Endo/Repro Exam 1: Histology - Pituitary, Thyroid, Parathyroid & Adrenal Glands (Dr. Marchant)
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
What has the following characteristics?
- Ductless glands
- Usually secrete hormones into bloodstream via fenestrated capillaries
- Generally have systemic effects
Endocrine organs
Endocrine tissue exists in many "non-endocrine" organs, such as...
- EPO & renin secreting cells in kidney
- Enteroendocrine cells in gut, lung
All of the following are functions of what?
- Regulation of other endocrine organs
- Regulation of metabolism and energy balance
- Regulation of smooth and cardiac muscle contraction
- Regulation of glandular secretions
- Regulation of growth and development
- Regulation of "flight or fight" responses and reproduction
Hormones
Hypophysis is also known as...
Pituitary gland
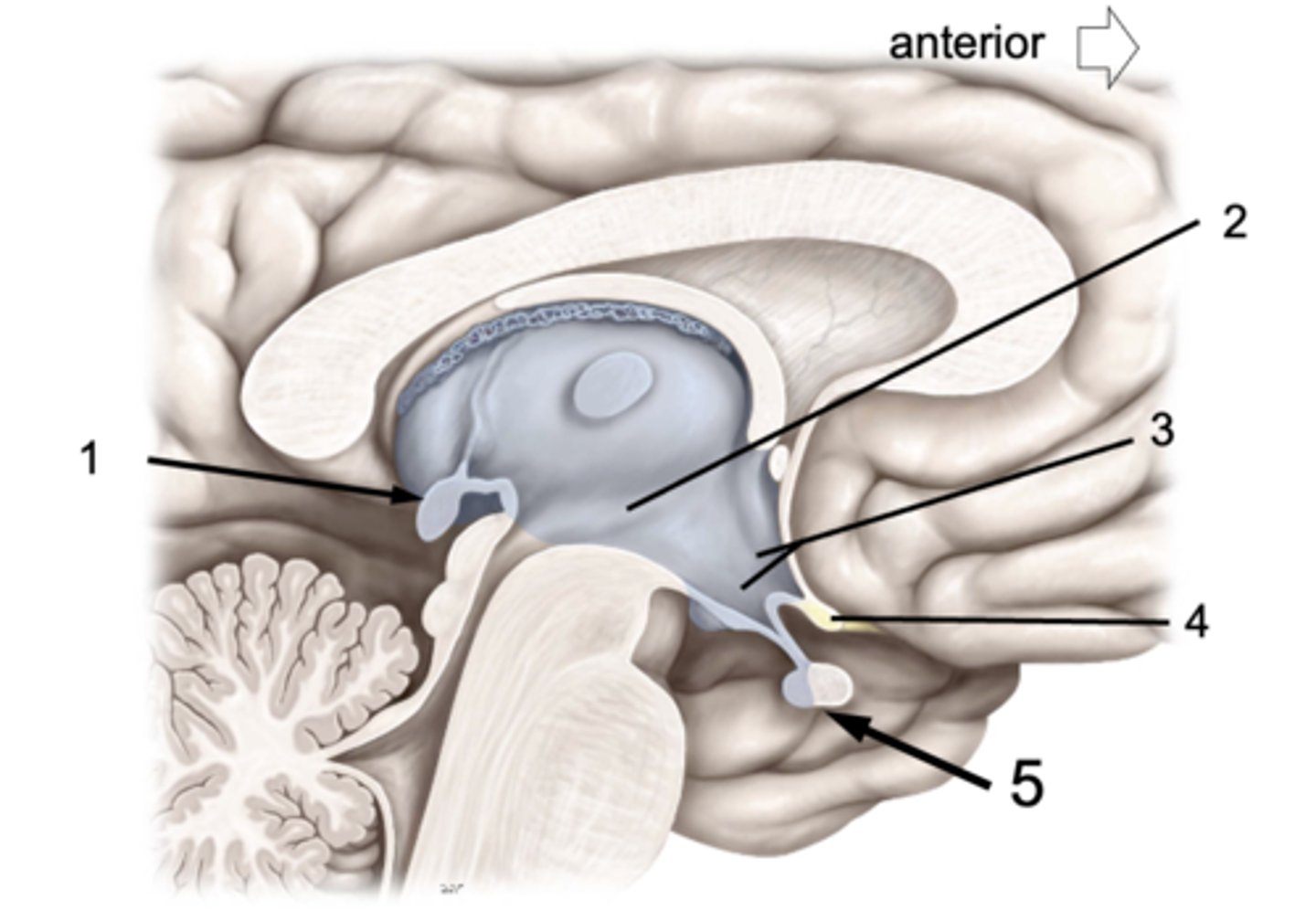
ID #1:
Pineal gland
