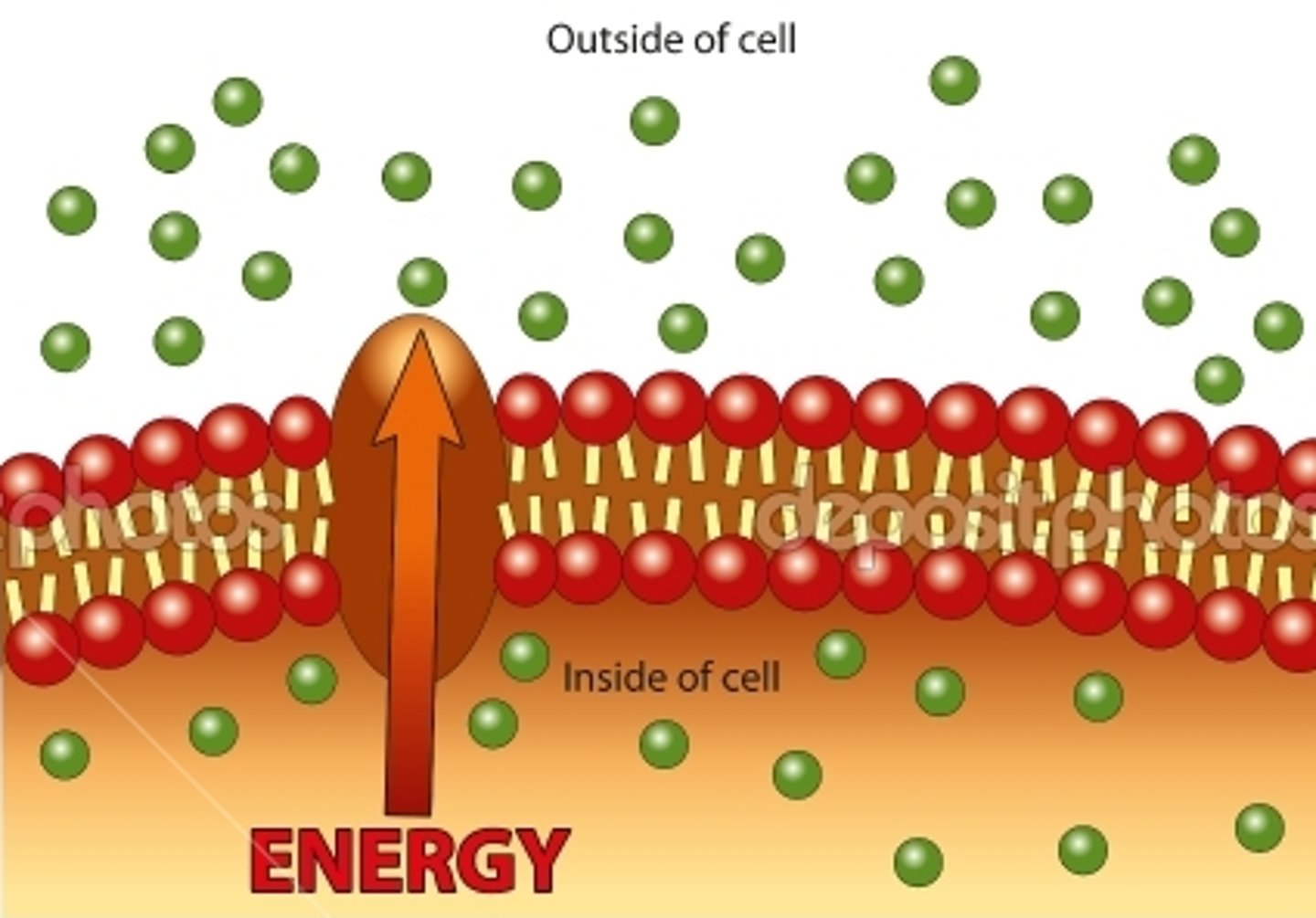
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
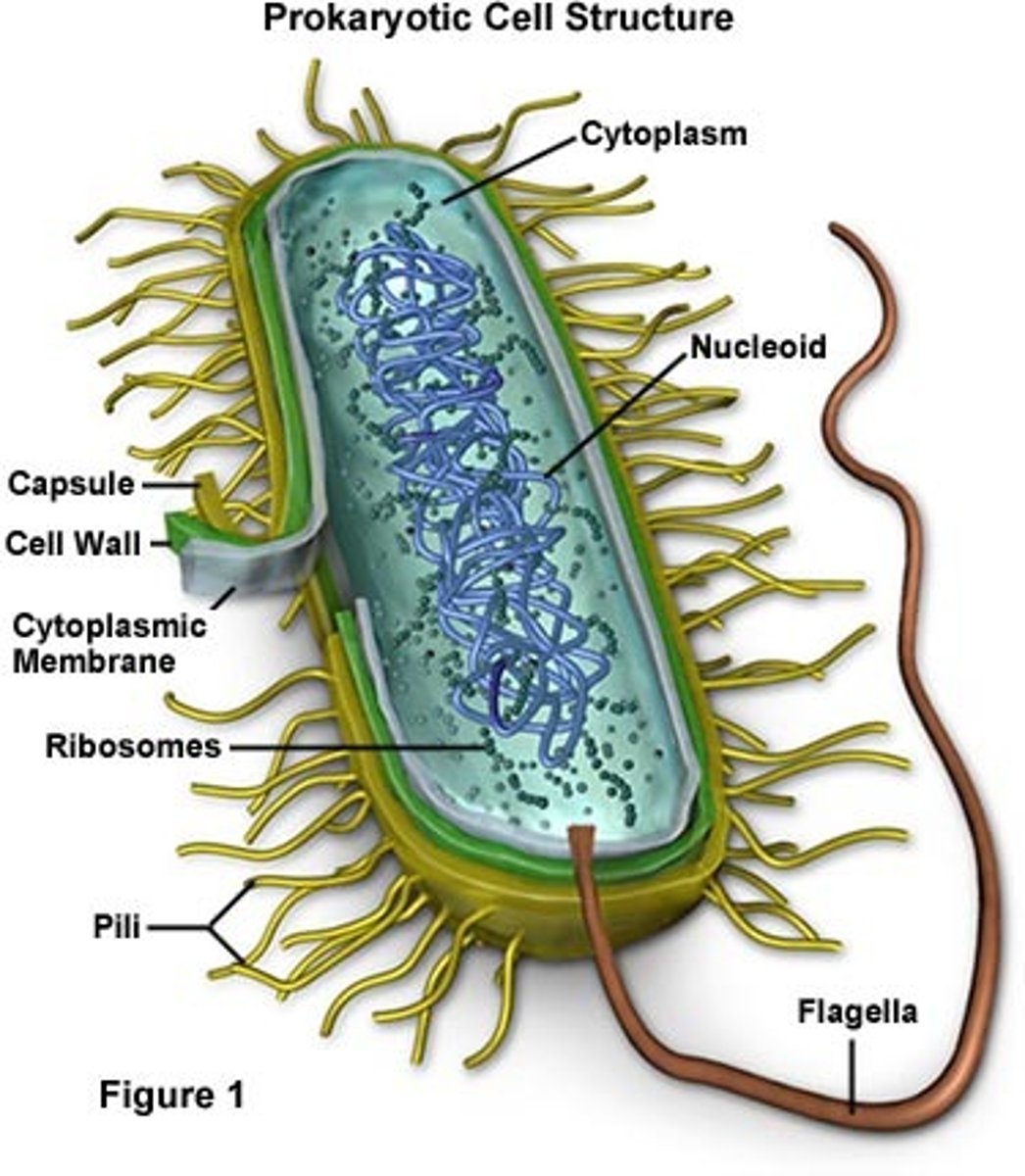
prokaryotic cell
1. No true nucleus
2. No membrane bound organelles
3. Ribosomes and DNA free floating
4. Unicellular
Eukaryotic cell
1. True nucleus
2. Membrane bound organelles
3. Ribosomes on Rough ER and DNA in nucleus
4. Multicellular
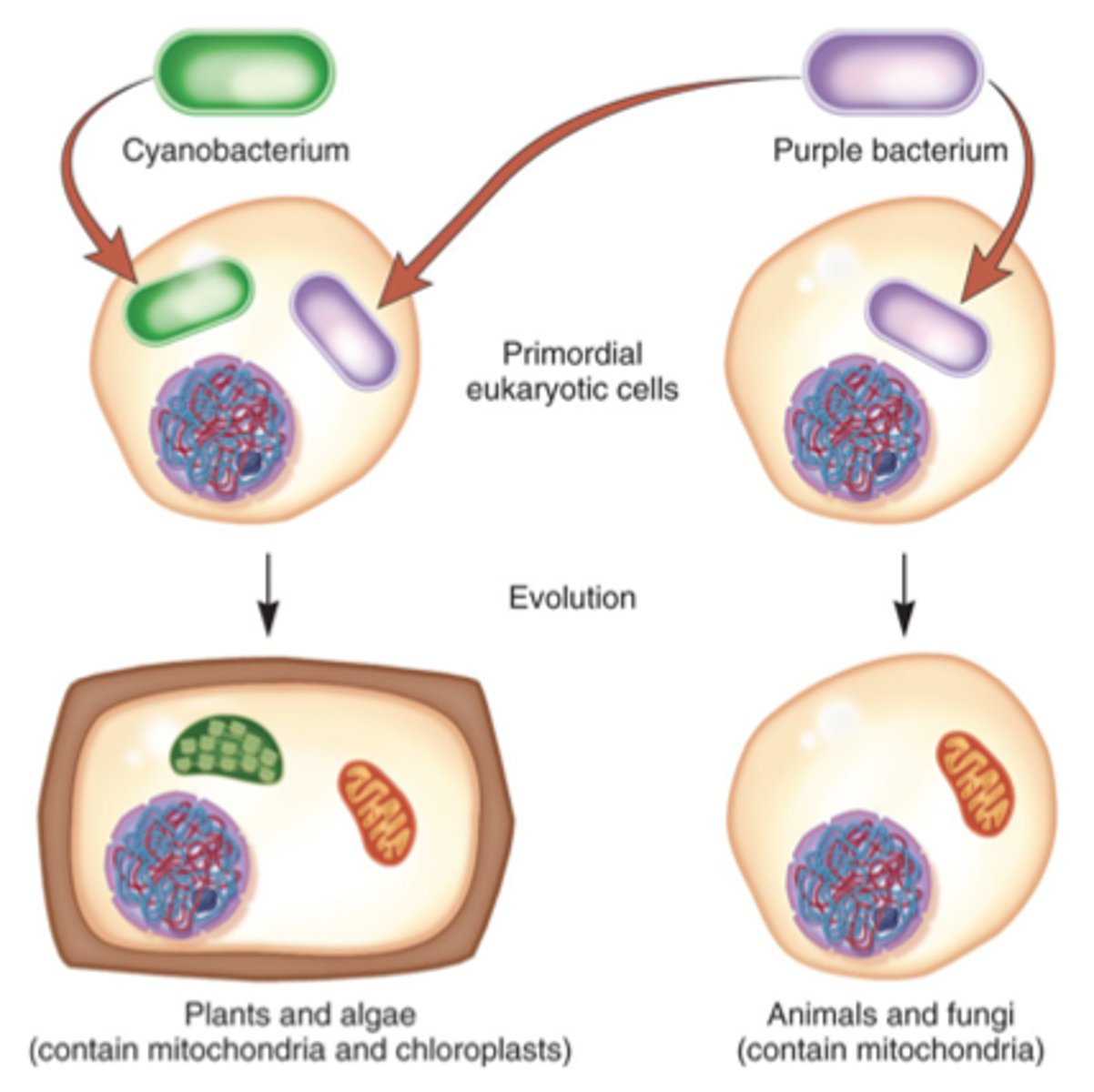
Endosymbiosis
The original internalisation of prokaryotes by an ancestral eukaryotic cell resulting in the formation of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
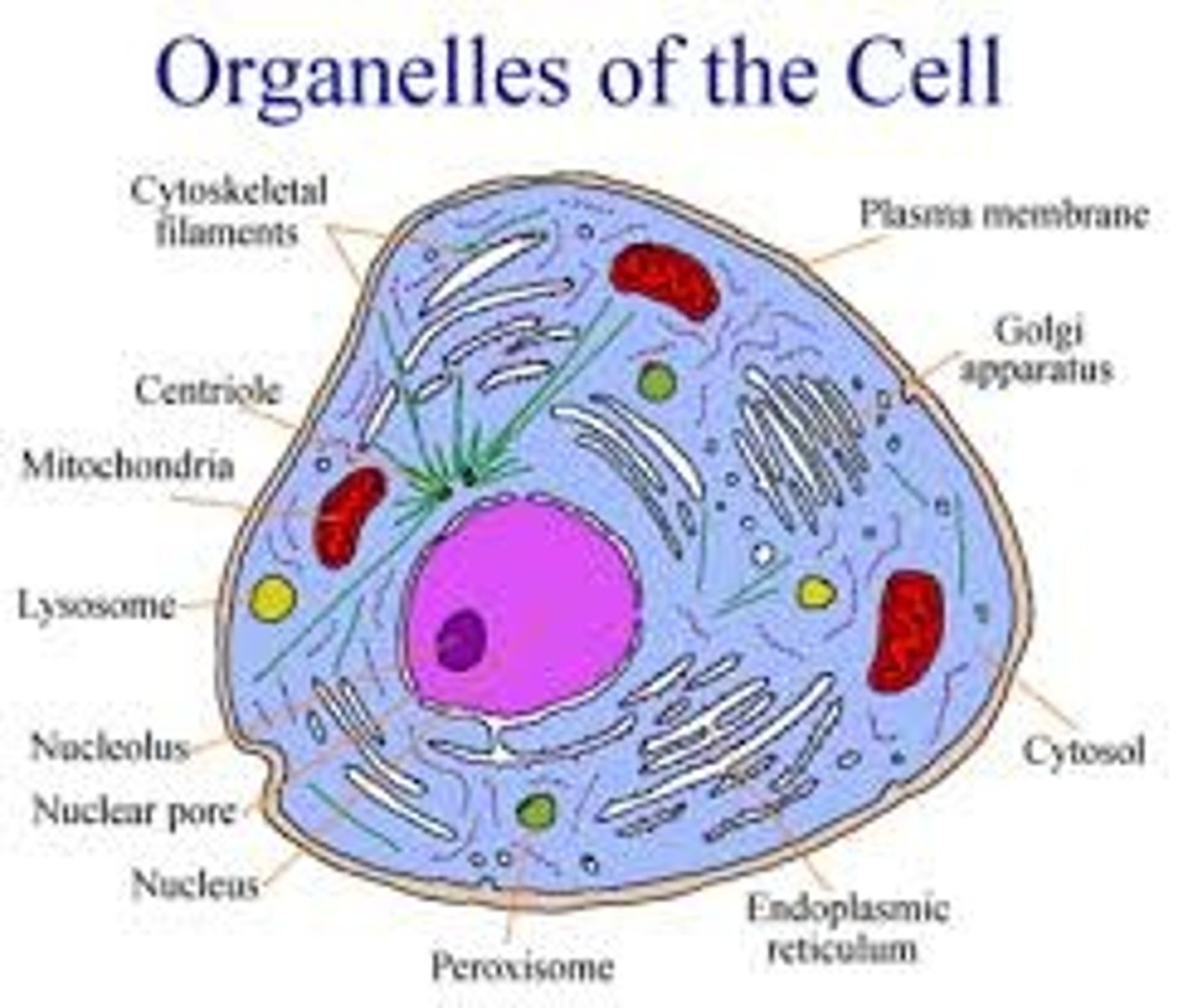
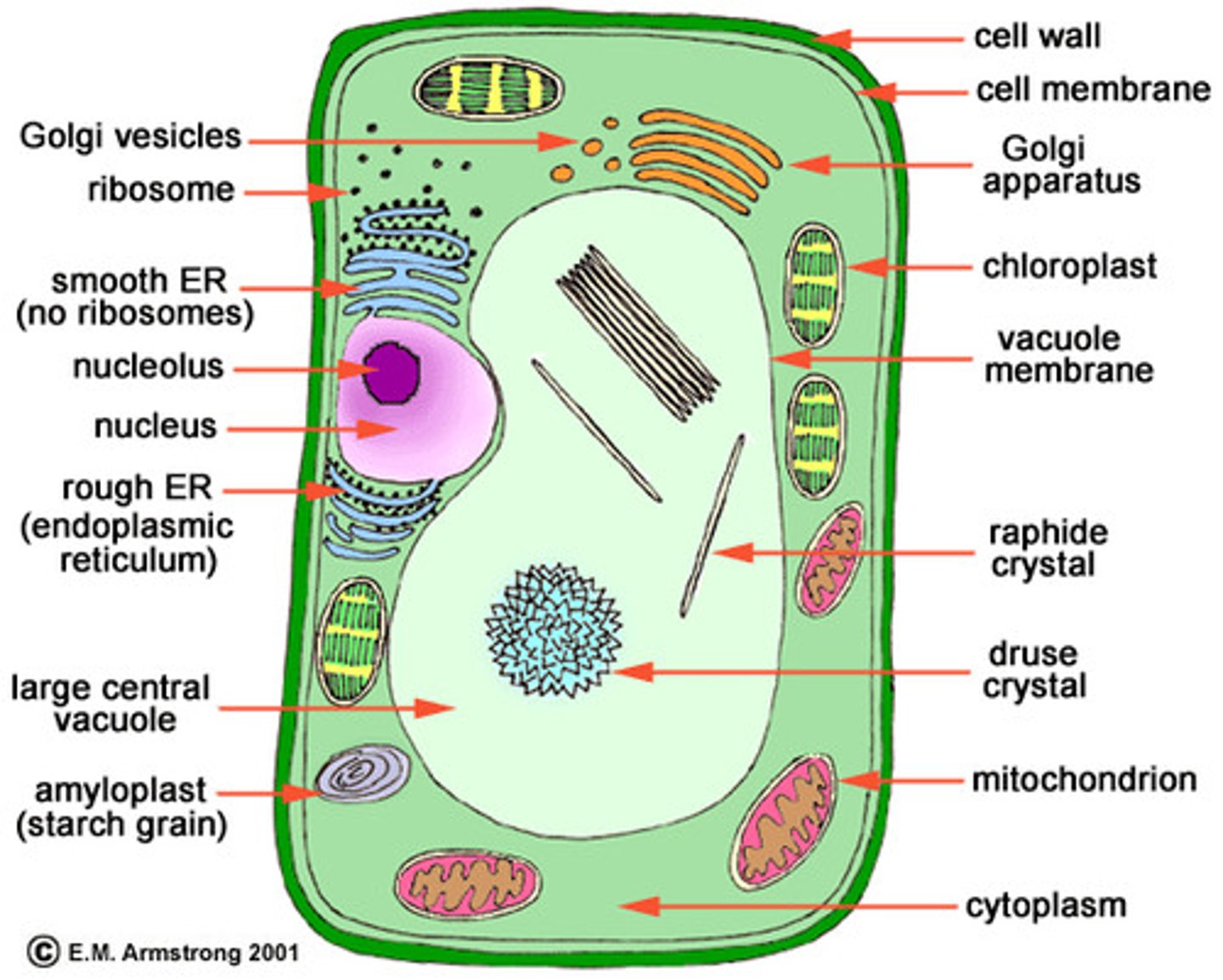
Organelles (ALL)
1. Nucleus-command centre
2. Nucleolus-Ribosomes produced
3. Nuclear envelope-membrane between cytoplasm/nucleus
4.Nuclear pore-opening that regulates passage
5. Rough ER-Contains ribosomes (Synthesise proteins)
6. Mitochondria-converts glucose into ATP
7. Lysosome-contains hydrolytic enzymes which breaks down macro molecules
8. Smooth ER-Manufacture lipids and metabolise carbohydrates and detoxify the cell
9. Golgi Complex-Collects, packages and modifies macromolecules and exports them
10. Peroxisome contain digestive enzymes
11. Centrioles-organise microtubules for structure
12. Vacuole hold material/waste
Organelles (PLANTS)
1. Large central Vacuole-hold material/waste
2. Chloroplasts-site of photosynthesis
3. Cell wall-gives structural support to plants
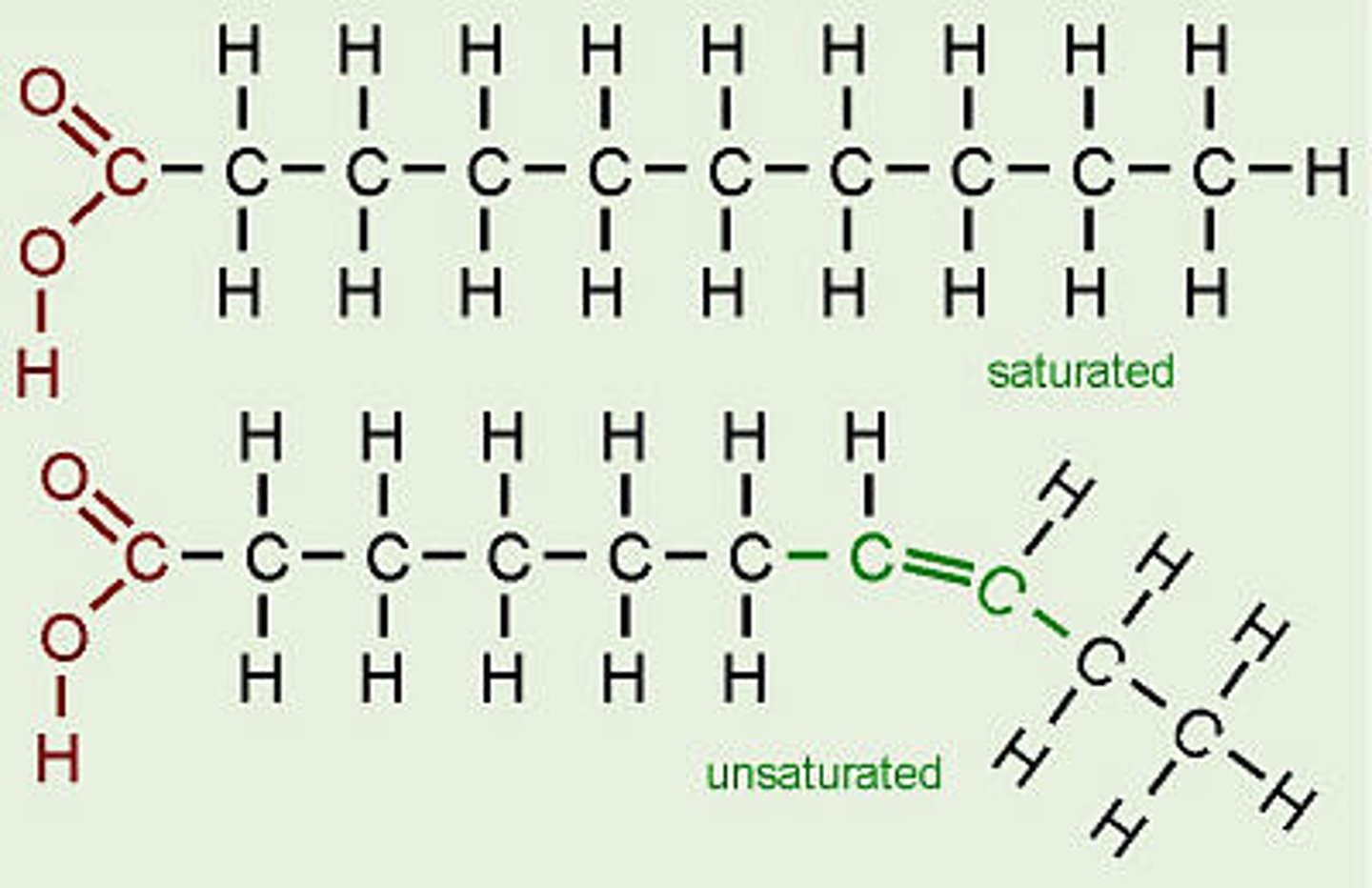
saturated vs unsaturated fats
saturated have NO double bonds
unsaturated have double bonds
cis vs trans fatty acids
Cis-have hydrogen on the same side of the C chain
Trans-have hydrogen bonds on different sides of the C chain
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule (Polymer) composed of many smaller monomers
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules that provide structure
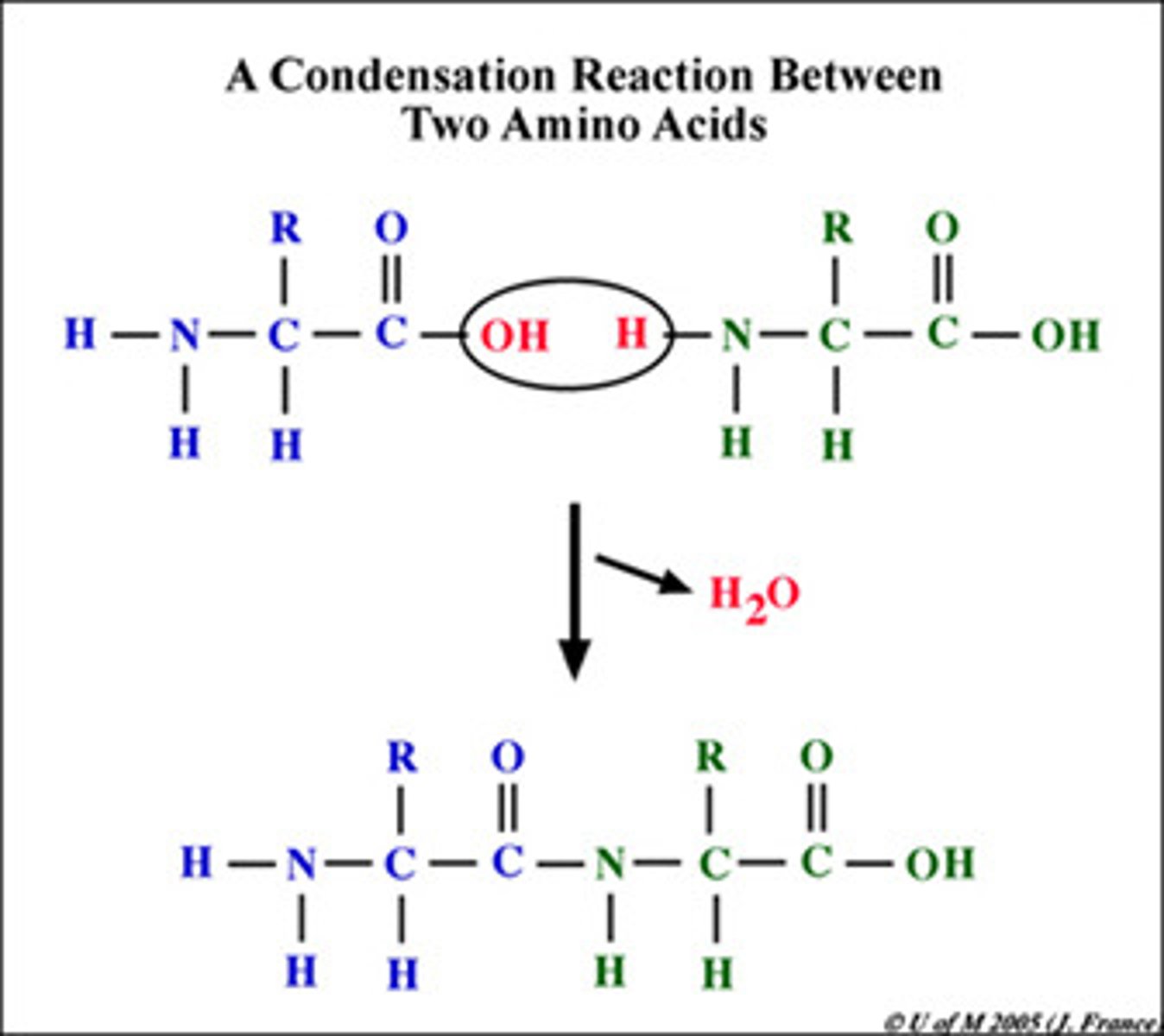
Dehydration (Condensation) Reaction
a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other through loss of a water molecule
hydrolosis reaction
Water is added to molecule to separate polymers (many pieces) into monomers (one piece)
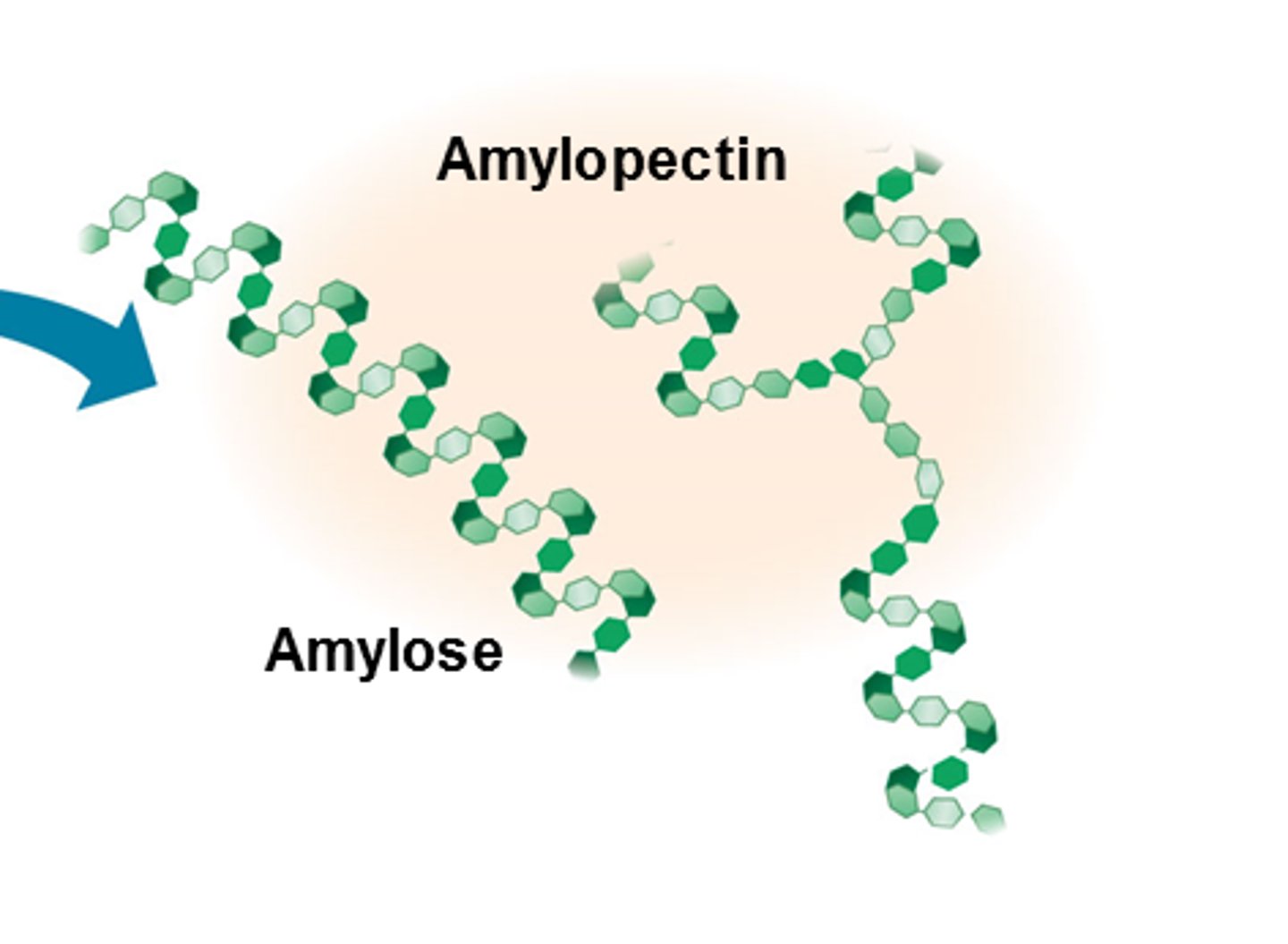
Starch
-Multiple Alpha glucose molecules undergo condensation reactions
-Amylose (1,4 bonds)
-Amylopectin (1,6 bonds and 1,4 bonds) branched
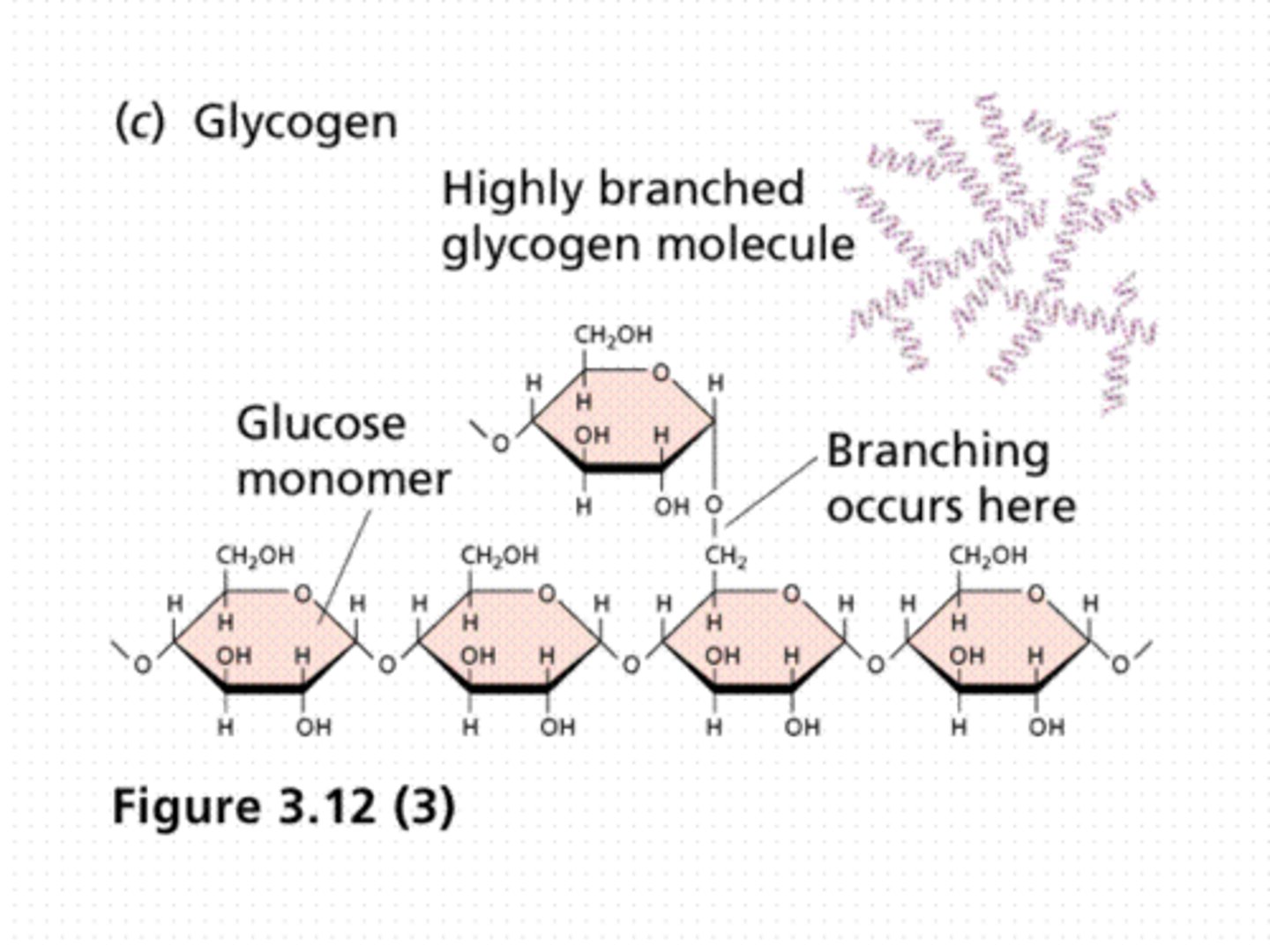
Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide ( Alpha 1, 6 bonds and 1, 4 bonds (LIKE amylopectin)
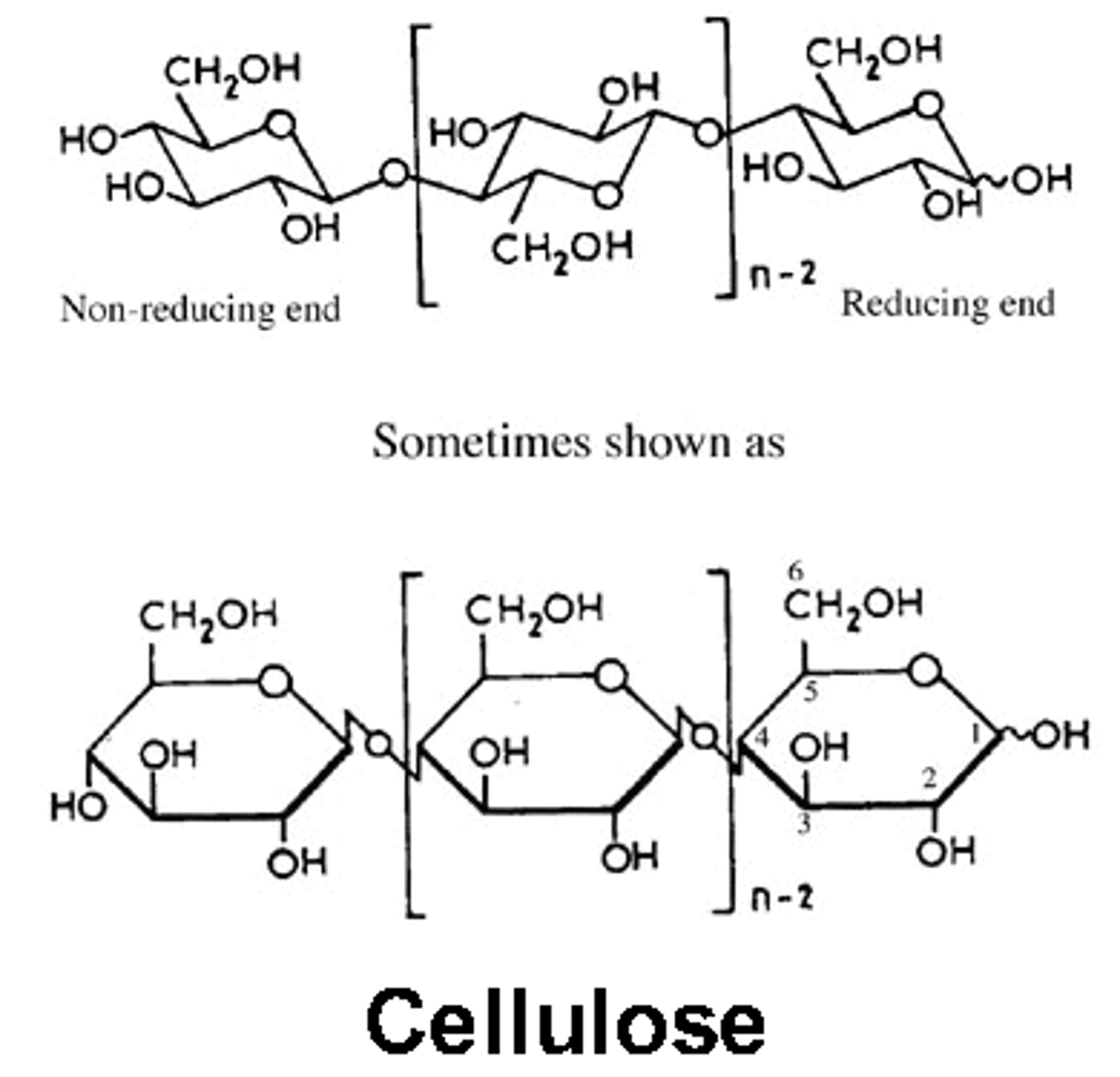
cellulose
Beta 1,4 bonds, BUT every second glucose molecule is flipped
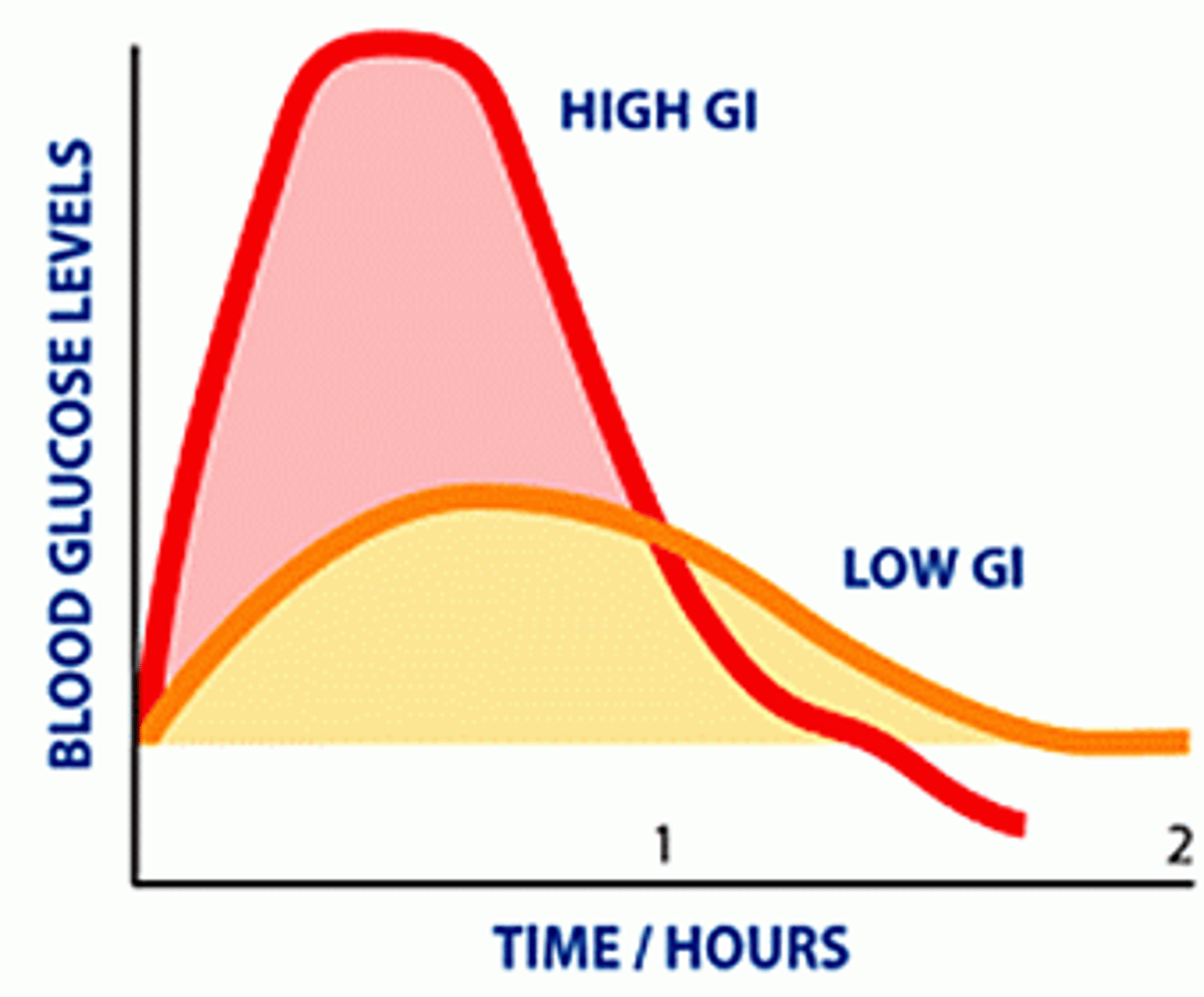
glycemic index
- A measure of how quickly your blood glucose level rises after eating.
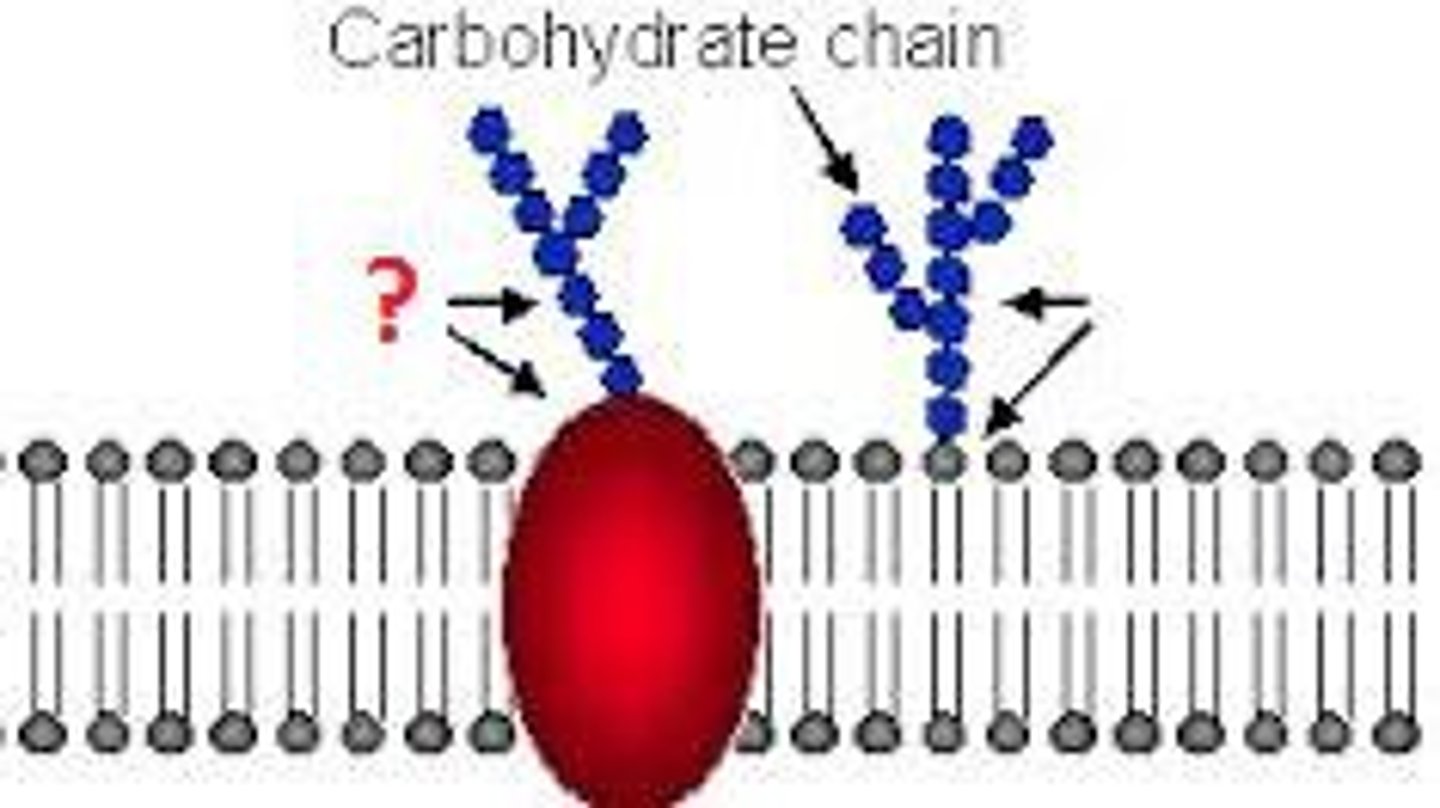
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins. (RESPONSABLE for cell-cell recognition)
amino acids
Monomers of proteins (N terminus=Amino Group) (C terminus=Carboxyl group)
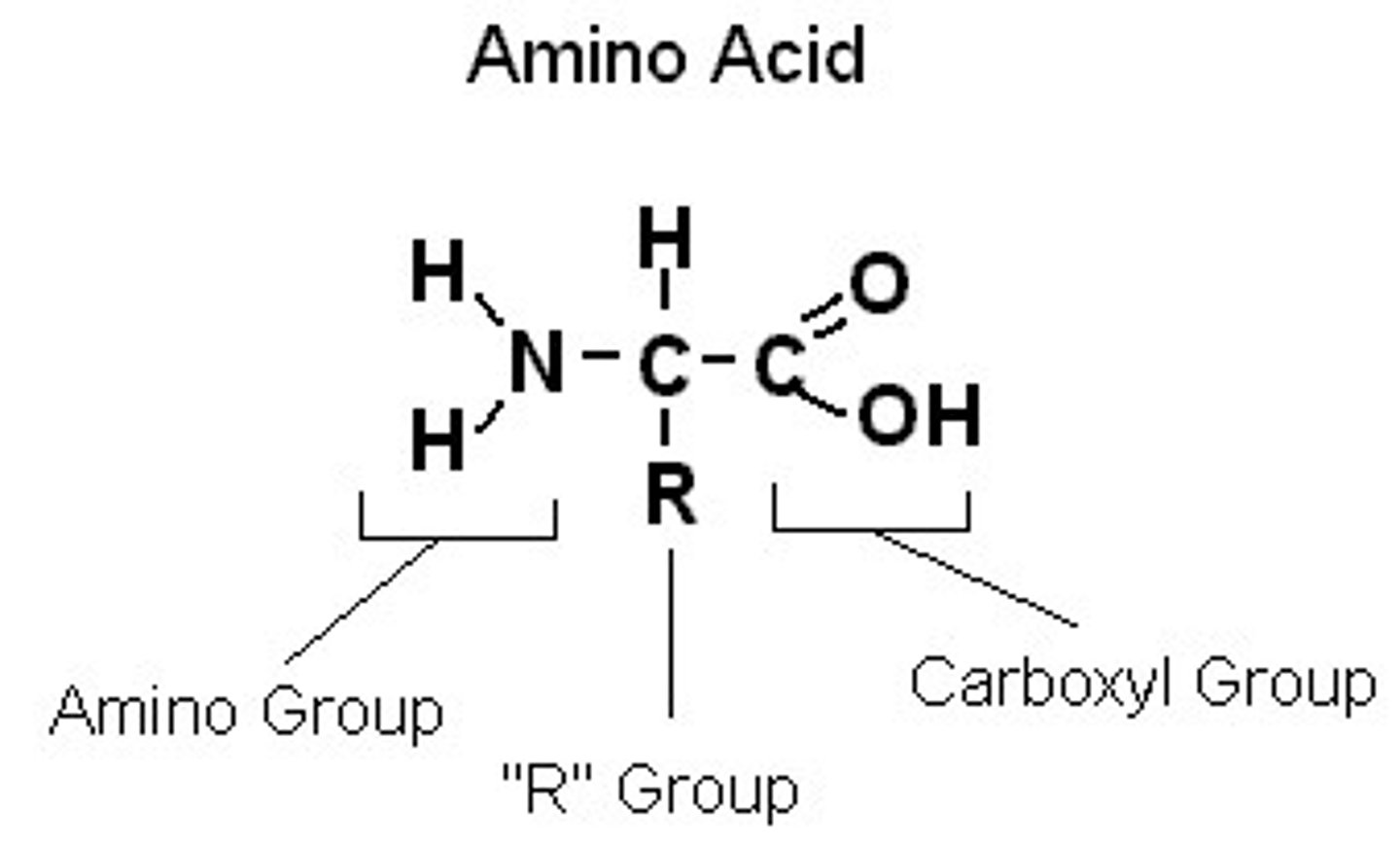
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure, sequence of amino acids
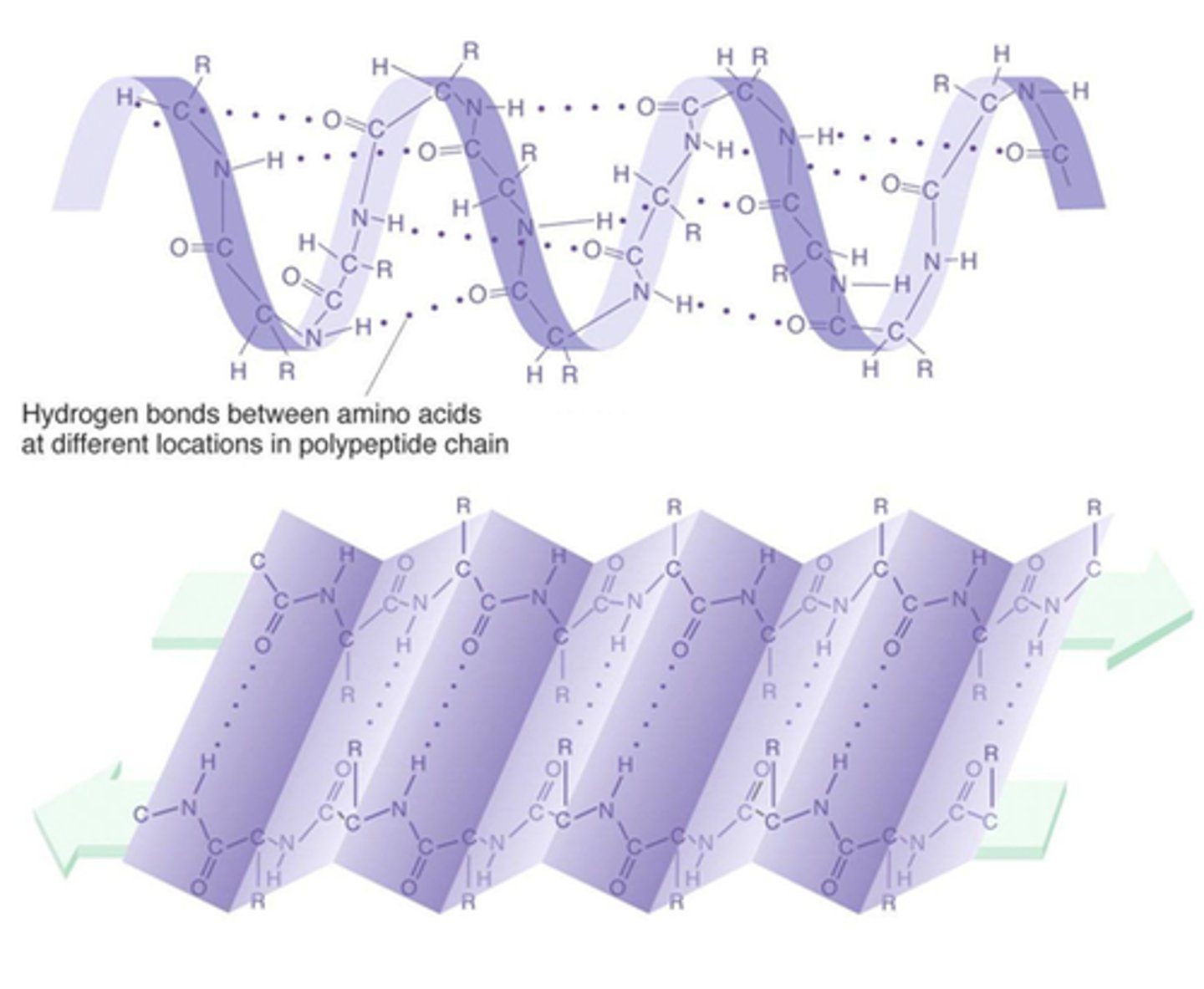
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils (ALPHA HELIX) or folds (BETA PLEATED SHEETS) of a polypeptide chain.