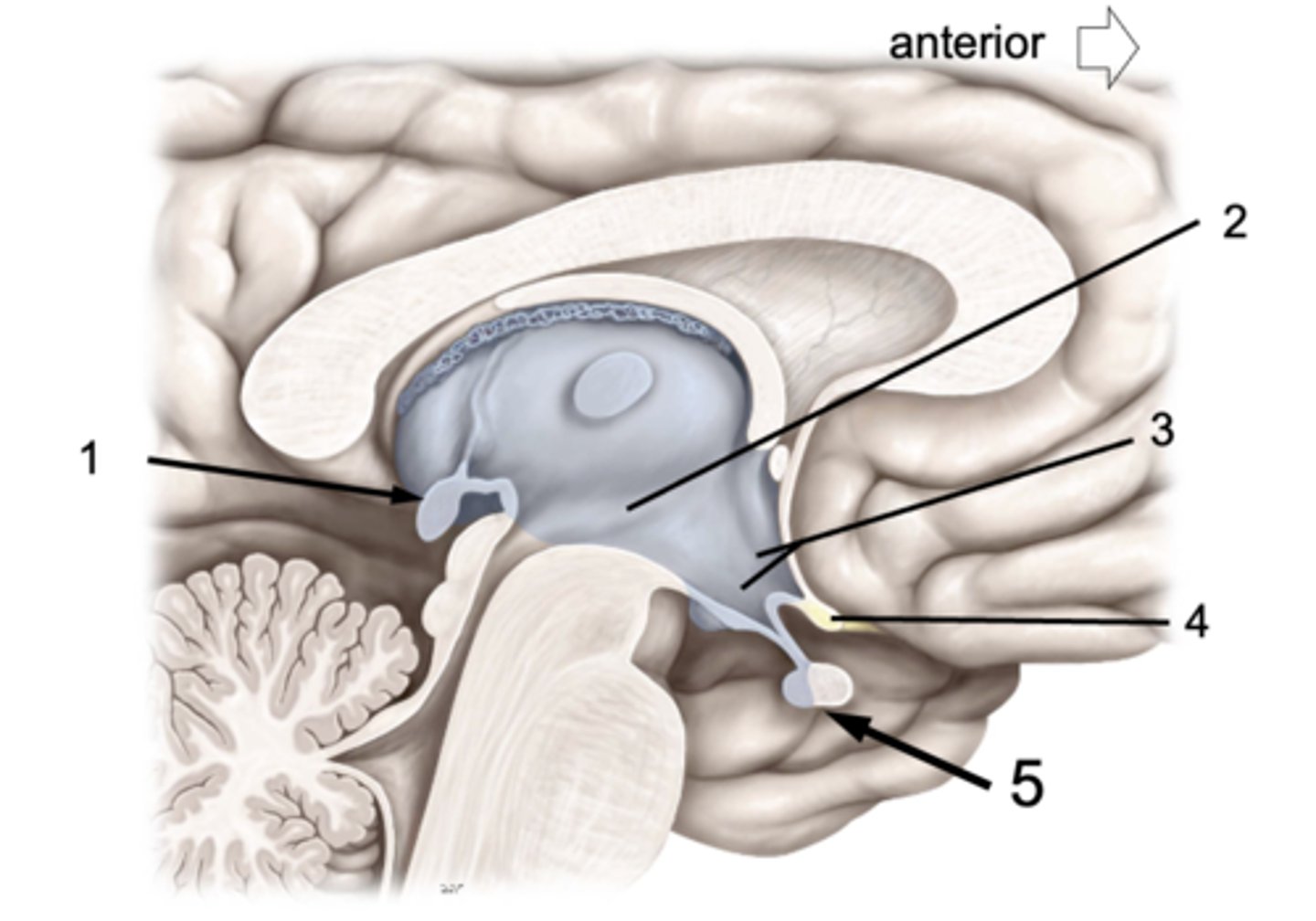
ID #2:
3rd ventricle
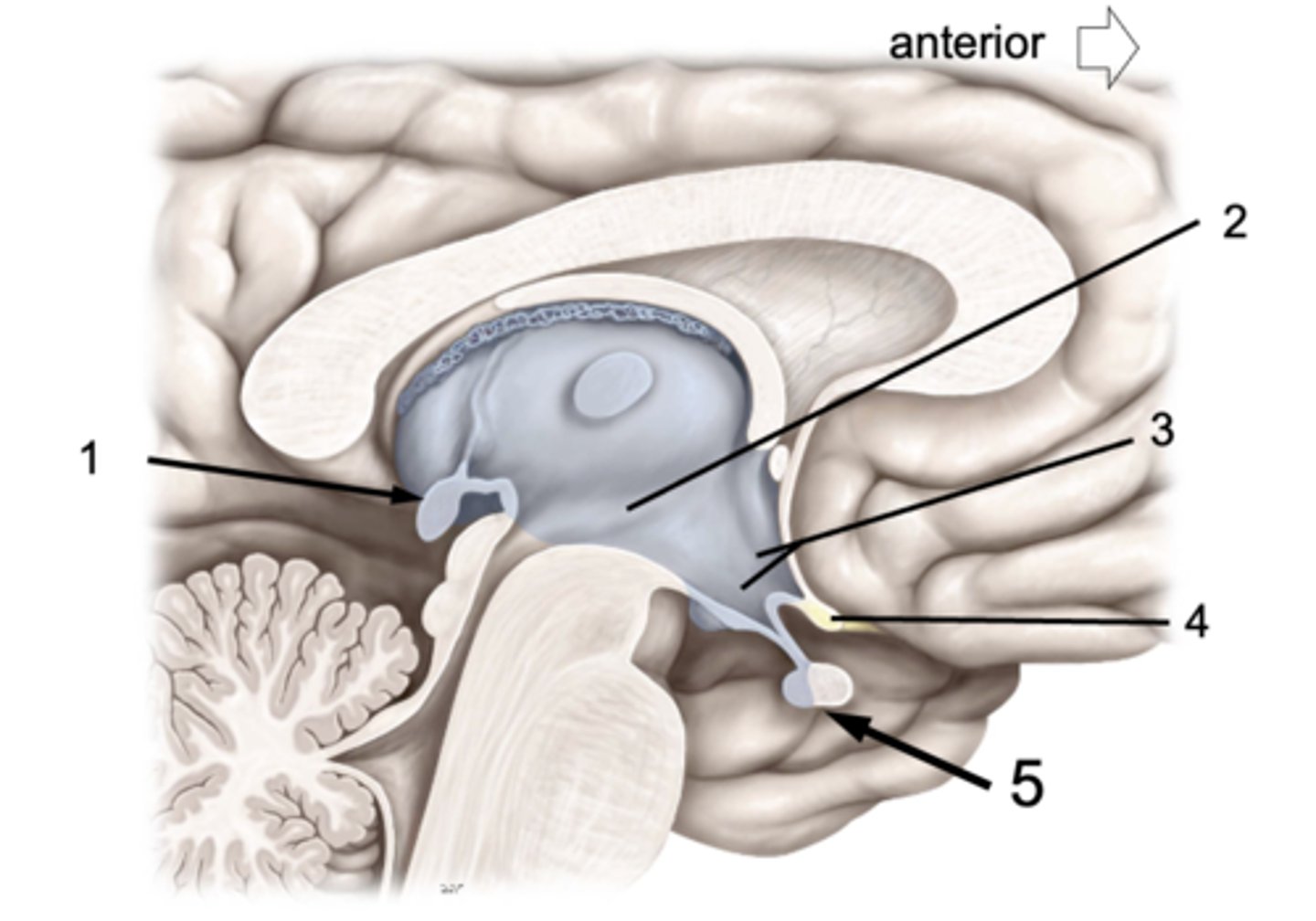
ID #3:
Hypothalamus
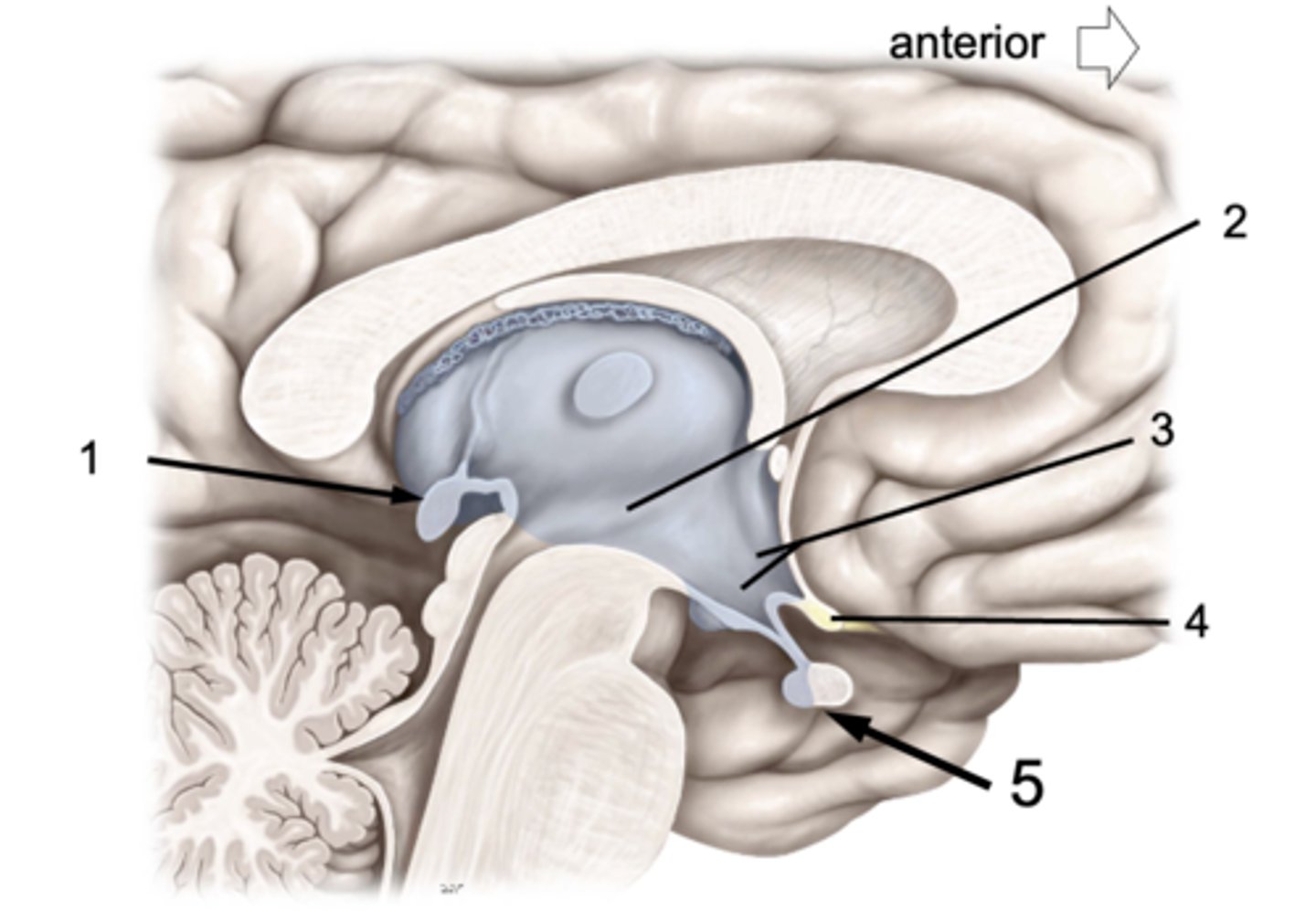
ID #4:
Optic chiasm
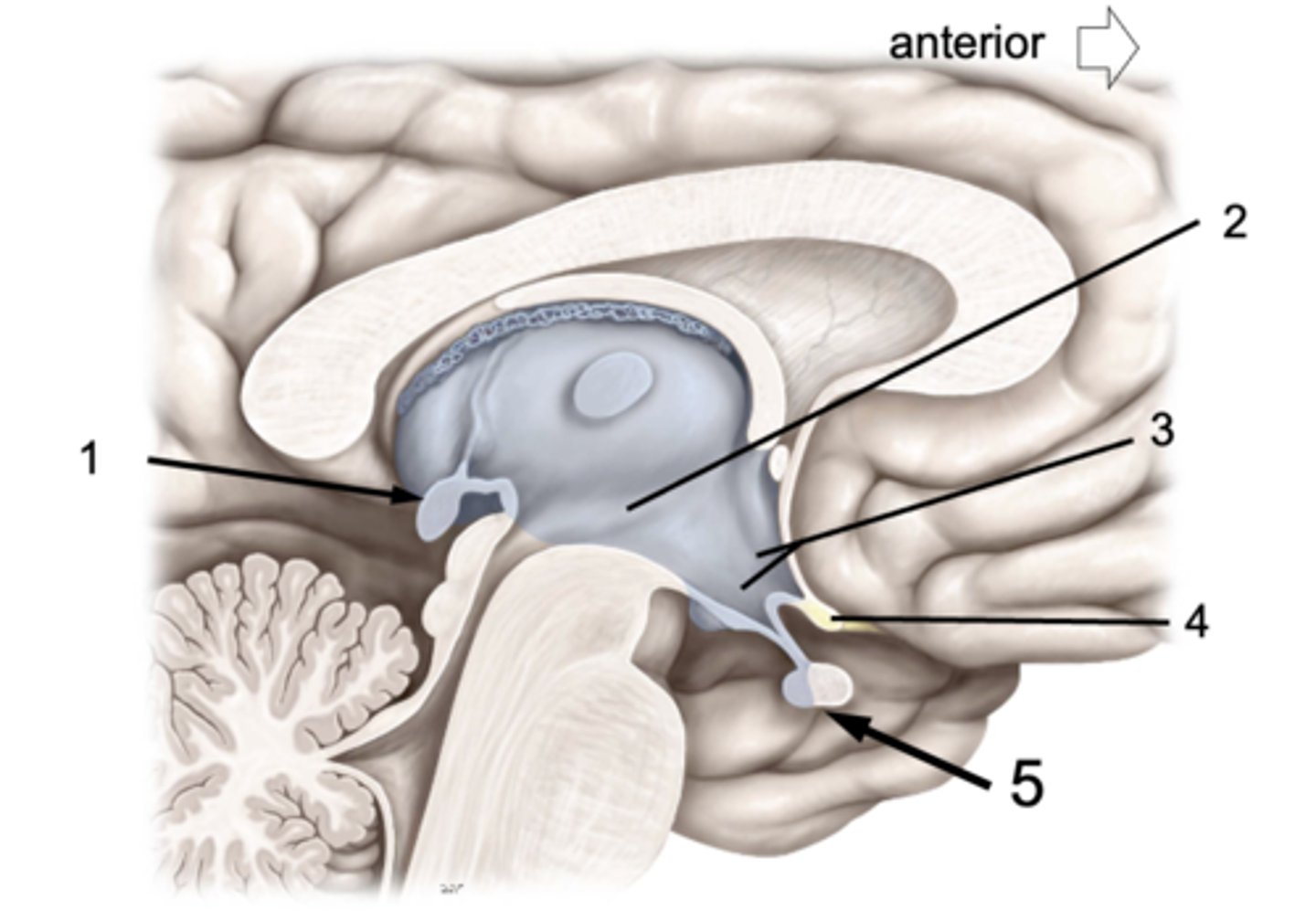
ID #5:
Pituitary gland (anterior and posterior lobes)
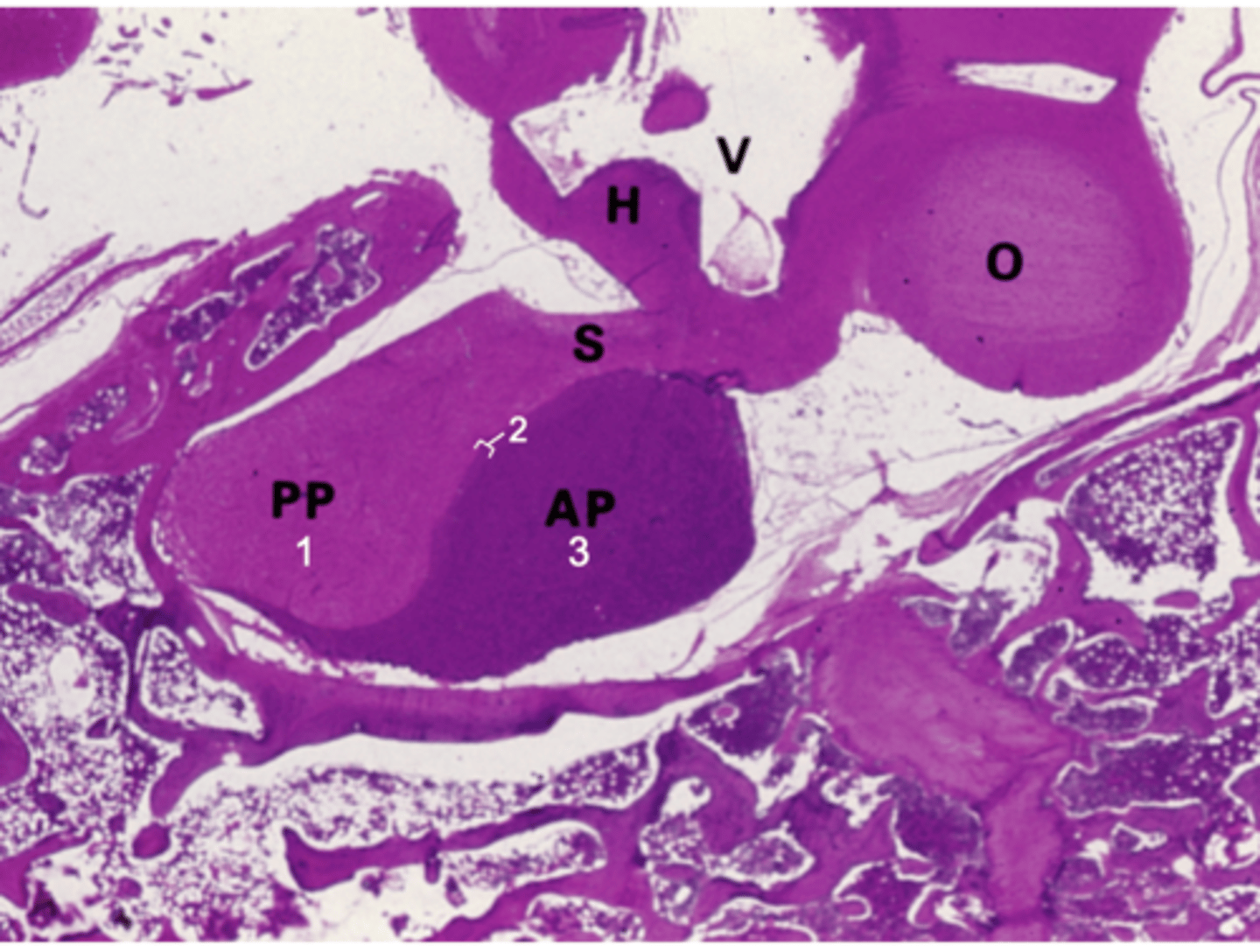
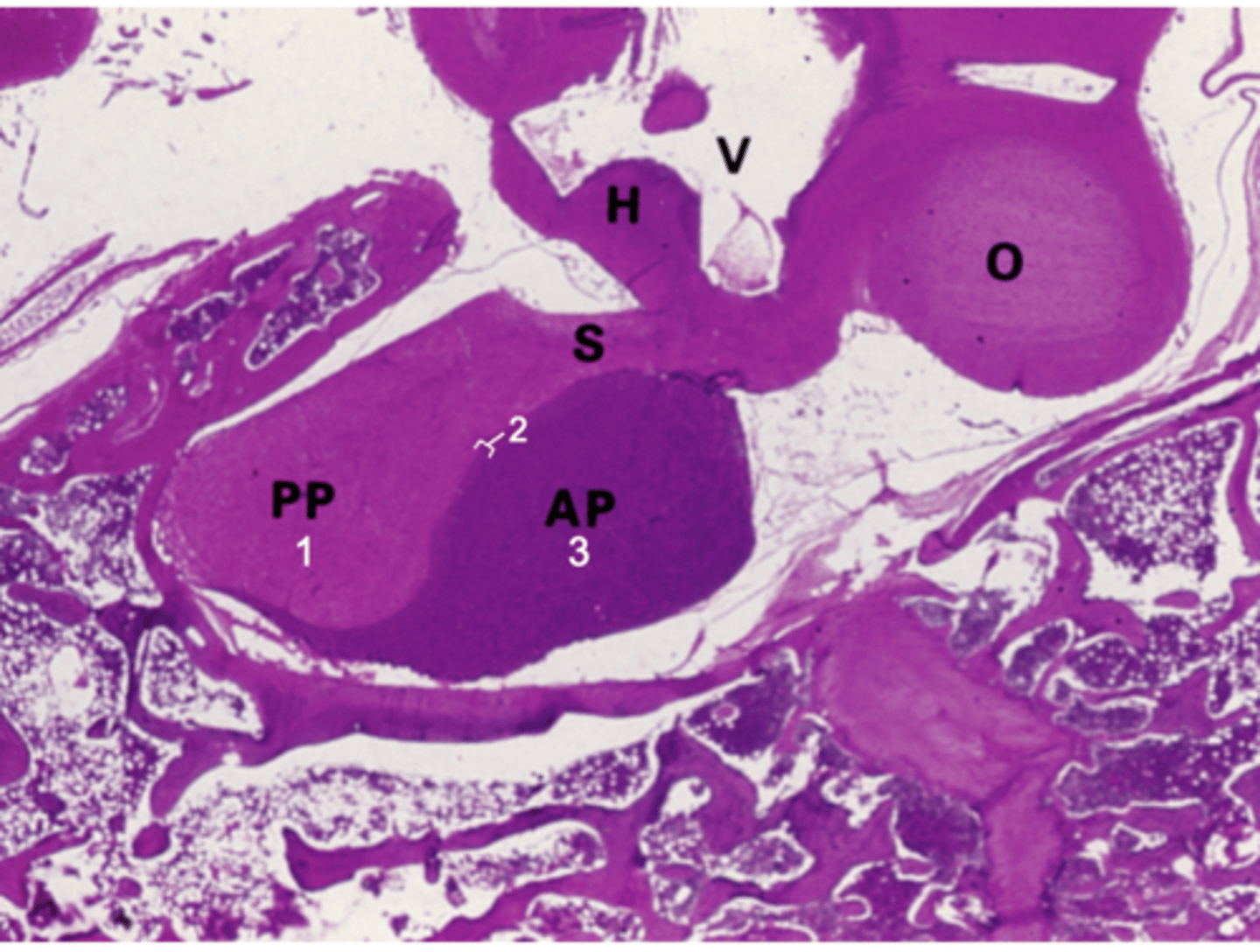
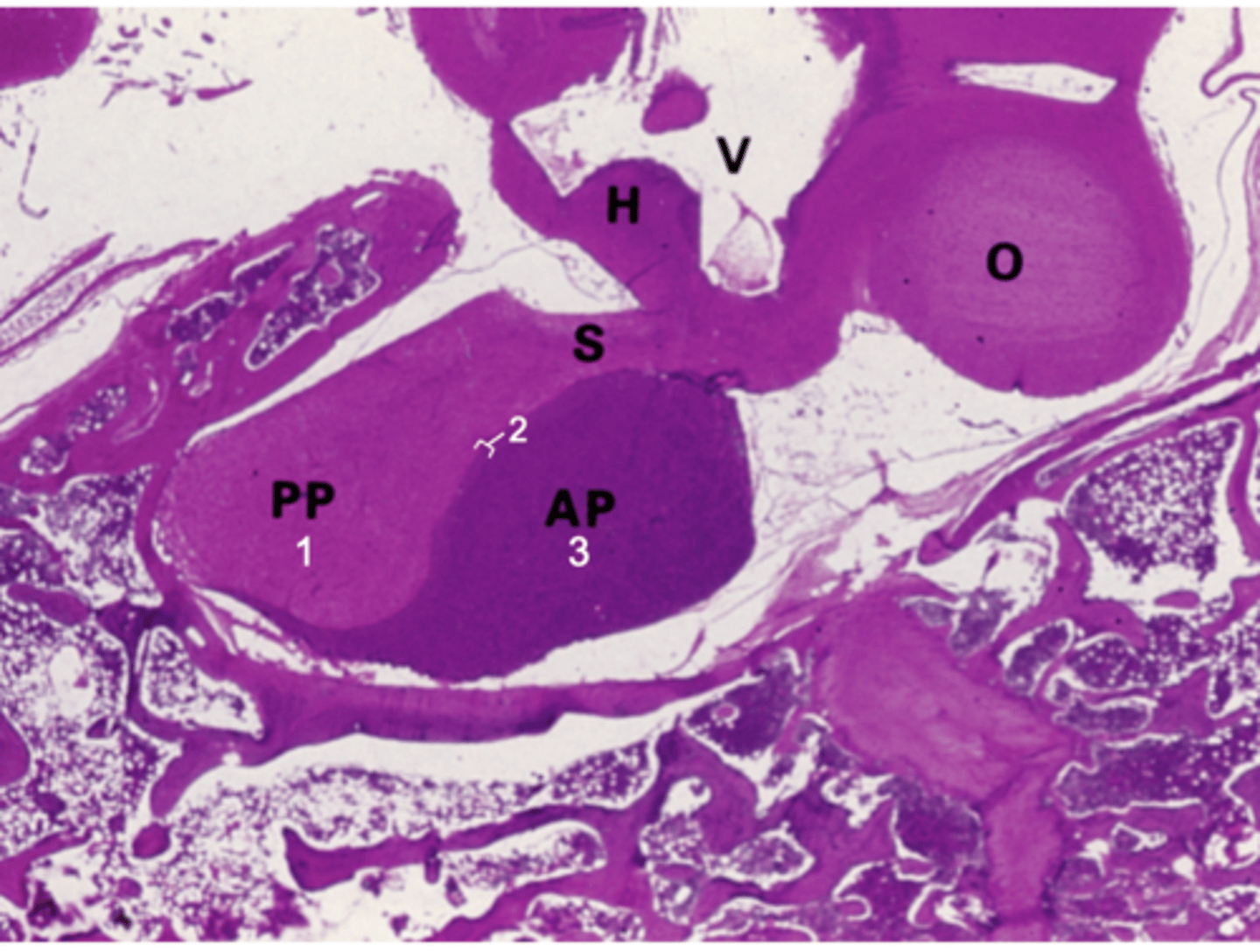
ID the organ this histological section is from:
Pituitary gland
ID #1:
Pars nervosa
ID #2:
Pars intermedia
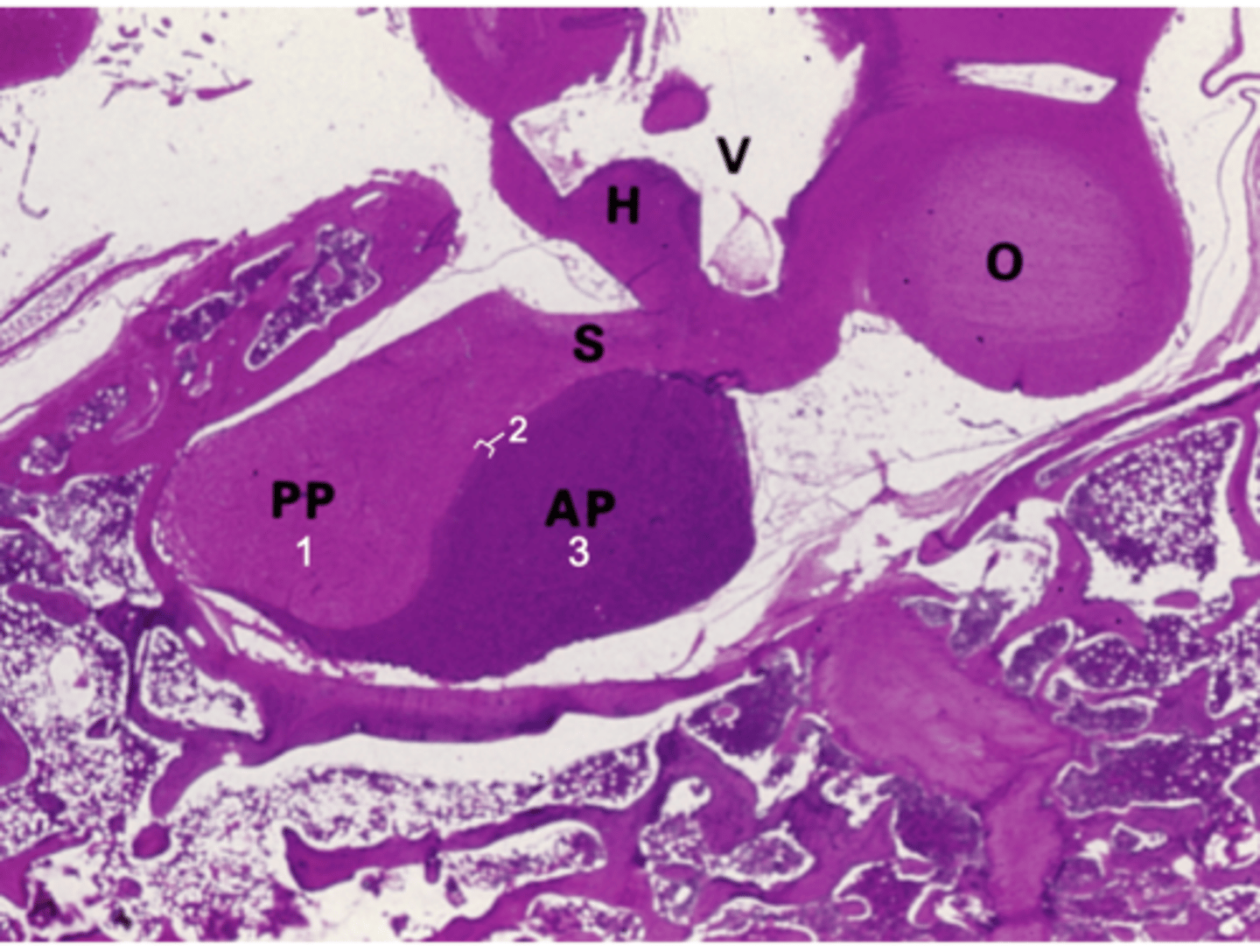
ID #3:
Pars distalis
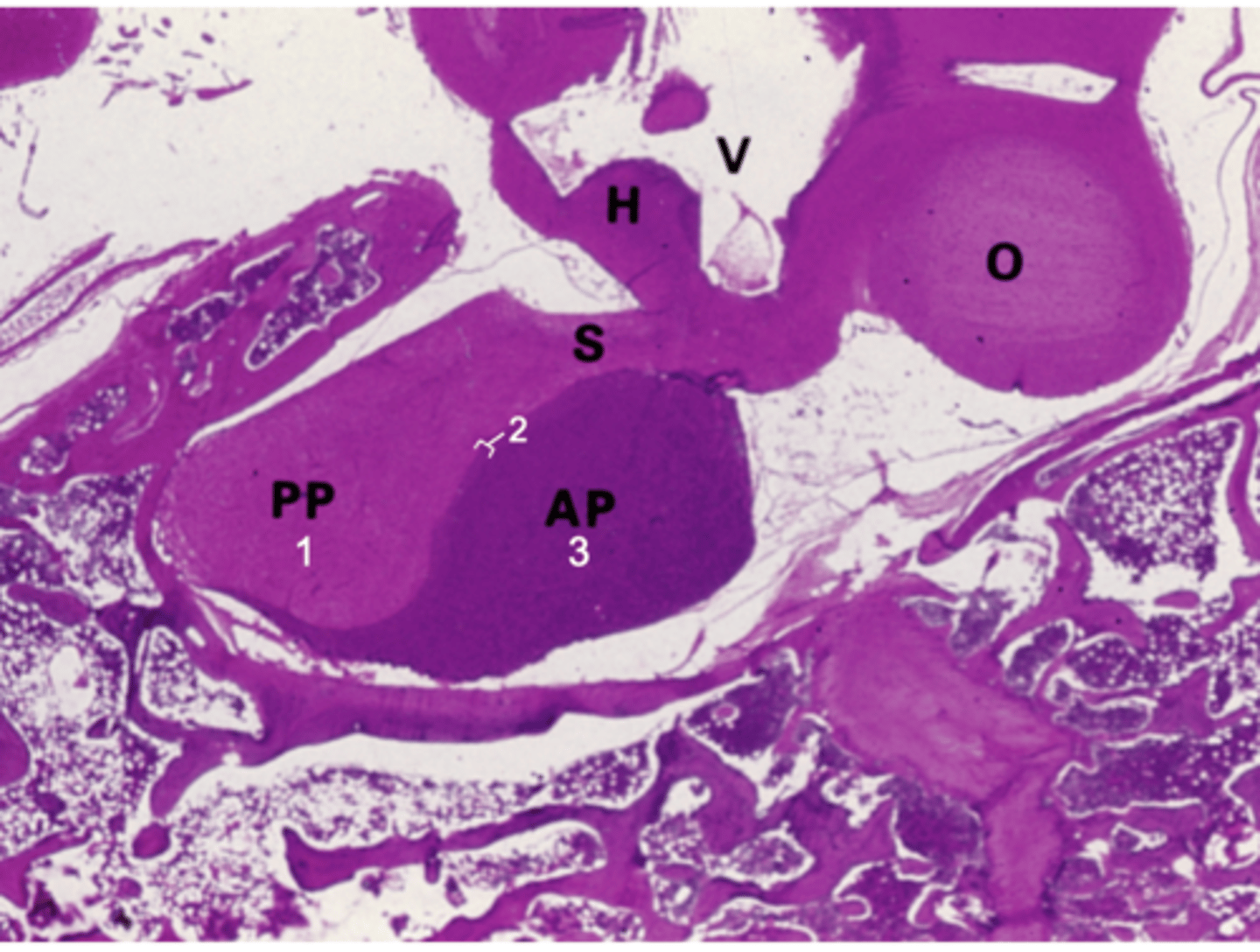
What does PP stand for?
Posterior pituitary
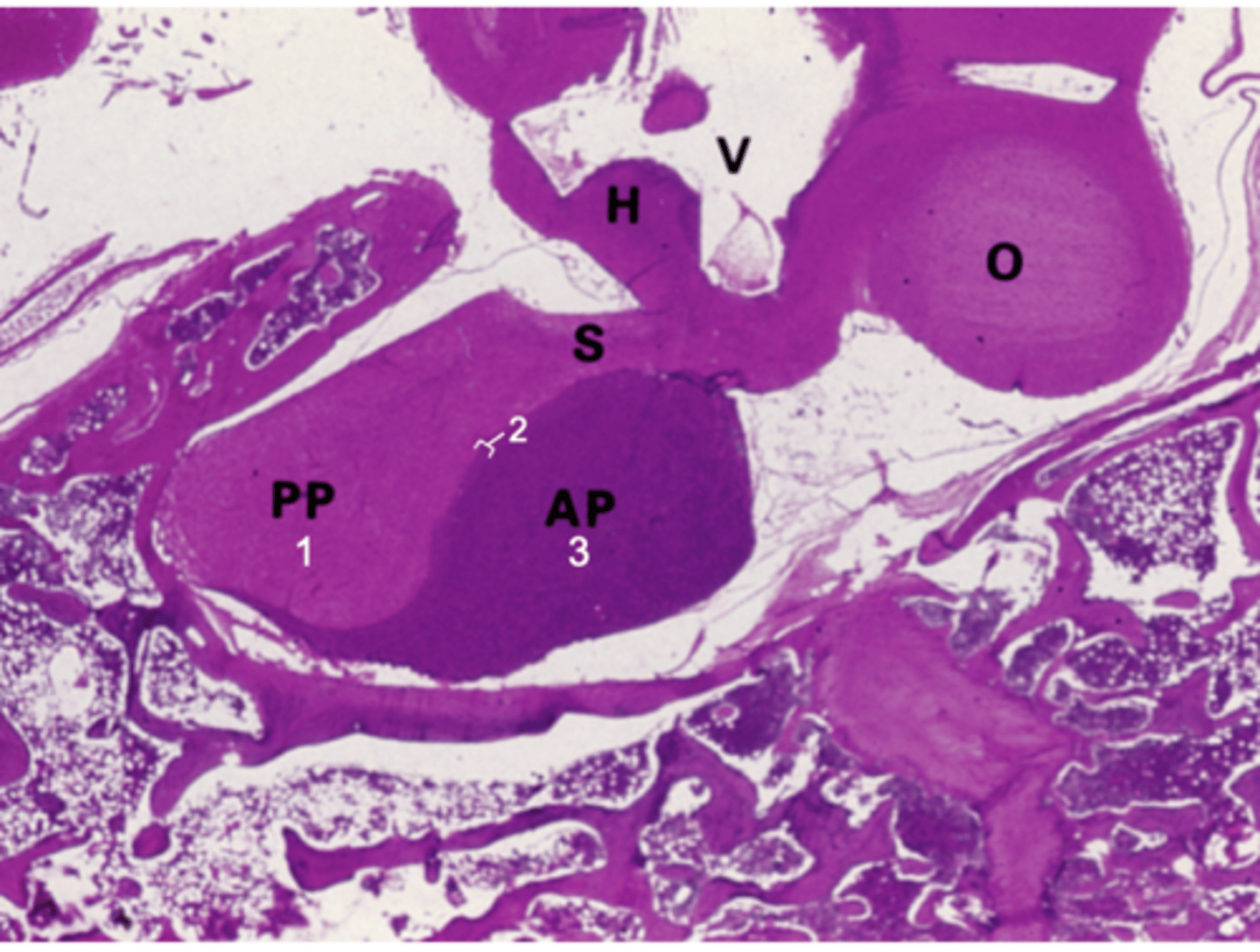
What does AP stand for?
Anterior pituitary
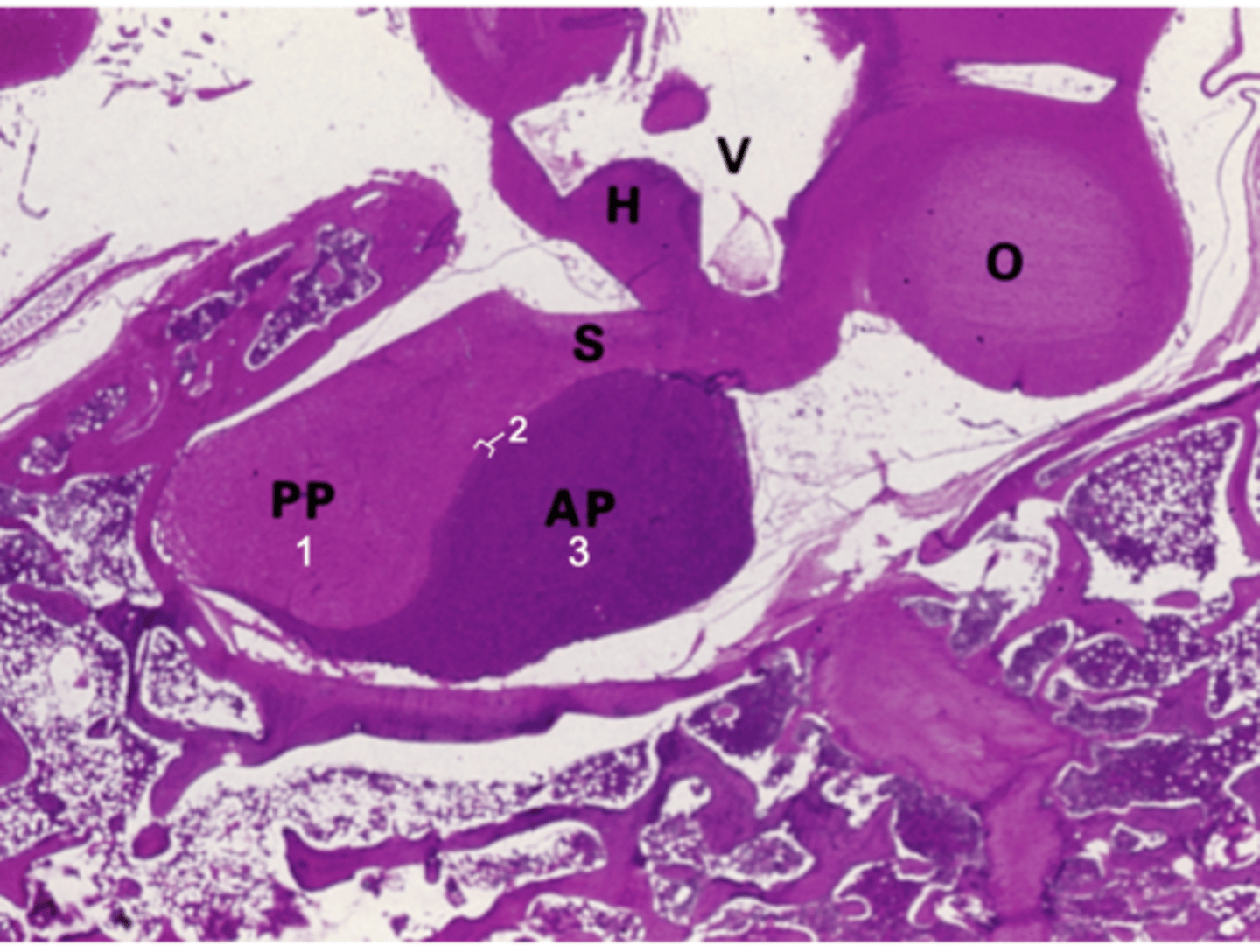
What does S stand for?
Stalk

What does H stand for?
Hypothalamus
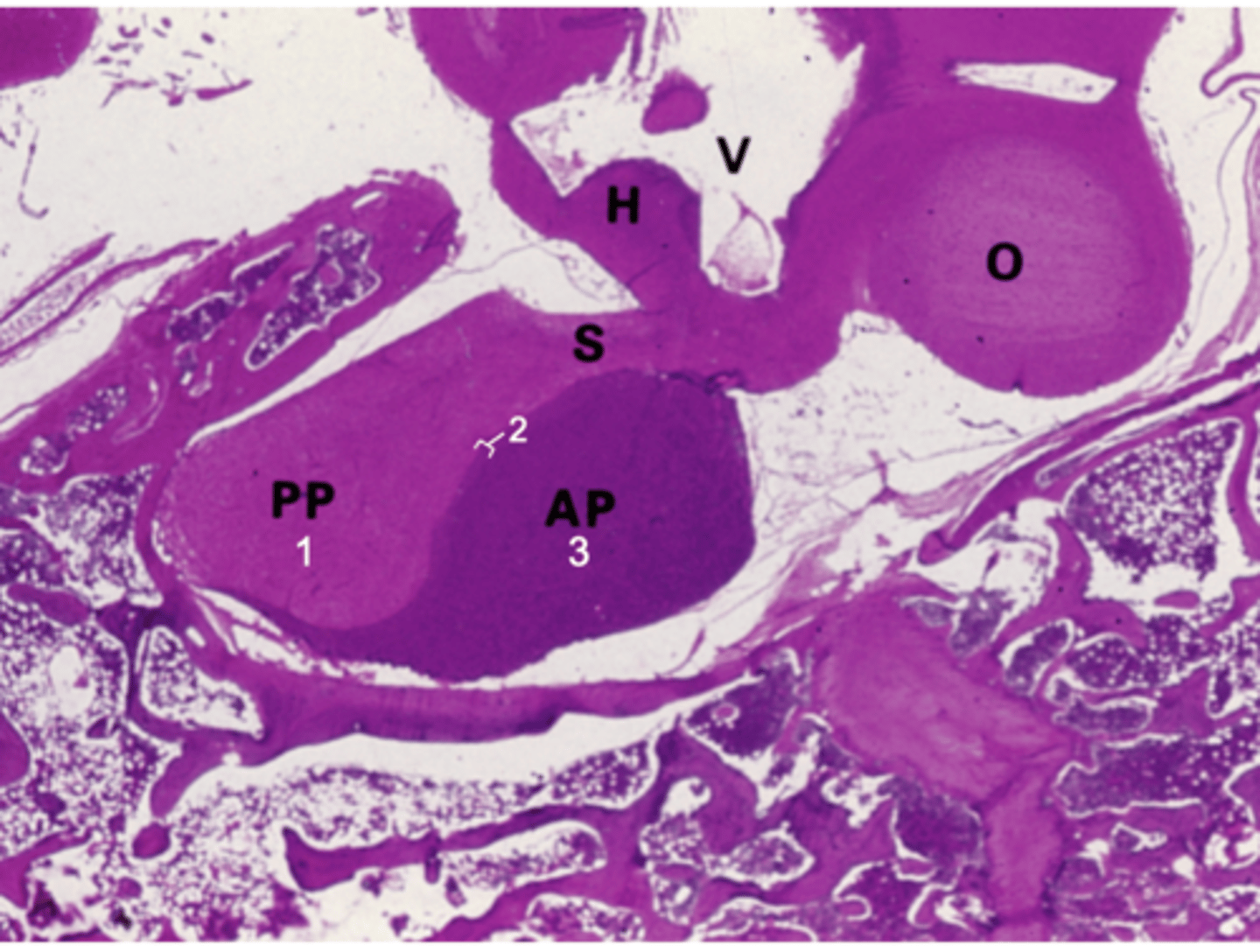
What does O stand for?