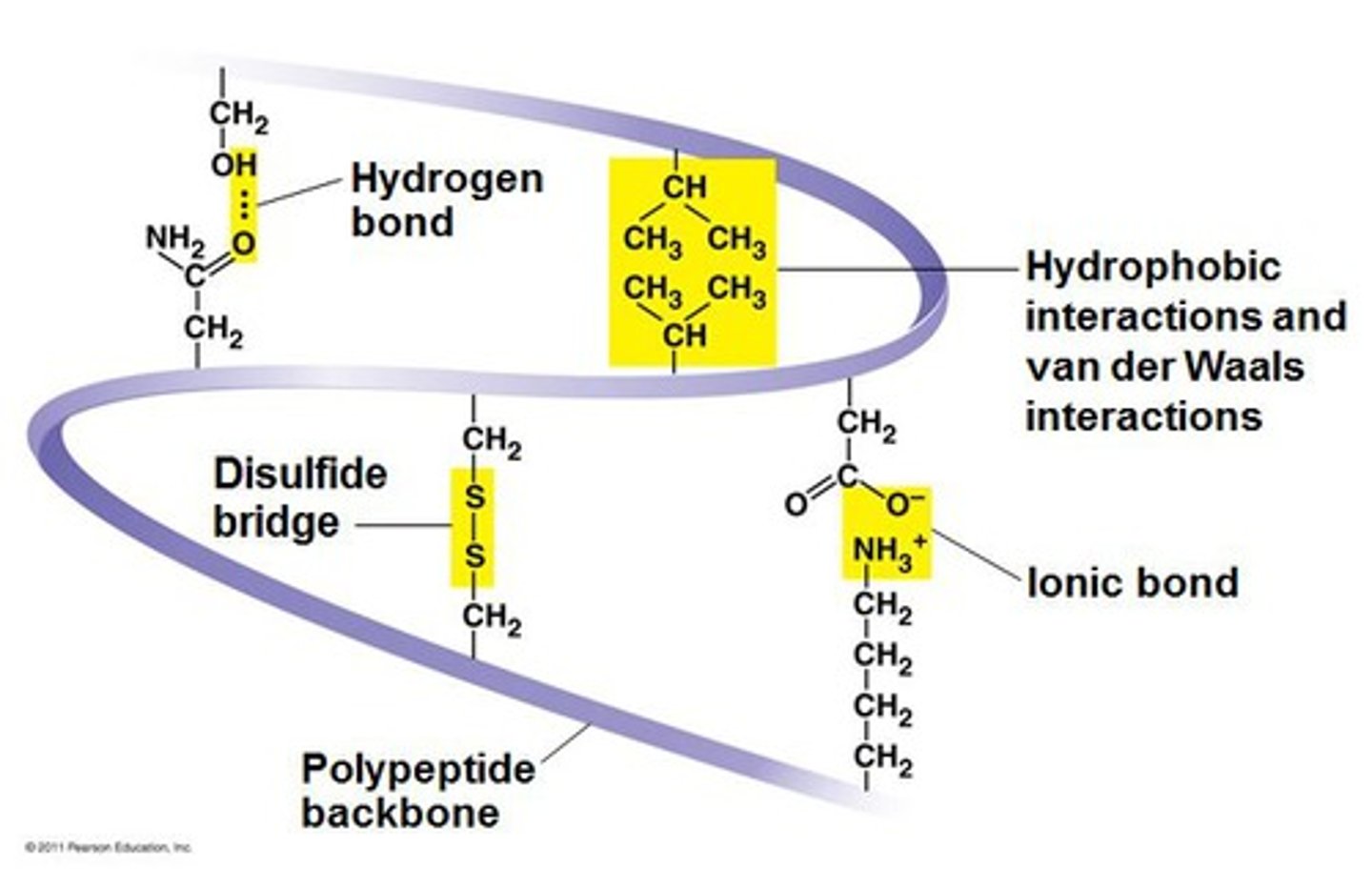
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain. (Disulphide bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and dispersion forces)
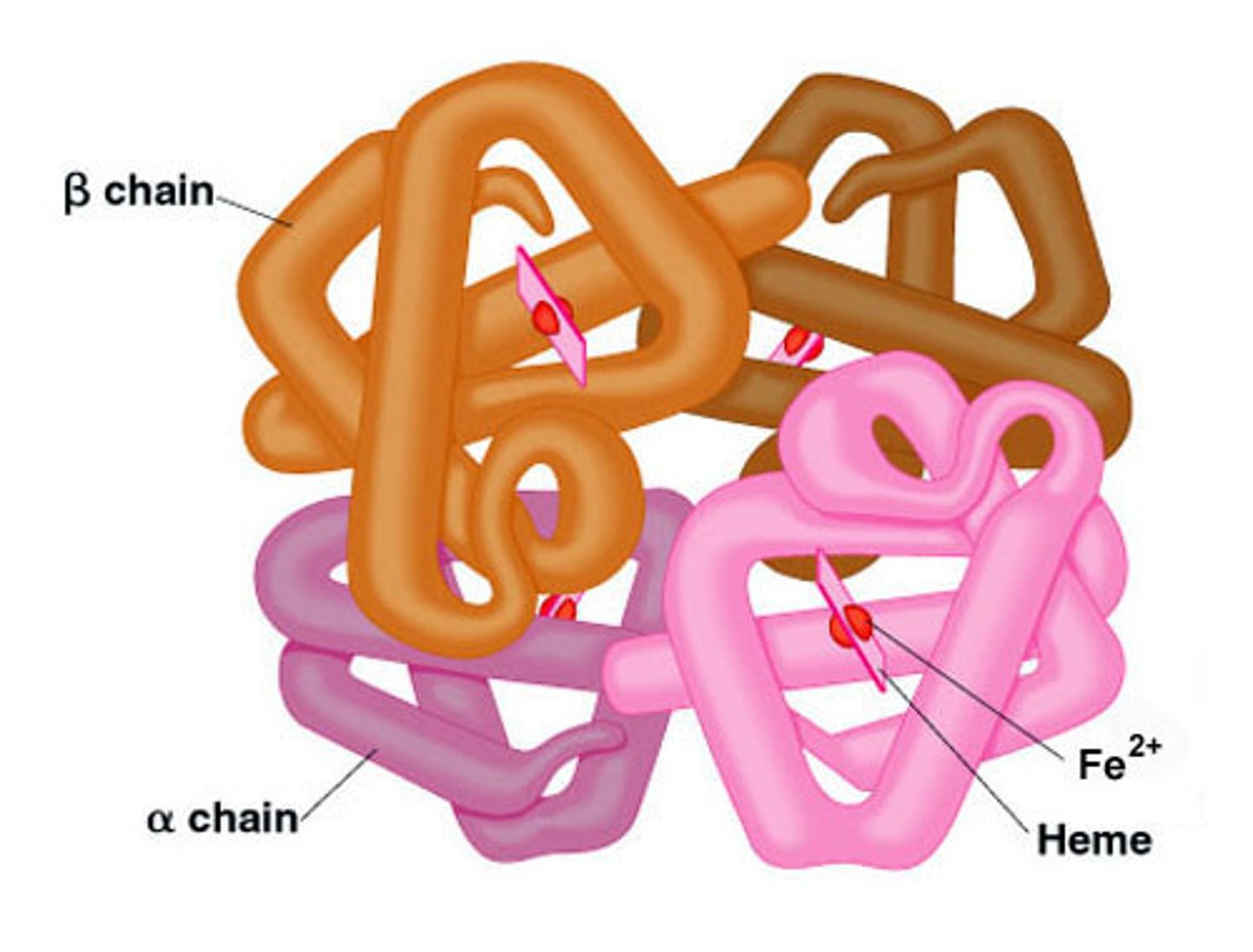
quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
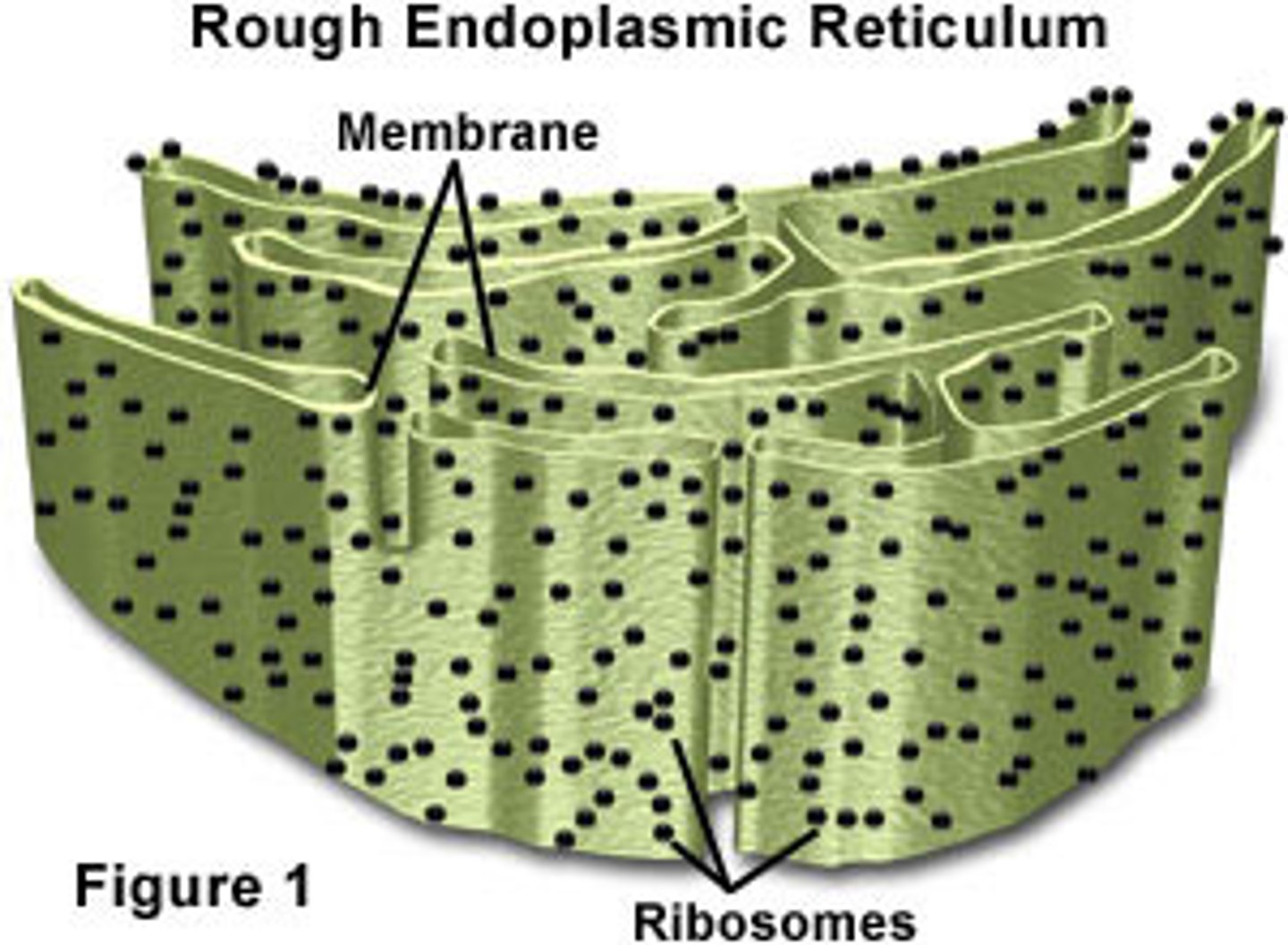
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm to the GOLGI BODY
Microtubules (Cytoskeleton 1)
-25nm Diameter
-Made of Tublin polymers
-Key for eukaryotic flagella
-DYNAMIC=MICRO
Microfilaments (Cytoskeleton 2)
-7nm Diameter
-Made of Actin Monomers
-Key for Cell Division
-DYNAMIC=MICRO
Intermediatefilaments (Cytoskeleton 3)
-8-12nm Diameter
-Made of Fibrous subunits (Keratins collided together)
-Key for support/Structure
-STABLE
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Thermodynamics
1st Law- Energy can be transferred/transformed
2nd Law- Every energy transfer/transformation increases the entropy of the universe
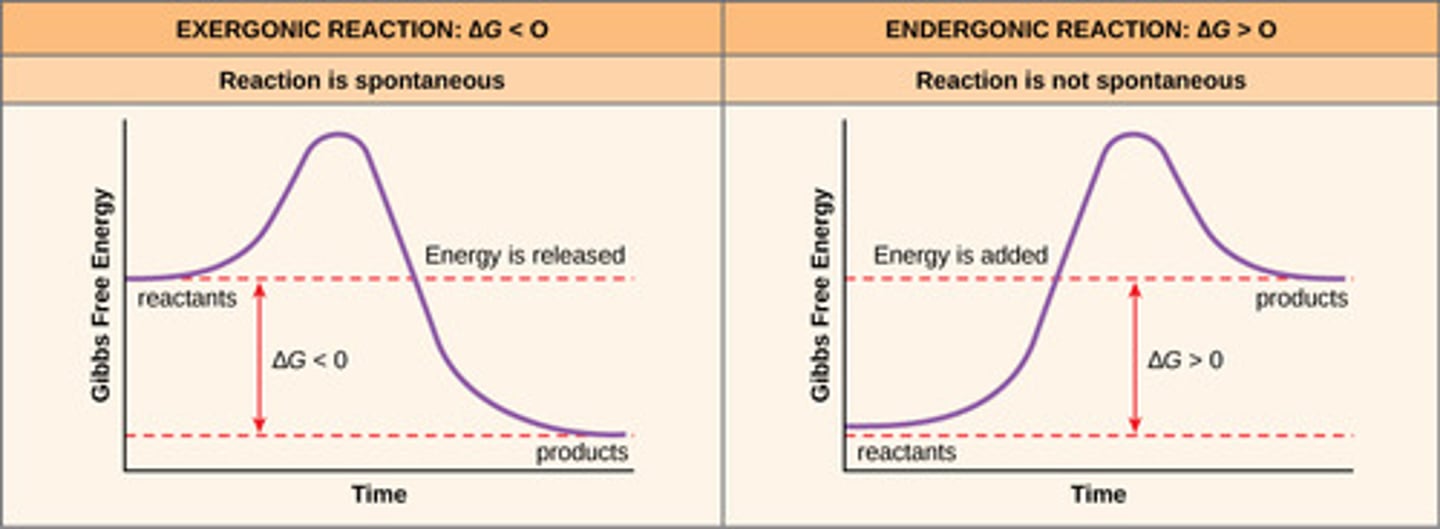
Endergonic Reactions and Exergonic Reactions
ENDERGONIC-Energy absorbing reactions (+ DELTA G NON-Spontaneous)
EXERGONIC-Energy Releasing reaction (- DELTA G Spontaneous)
4 steps of cellular respiration
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate Oxidation
3. Citric acid cycle
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron transport and chemiosmosis)
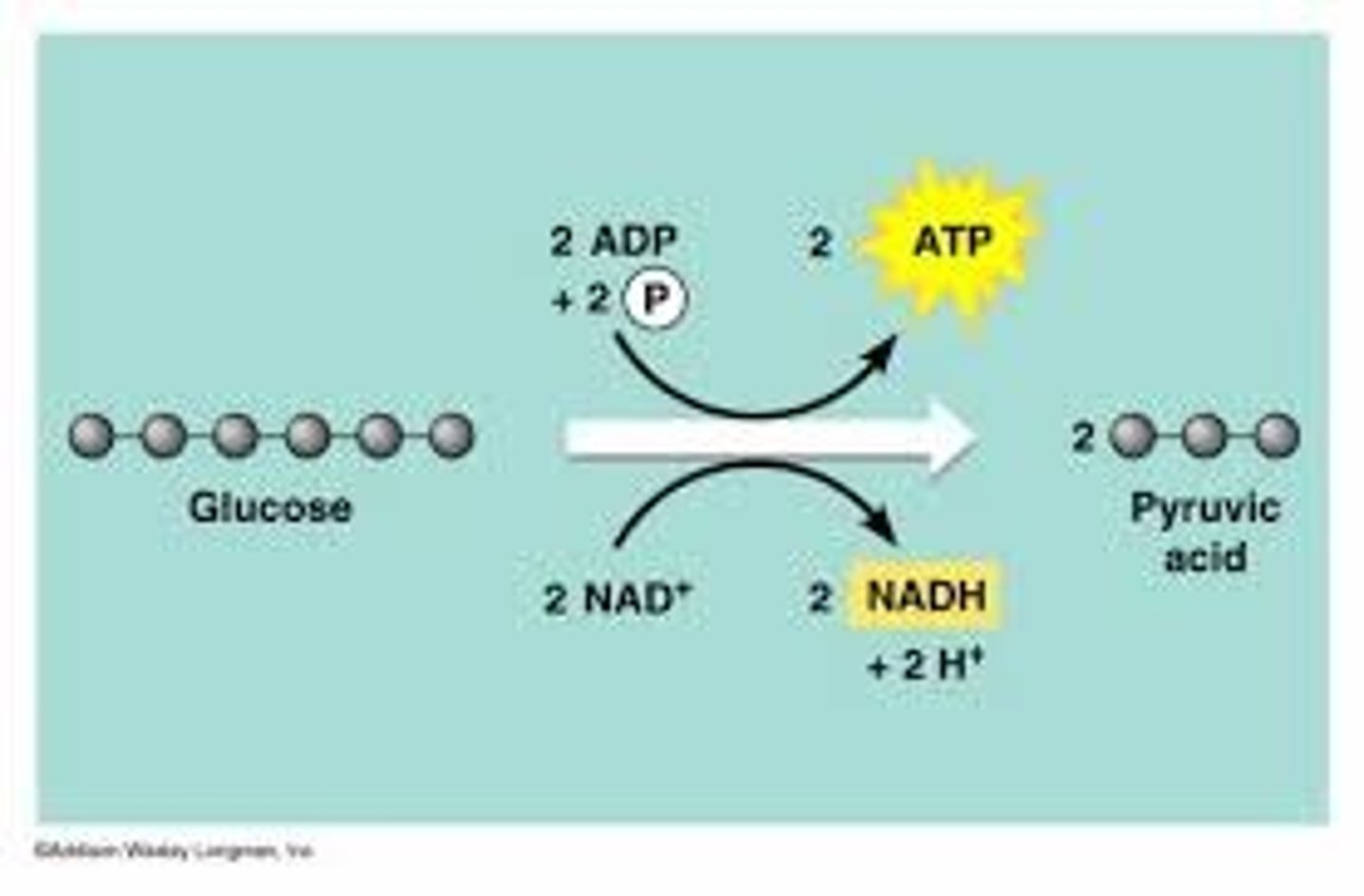
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
INPUT: Glucose, 2ATP, NAD+ and 4H+
OUTPUT: 2NADH, 2H+ 2H2O and 2 pyruvate
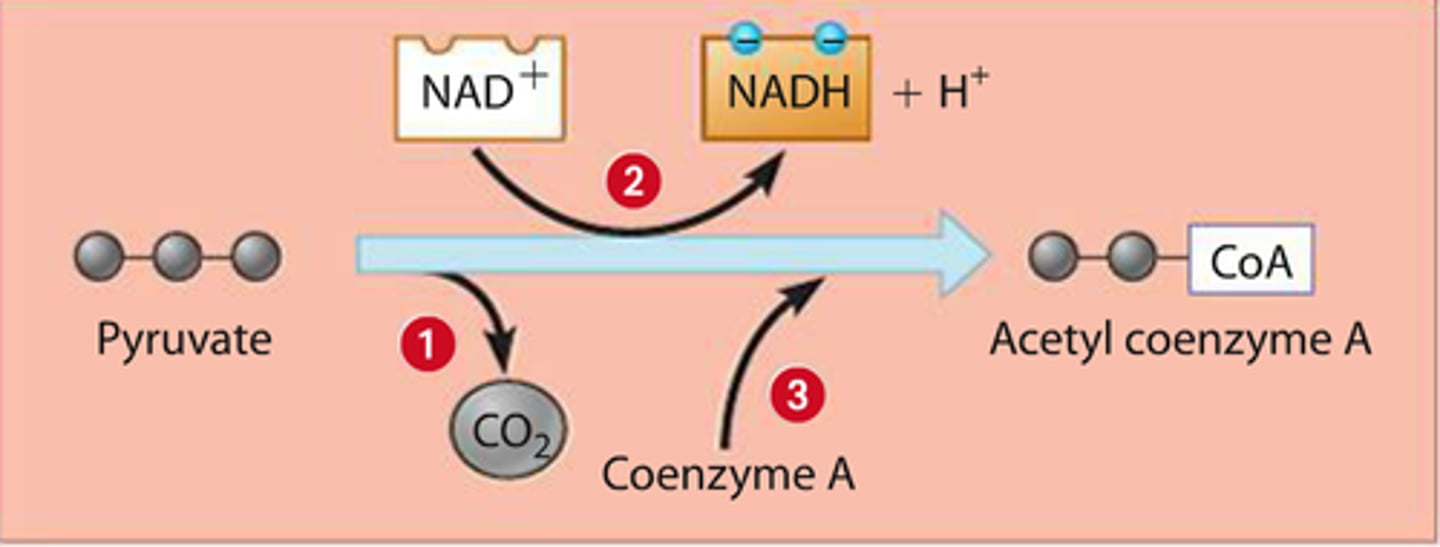
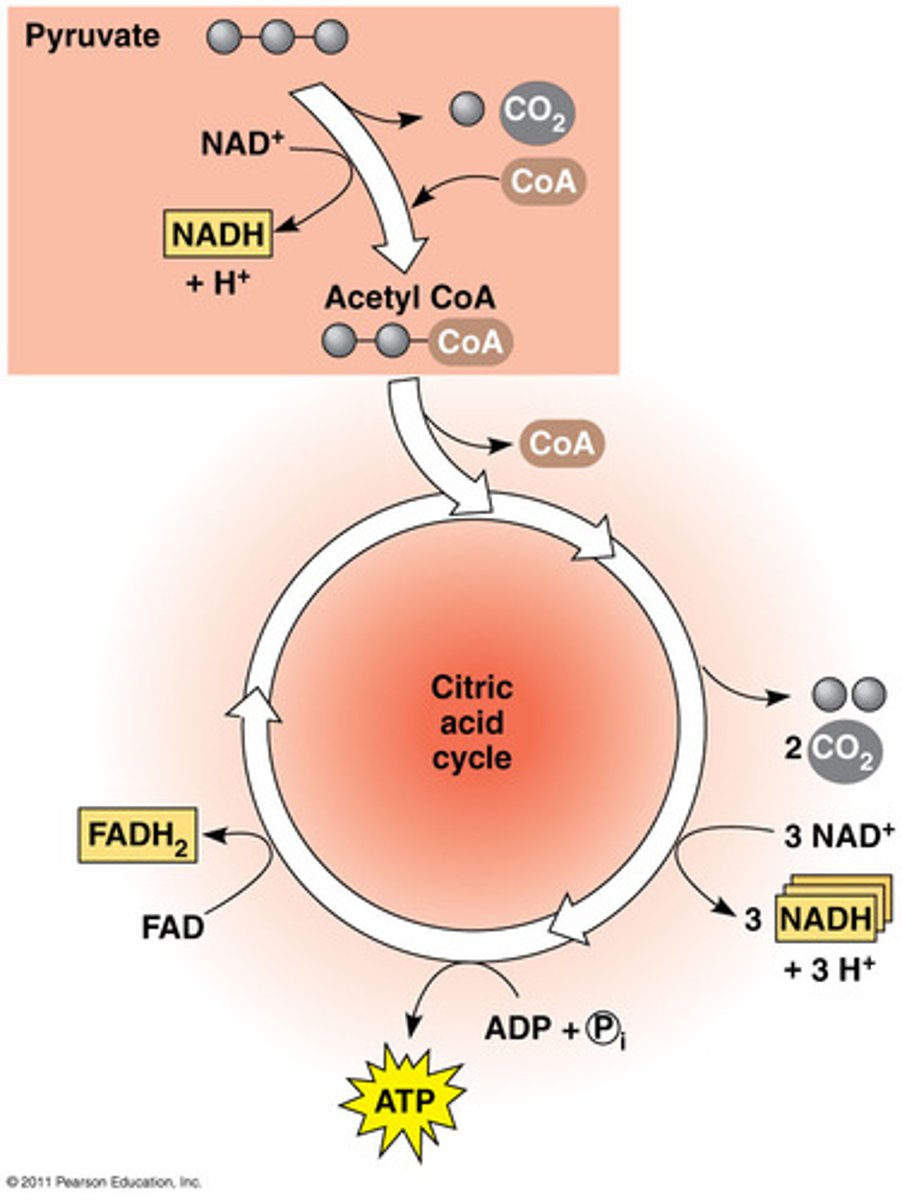
Pyruvate oxidation
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and CO2 that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix in the presence of O2.
INPUT: Pyruvate, NAD+ and Coenzyme A
OUTPUT: Acetyl-COA, NADH and CO2
Citric Acid Cycle
A chemical cycle involving eight steps that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules to carbon dioxide; occurs within the mitochondrion;.
INPUT: 2 Acetyl CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD,
OUTPUT: 2 cycles so 2x (FADH2, 3NADH and 1ATP)
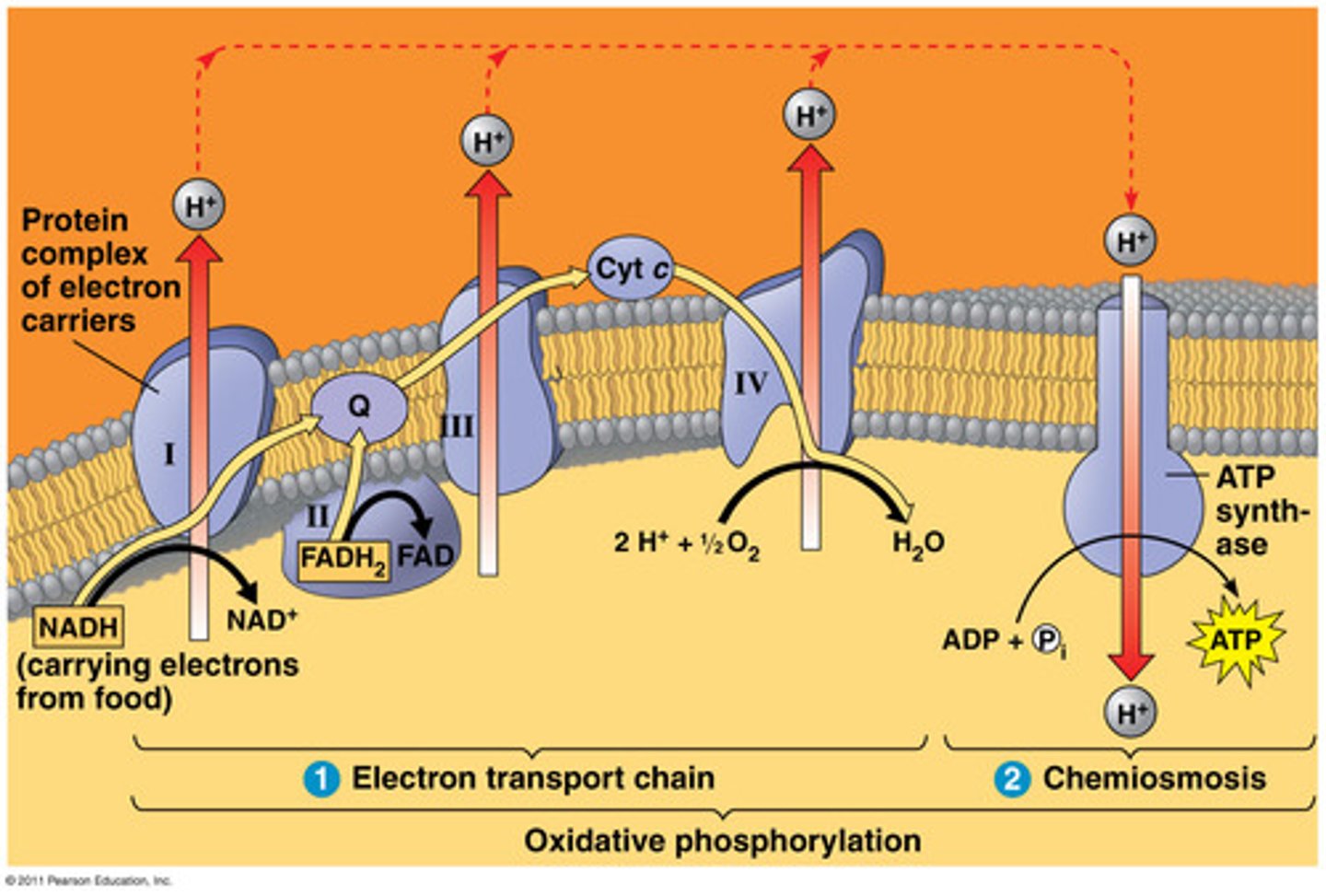
oxidative phosphorylation (ETP and Chemiosmosis)
Made of 2 parts, The Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis (Proton Gradient that can be converted into energy to create ATP).
INPUT: 9NADH, 2FADH2 and O2
OUTPUT: 26-28 ATP per glucose molecule NAD+ and FADH
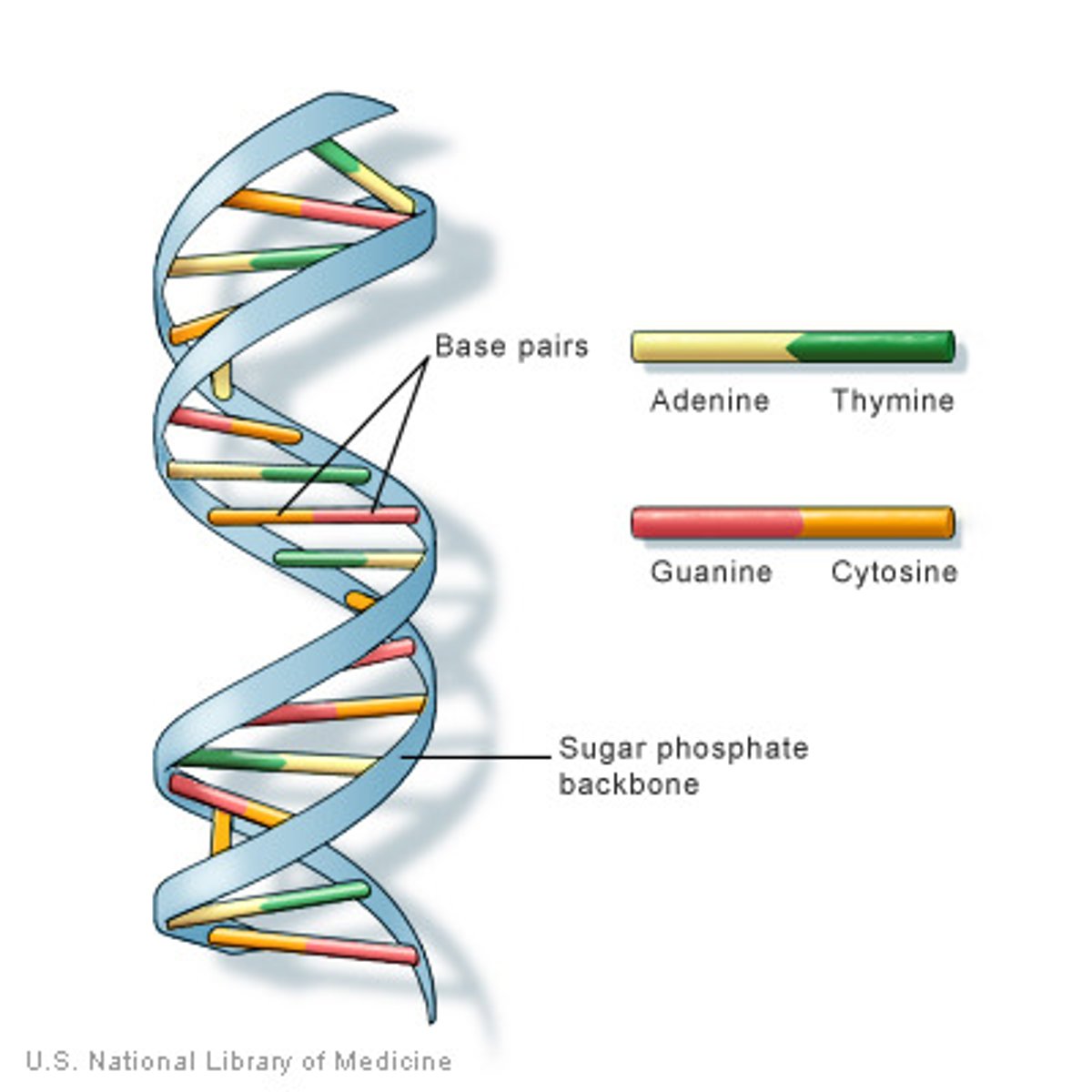
DNA strcuture
A 5 Carbon sugar (deoxyribsoe)
A phosphate group
A nitrogenous base (A-T G-C and U-A) Triphosphate when unbounded
Double Helix
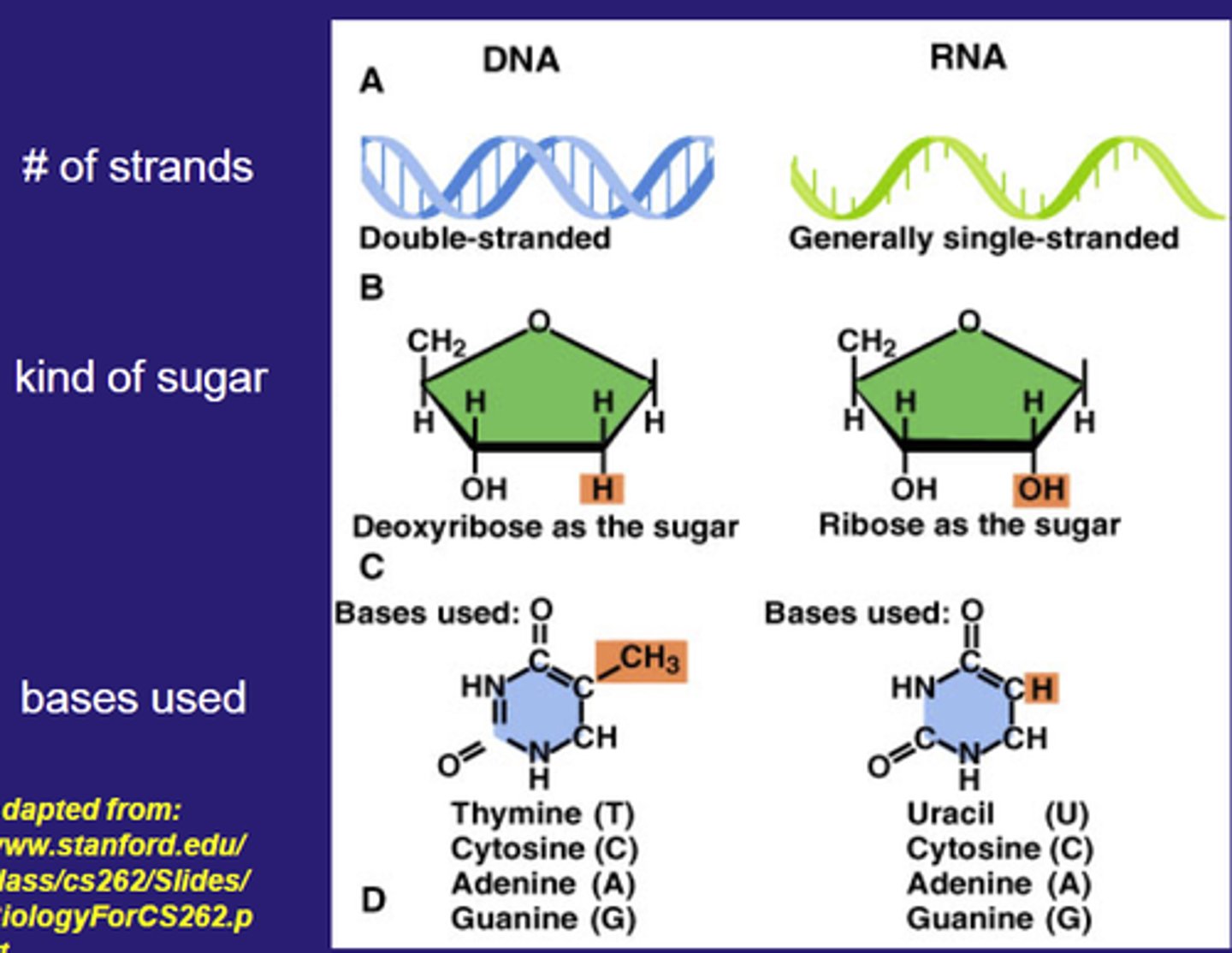
RNA vs DNA structure
RNA has a single polynucleotide strand, DNA is double helix (two polynucleotides)
DNA Replication
the process of making a copy of DNA, replication begins at the 3' end to the 5' end. DNA is replicated from 5' to 3'.
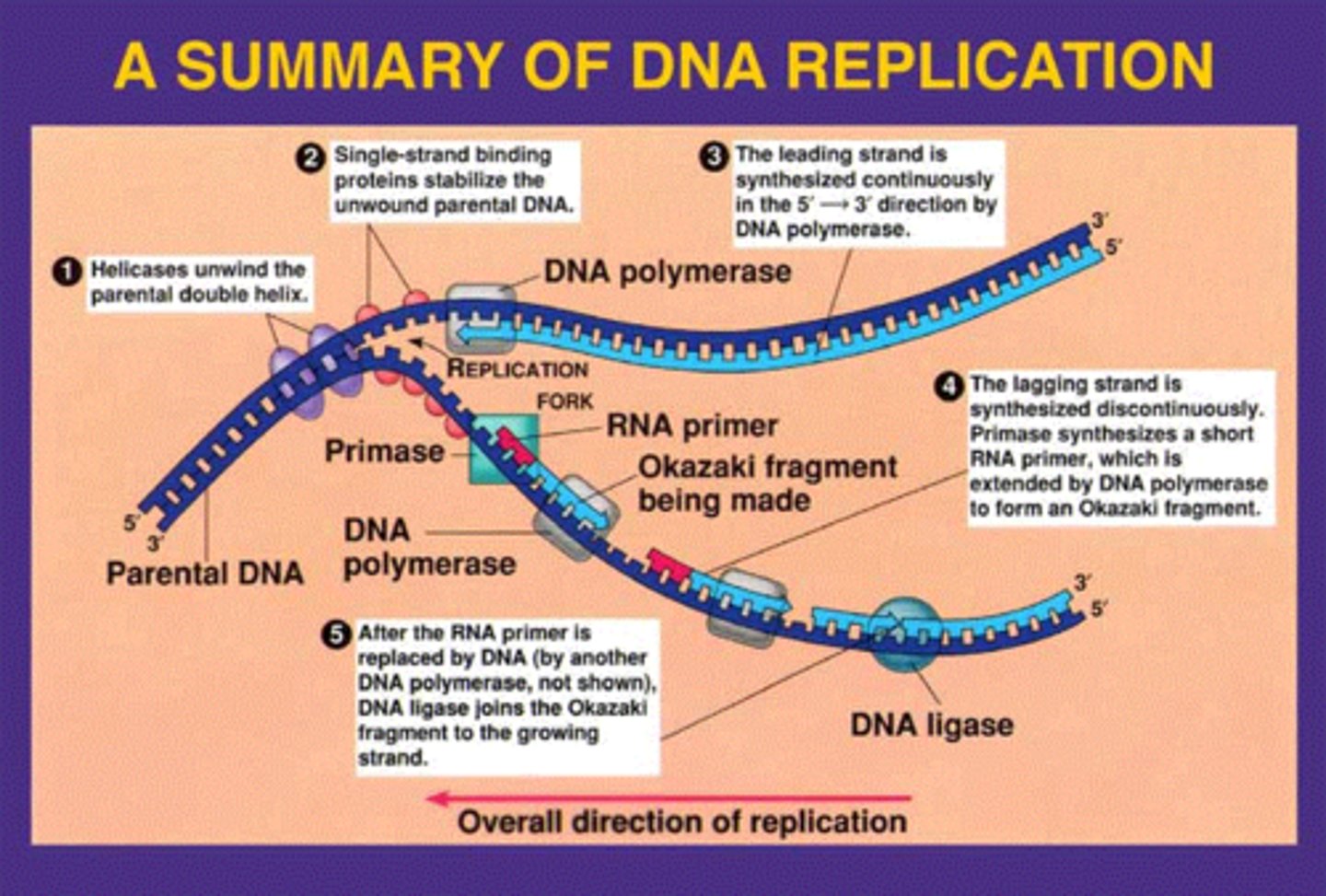
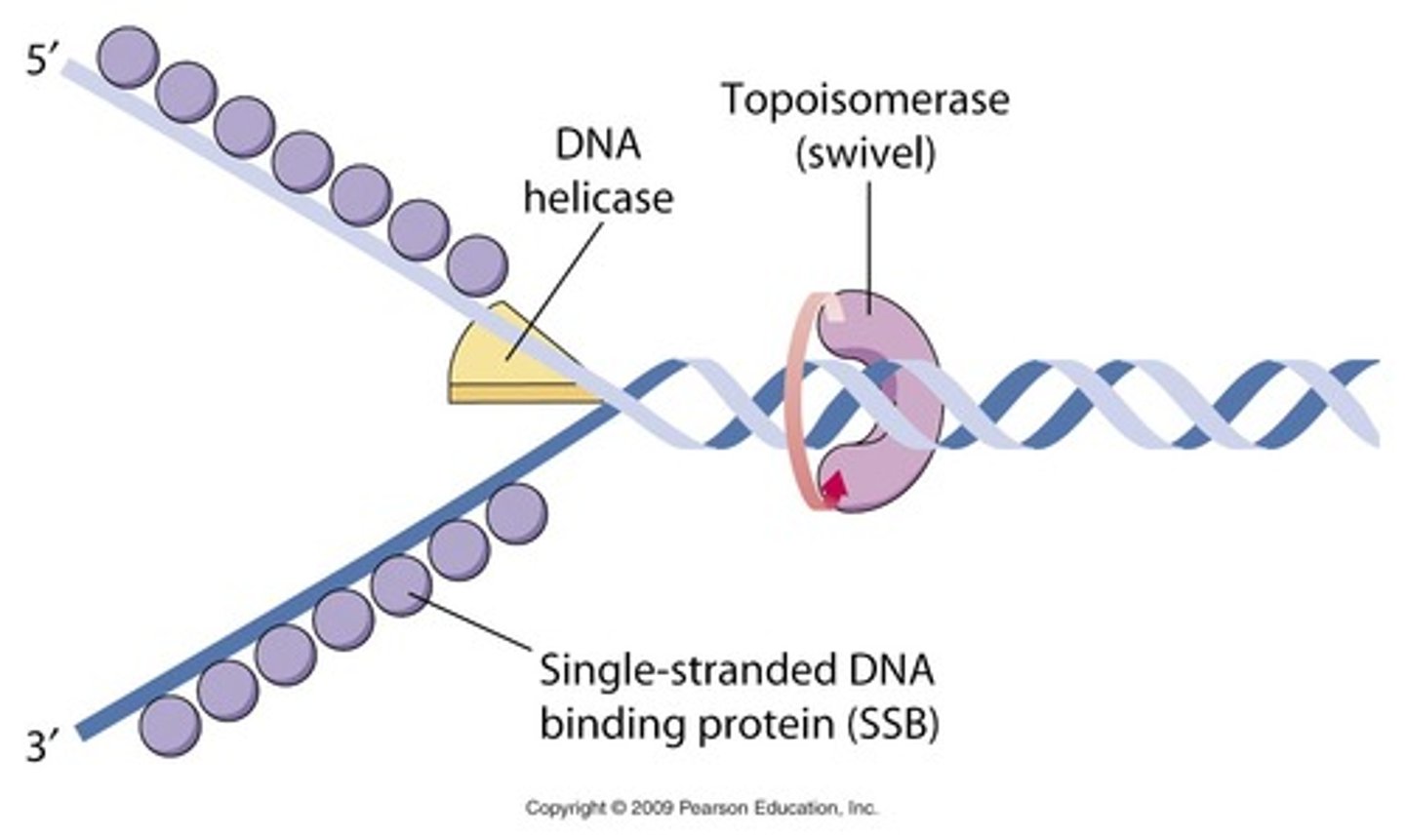
Helicase
An enzyme that unzips the double helix of DNA at the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds
Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
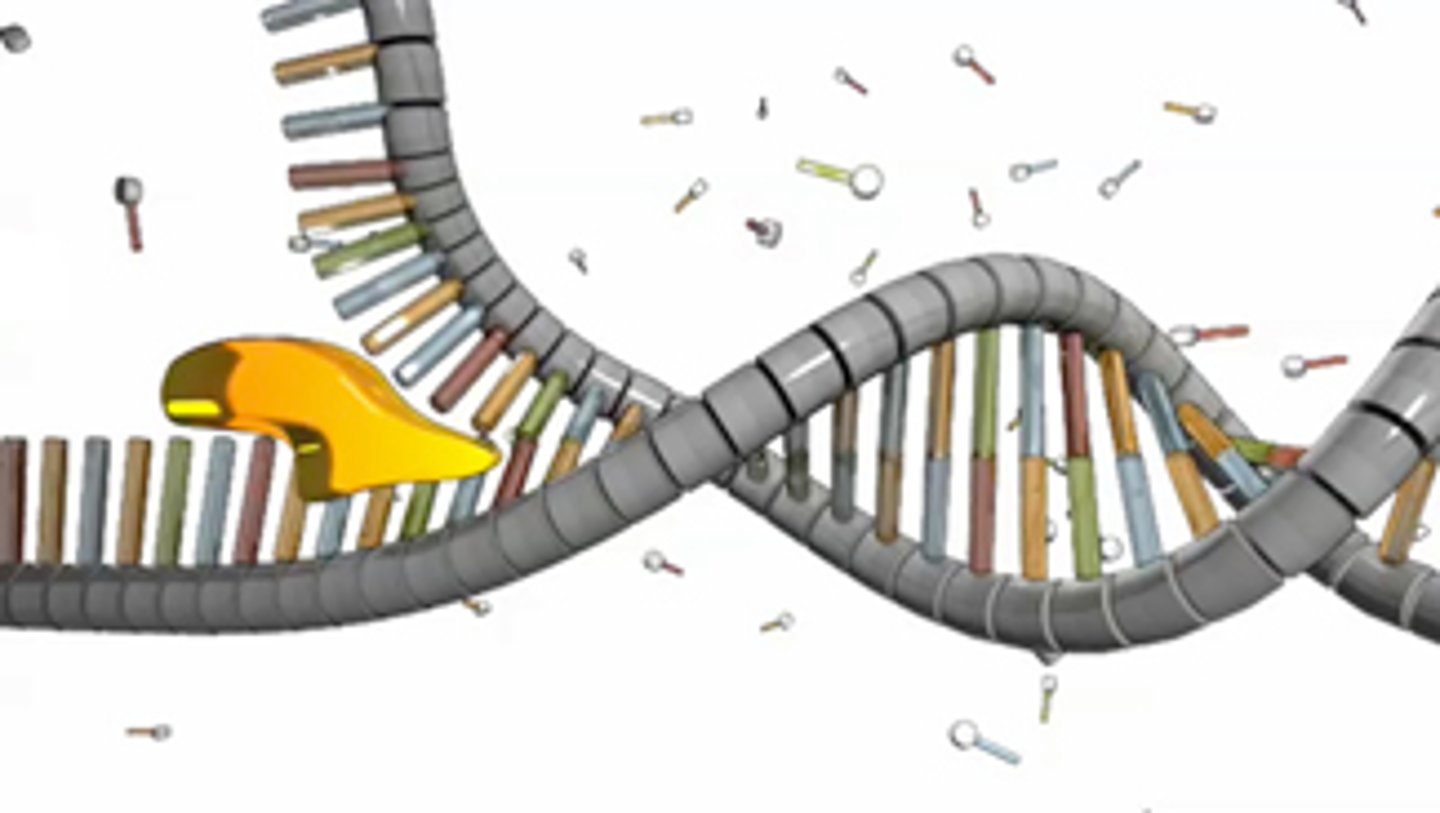
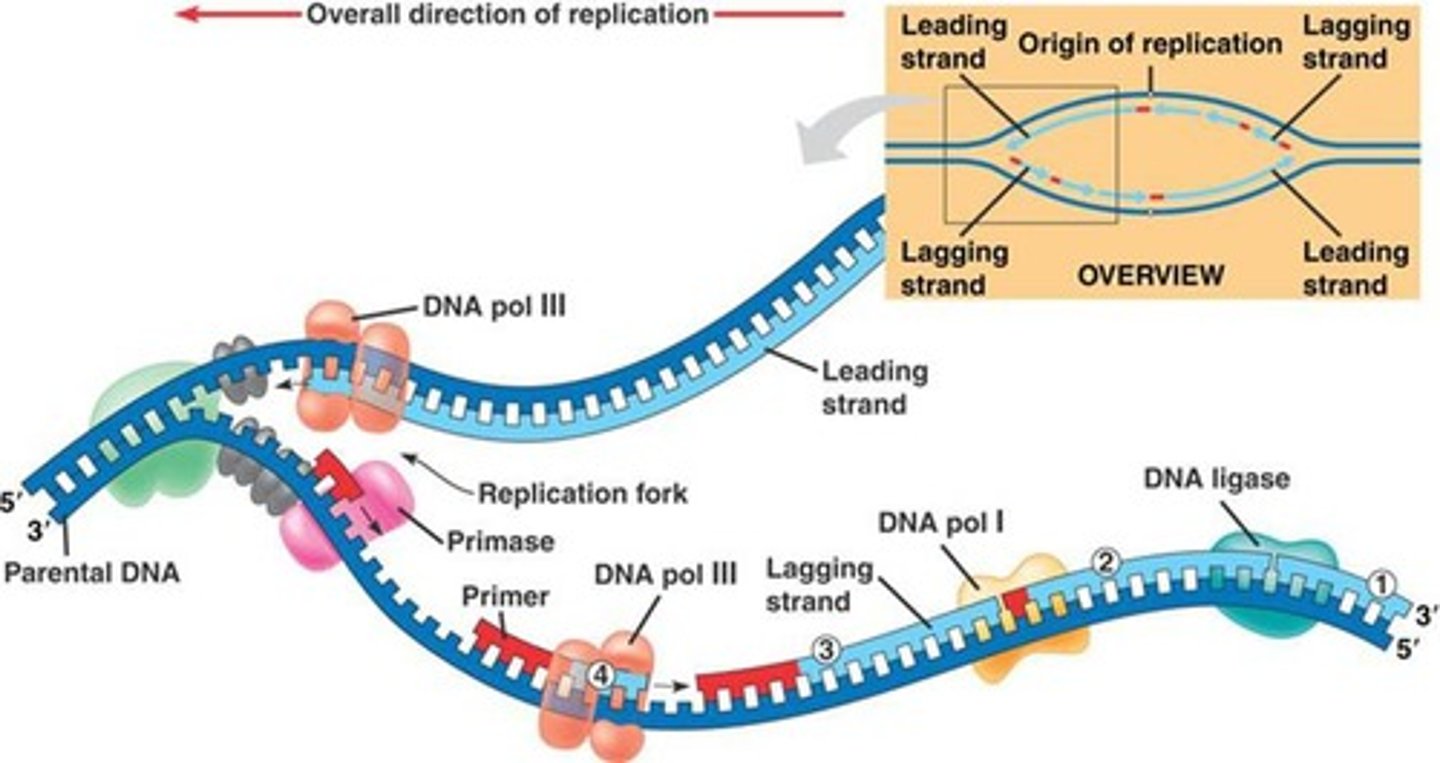
DNA polymerase 1 and 3
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule (DNA Polymerase 3)
RNA primers removed by exonuclease activity, DNA is synthesised in its place at the same time (DNA Polymerase 1)
DNA Primase
synthesizes a short RNA primer to provide a 3'-OH group for the attachment of DNA nucleotides
single strand binding proteins
bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
DNA Ligase
A linking enzyme essential for DNA replication; catalyzes the covalent bonding of the 3' end of a new DNA fragment to the 5' end of a growing chain.