Optic chiasm
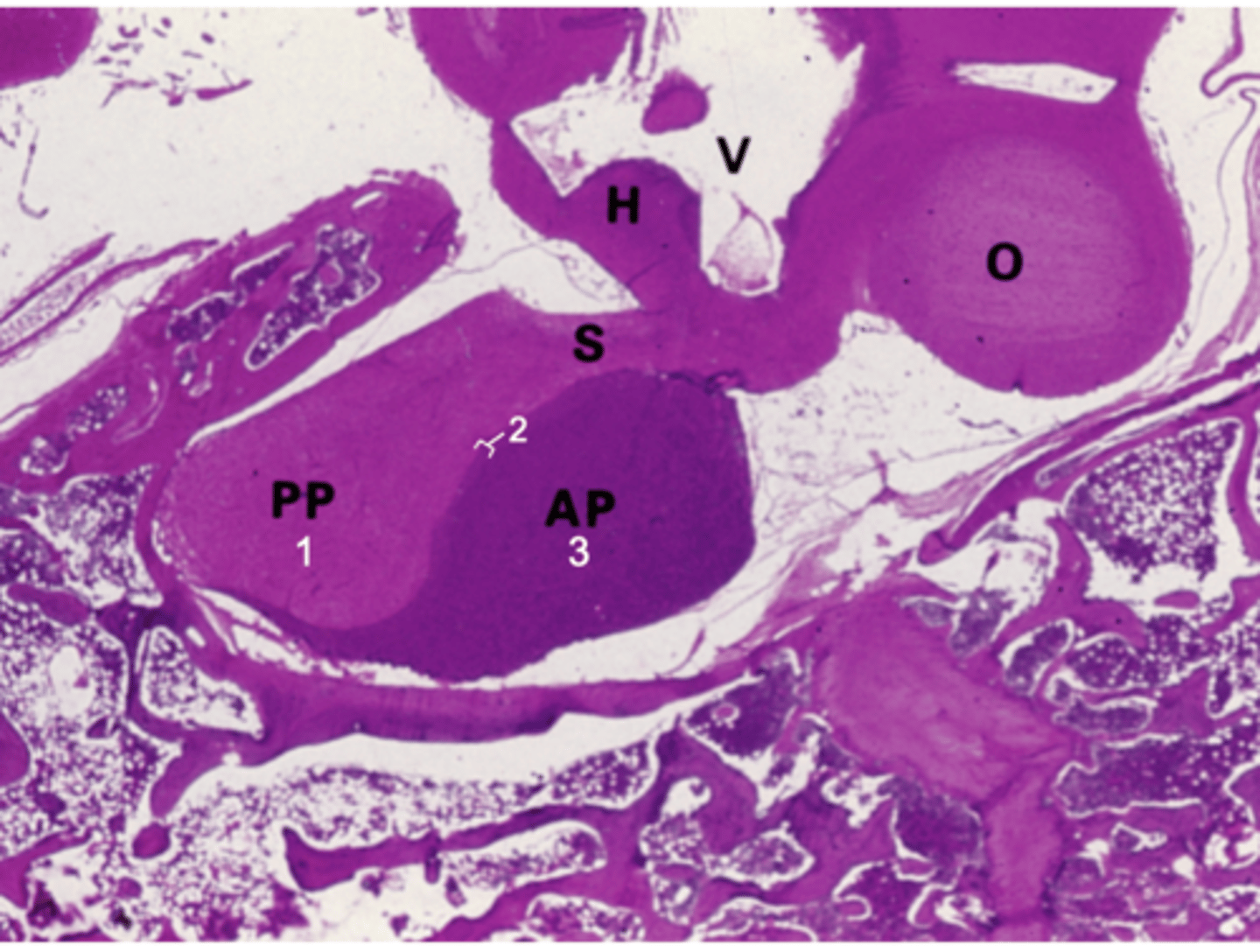
What does V stand for?
3rd ventricle
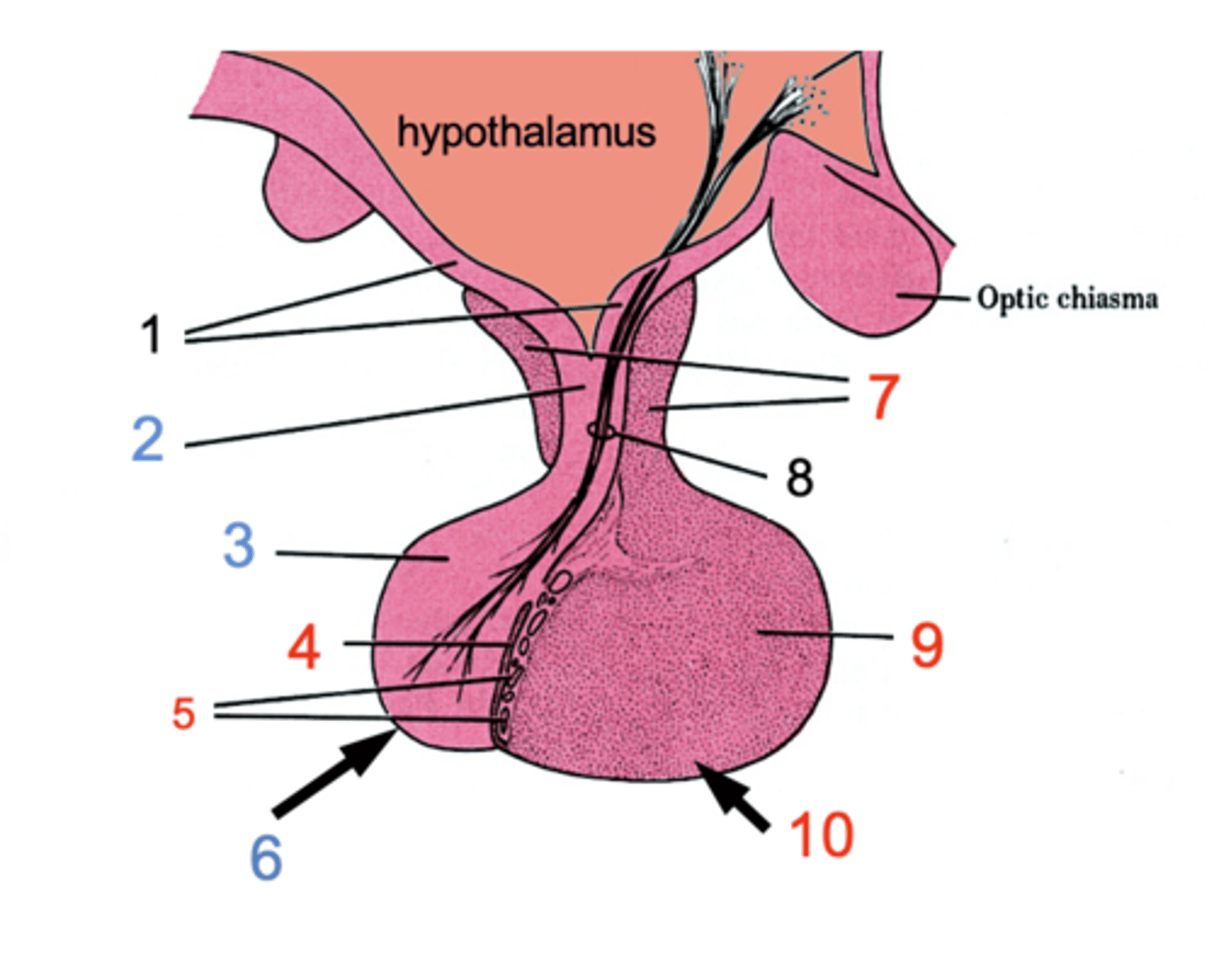
ID #1
Median eminence
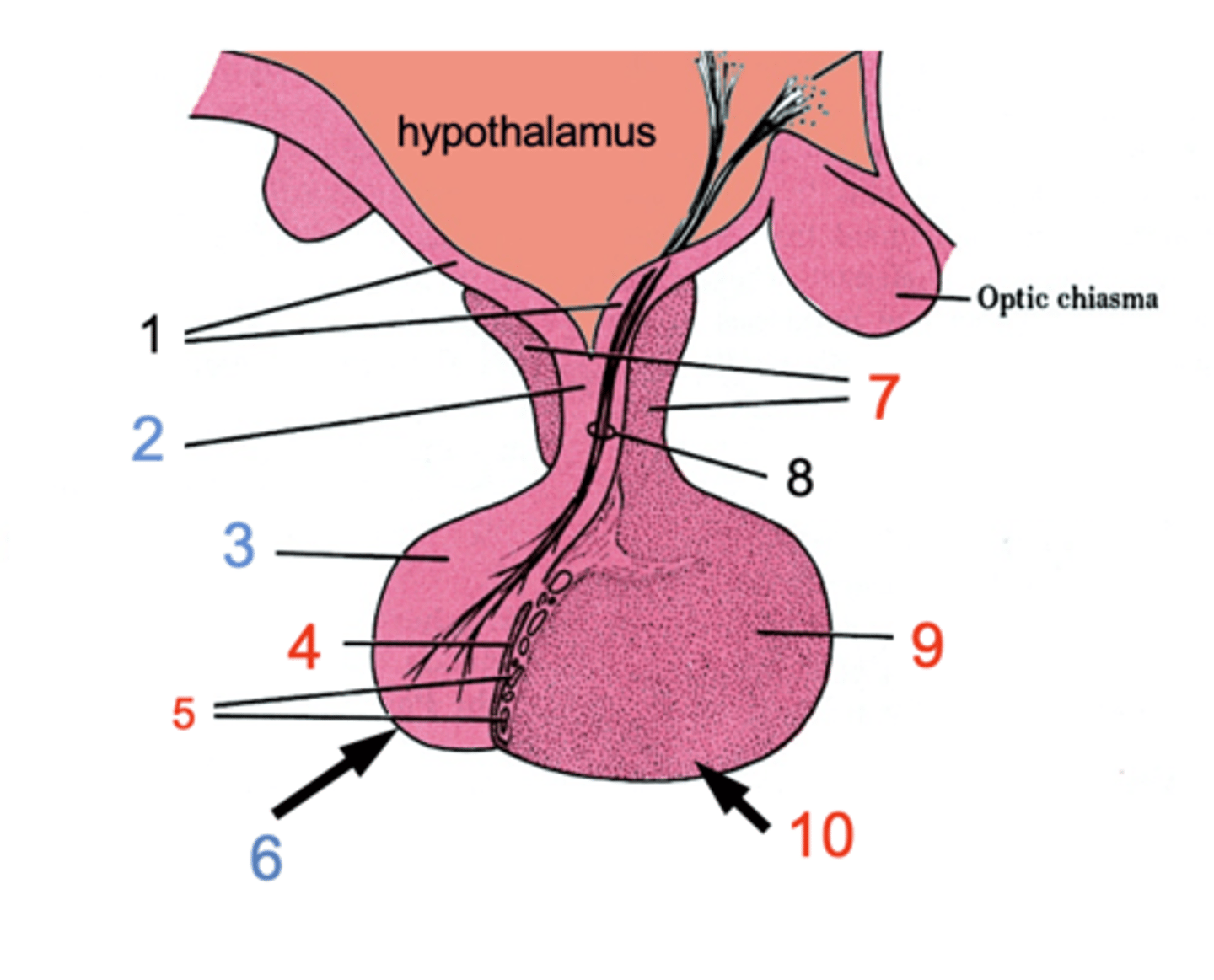
ID #2:
Infundibulum
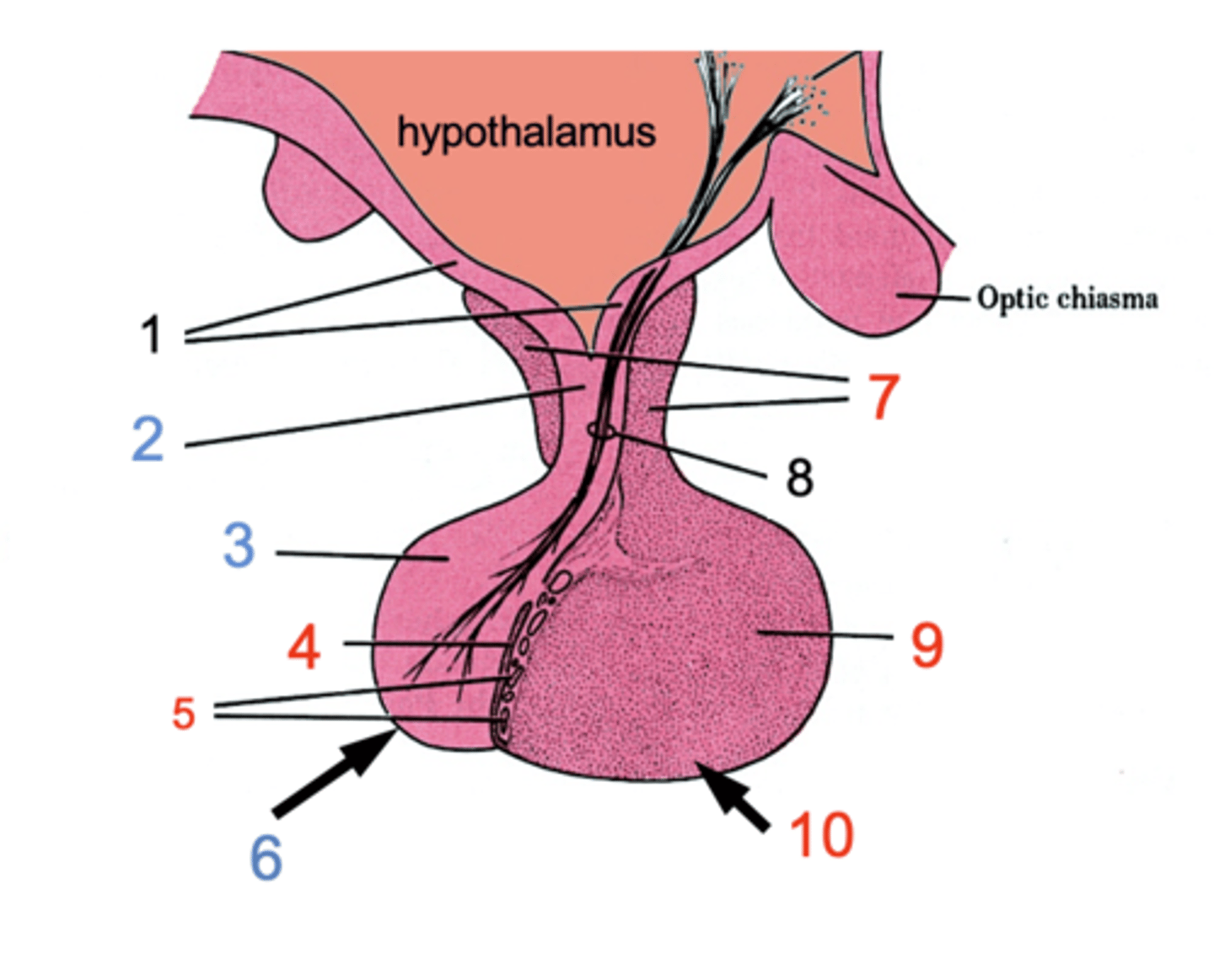
ID #3:
Pars nervosa
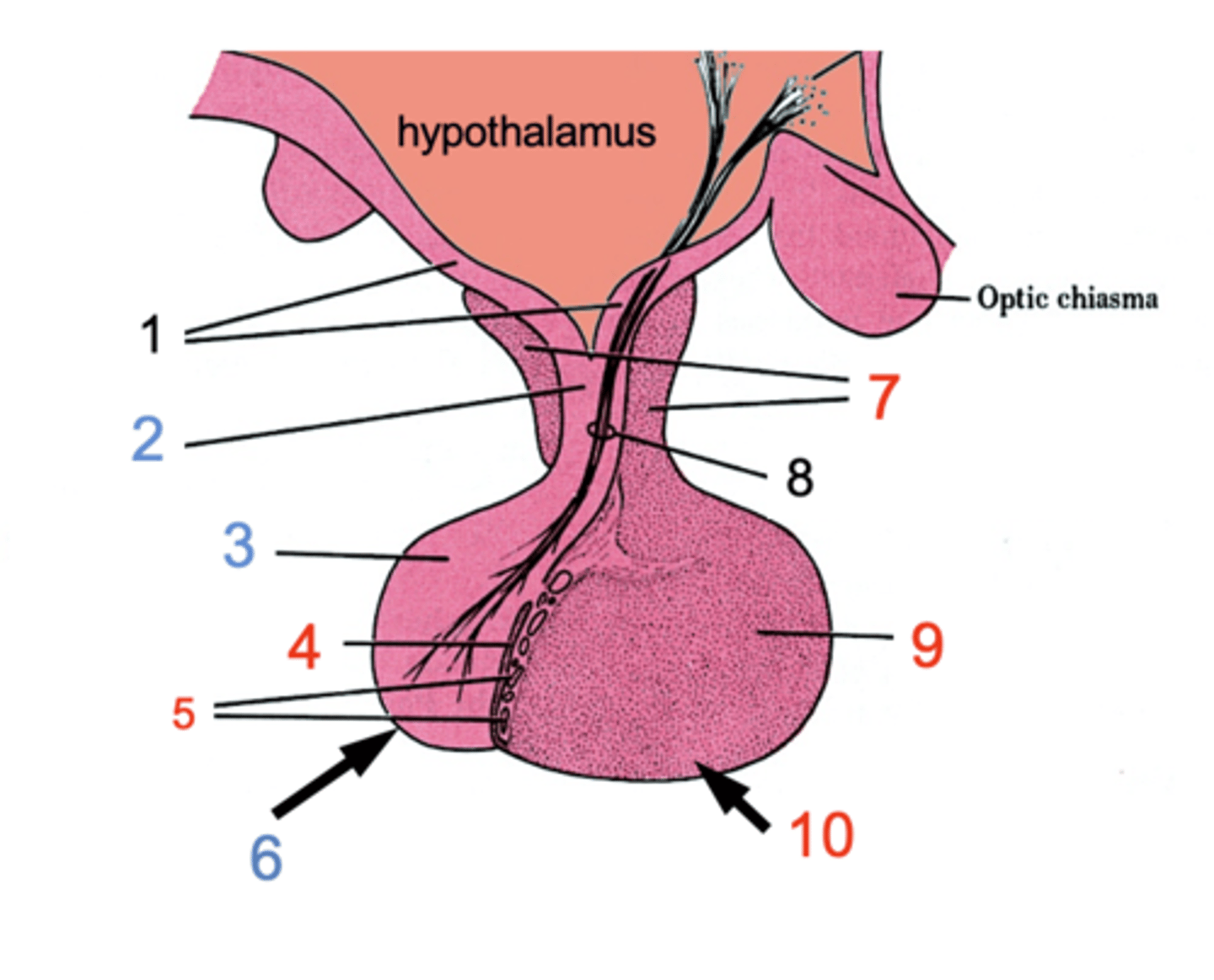
ID #4:
Pars intermedia
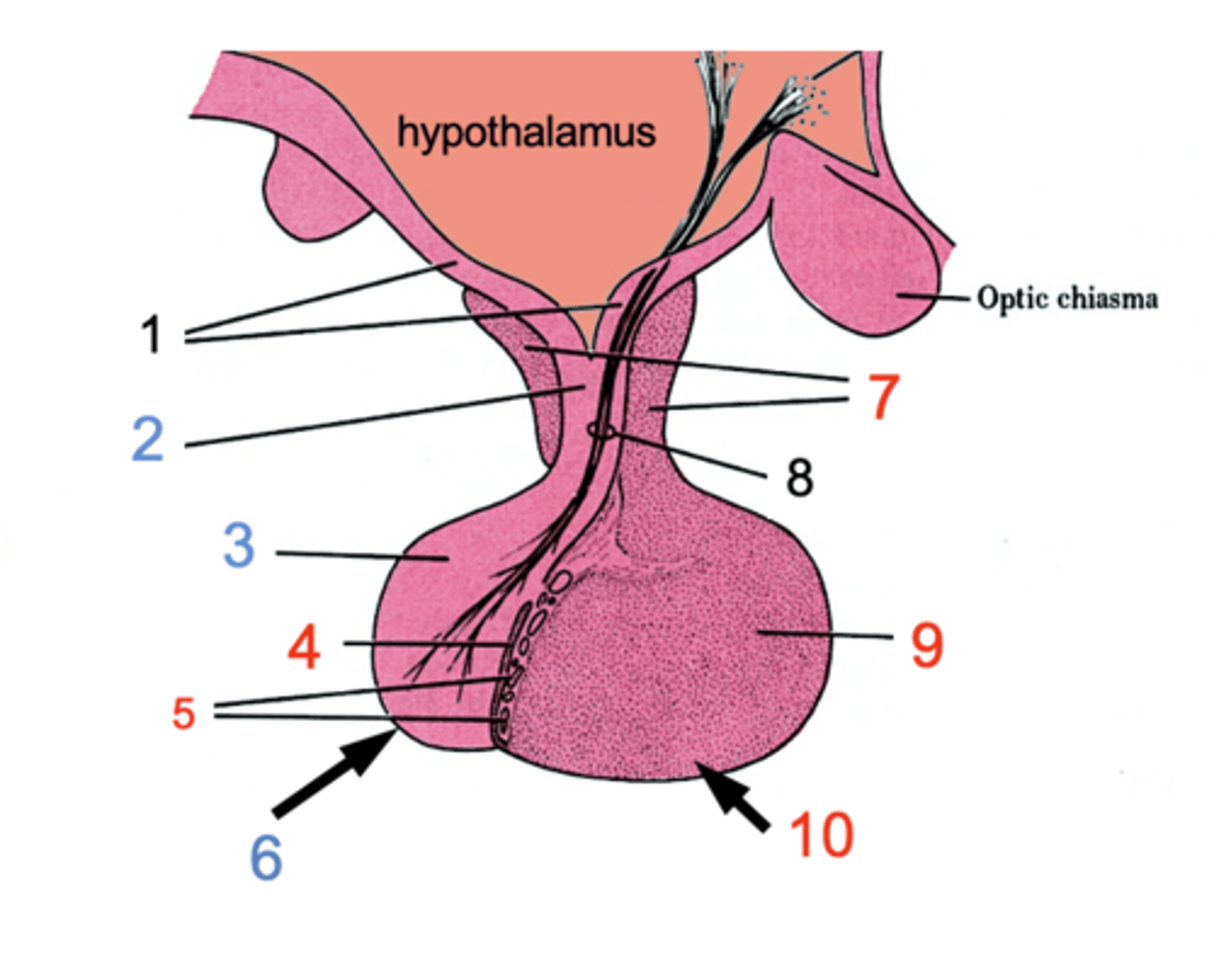
ID #5:
Cystic cavities
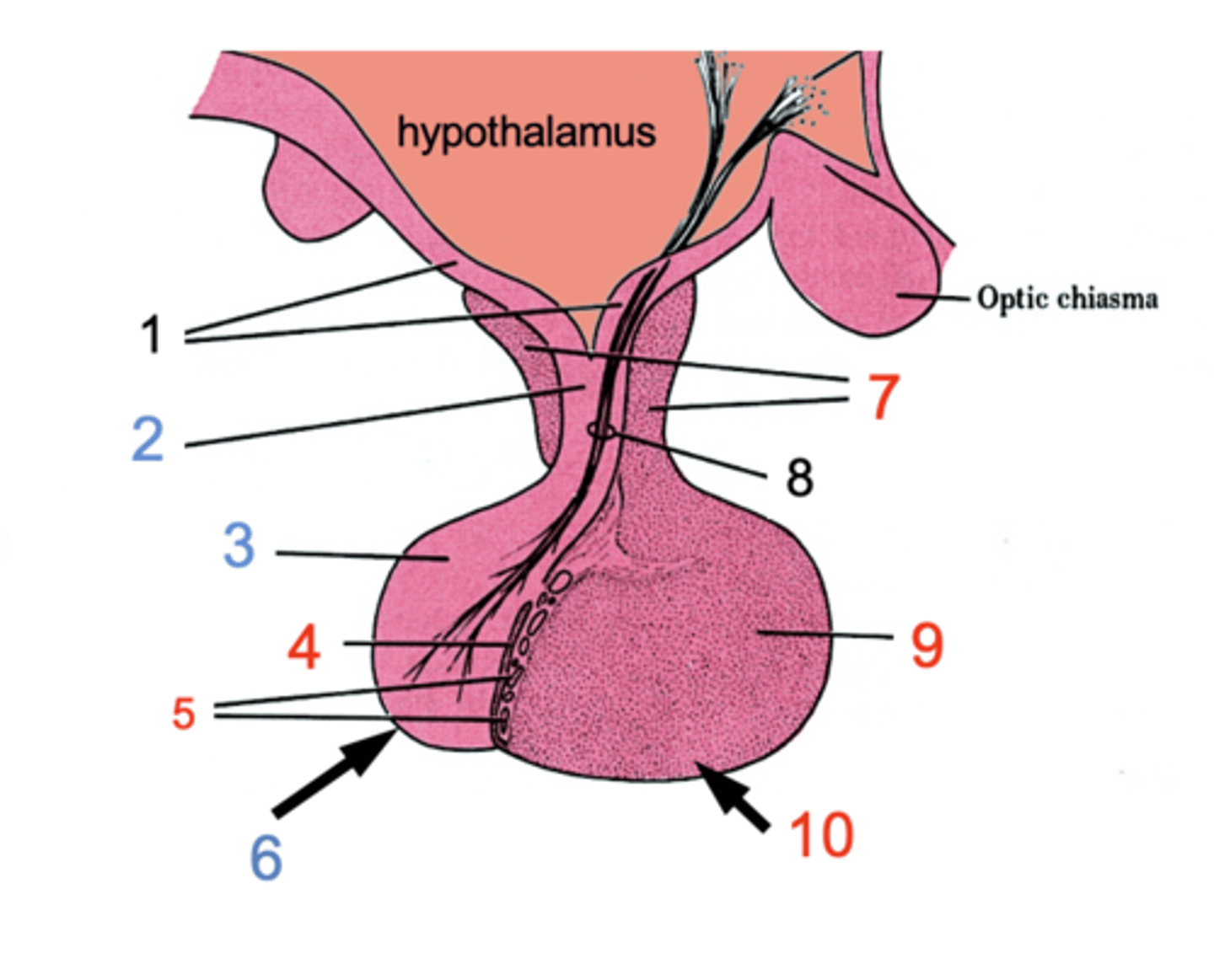
ID #6:
Posterior pituitary
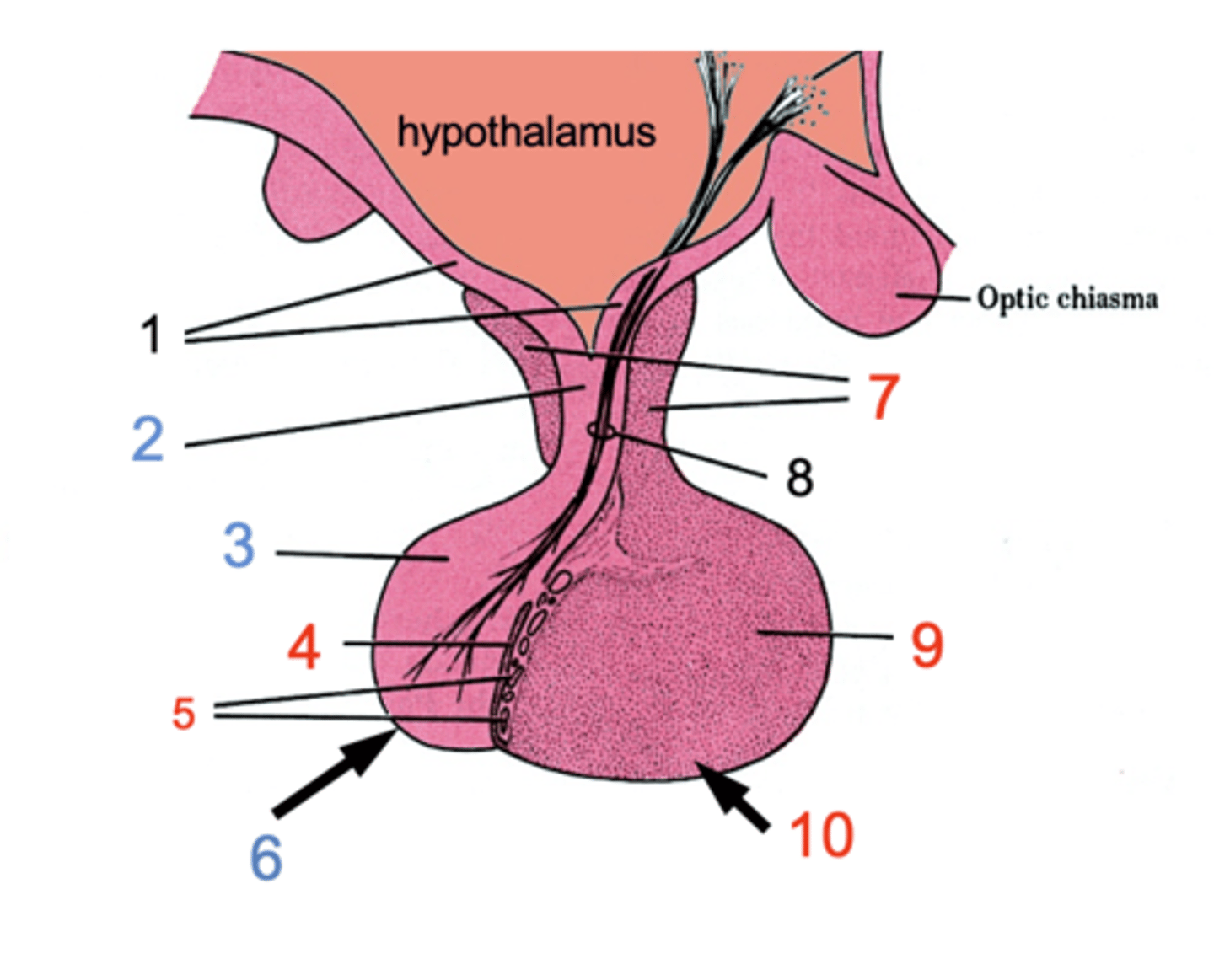
ID #7:
Pars tuberalis
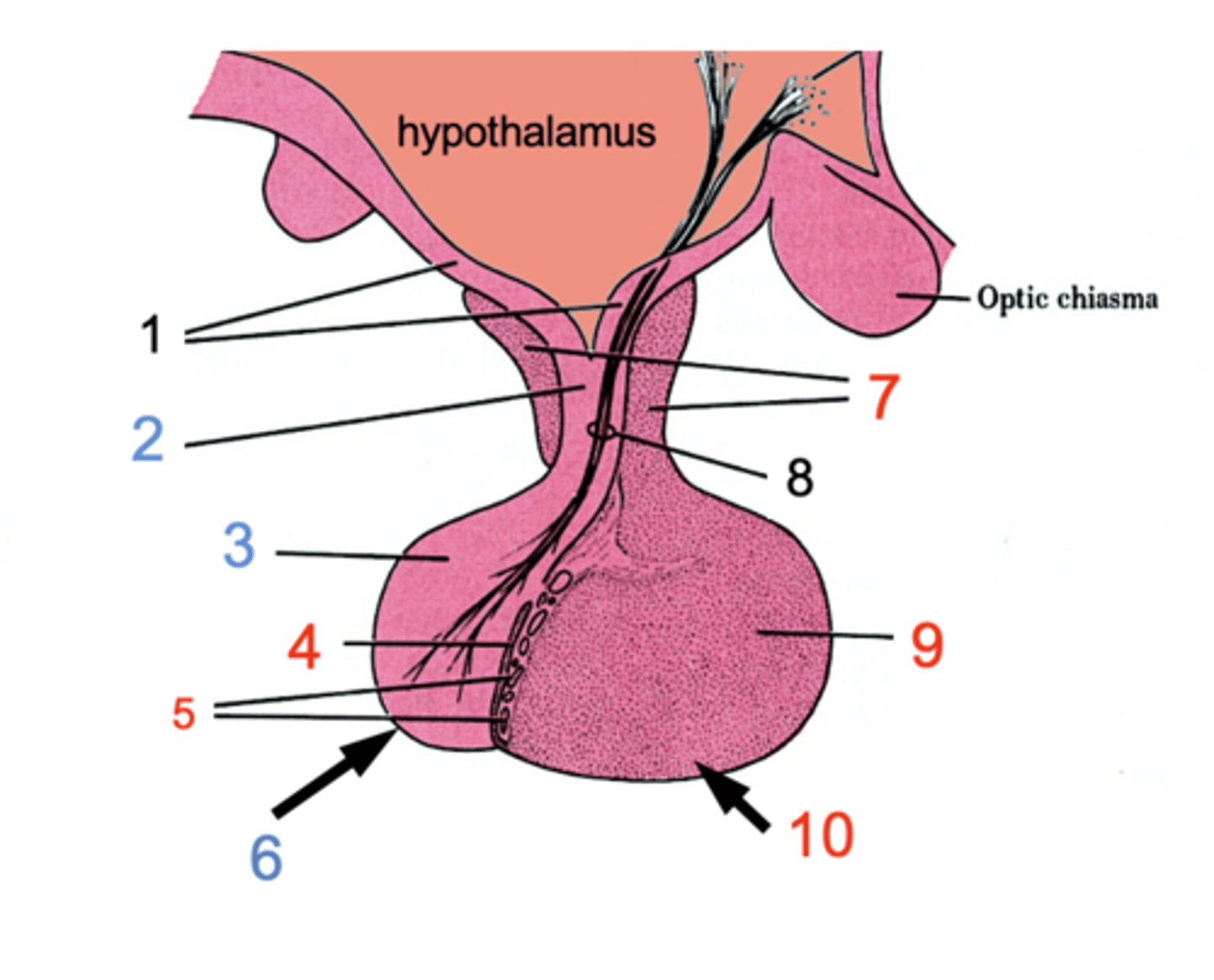
ID #8:
Hypothalamohpophyseal tract
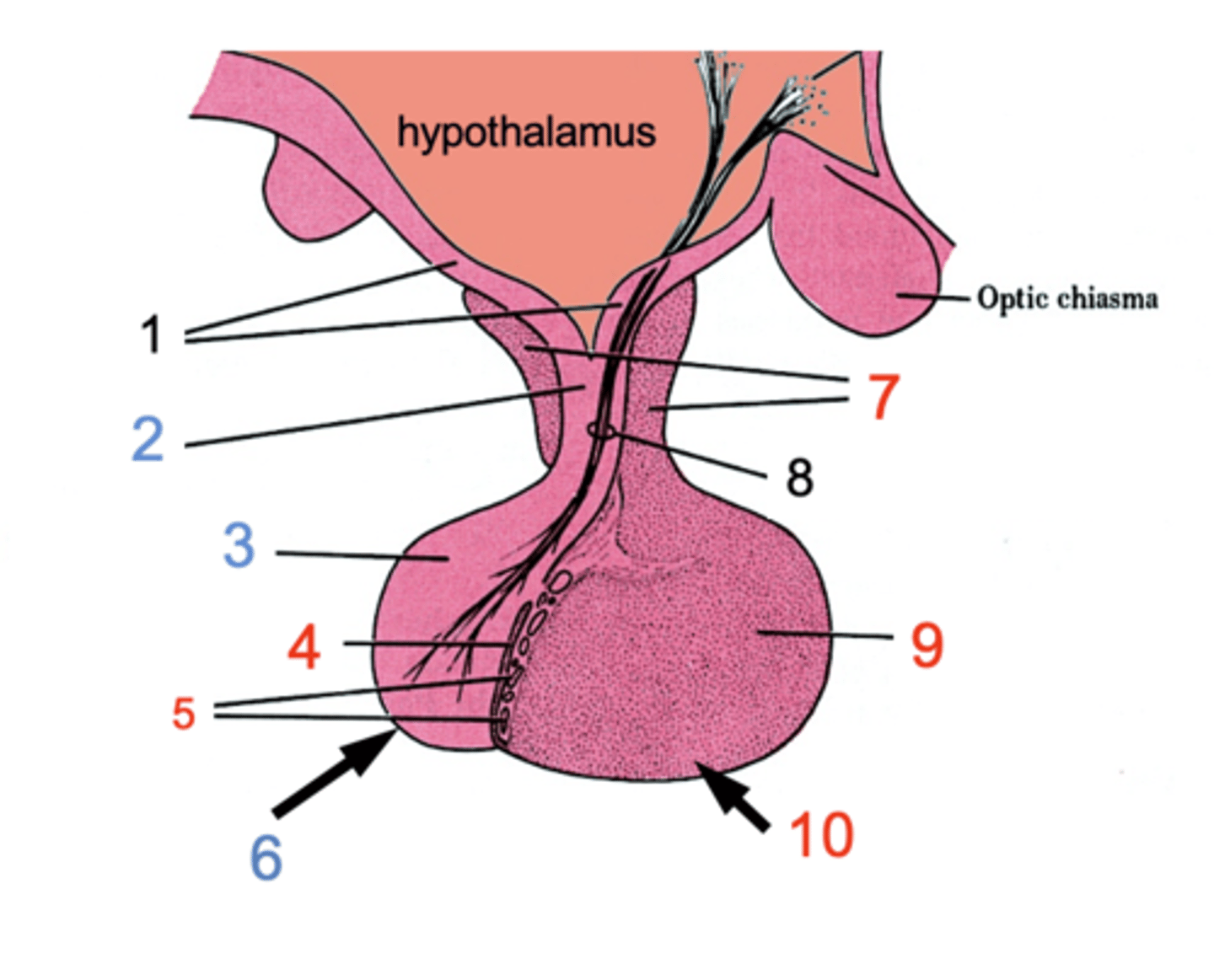
ID #9:
Pars distalis
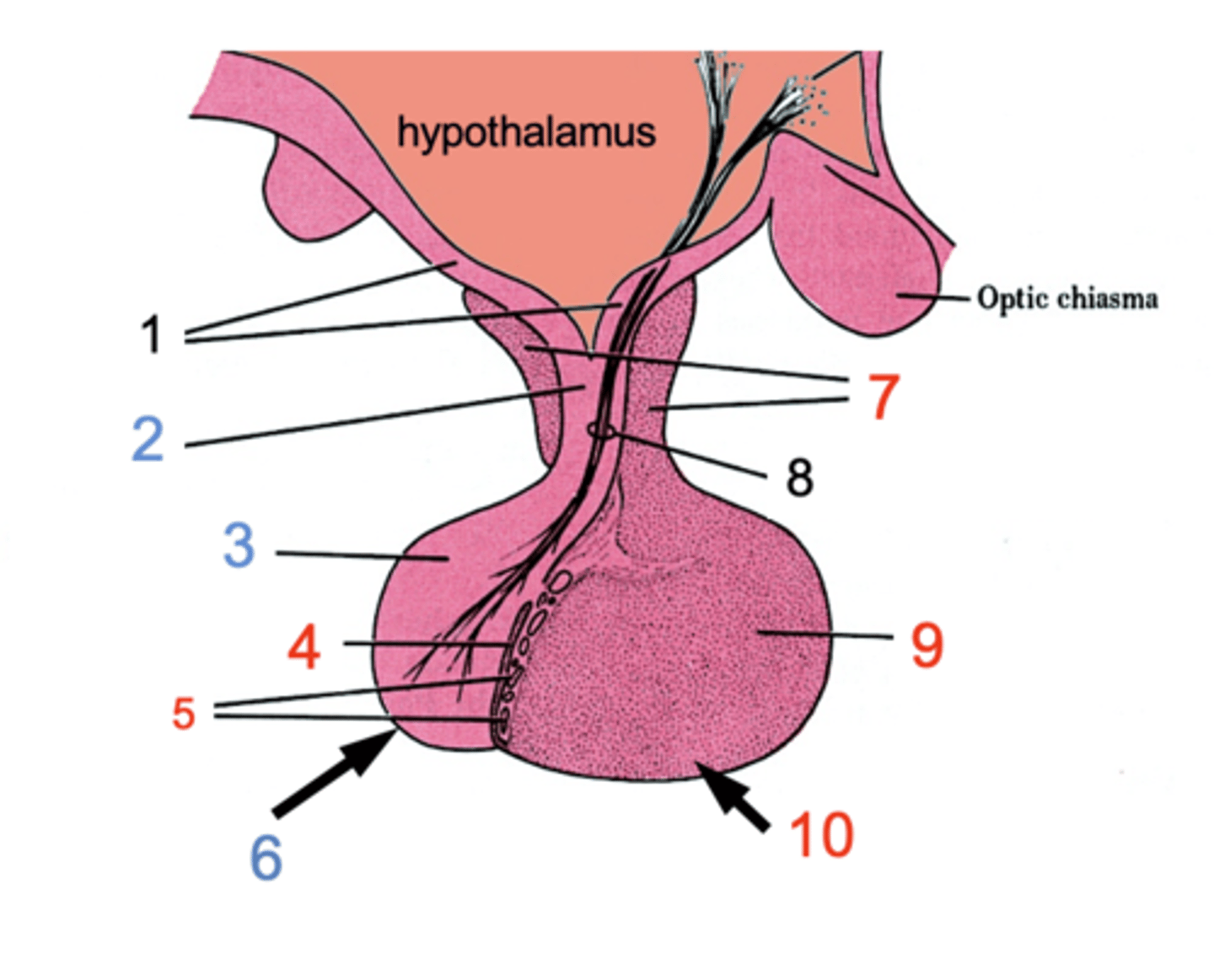
ID #10:
Anterior pituitary
What is the glandular portion of the anterior pituitary called?
adenohypophysis
What is the intermediate part between the anterior and posterior pituitary?
Remnants of Rathke's pouch
What lobe does the oropharynx ectoderm form into in the pituitary?
Anterior lobe
What lobe does the neuroectoderm form into in the pituitary?
Posterior lobe
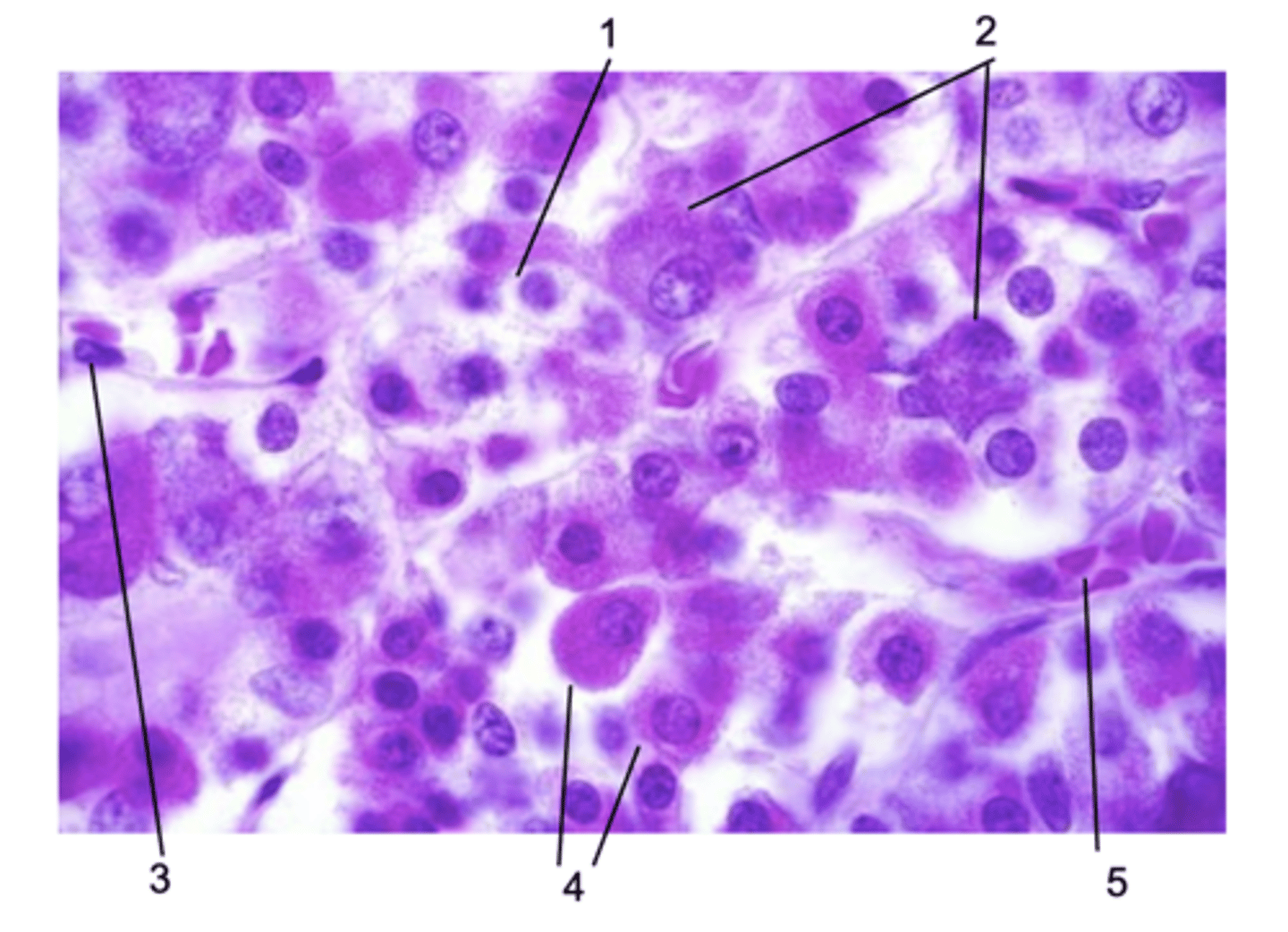
Where does this histological section come from in the pituitary gland?