Cell Division
the process in reproduction and growth by which a cell duplicates its genetic information before dividing to form daughter cells.
Stages
Interphase
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
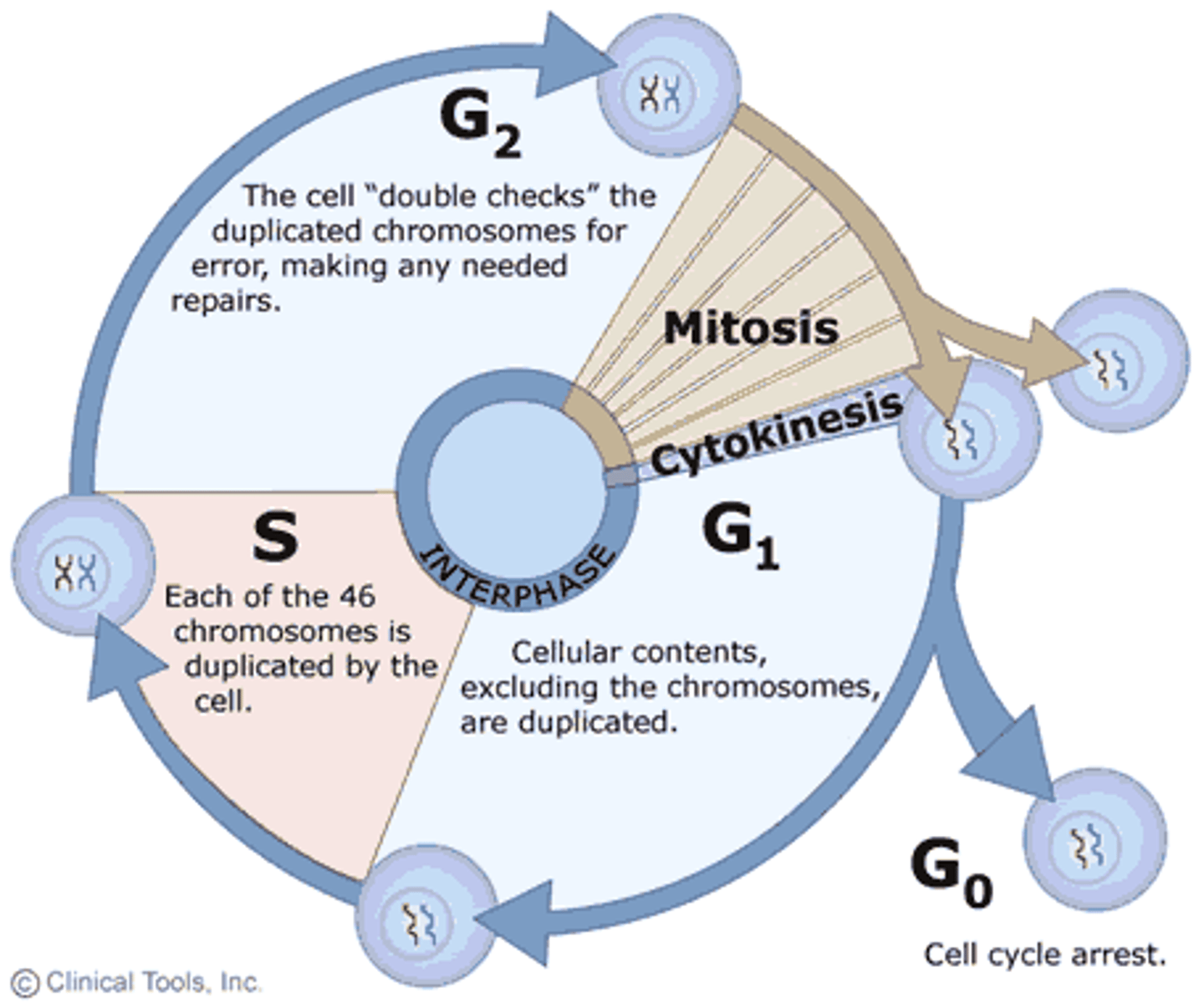
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases.
G1 phase-the cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and protein.
S phase- DNA replication occurs
G2 phase- Cell grows and prepares for the mitotic division
M Phase -Mitosis
Prophase
First and longest phase of mitosis in which the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses from chromatin and become chromosomes.

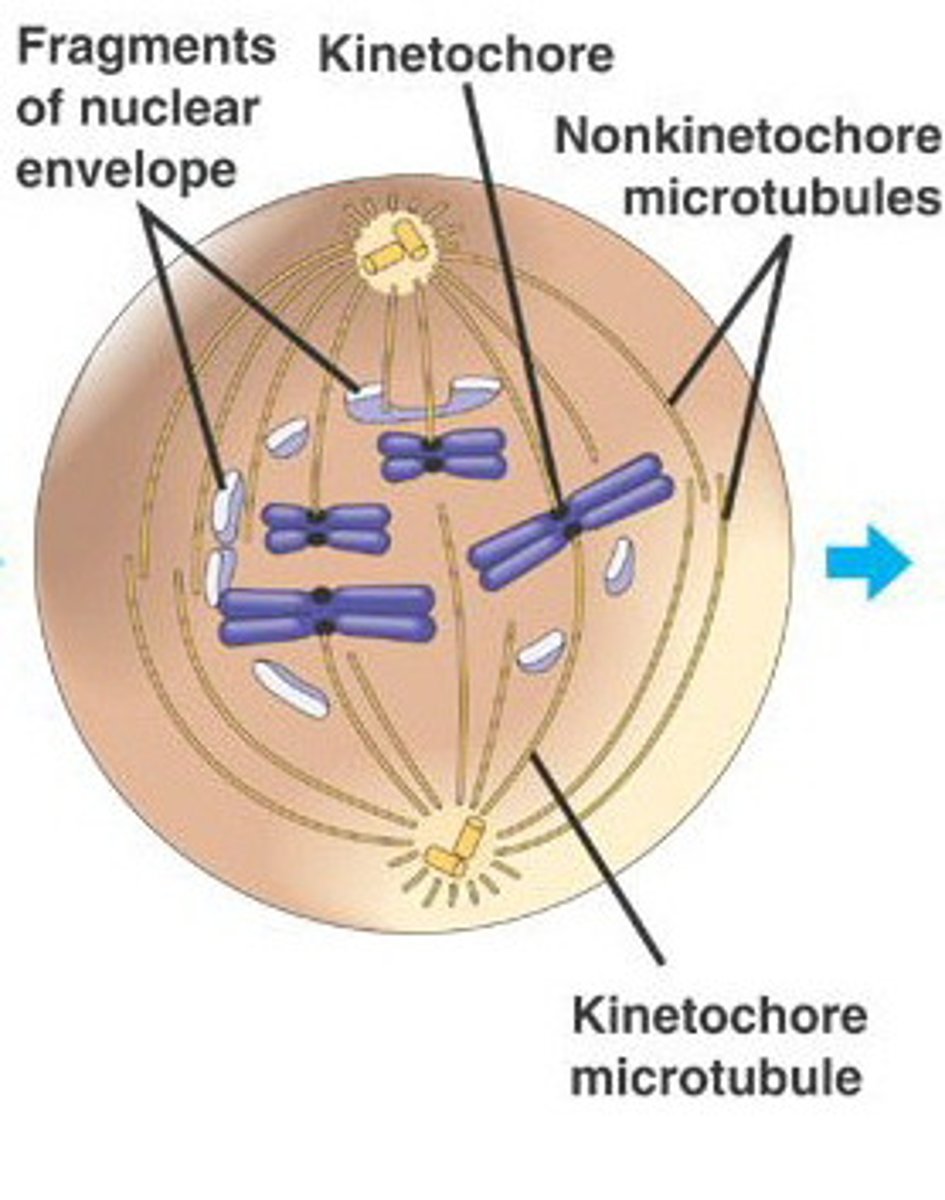
Prometaphase
The second stage of mitosis, in which the nuclear envelope fragments and the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes.
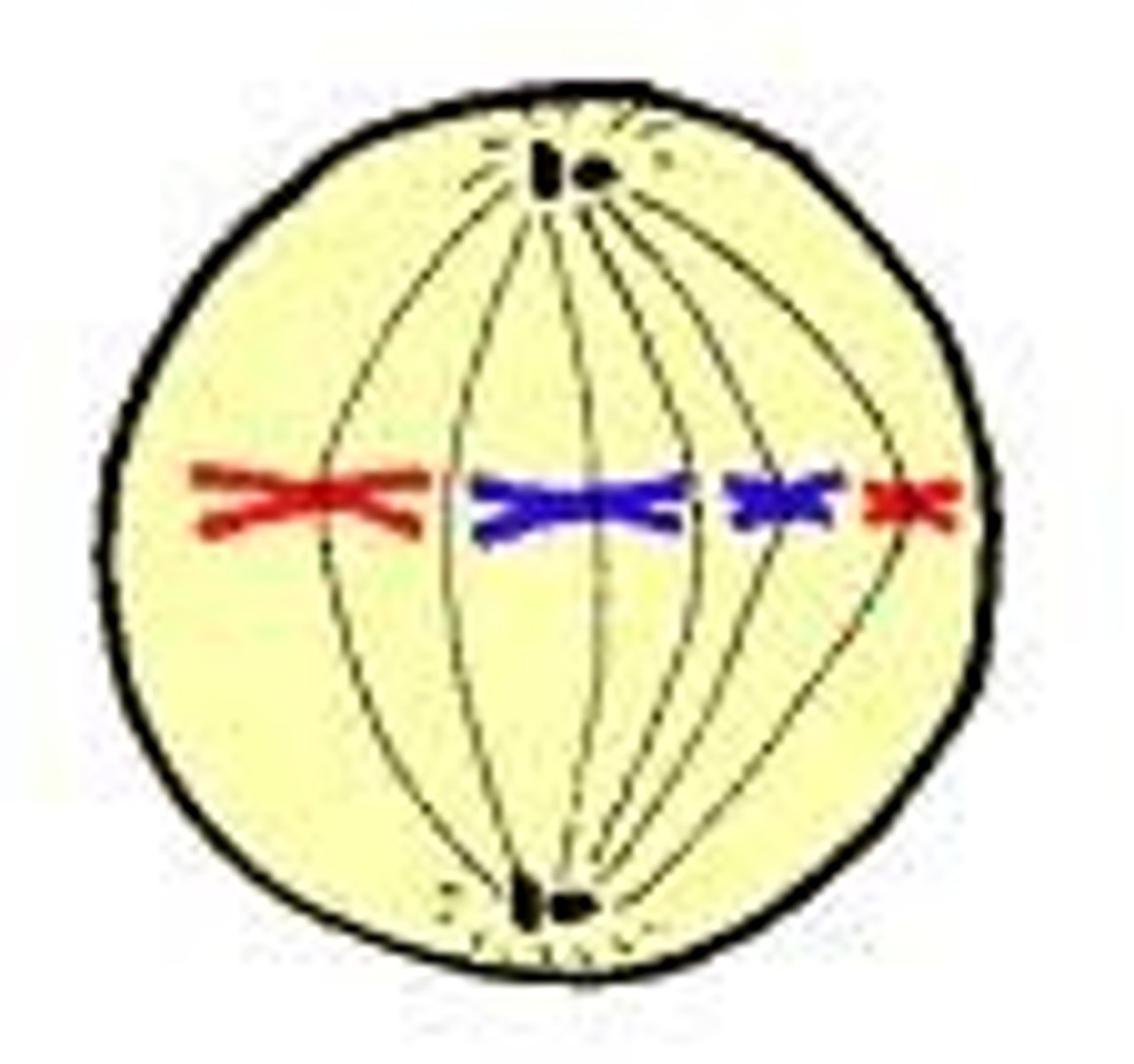
Metaphase
Third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
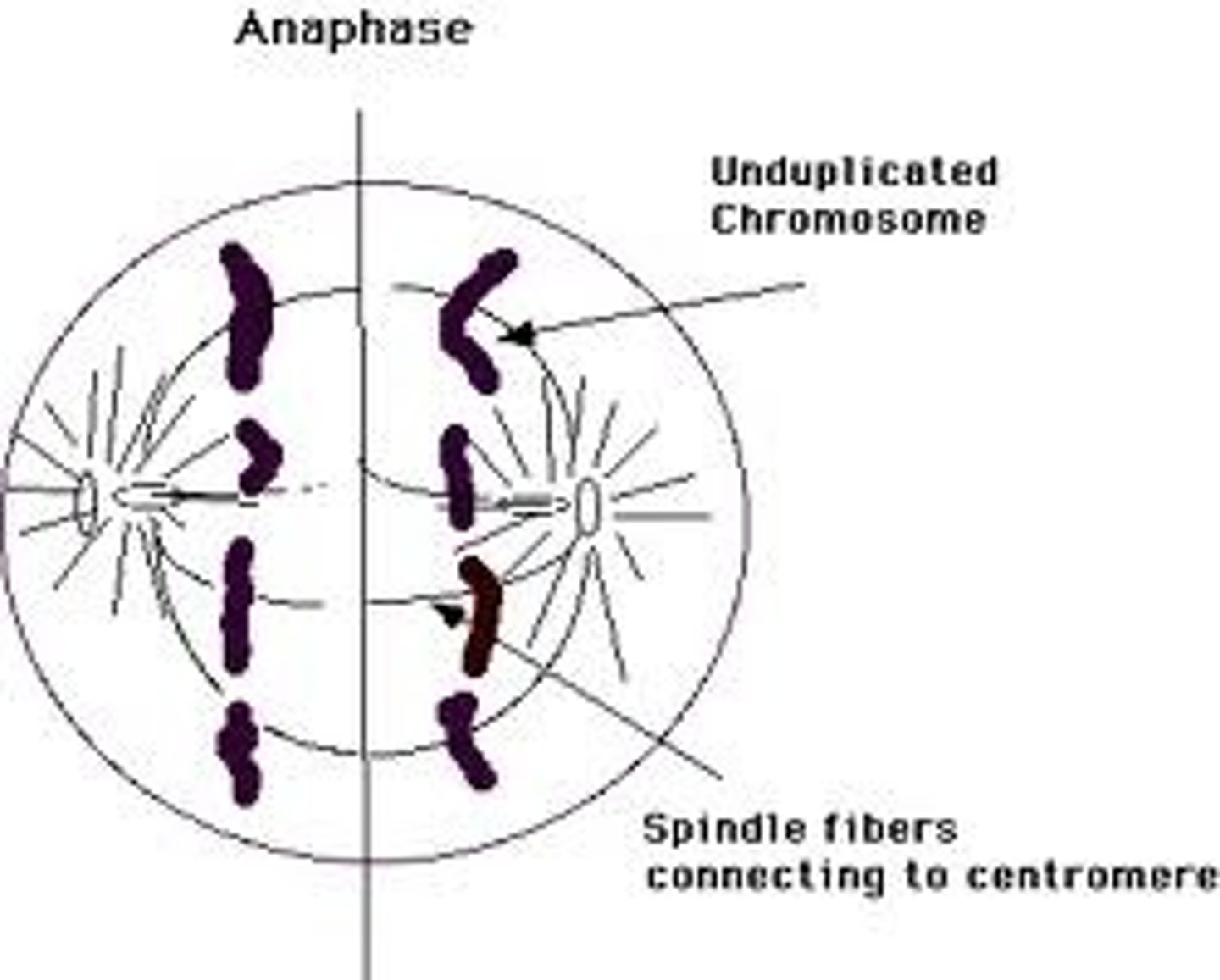
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and sister chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell via spindle fibres.
Telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin. Two nuclei have formed.
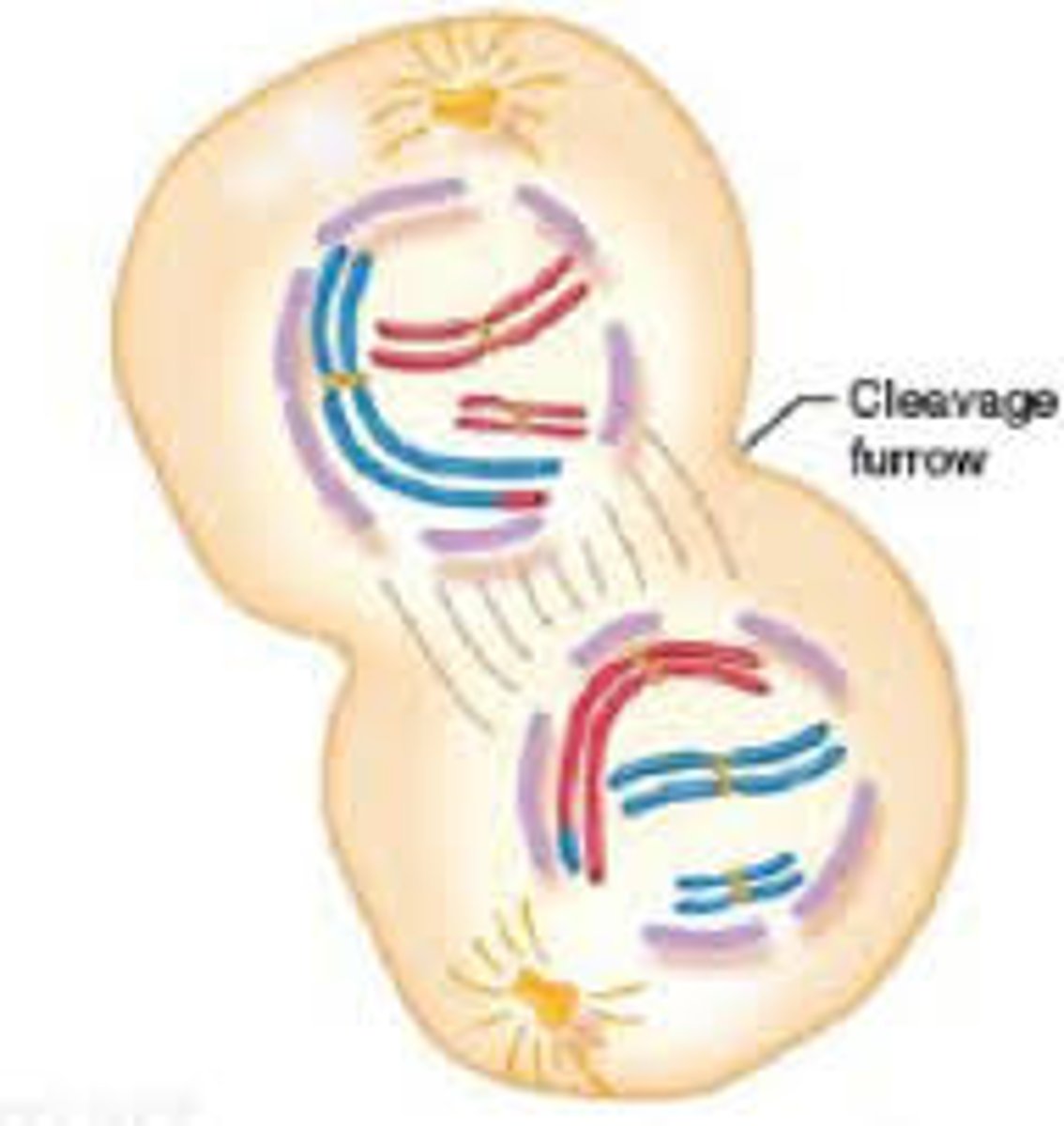
Cytokensis
-Actin filaments congregate near the metaphase plate to form a ring inside the cell.
-Pinching action separates cytoplasm into 2 separate cells.
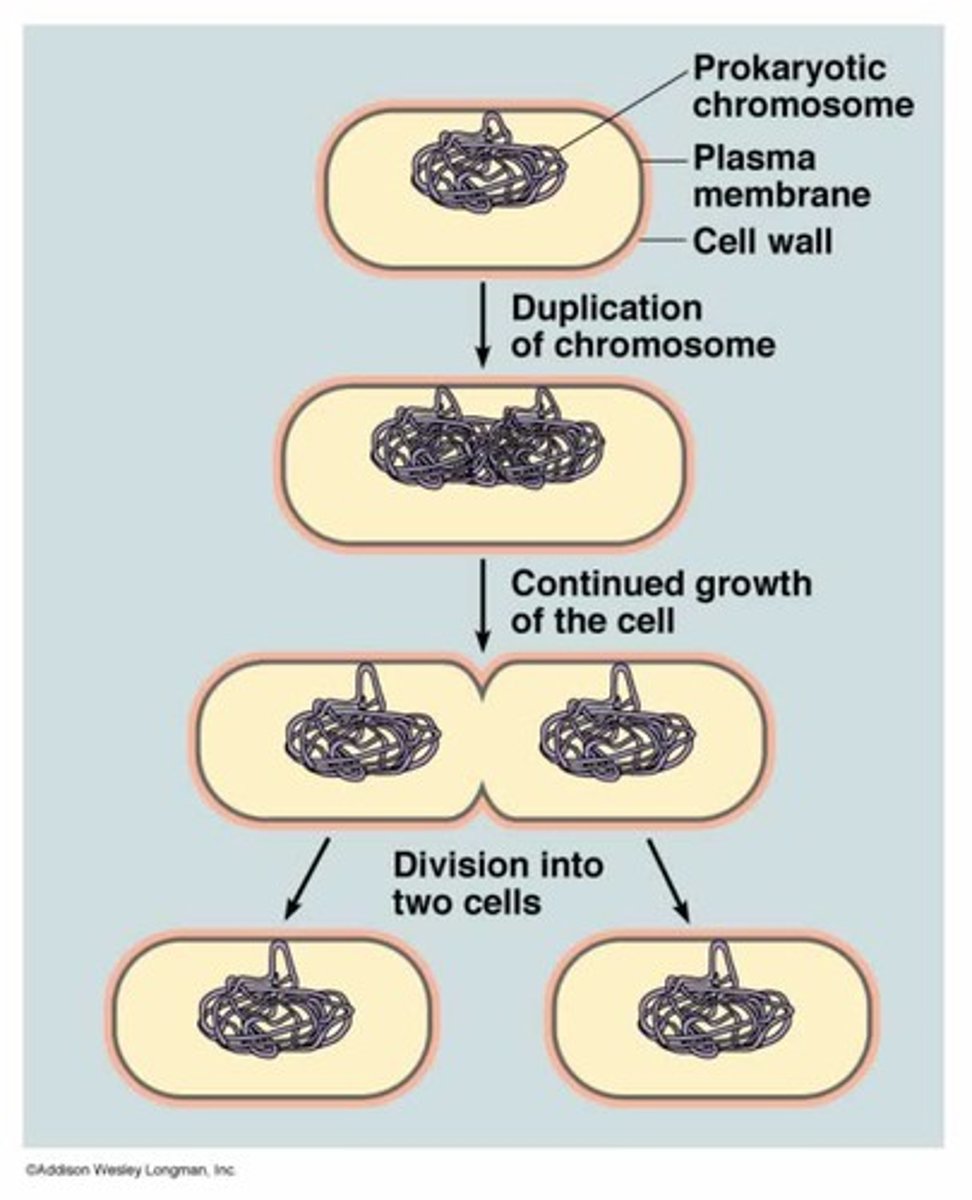
binary fission prokaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission.