Pars distalis

ID #1:
Chromophobe
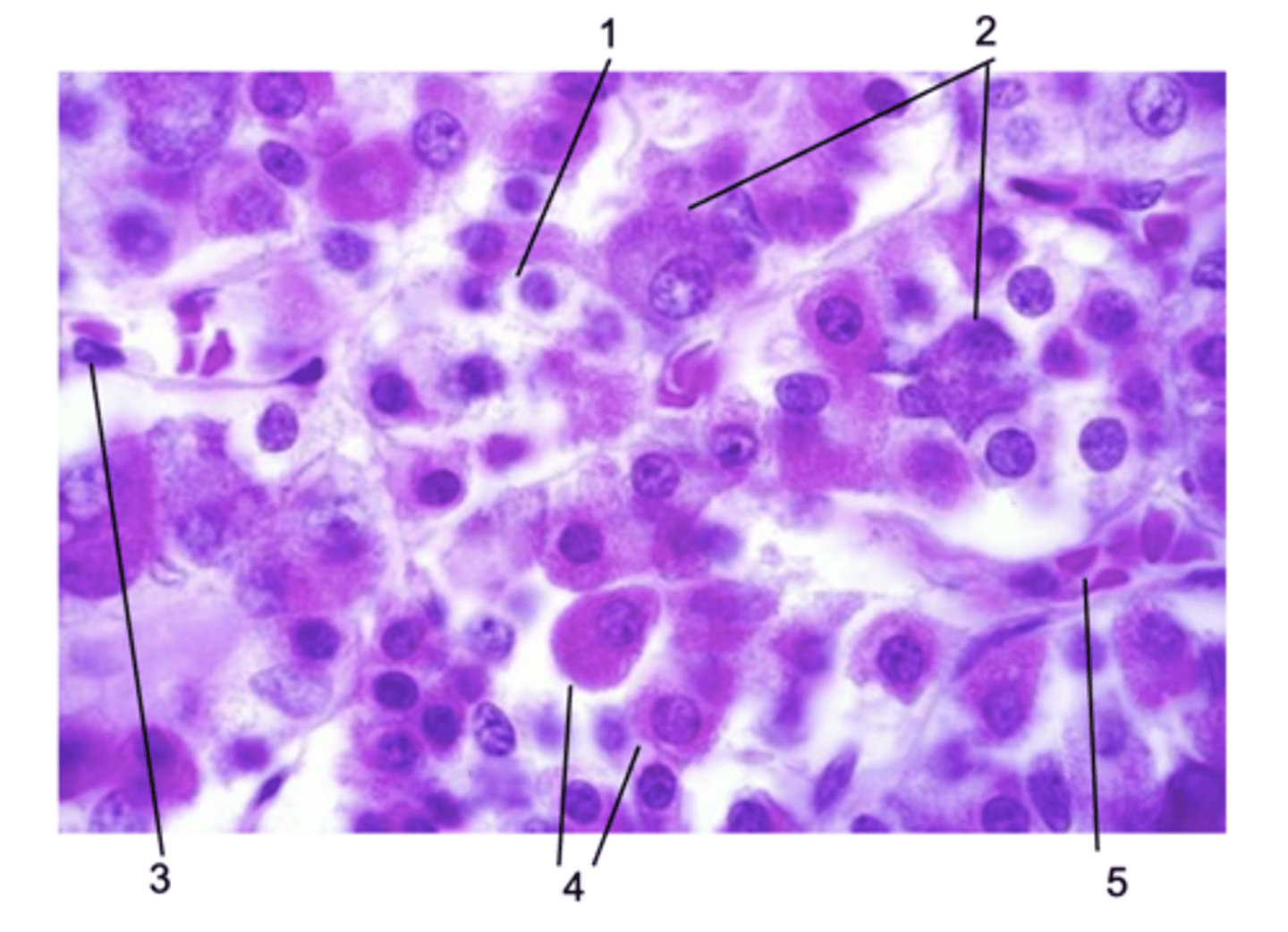
ID #2:
Basophils
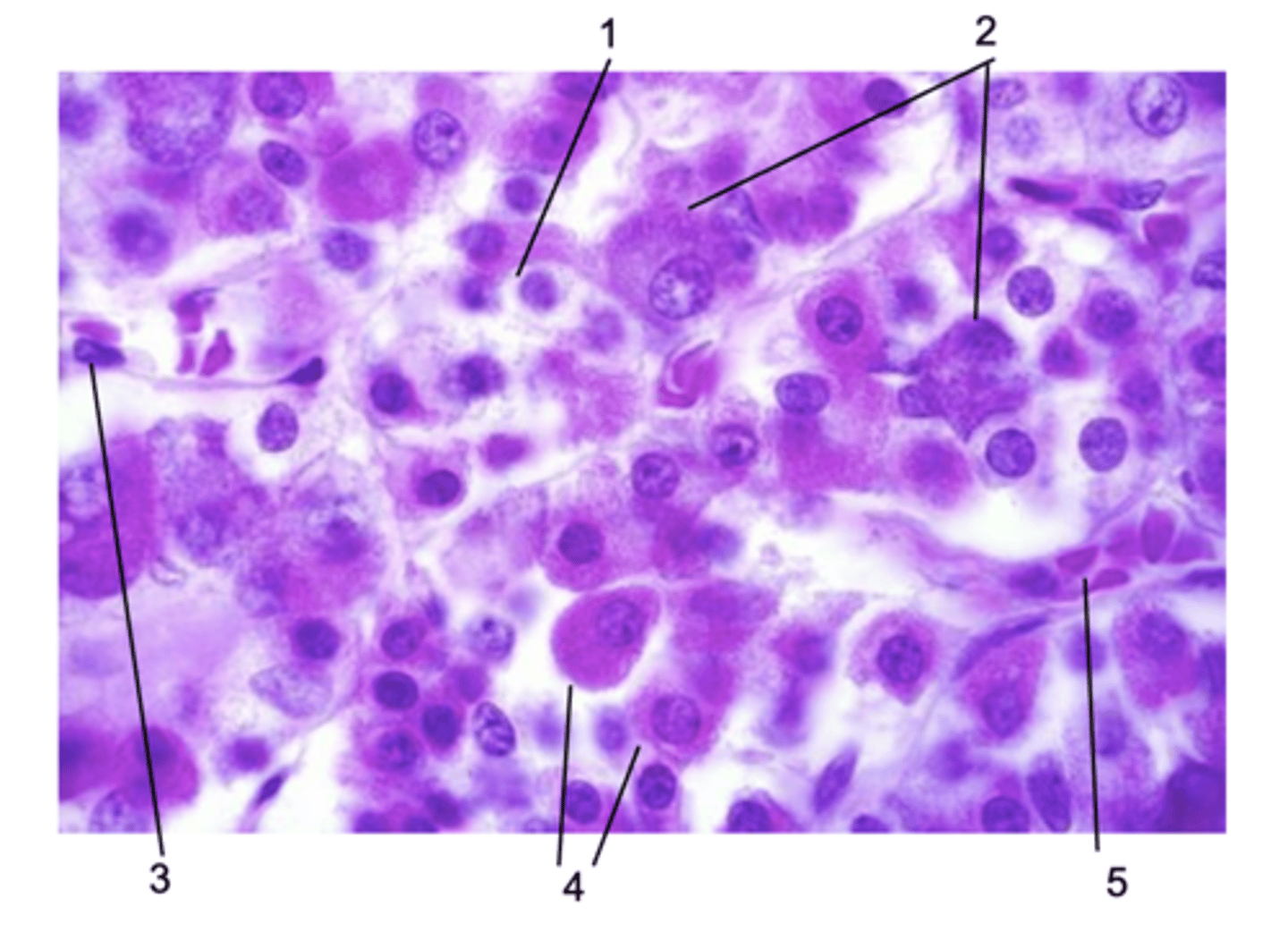
ID #3:
Endothelial cell
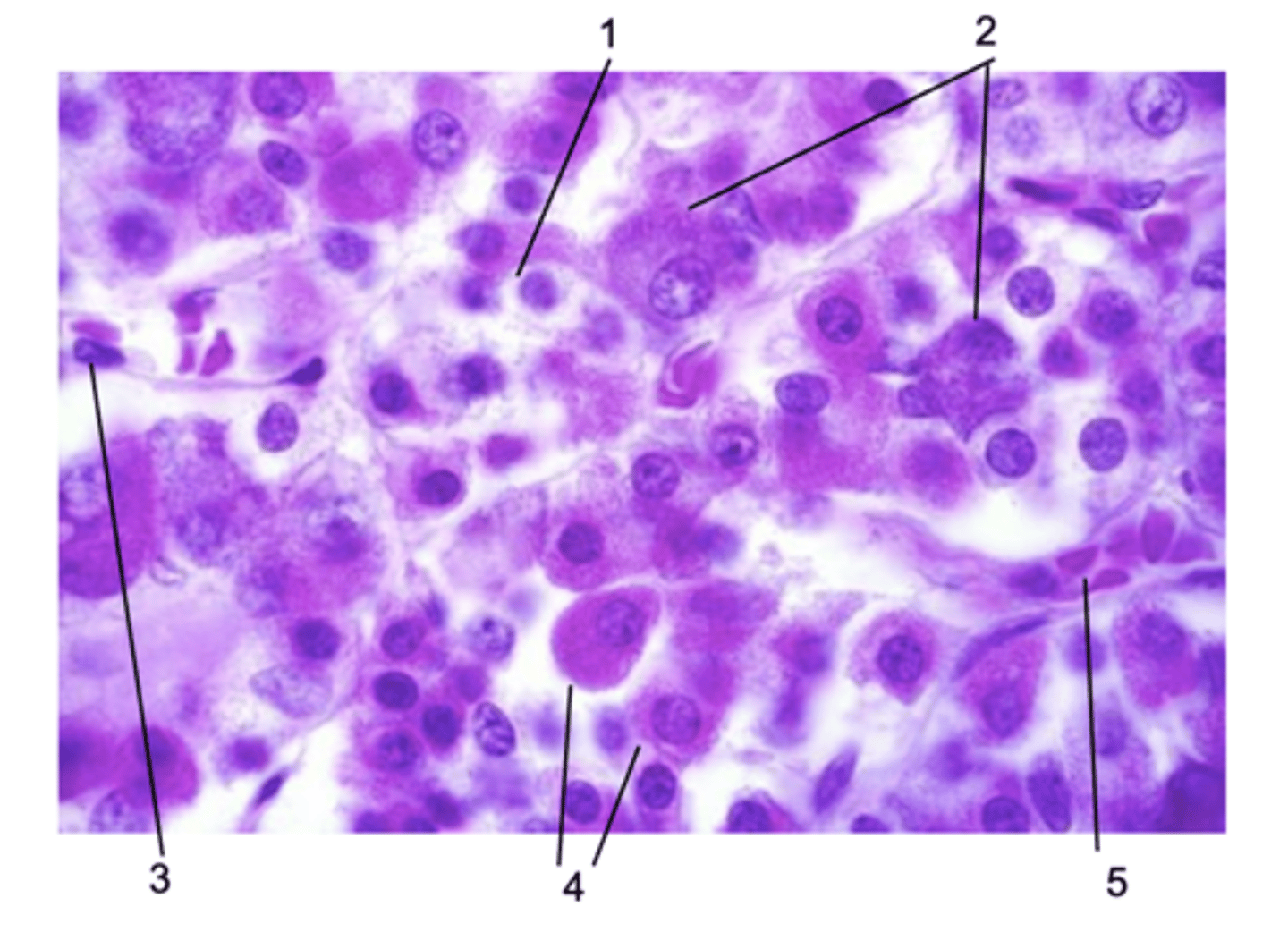
ID #4:
Acidophils
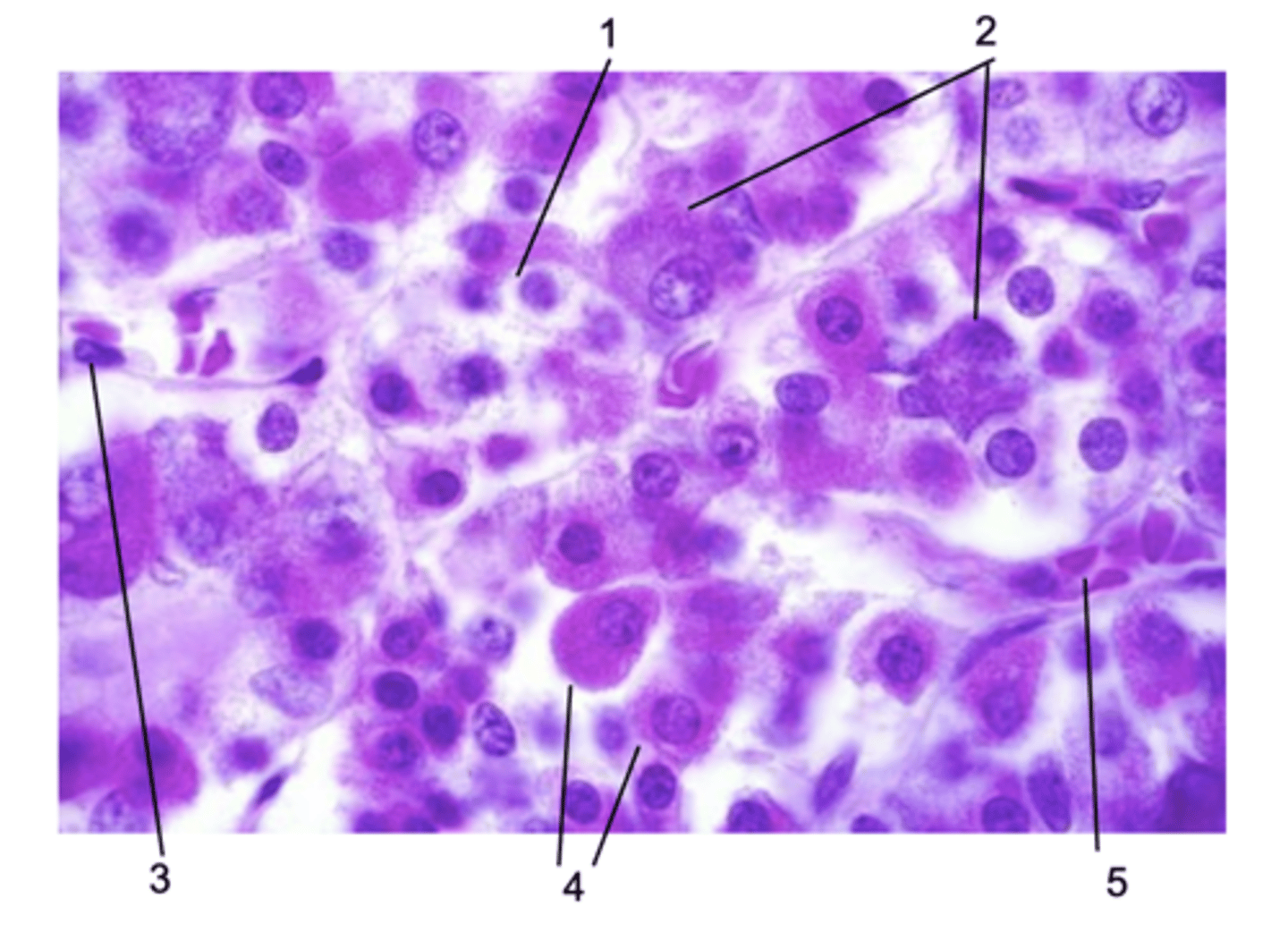
ID #5:
Fenestrated capillary
What is indicated at the red * ?
Fenestrated capillary
What are roughly 50% of acidophiles?
Somatotropes (growth hormone)
What are roughly 15% of acidophiles?
Lactotropes/mammotropes (prolactin)
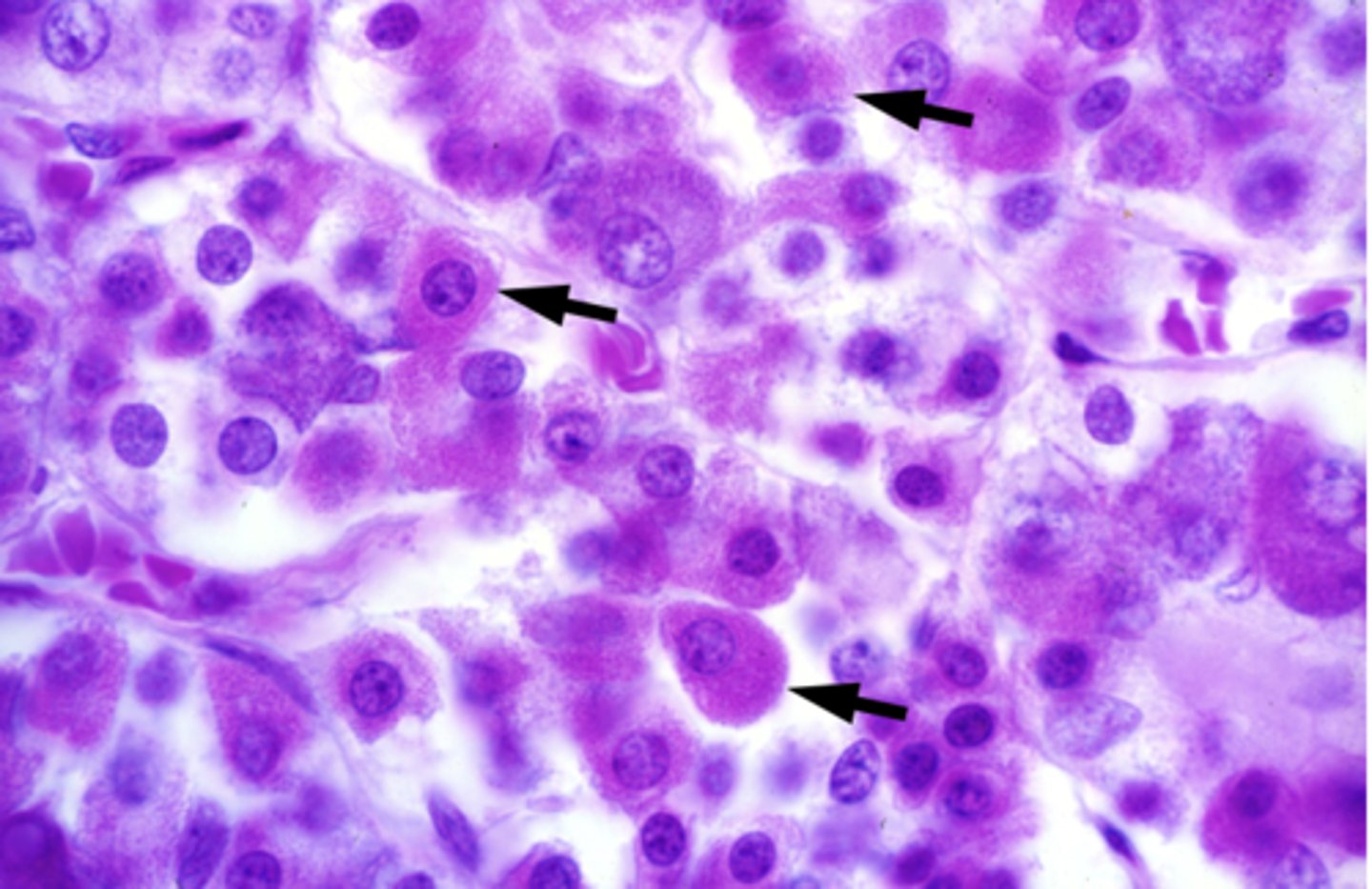
What are the arrows pointing at?
Acidophiles
What are roughly 15% of basophils?
Corticotropes
What are roughly 5% of basophils?
Thyrotropes
What are roughly 10% of basophils?
Gonadotropes
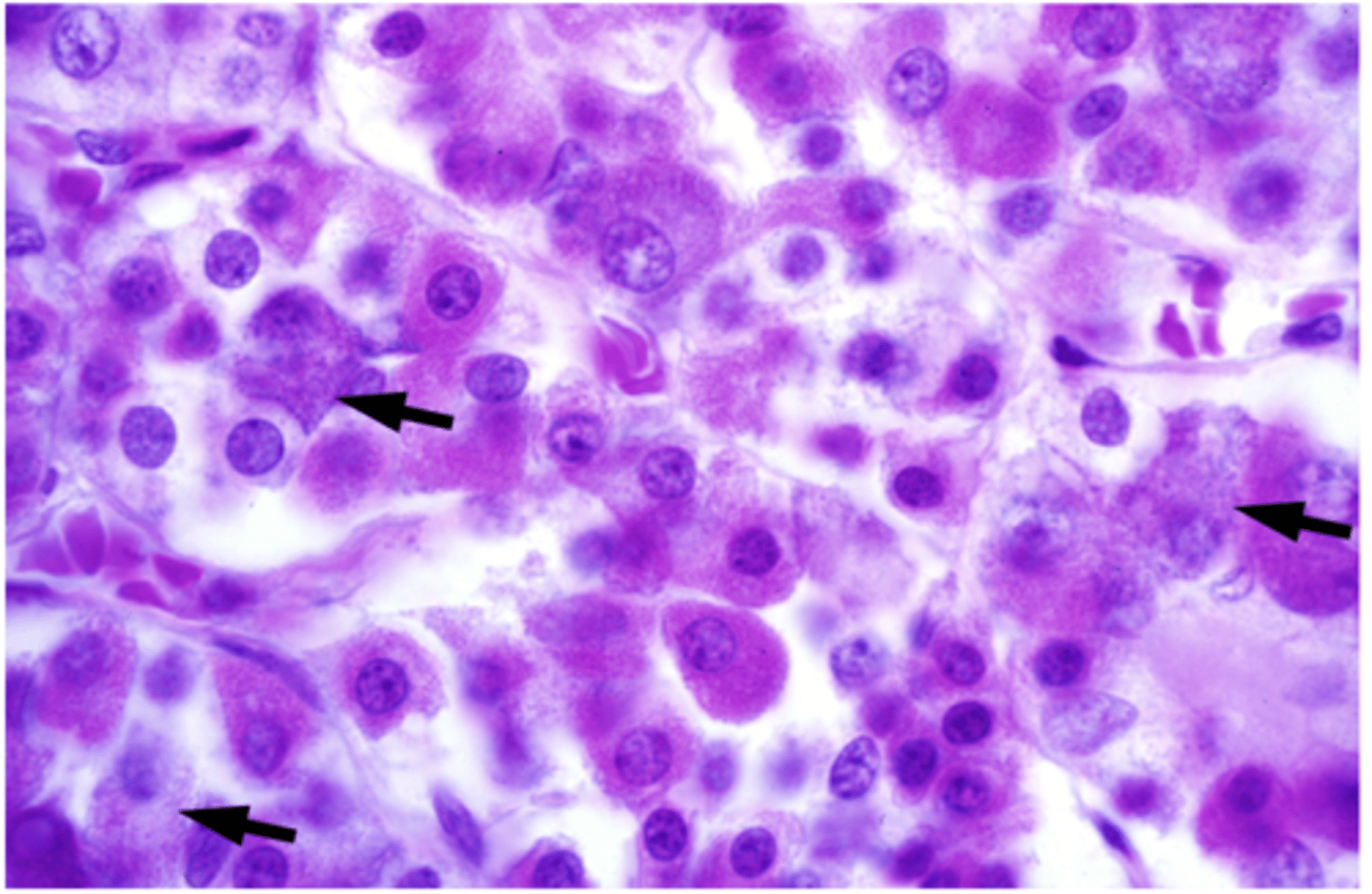
What are the arrows pointing at?