The bacterial cell copies its chromosome in preparation for division. Cell membrane pinches inward to divide the cell
2 new daughter cells are made
Cell Cycle Checkpoints (Interphase)
G1 checkpoint- cells decide whether or not to divide
G2 checkpoint- prevents cells from entering mitosis when DNA is damaged
M checkpoint- Ensures spindle fibres are correctly attached before continuing mitosis
Molecular control
-Passage of cells through checkpoints requires activation of a 2-subunit complex cyclin and CDK to form MPF complexes
Cyclin in the cell
-Cyclin concentration varies depending on the current phase of the cell cycle
-It accumulates in G2 and S phases
Entering M Phase Steps
1. Cyclin levels increase- Cyclin and CDK come in contact and become MPF
2. MPF use the kinase activity of the interaction to add phosphate groups
3. This allows cells to bypass the G2 checkpoint and enter M phase (Mitosis)
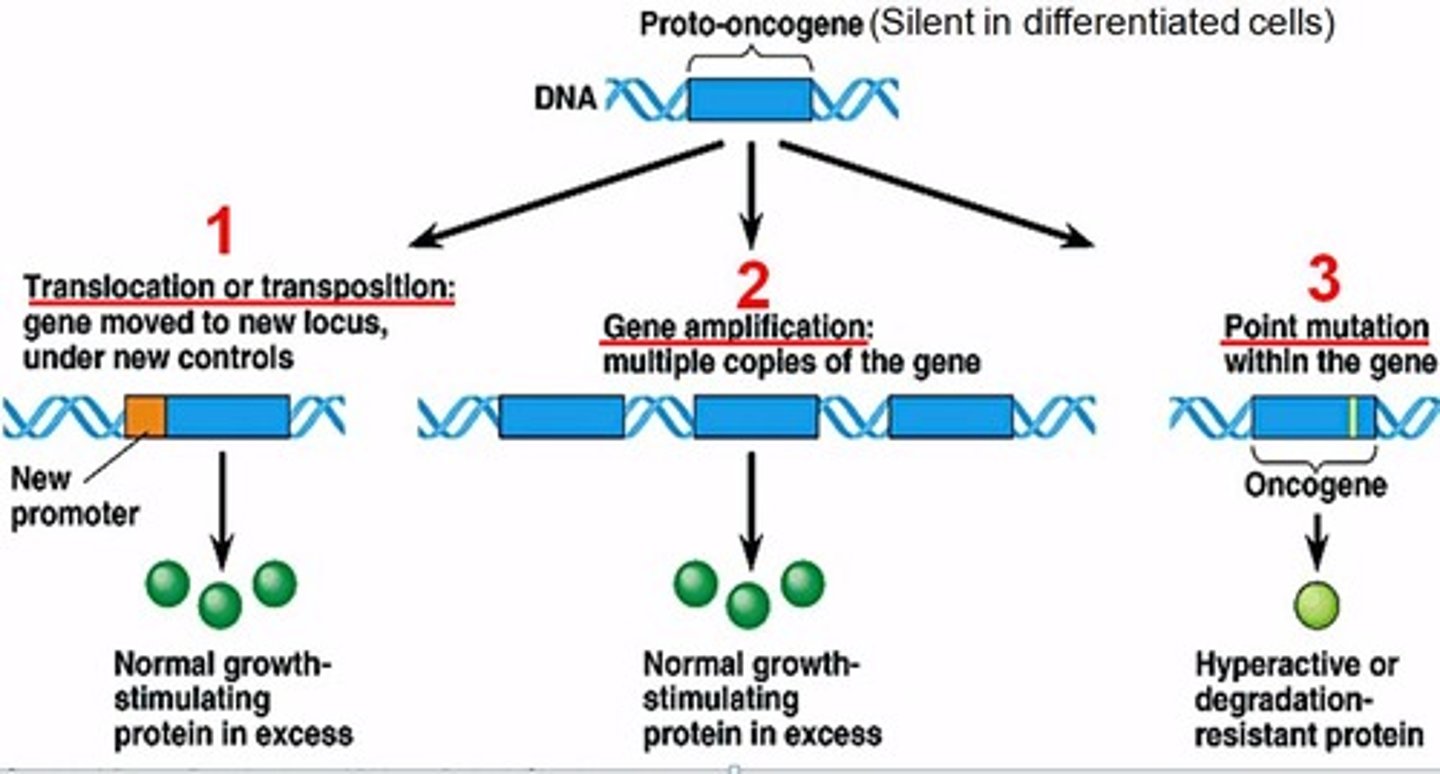
oncogenes and protooncogenes
If genes actively promote cell division (Protooncogenes) are not turned off at the right time they become oncogenes which leads to cancer.
Stops working due to
-Translocation
-Amplification of the gene
-Mutation (In promoter region)
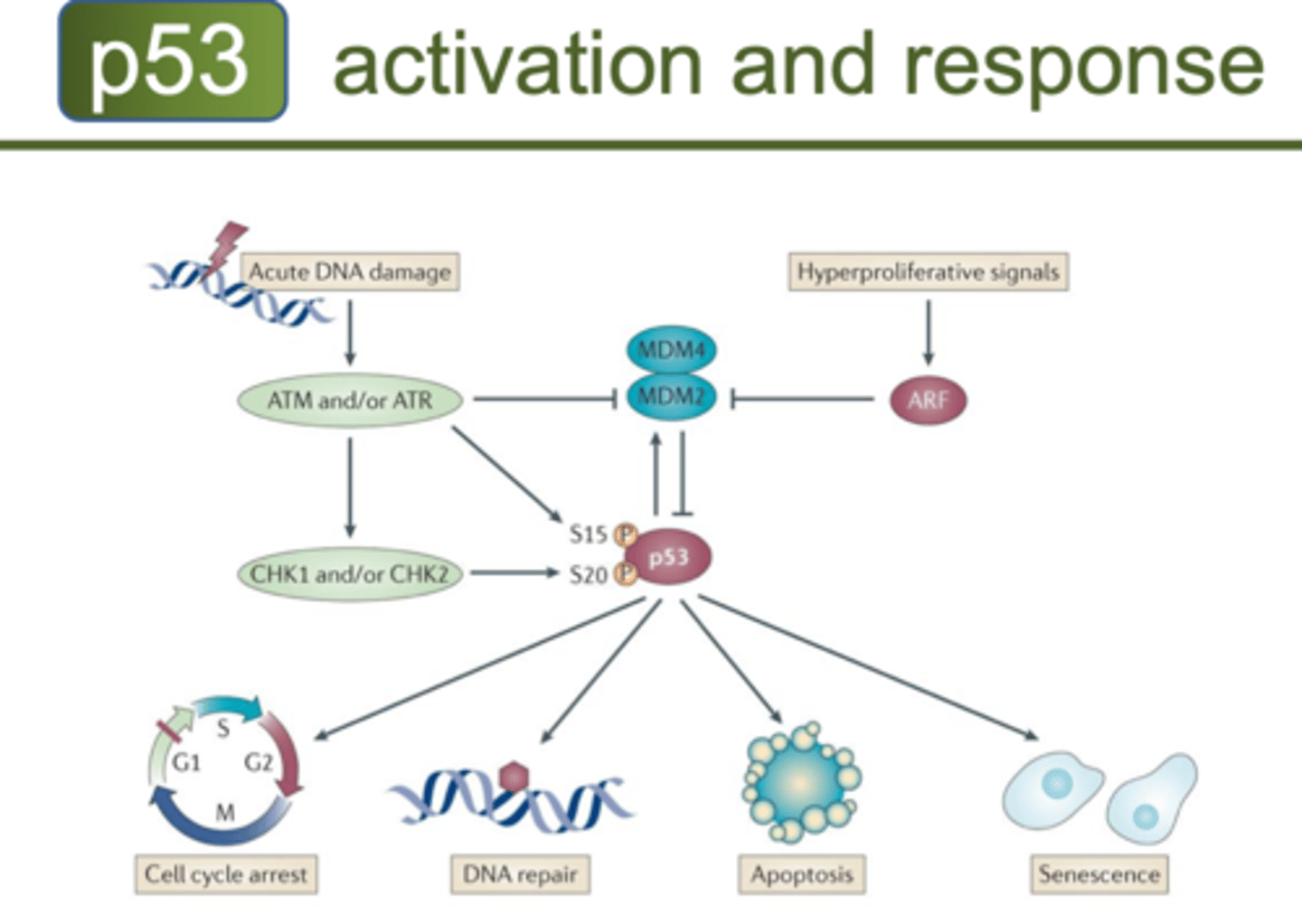
Tumour Suppressor Genes (P53)
-Genes that normally inhibit cell division
Stops working due to
-Translocation (transfer of one part of a chromosome to another part, rearrangements of genes)
-Gene deletion
-Point Mutation
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site.
Malignant Tumours
Cancerous tumours
Will invade surrounding tumours
Benign Tumours
Non-cancerous tumours
Do not invade surrounding tumours
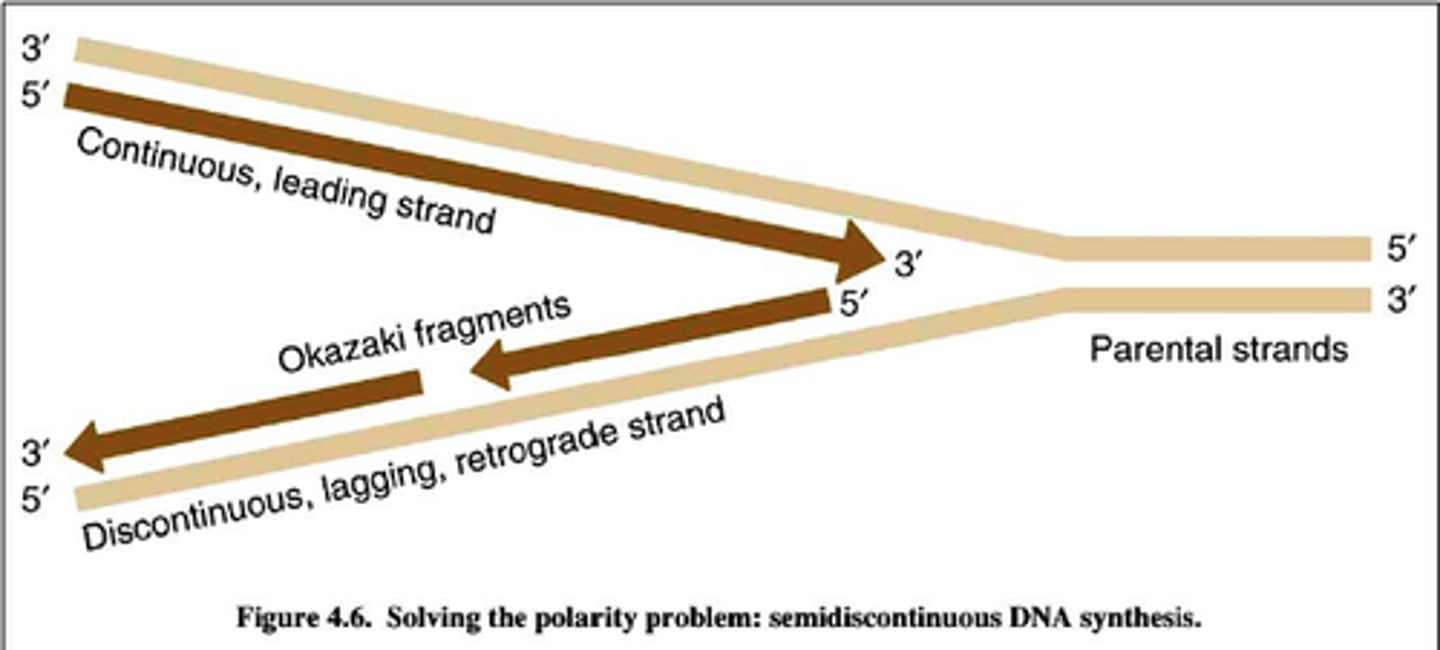
Leading vs Lagging strand
Leading: elongate continuously into the widening replication fork from parental 3' to 5' ends
Lagging: replicates away from the fork, must wait until it widens to polymerize and is discontinuous, leading to Okazaki fragments from parental 3' to 5' ends
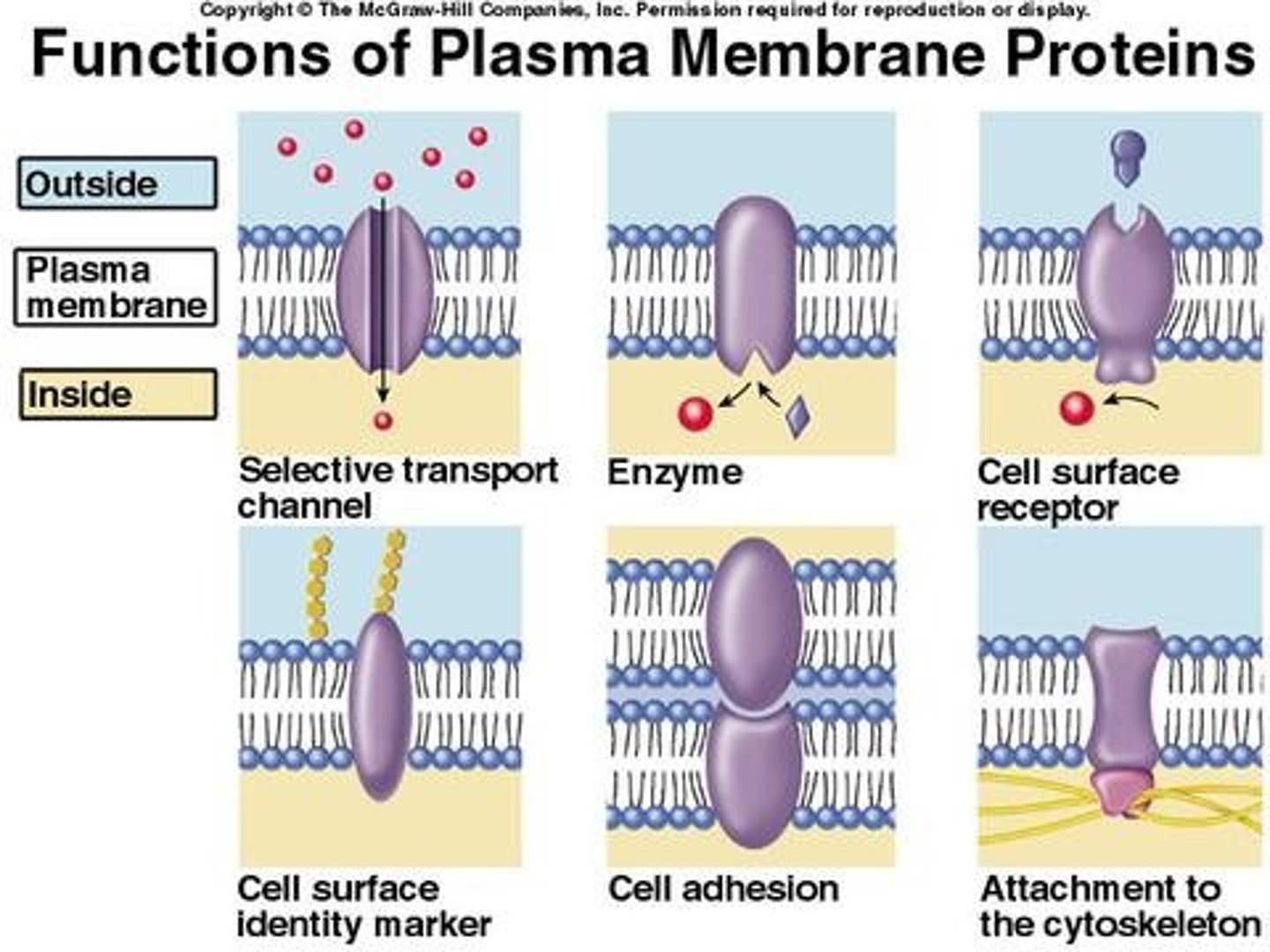
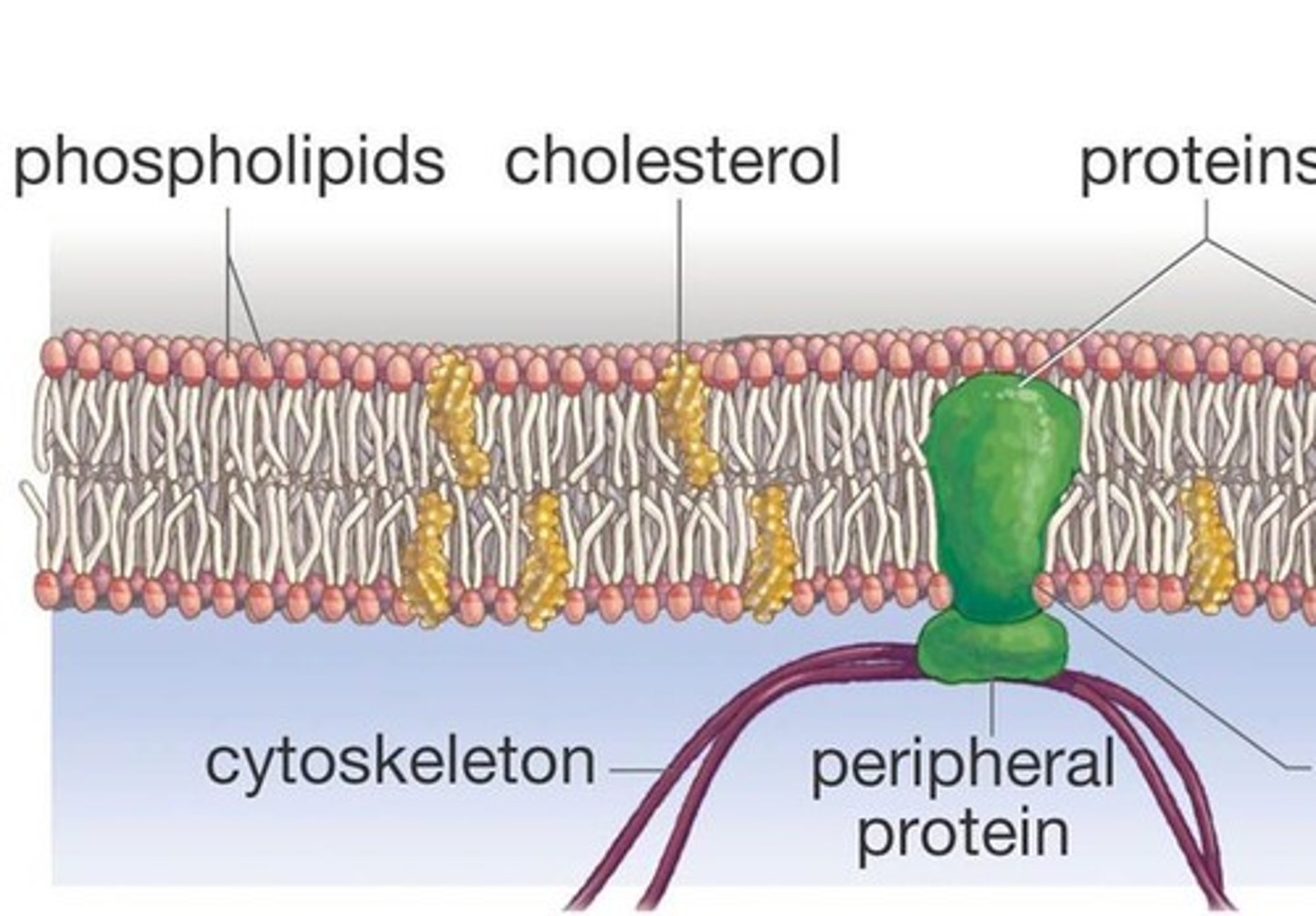
membrane protein functions
1. Transport
2. Enzymatic activity
3. Signal transduction (Receptor+Messenger)
4. Cell-cell recognition (Glycoproteins=tags)
5. Intercellular joining (Adjacent cells hook together)
6. Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
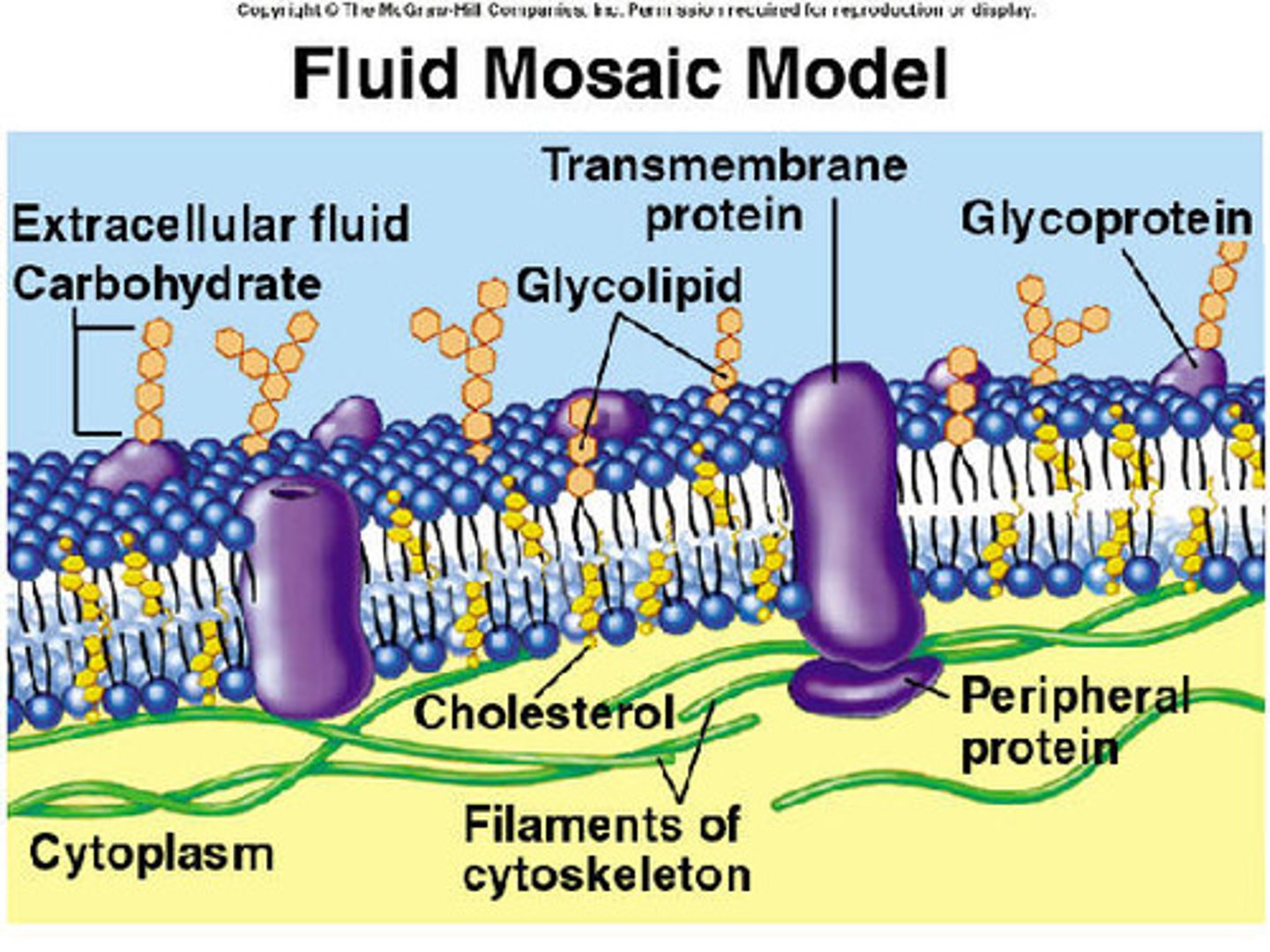
Cholesterol in membrane
Wedged into the bilayer, increases fluidity resistance to temperature change, important for the integrity and fluidity of the membrane.
hemiacetal group
carbon with an ether group and an alcohol group attached to it; R-O-C-OH
Gibs free energy
energy available to do work in a system.
Gene
-A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait.
-Basic unit of inheritance
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
Exons and Introns
Exons code for amino acids,
Introns are noncoding segments that need to be spliced out by spliceosomes.
transcription factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
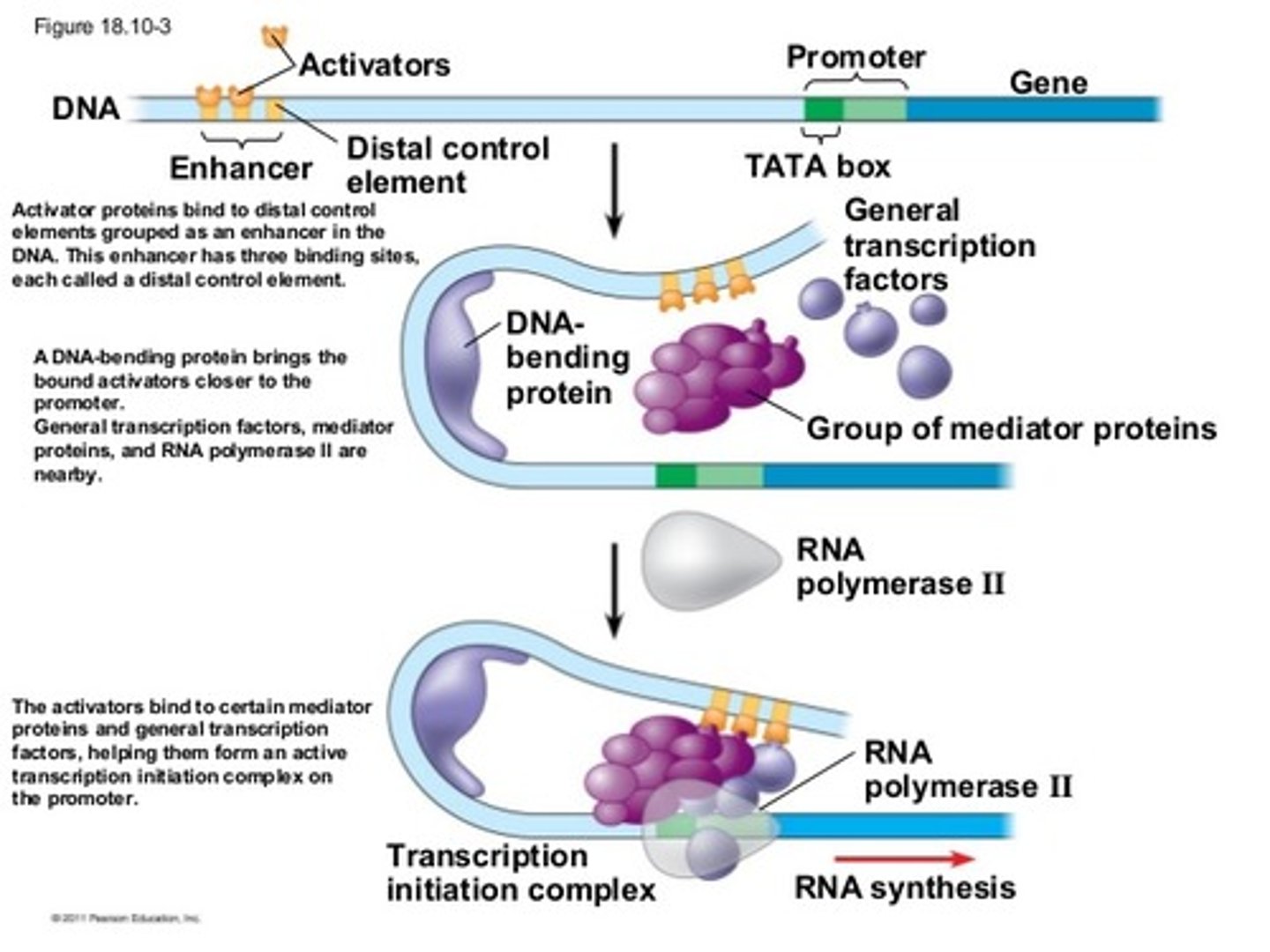
Promoter region and Stop triplet
One is the a region of DNA where RNA polymerase begins to transcribe a gene and the other is a sequence of three nucleotides in DNA or messenger RNA that signals a halt to protein synthesis in the cell.