Basophils
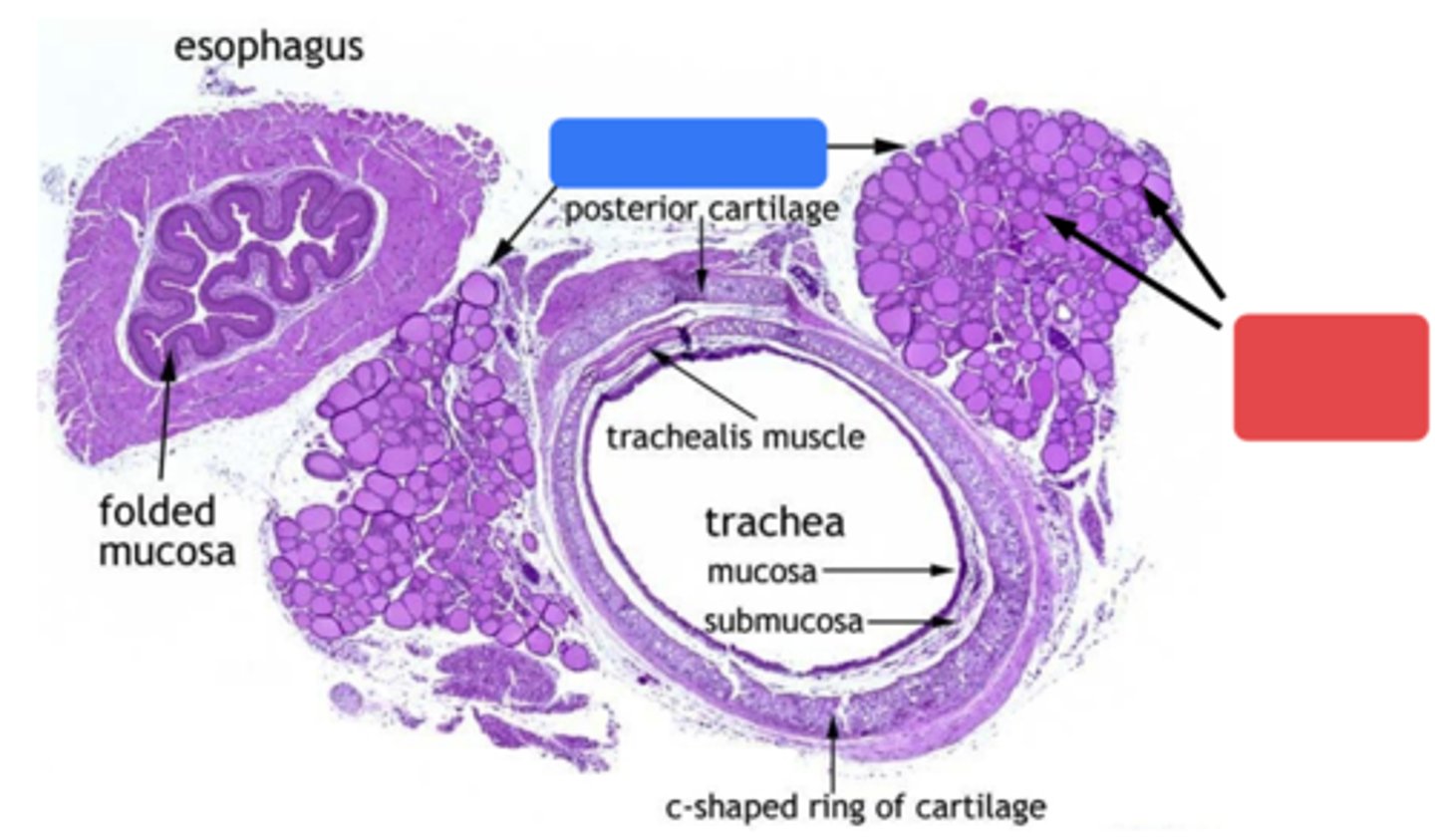
ID the region in blue:
Thyroid gland
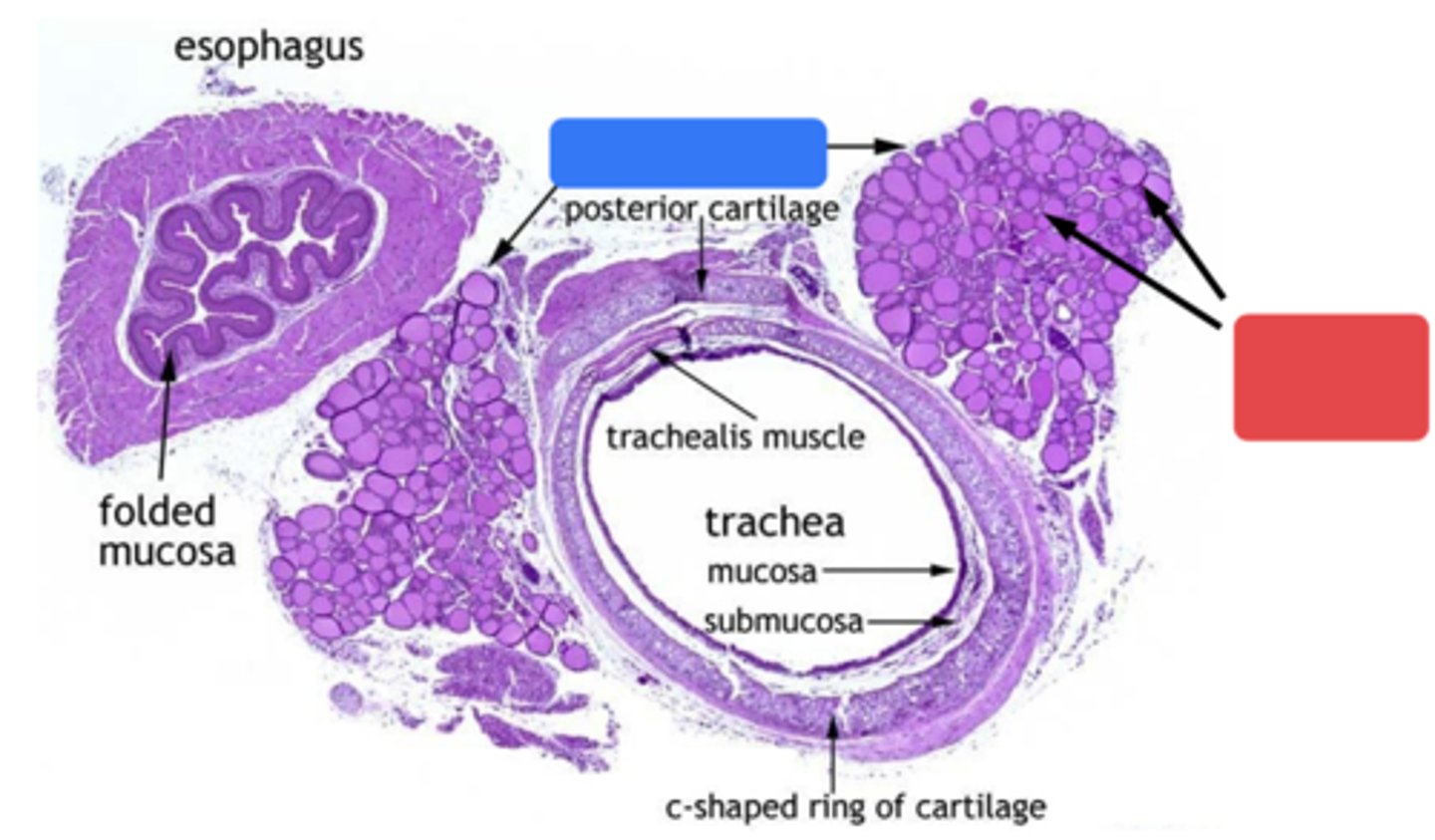
ID the region in red:
Thyroid follicles
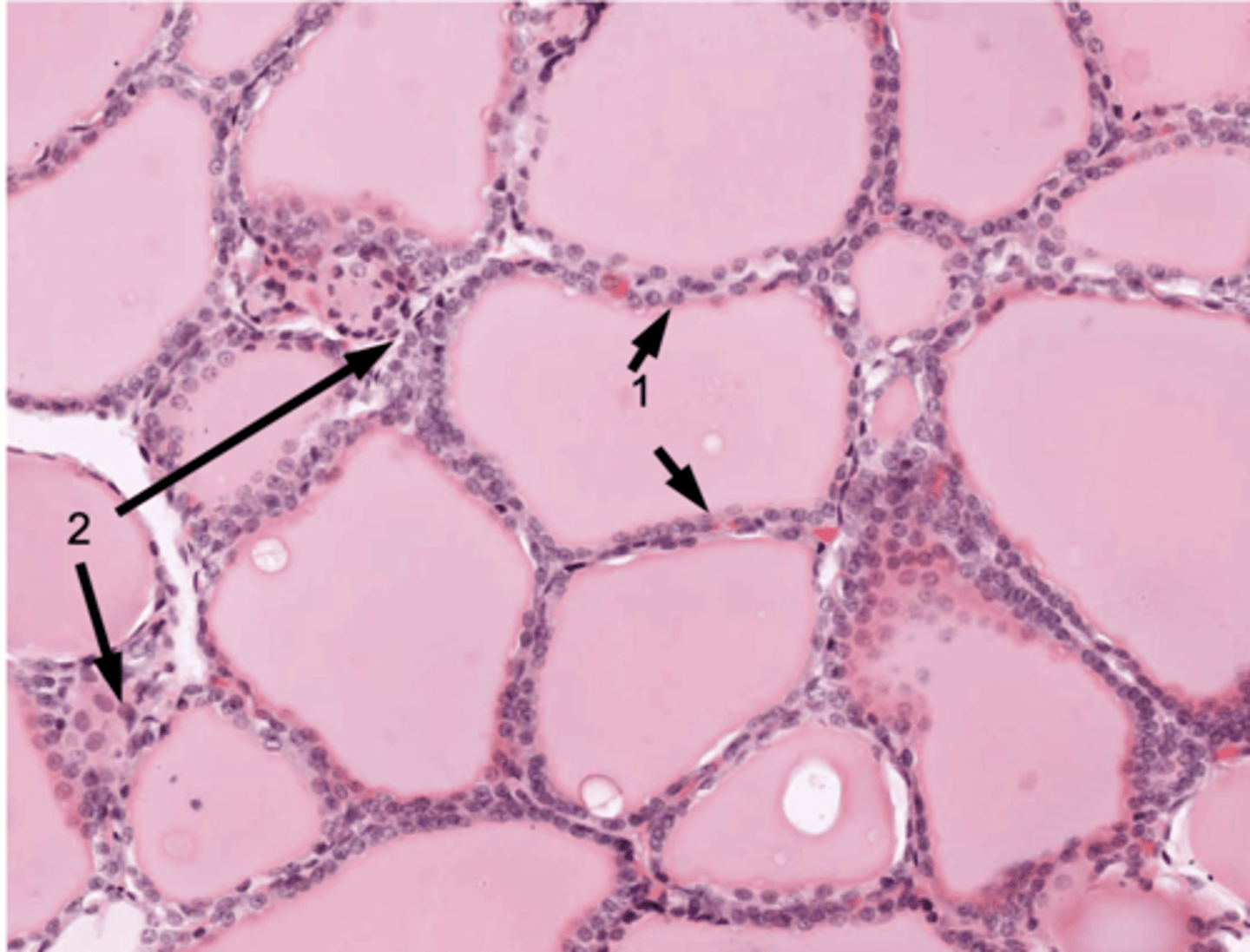
ID #1:
Follicular cells
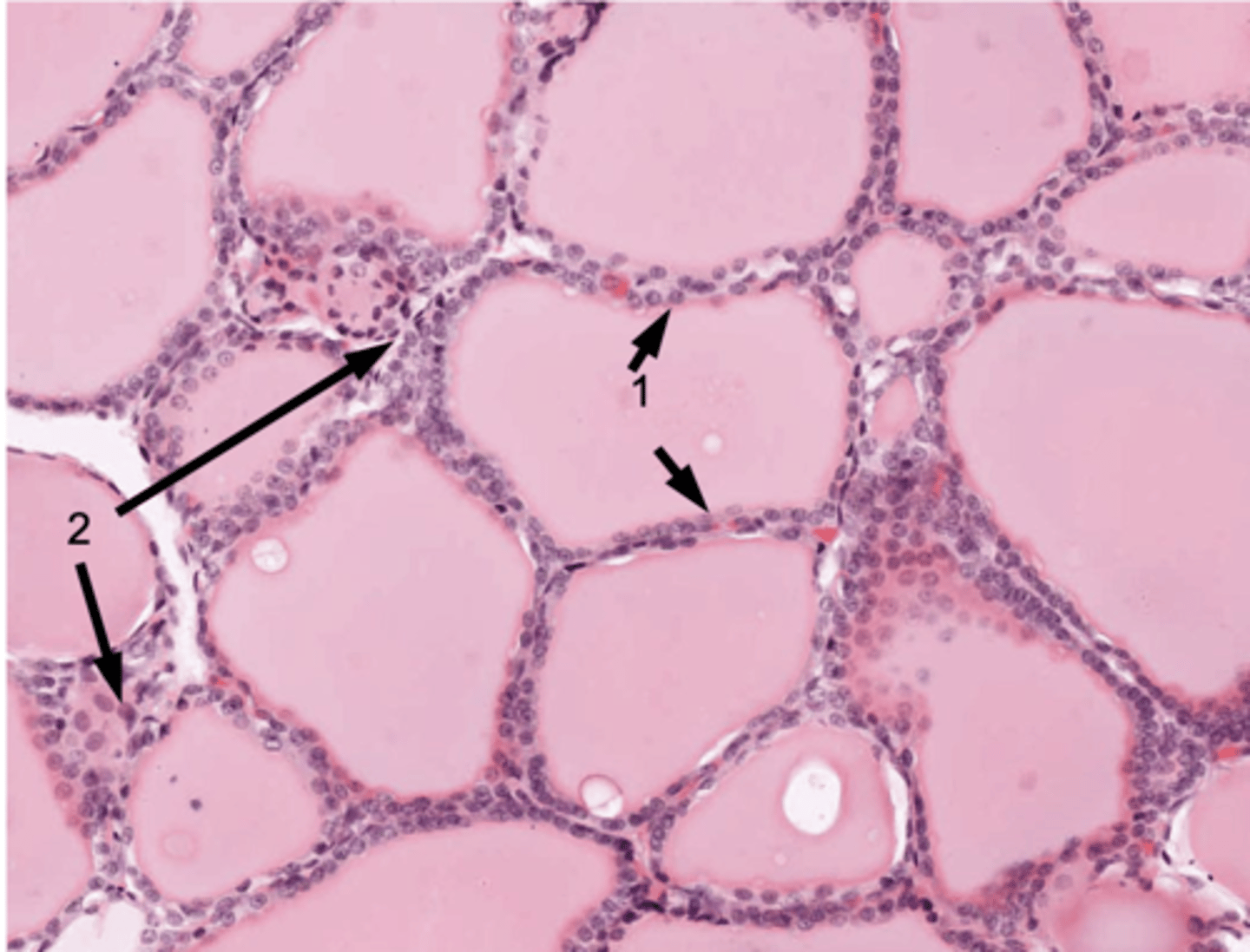
ID #2:
Parafollicular cells
What has the following characteristics?
- Iodinated glycoprotein (660kDa with ~120 tyrosine residues)
- Comprises the major colloid component
- Extracellular storage form of thyroid hormone precursor
- Also present:
- - Thyroid peroxidase
- - Iodide (I-) and iodine (I)
Thyroglobulin
What has the following characteristics?
- Contain minimal or no hormonal content
- May represent degranulated acidophils or basophils
- May also represent stem cells
Chromophobes
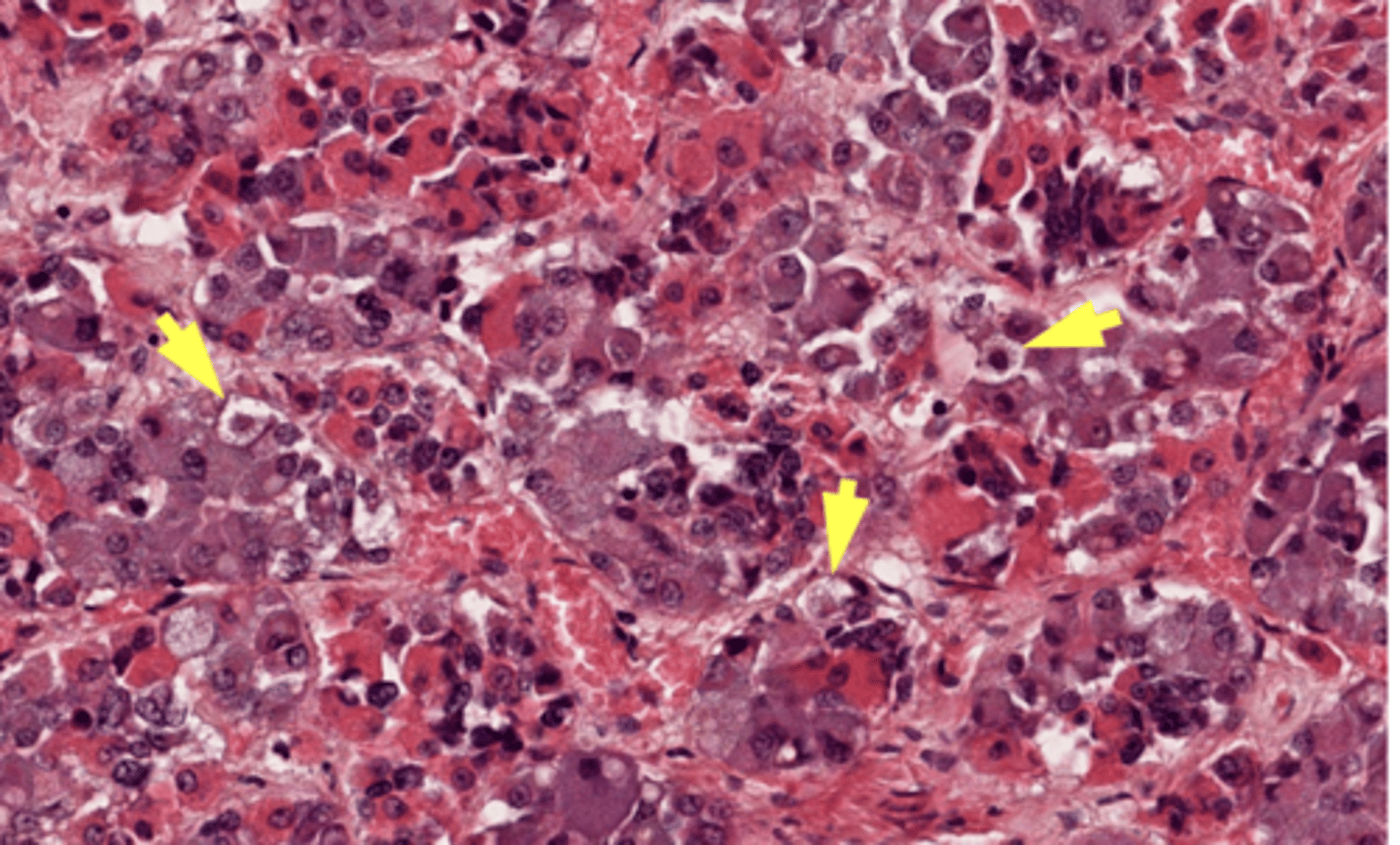
What are the arrows pointing at?
Chromophobes
What are the most common source of pituitary-related problems - they rarely secrete any hormones?
Pituitary chromophobe adenomas
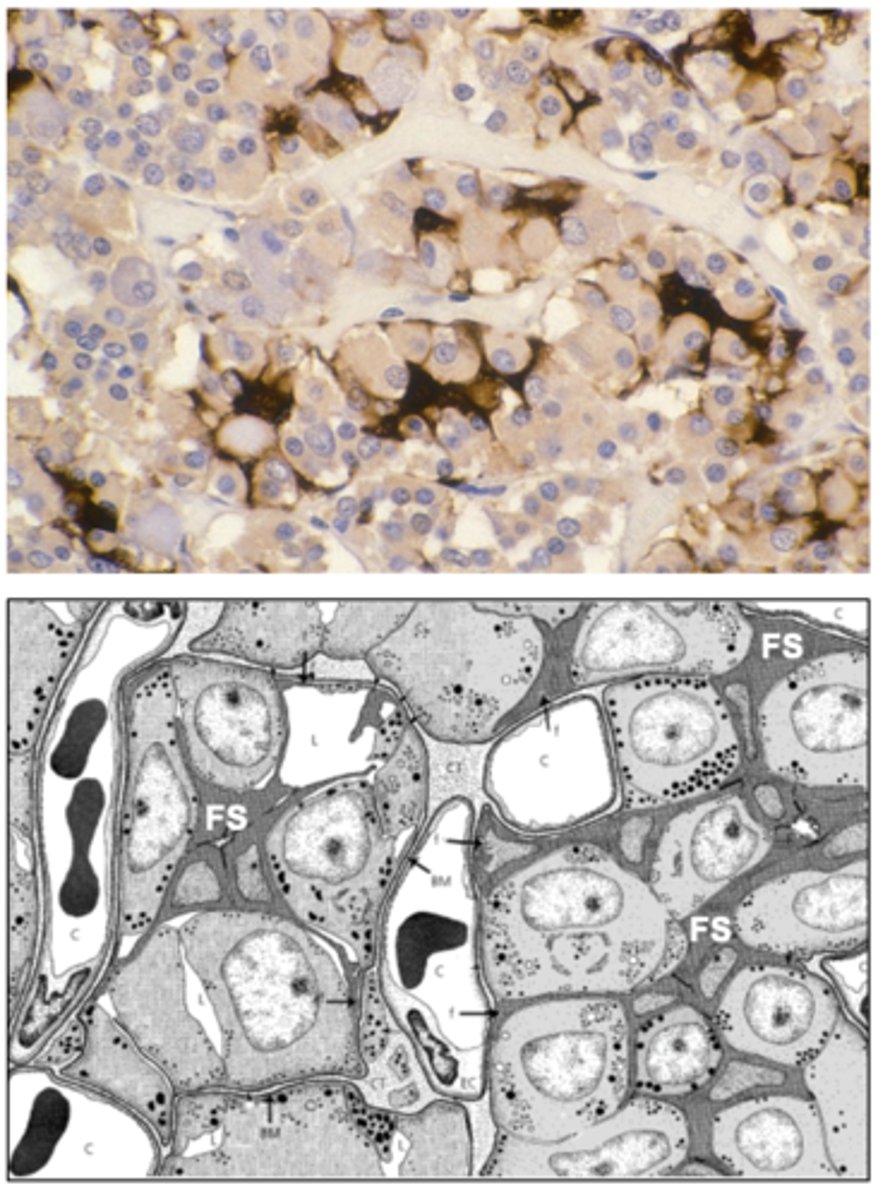
What has the following characteristics?
- Devoid of granules, occupy - 10% of anterior pituitary
- Form cell clusters ("follicles")
- Dendritic morphology
- Possess gap junctional connections to other FS cells and to acidophils/ basophils
Folliculostellate cells
What cells have the following functions?
- Paracrine regulation
- Neuro/immune regulation of inflammation
- Stem cells?
Folliculostellate cells
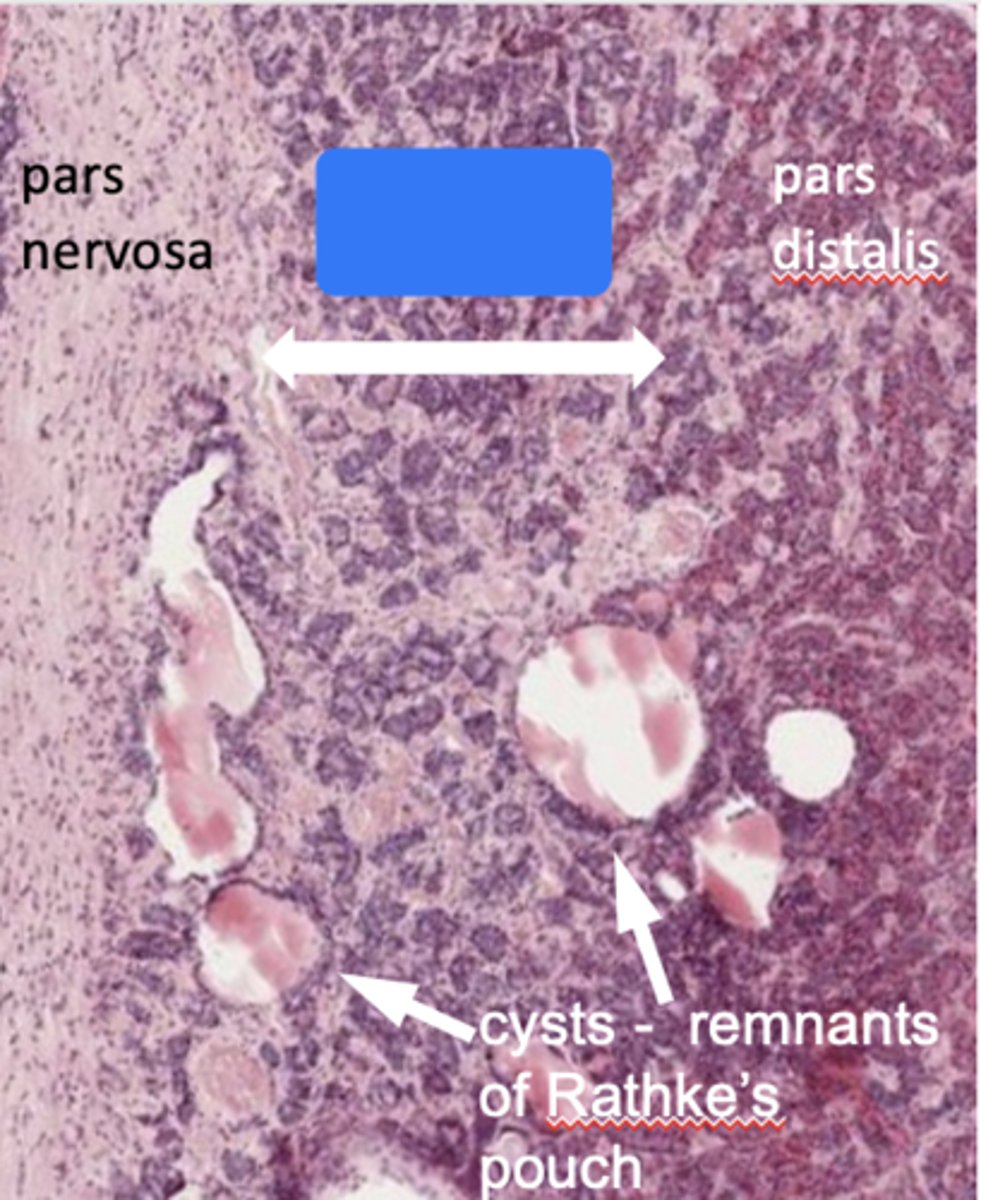
ID the section in blue:
Pars intermedia
What has the following characteristics?
- Part of the anterior lobe
- Consists mostly of basophils (corticotrophs)
- Synthesizes proopiomelanocortin (POMC)
which is cleaved to form:
- - MSH
- - β-endorphin
- - ACTH
- Contains colloid-filled cysts
Pars intermedia
How are cells regulated to release TRH, CRH, GnRH, and GHRH?
Through the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
Hormones/carriers are synthesized in hypothalamic nuclei as ______________
Preprohormones
Hormones (oxytocin, ADH, 9 a.a. each) are coupled to _________ during neurosecretion
Neurophysin (N) I & II
During axonal transport, _____________ release hormones and neurophysin
Endopeptidases
distal axon swellings known as ____________ store hormone and neurophysin
Herring bodies
During neurosecretion, ___________ release stimulates exocytosis of hormone and neurophysin into blood
Calcium
What has the following characteristics?
1) Smooth m. contraction (uterus)
2) Myoepithelial cell contraction (mammary gland)
3) Emotional (trust, calmness)
oxytocin
What has the following characteristics?
1) increases collecting duct permeability
2) vasoconstrictor (minor role)
ADH (vasopressin)
Absence or deficiency of _____________ leads to diabetes insipidus
ADH
What has the following characteristics?
- Stable, long ½ life [one week]
T4
What is Thyroxine also known as?
T4
What is thriiodothyronine also known as?
T3
Is there more T3 of T4 in the blood stream?
T4
Is T3 of T4 more potent?
T3
T4 can be converted to the more active T3 via ____________ in the liver, kidney etc.
deiodinases
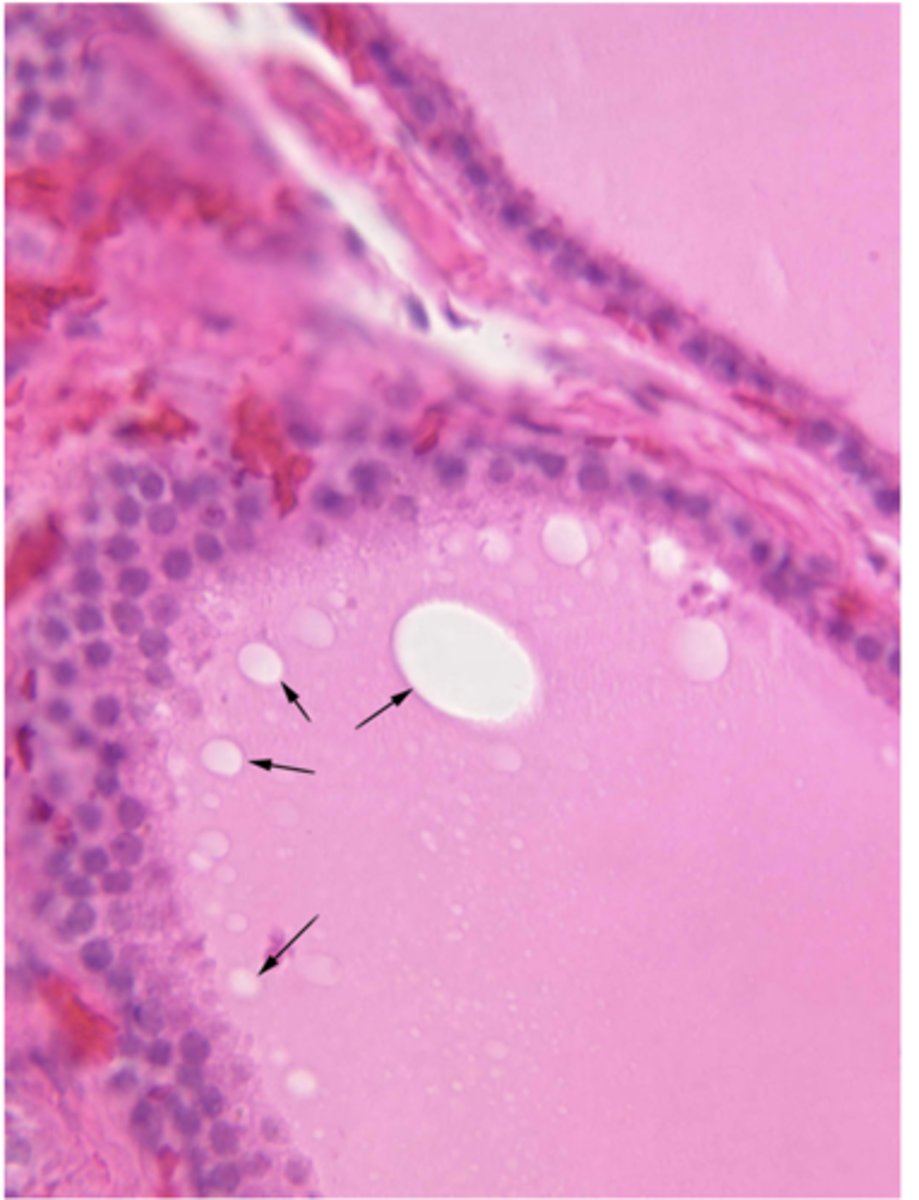
What are the arrows pointing to?
Resorption lacunae
What is the cycle of goiter?
- Low thyroxine (hypothyroidism)
- Increased TRH from hypothalamus
- Increased TSH from pituitary
- Hypertrophy & hyperplasia of thyroid cells & increased colloid
What condition is the following:
- Autoantibodies against TSH receptor (resulting in excess activation)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Goiter develops from follicle cell hyperplasia
- Excess periorbital CT/fat deposition leads to exophthalamos (periorbital fibroblasts express TSH receptors)
Graves disease
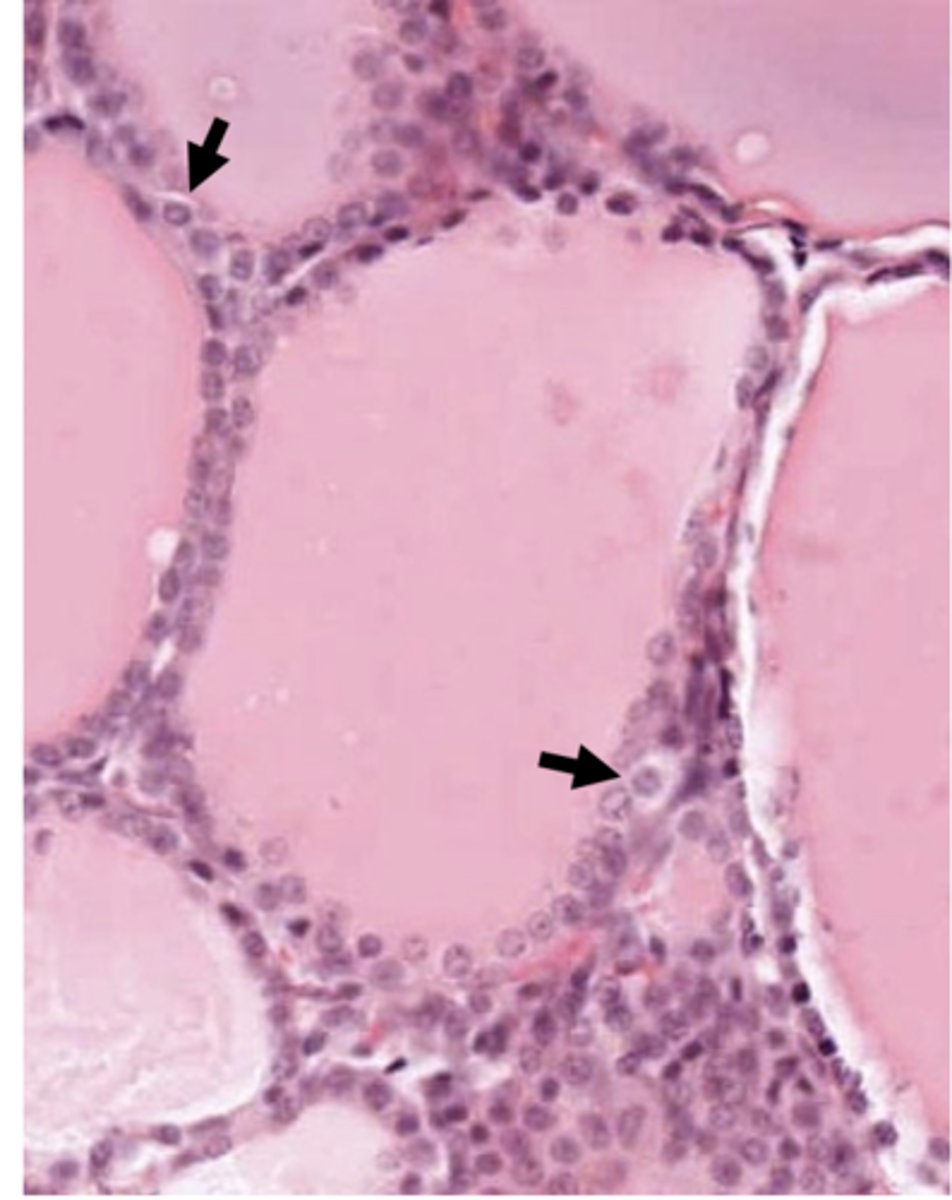
What are the arrows pointing to?
Parafollicular, clear (C) cells
What has the following characteristics?
- Reside within basal lamina
- Derived from oral epithelium
Parafollicular, clear (C) cells
What has the following characteristics?
- Stimulated by high Ca2+
- Is stored
- Opposes parathyroid hormone
- Lowers blood calcium levels:
- - Decrease osteoclast activity
- - Increase osteoblast activity
- - Decrease Ca2+ absorption
Calcitonin
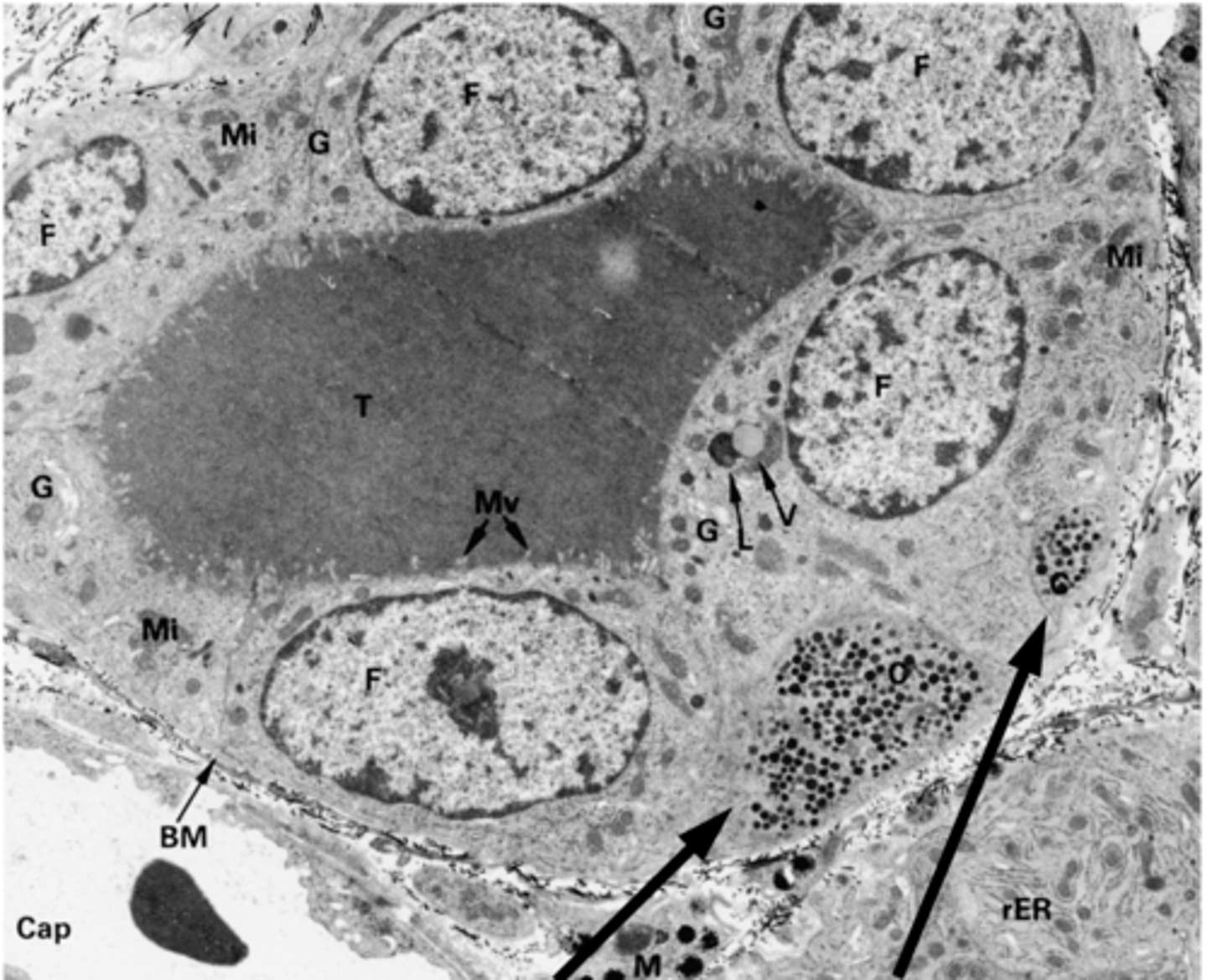
What are the arrows pointing to?
Parafollicular cells with calcitonin-containing granules
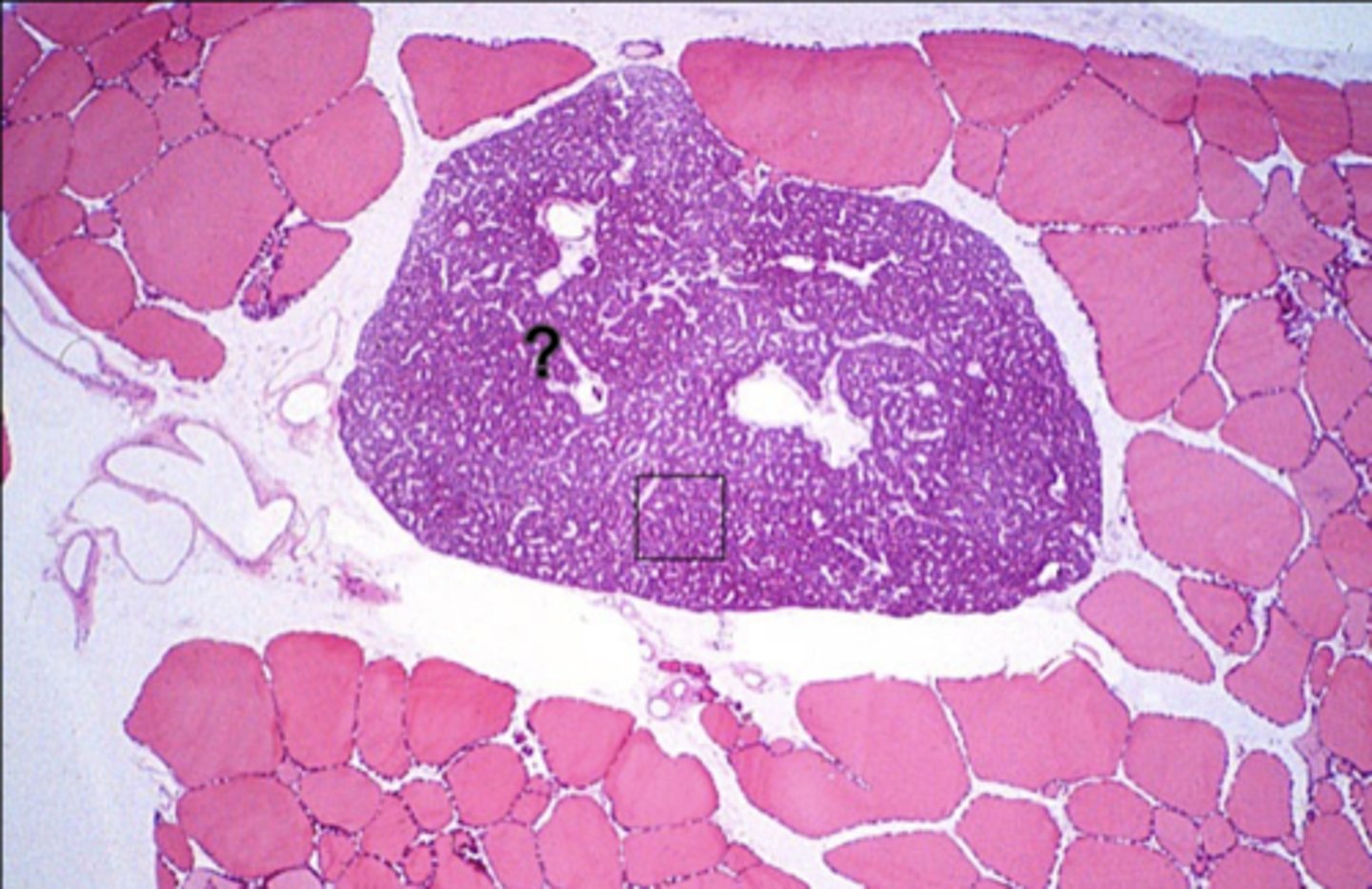
What is the ? indicating?
Parathyroid gland
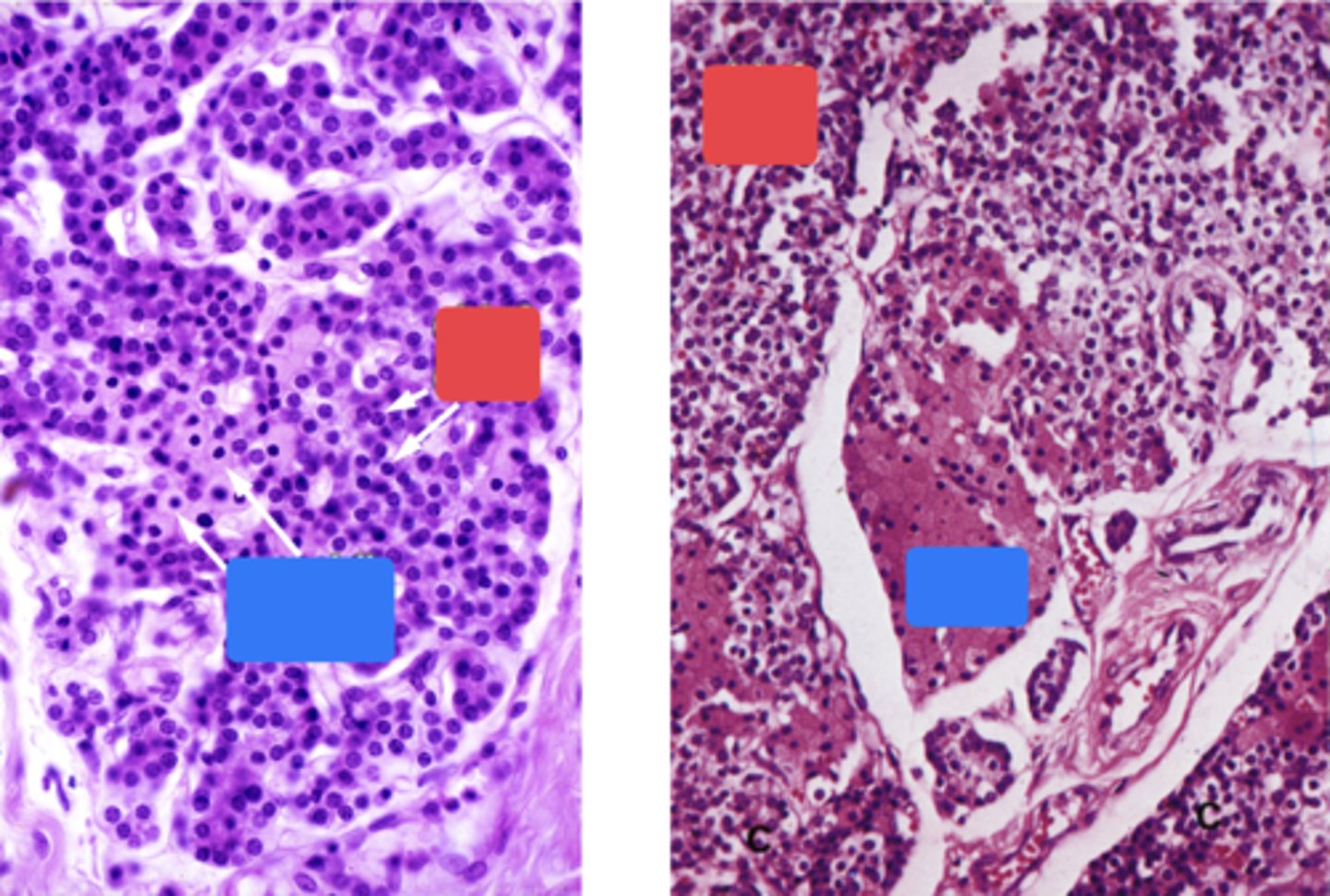
ID the red boxes:
Chief cells
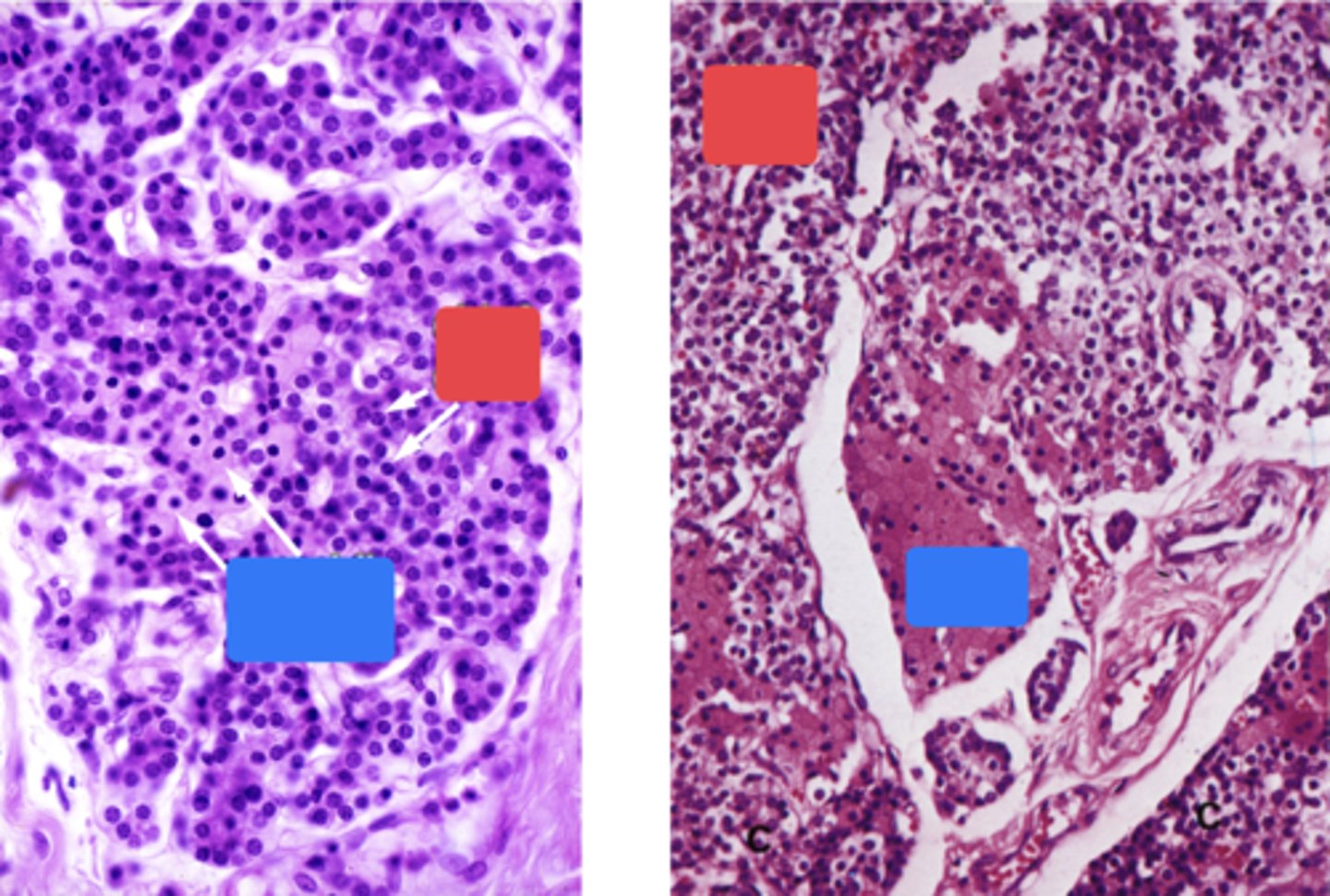
ID the blue boxes:
Oxyphil cells
What has the following characteristics?