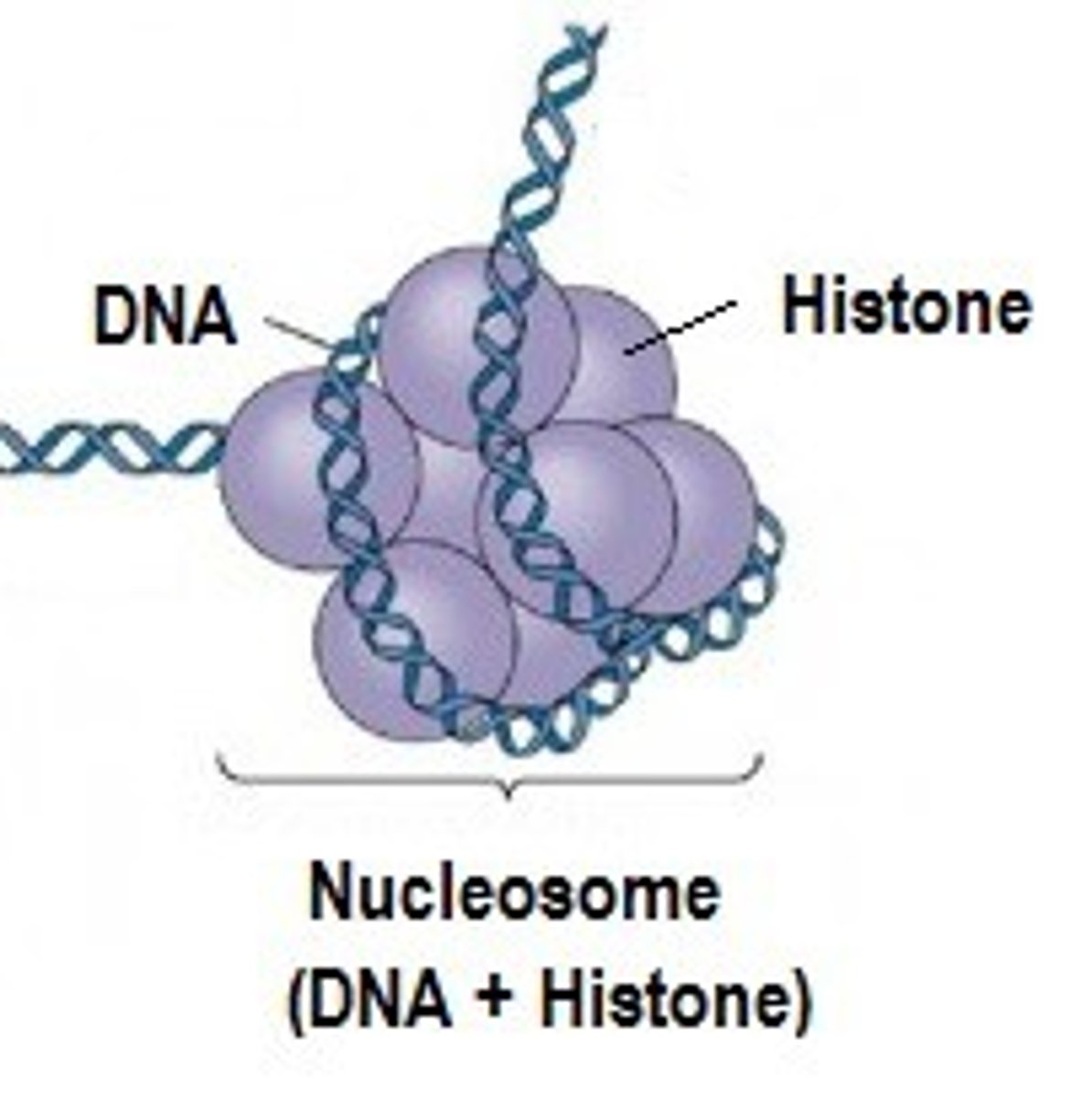
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin. Types include H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. They are positively charged and associate with the negatively charged DNA.
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell. Types include. Euchromatin - a lightly packed form of chromatin and Heterochromatin - a compact form of chromatin.
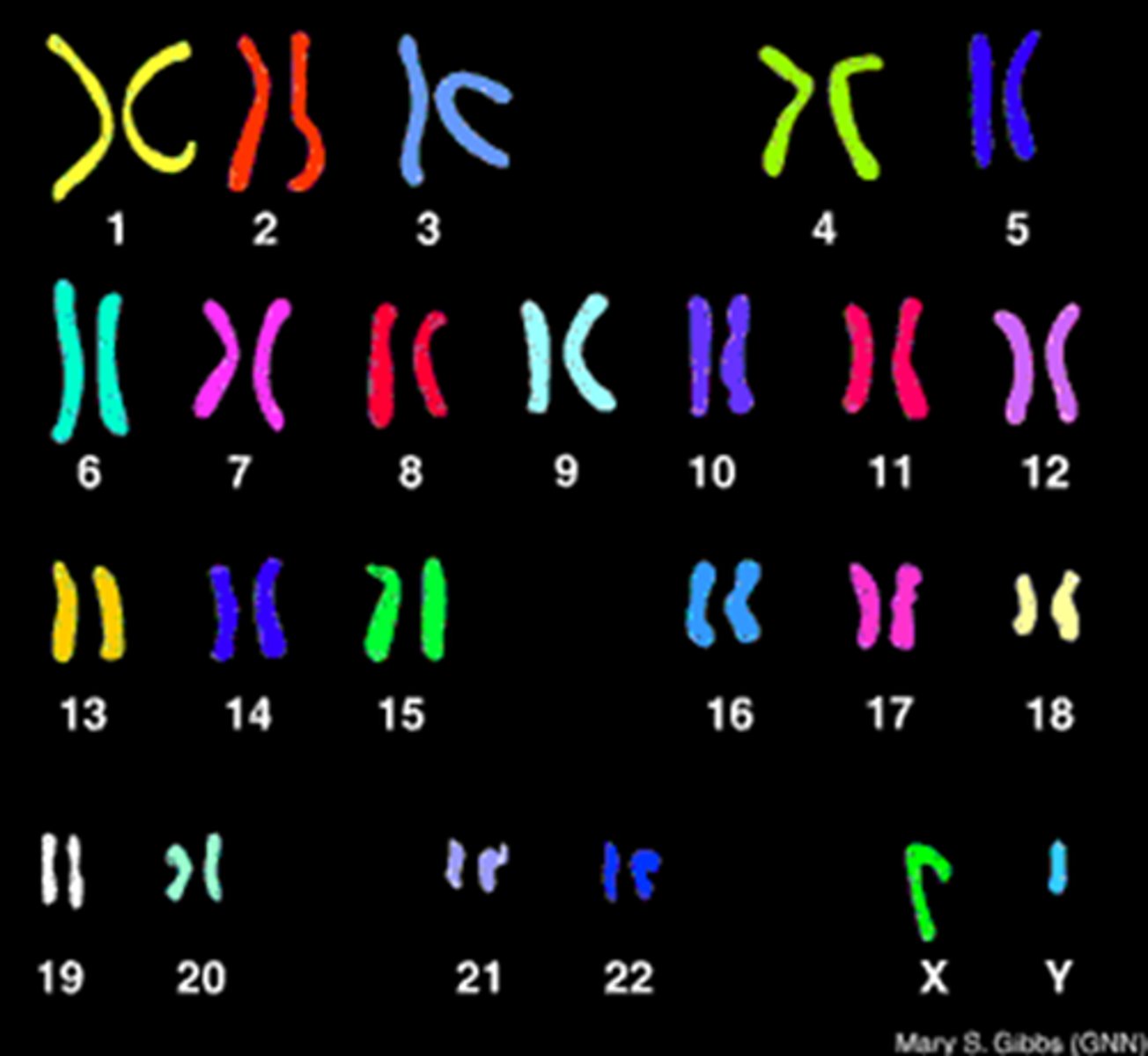
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
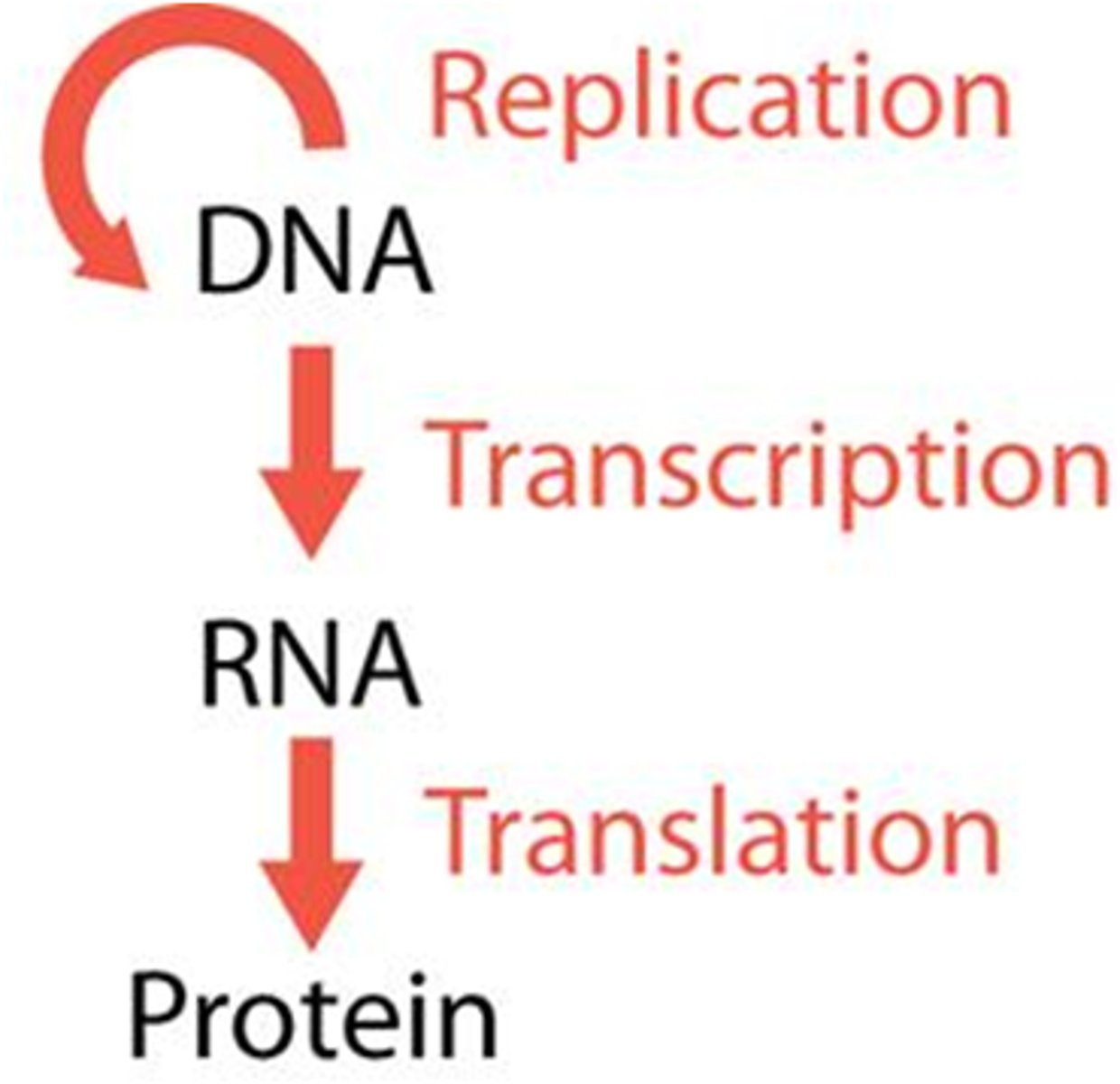
The Central Dogma
Information is encoded in the DNA sequence of a gene - transcribed by mRNA - translated into amino acids
Transcription
Step 1 (Initiation): Transcription factors bind to the promoter region and RNA polymerase-unwinds DNA and breaks the H bonds
Step 2 (Elongation): RNA Polymerase (3'-5') builds a mRNA molecule in the 5' to 3' template strand direction.
Step 3 (Termination): RNA Polymerase reaches a stop codon which signals termination.
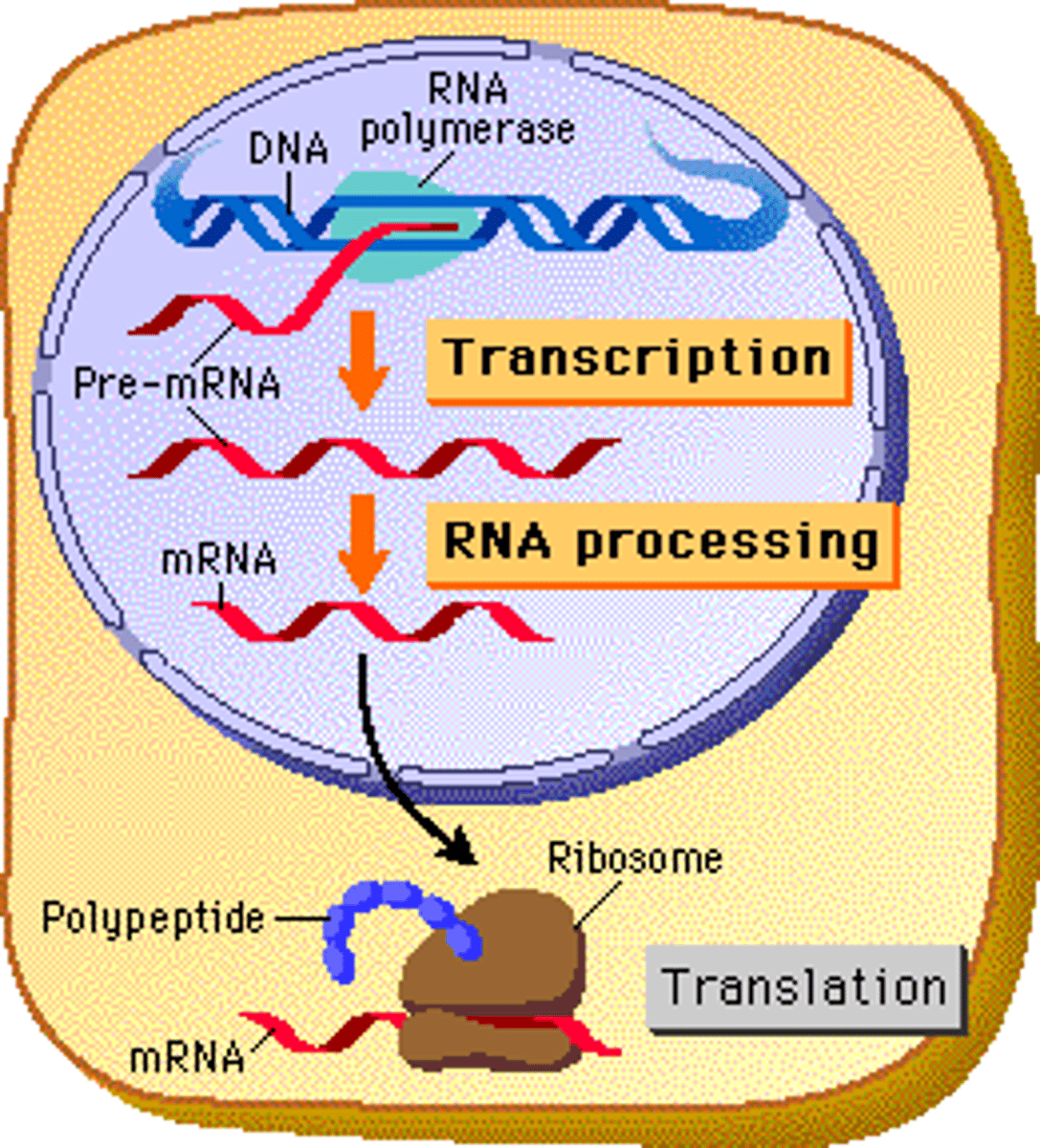
Splicing
the process of removing introns through spliceosomes and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA
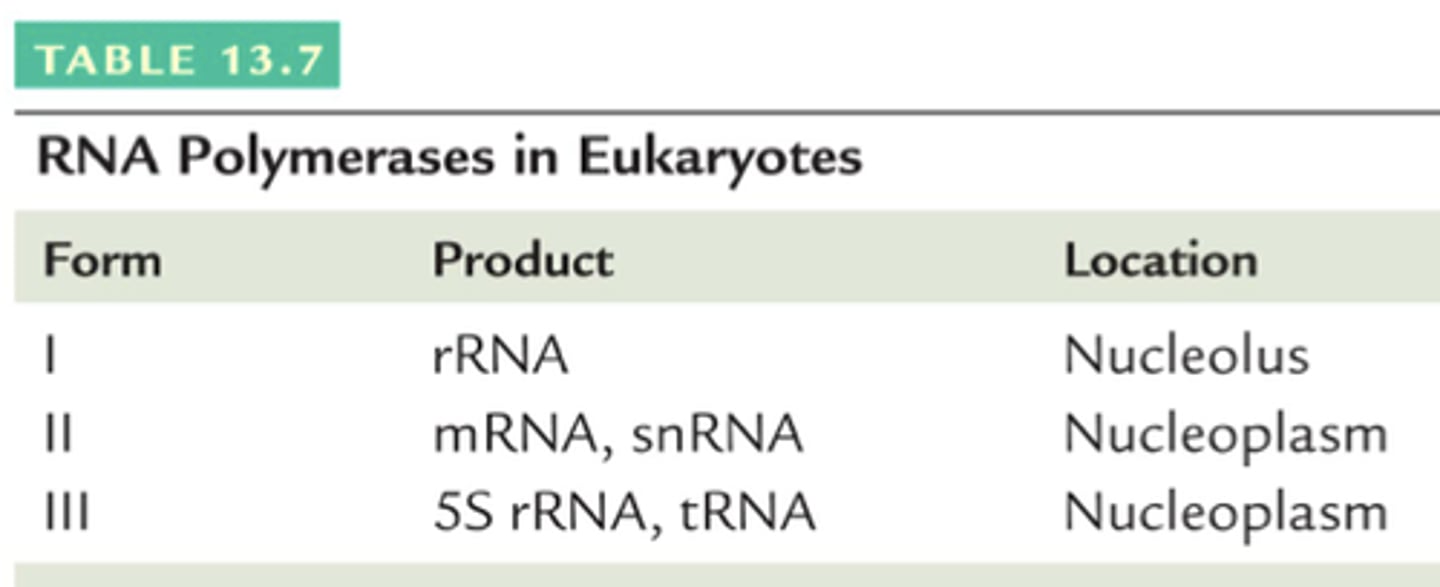
Types of RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase I: Transcribes ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA polymerase II: Transcribes mRNA, miRNA, snRNA
RNA polymerase III: Transcribes tRNA, 5S rRNA
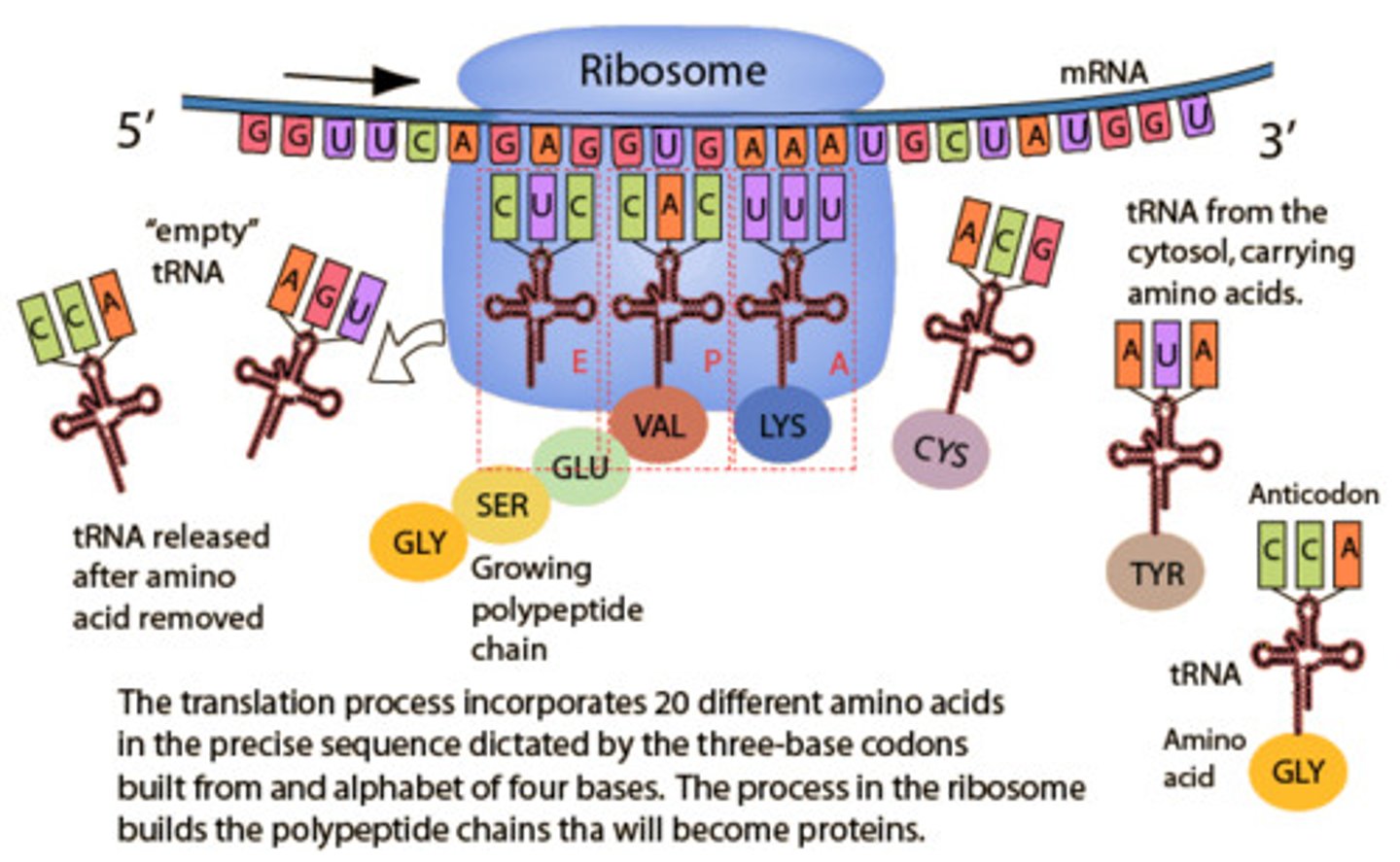
Translation
A site: tRNA enters the ribosome and is tested for an anticodon match, mRNA attaches to the ribosomes (5') and moves along until a start codon is reached.
P site: Provided a correct match, tRNA shifts to the P site and deposits its amino acid to the chain.
E site: tRNA is ejected and the process continues until a stop codon is reached and the polypeptide detaches.
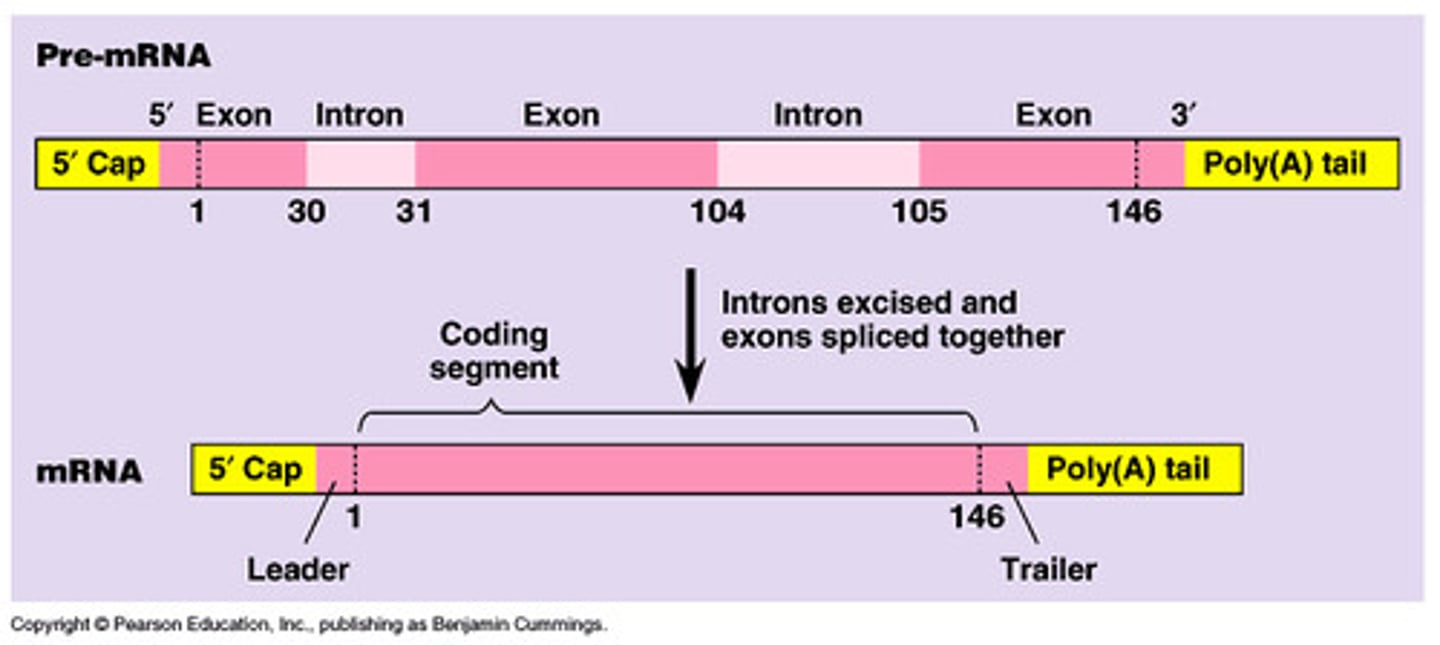
mRNA processing
- 5' guanine cap
- 3' poly-A tail
- RNA splicing of exons = remove introns + "splice" together exons
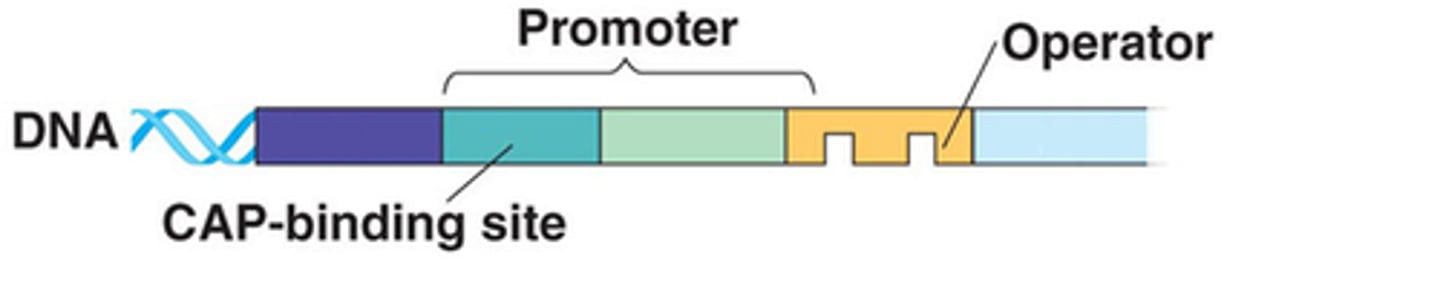
Operon Structure
Promoter: Site where RNA polymerase binds
Operator: The on/off switch positioned within the promoter
Repressor: Binds to the operator preventing RNA polymerase from binding
Tryptophan Absent Operon
Operon on-RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at the operon's promoter and transcribes the operons genes (TRP repressor is inactive). Enzymes for tryptophan synthesis are made.