- 84aa polypeptide
- Increases blood calcium:
- - Increases osteoclast activity
- - Stimulates vitamin D activation in kidney
- - Vitamin D stimulates Ca2+ resorption in GI tract & kidney
- Opposes action of calcitonin, but only ______ is vital
Chief Cells: Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Rising blood levels of calcium increase...
Calcitonin
Falling blood levels of calcium increase...
PTH
What has the following characteristics?
- Appear at puberty
- Unknown function
Oxyphil cells
Define the following:
Remnant of thyroglossal duct
Pyramidal lobe
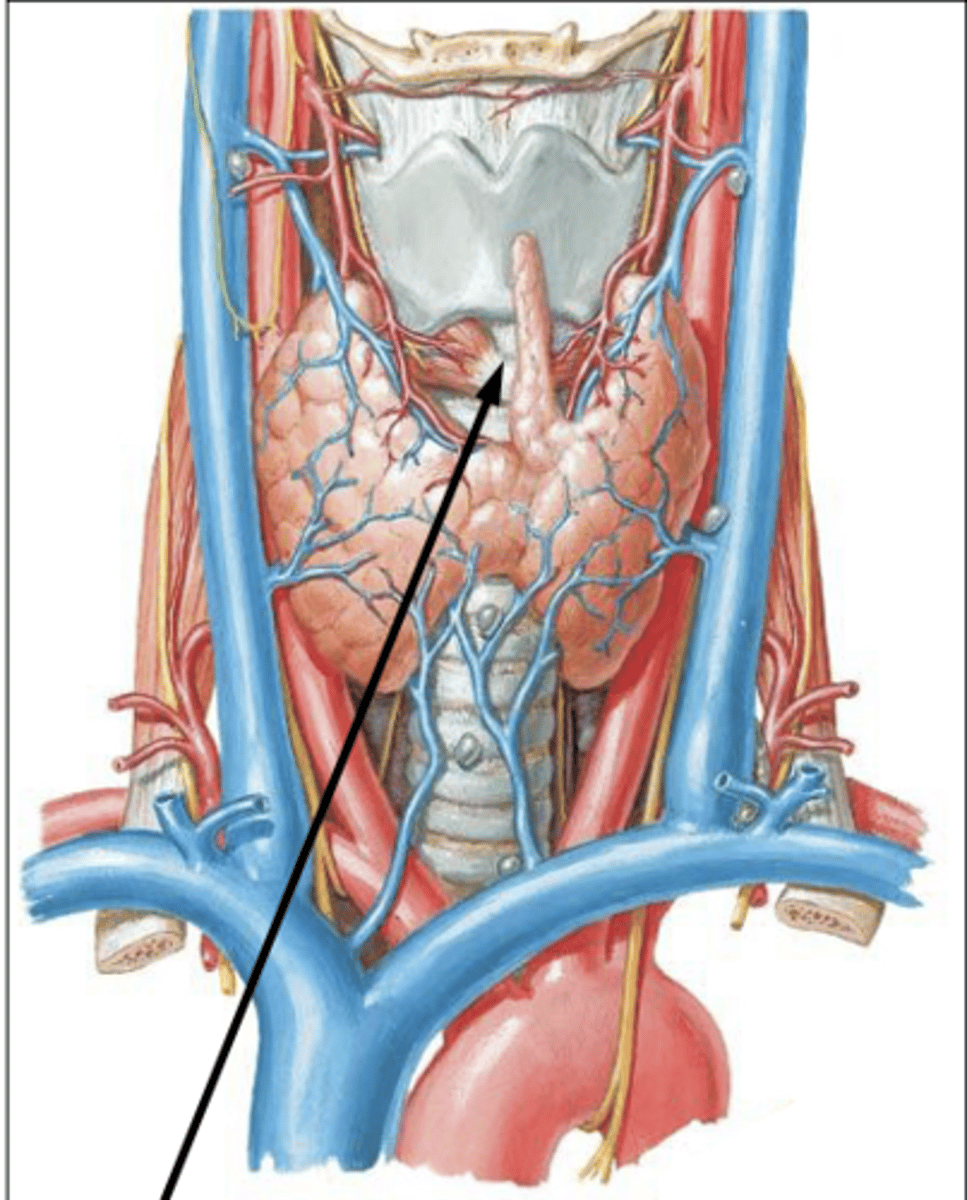
What is the arrow pointing to?
Pyramidal lobe (remnant of thyroglossal duct)
What has the following characteristics?
- CT capsule
- Cortex/medulla
Adrenal gland
Where are the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis found in the adrenal gland?
Cortex
Where does steroid hormone synthesis occur in the adrenal gland?
Cortex
Where does catecholamine synthesis occur in the adrenal gland?
Medulla
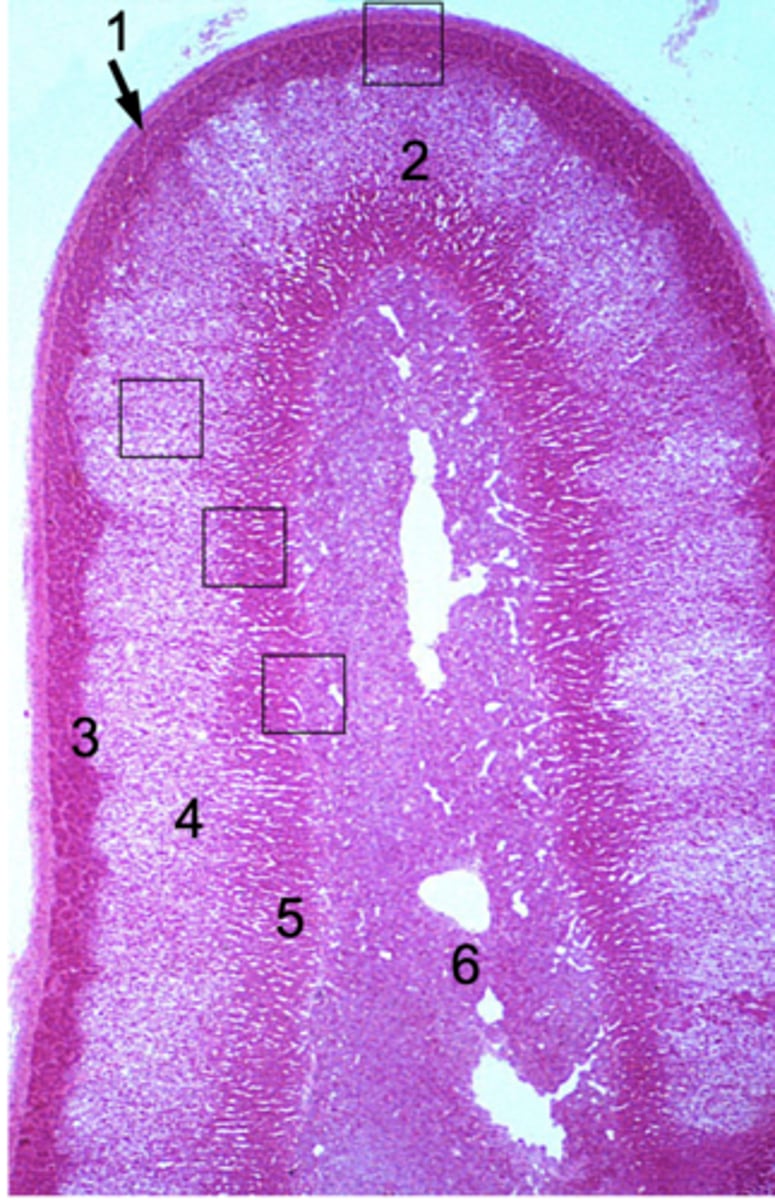
ID #1:
Capsule
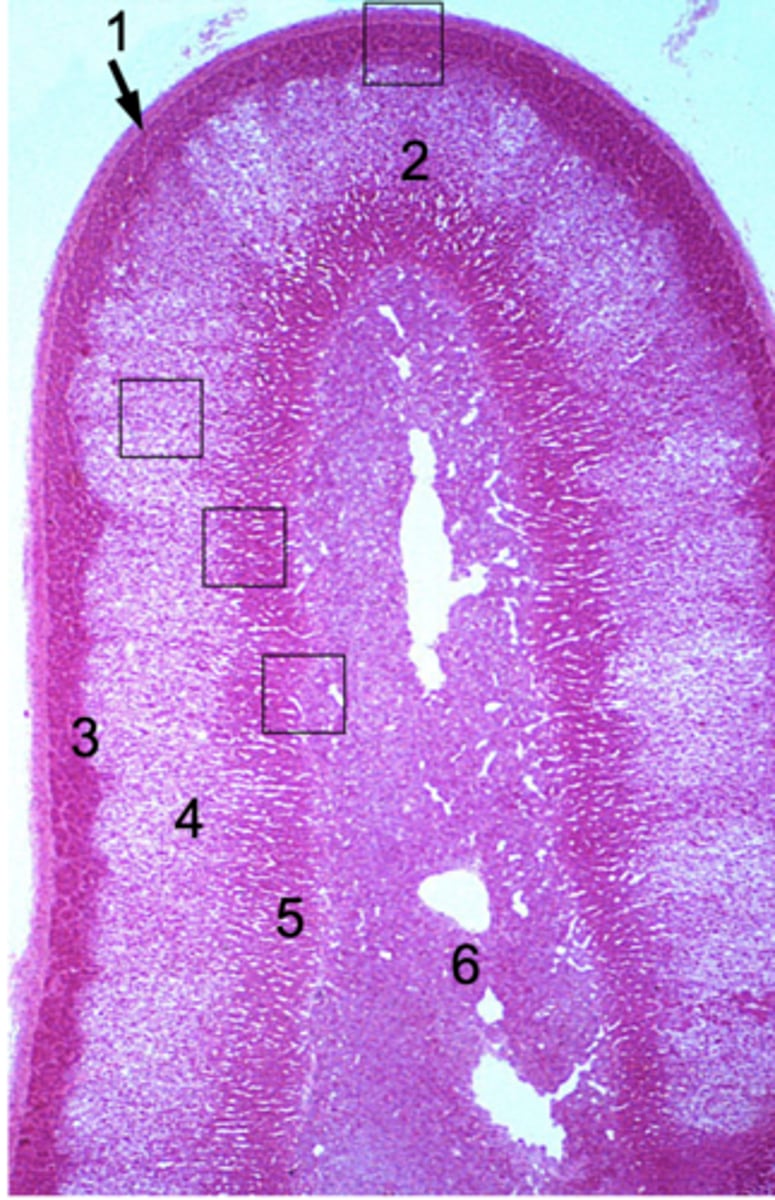
ID #2:
Adrenal cortex
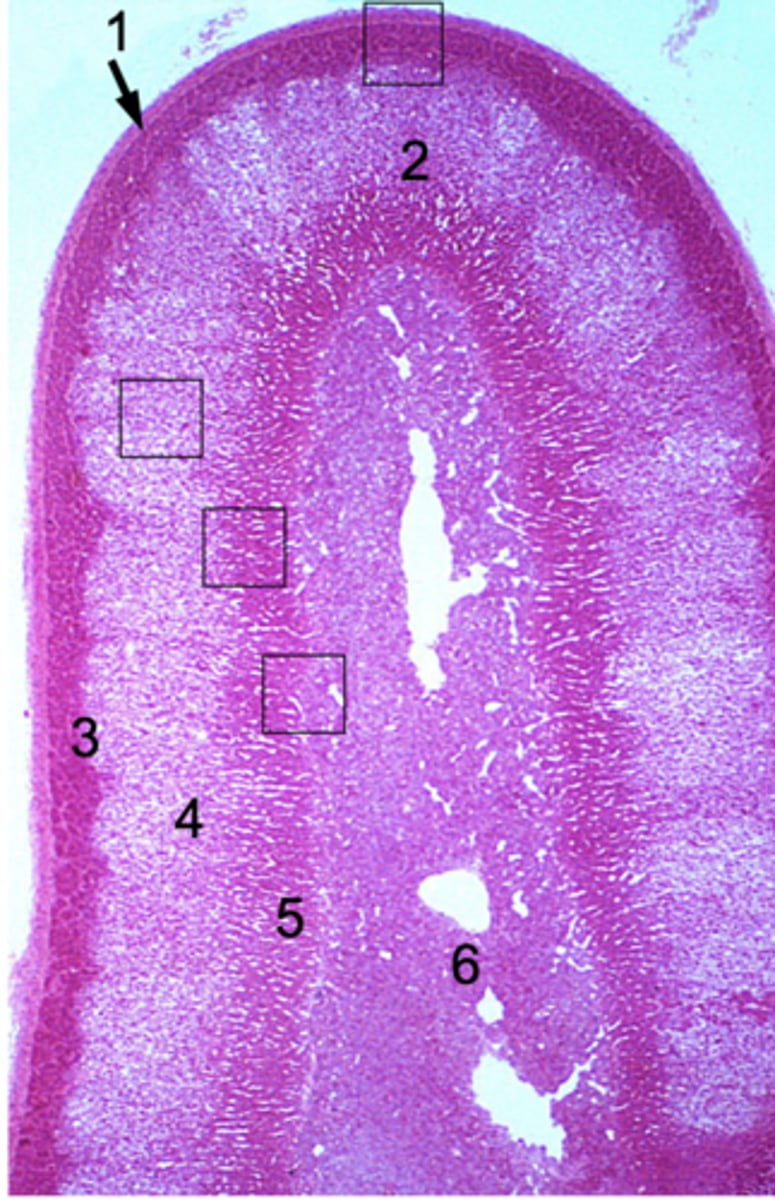
ID #3:
Zona glomerulus
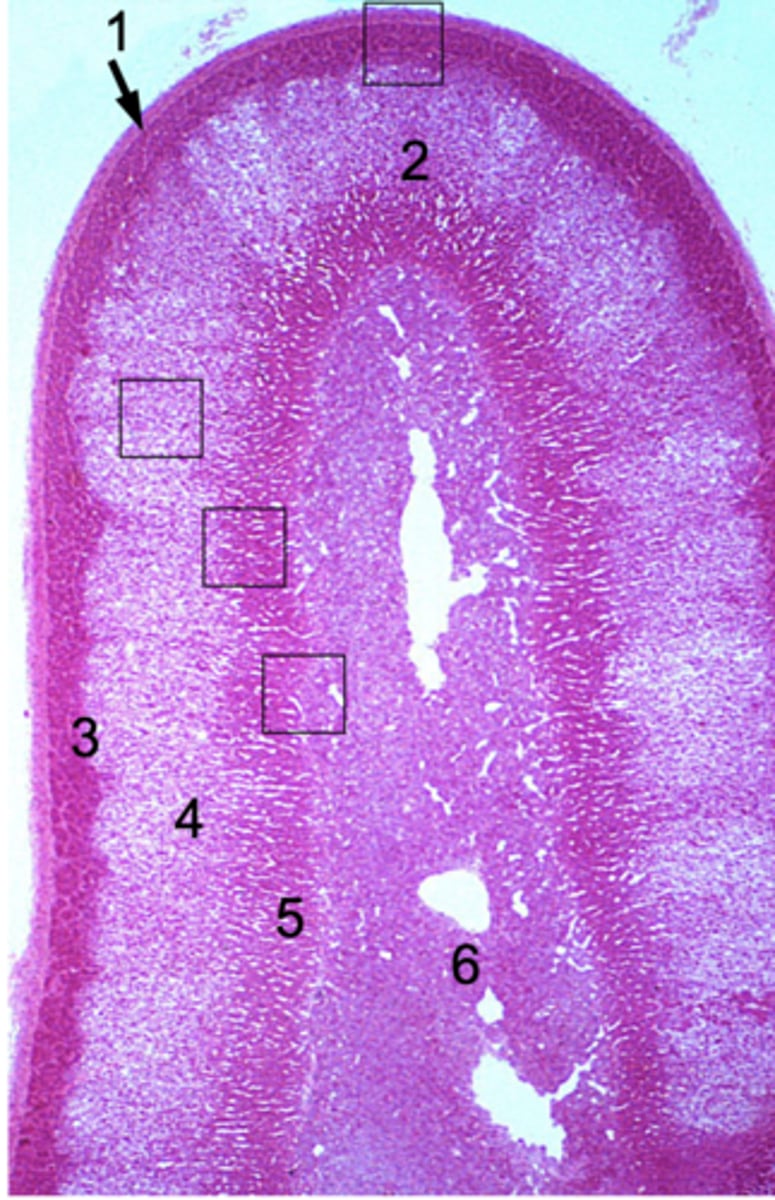
ID #4:
Zona fasciculata
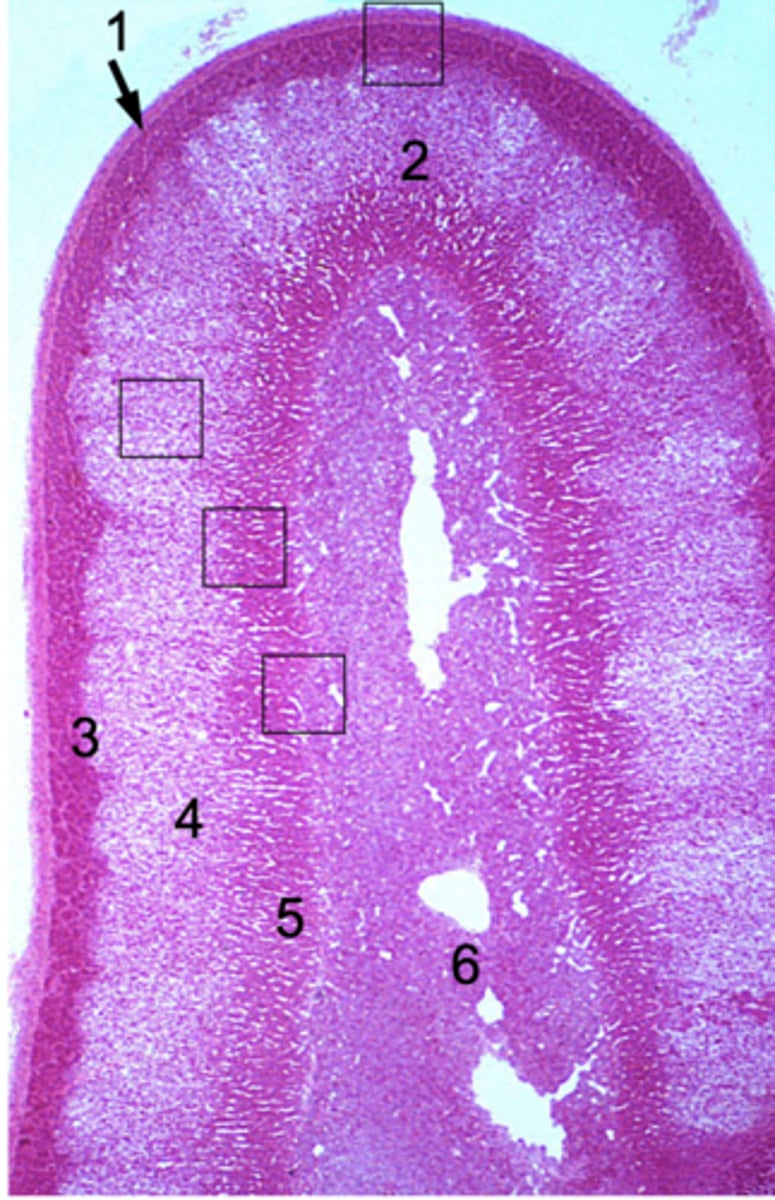
ID #5:
Zona reticularis
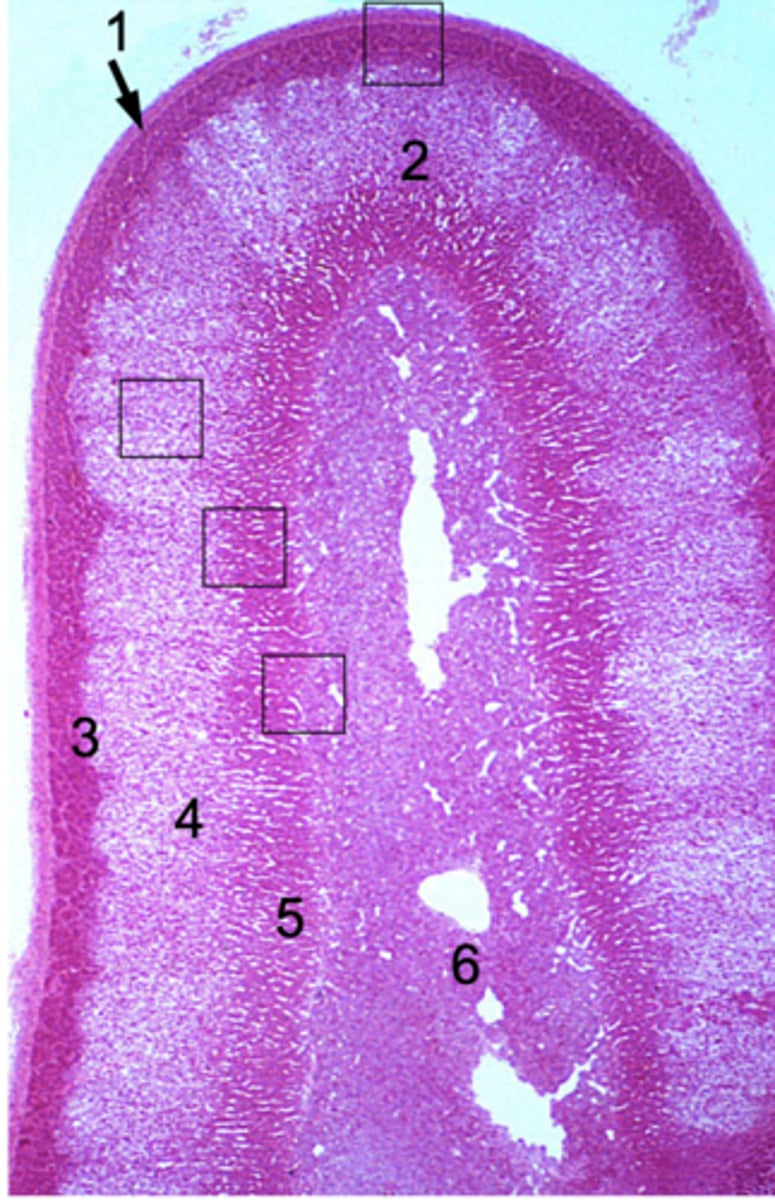
ID #6:
Adrenal medulla