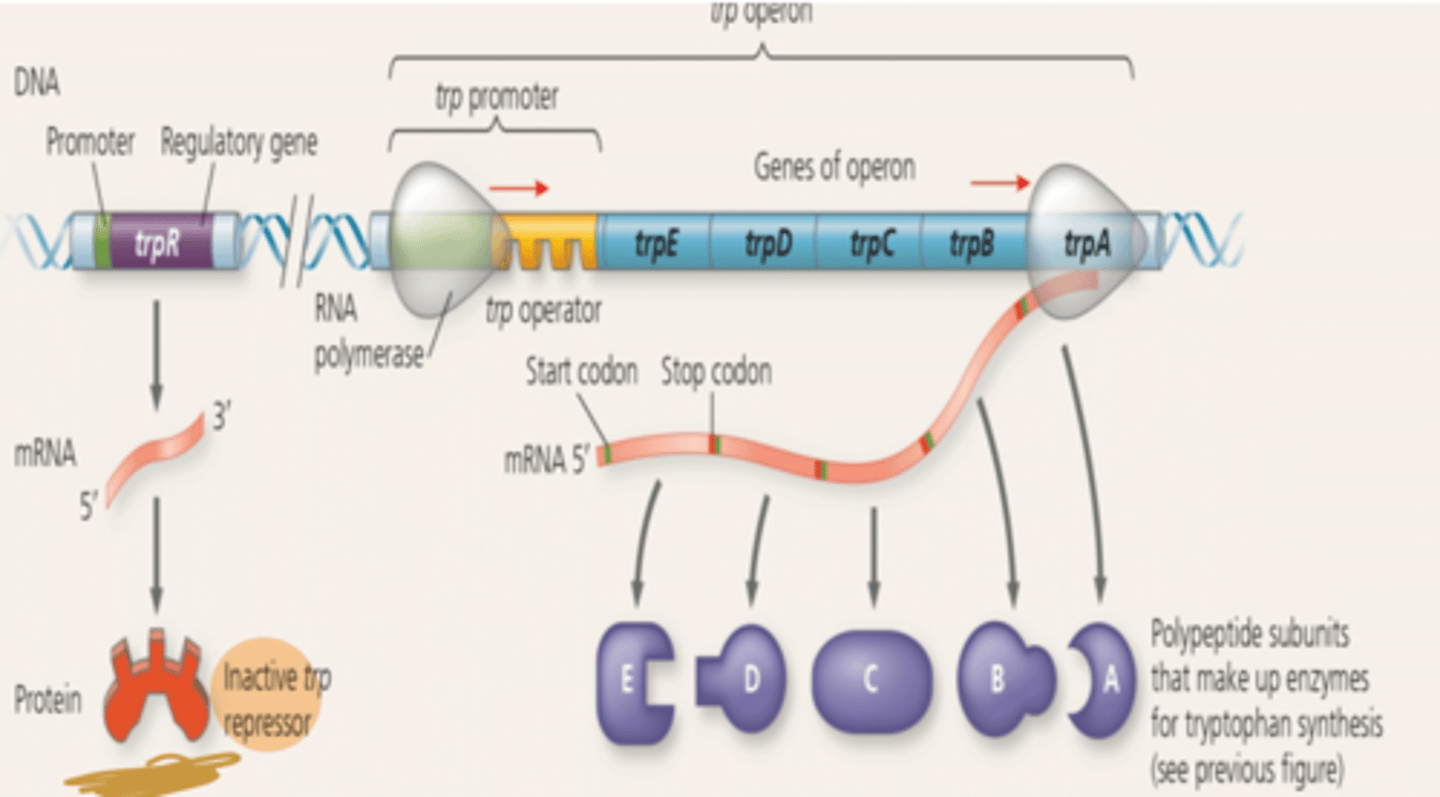
Tryptophan Present Operon
Operon off-As tryptophan accumulates it inhibits its own production by activating the repressor protein which binds to the operator blocking transcription. Enzymes for tryptophan synthesis are not made.
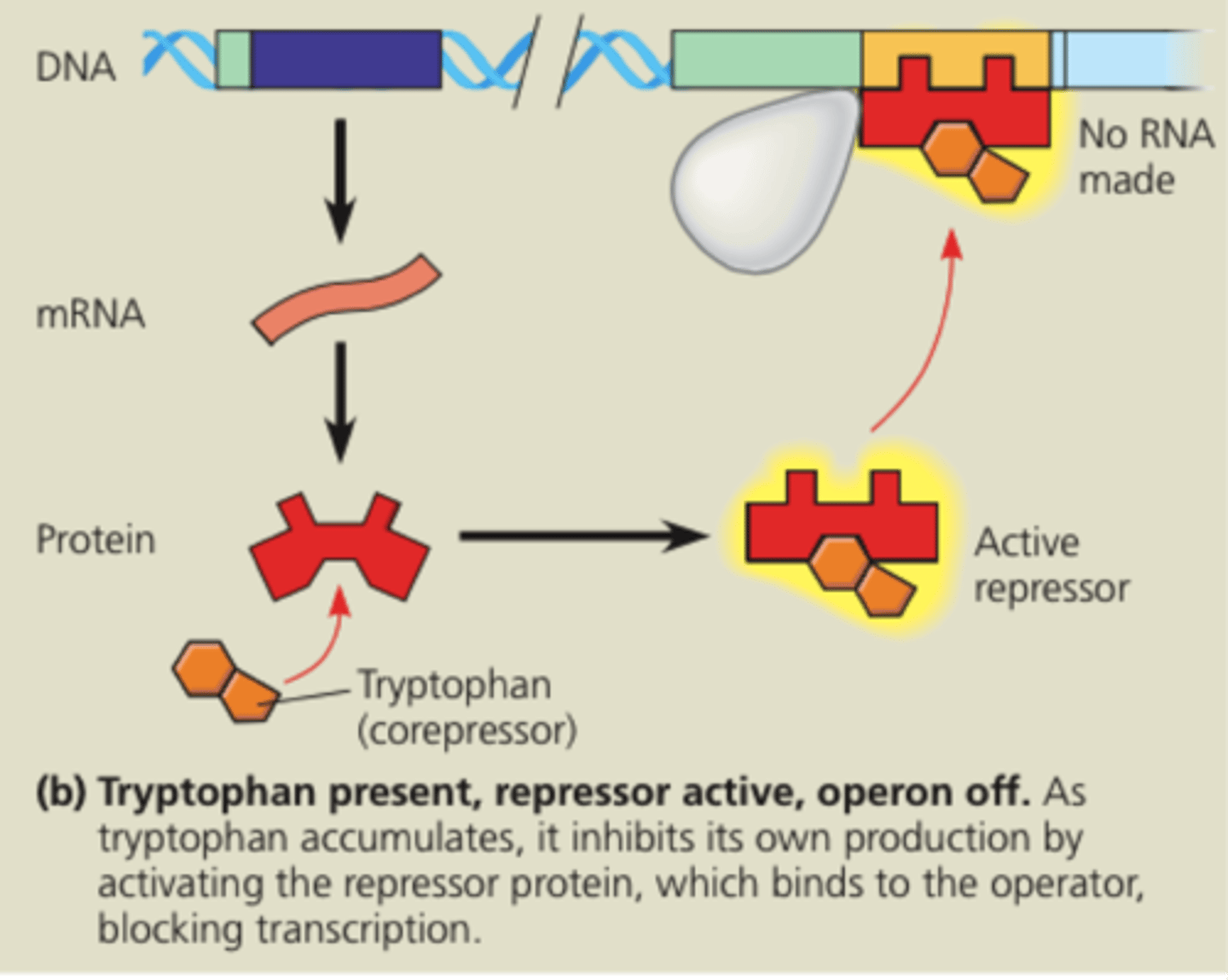
Tryptophan
A corepressor: a molecule/aminoacidic that cooperates with a repressor protein to switch an operon off
repressible operon
Transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a molecule binds allosterically (TRP operon/ Tryptophan)
Repressor becomes active with binding of Corepressor
Inducible Operon
Transcription is usually off, but can be stimulated (induced) when a molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (lac operon/Allolactose)
Repressor is active without binding of inducer
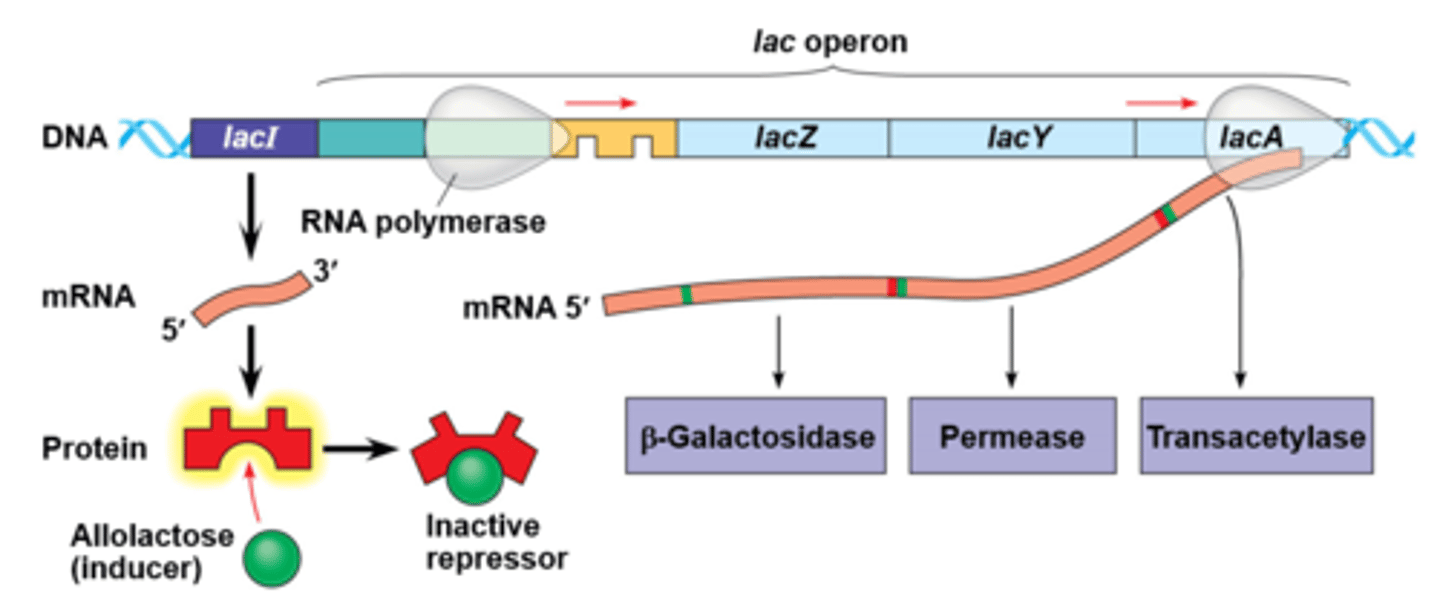
lactose present operon
Operon on-Allolactose binds to the repressor inactivating it, so the inactive repressor cannot bind to the operator- genes of the lac operon are transcribed and enzyme for using lactose are transcribed.
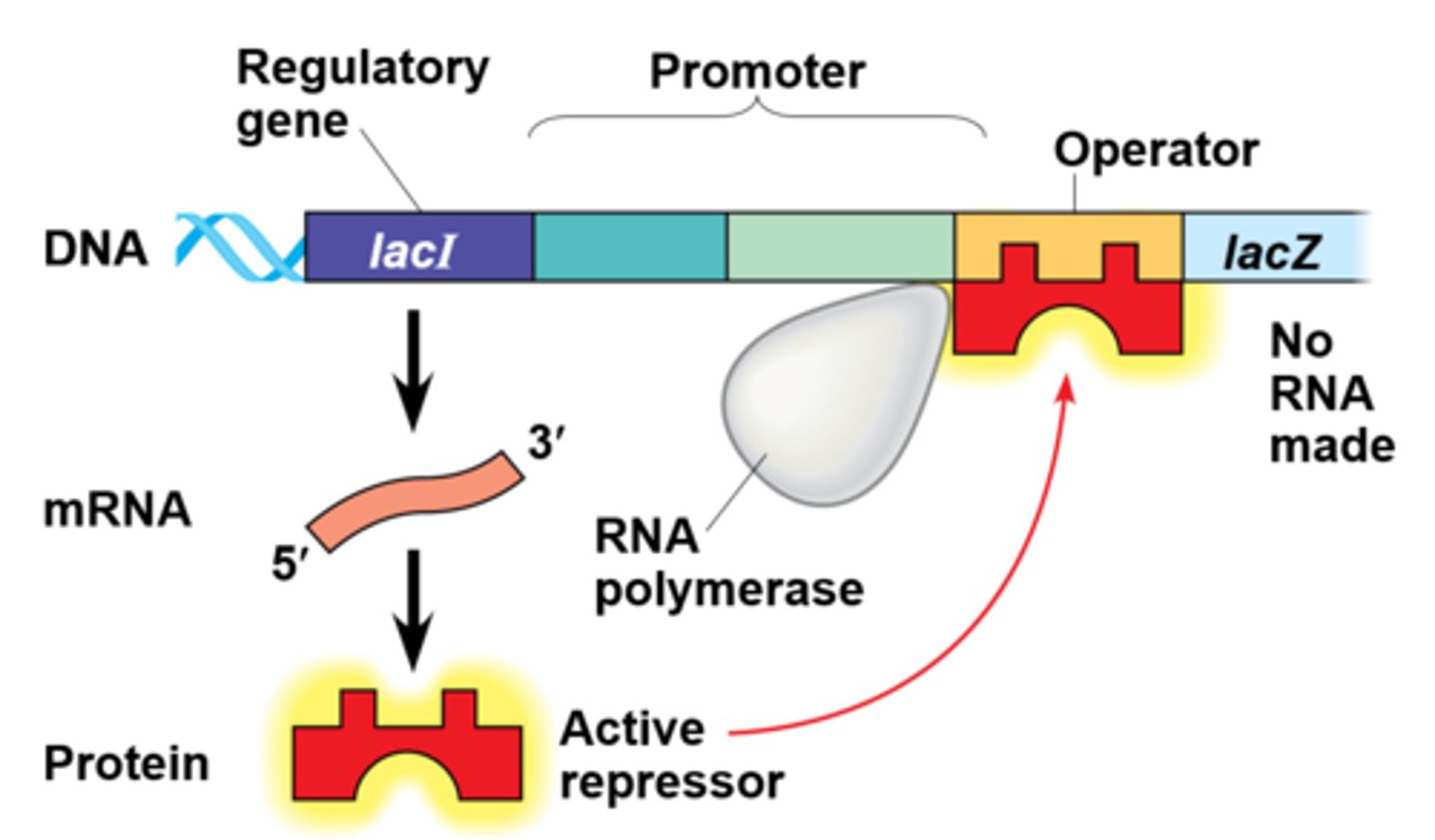
lactose absent operon
The lac repressor is innately active, and in the absence of lactose it switches off the operon by binding to the operator. Enzymes for using lactose are not made.
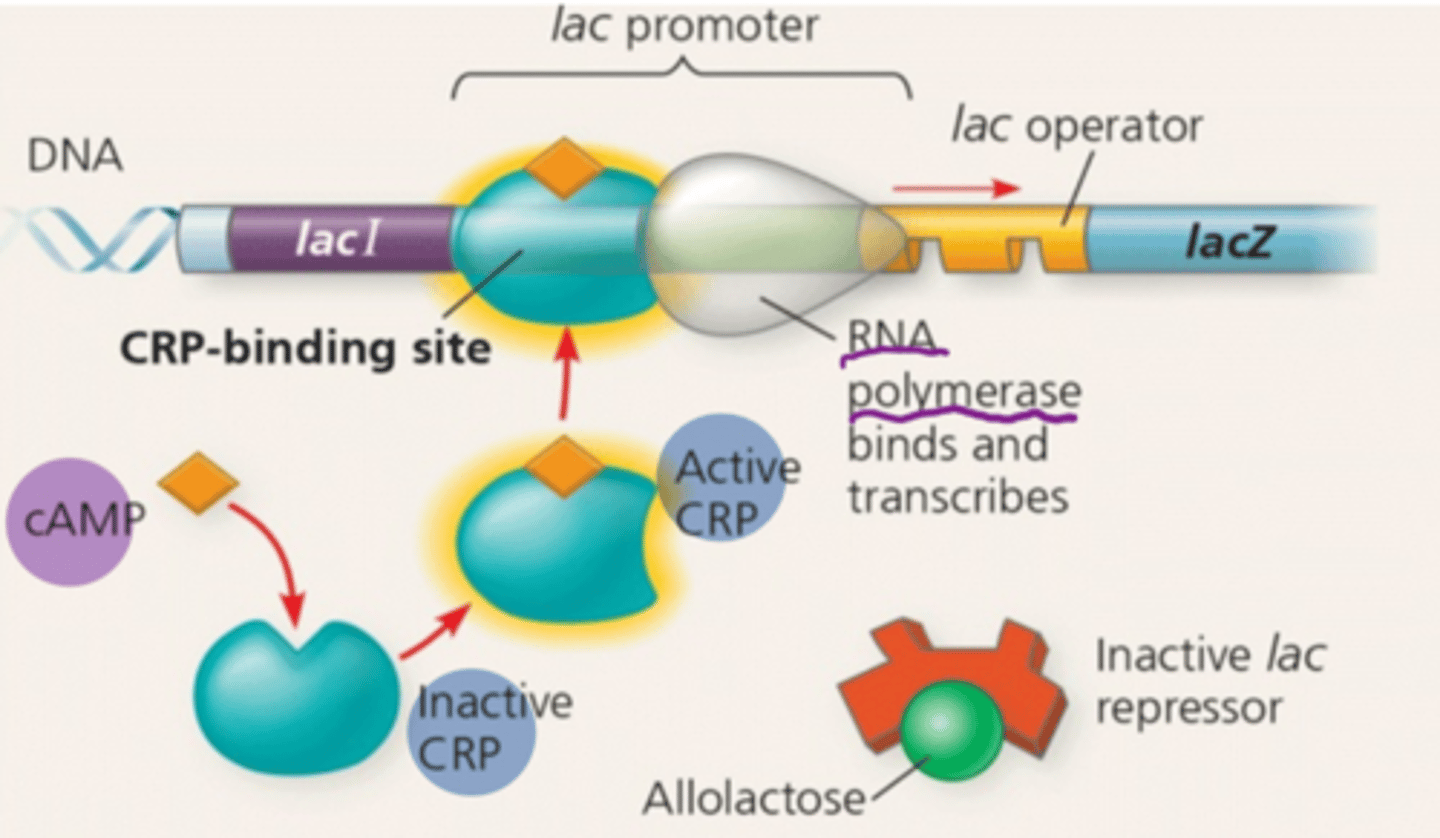
positive gene regulation
The process by which gene expression is increased or enhanced in response to specific regulatory signals or factors
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
An allosteric regulatory protein which accumulates when glucose is scarce
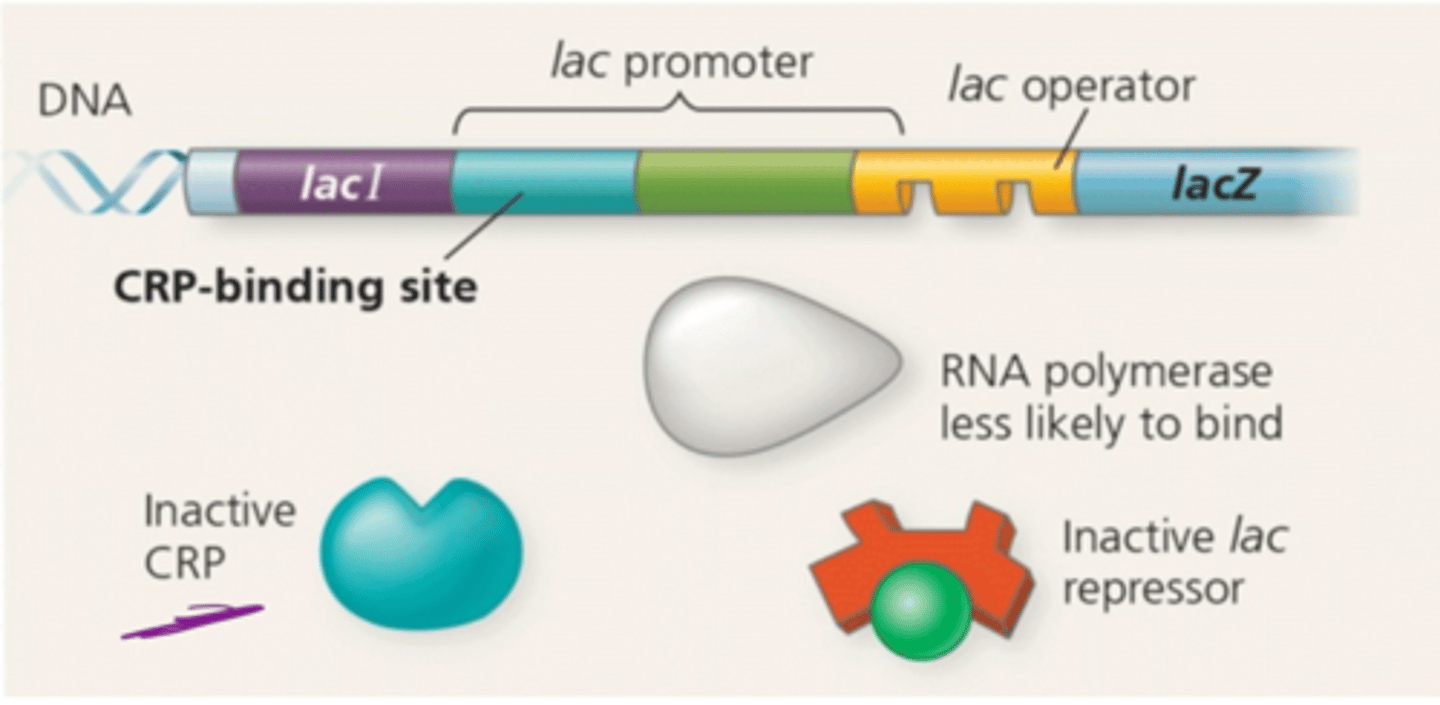
cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
the activator protein that binds with cyclic AMP to increase the rate of lac operon transcription
lactose is present and glucose is absent
The high level of cAMP activates CRP which binds to the promoter and increases RNA polymerase binding there.
The lac operon produced large amounts of mRNA coding for the enzymes the cell needs to use lactose
Lactose present and glucose is present
Low cAMP levels and CRP is unable to stimulate transcription at a significant rate, even though no repressor is bound
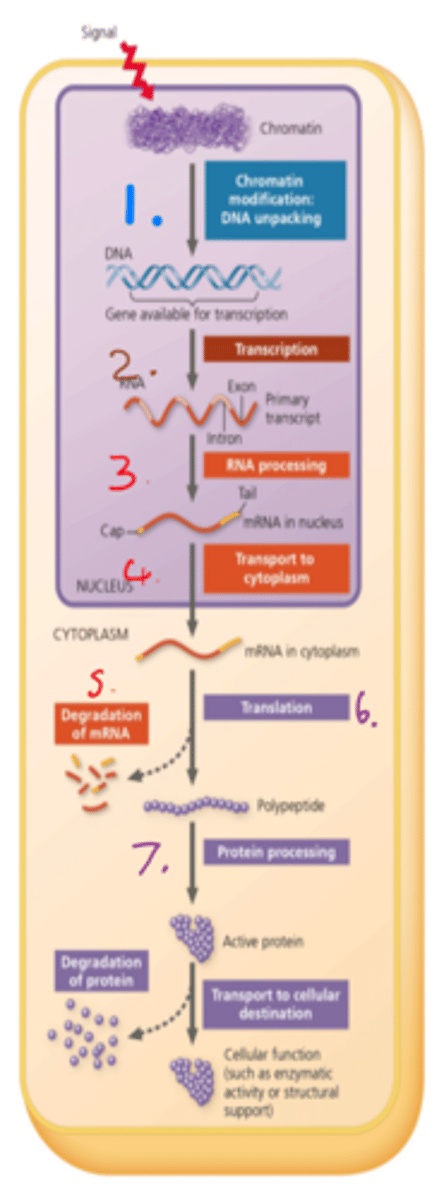
7 step gene regulation in Eukaryotes
1. Regulation of chromatin structure
2. Transcription control
3. RNA processing
4. Mature RNA is localised
5. Degradation of mRNA
6. Translational control
7. Protein Folding + Post Translational Modification
Activator Protein
a regulatory protein that binds to specific sites on DNA and stimulates transcription; involved in positive control
