Mitosis and the cell cycle flashcards
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Mitosis
the division of body cells to produce 2 genetically identical daughter cells
Meiosis
division of sex cells to produce 4 genetically unique daughter cells
Why do cells divide?
Cells divide to grow, repair tissues, and reproduce new cells.
Nucleolus
a dense region within the nucleus that produces and assembles ribosomes
Chromatin
stringy complex of DNA and protein.
chromosome
dense and compact bundles of chromatin that help DNA separate precisely during cell division
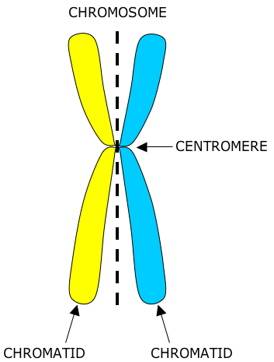
sister chromatins
2 identical halves of a chromosome
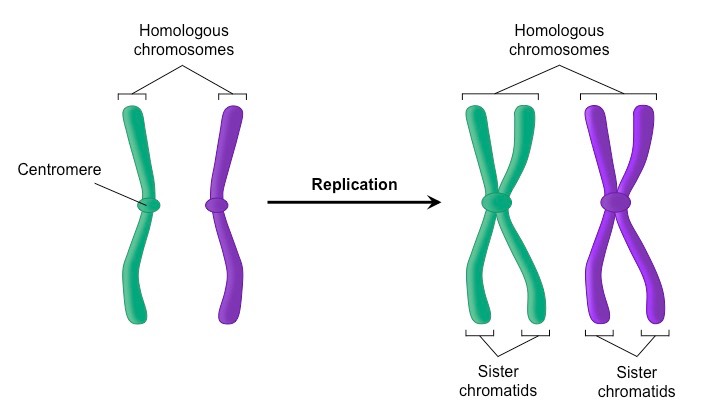
centromere
the place where the 2 sister chromatin’s are joined together
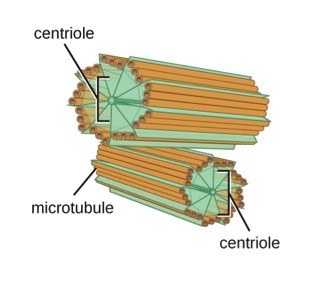
centrioles
organize spindle fibers during cell division (IN ANIMAL CELLS ONLY)
spindle fibers
microtubules that help separate and move duplicated chromosomes during cell division
what are the 3 parts of cell division?
interphase
mitosis
cytokinesis
what is the longest phase of cell division?
interphase
what happens in interphase?
the cell gets prepared for mitosis by:
growing larger
having the DNA and organelles replicated
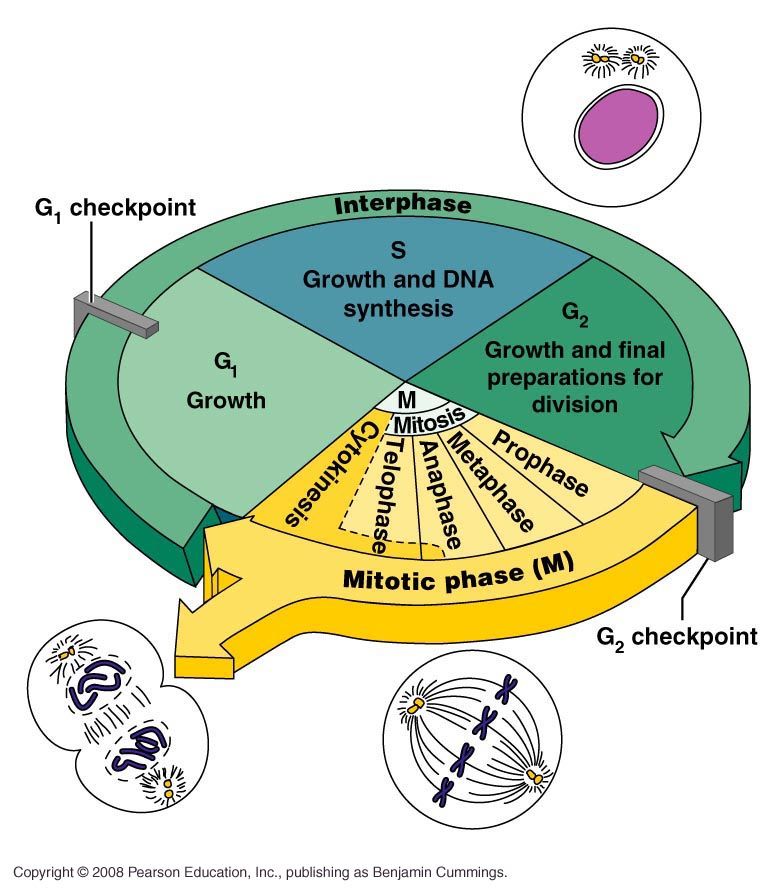
what are interphases’ 3 stages called?
G1 (GAP 1)
S (synthesis)
G2 (GAP 2)
what happens in G1?
the cell grows in size and duplicate’s its organelles
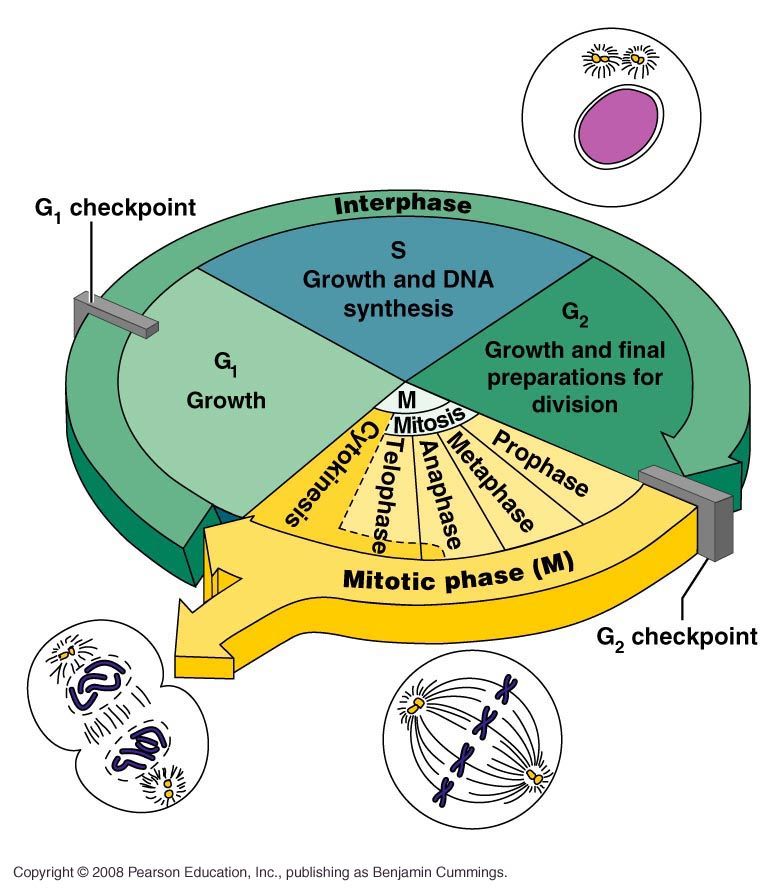
what happens in S (synthesis)?
the cell synthesis’ a copy of its DNA and replicates chromosomes
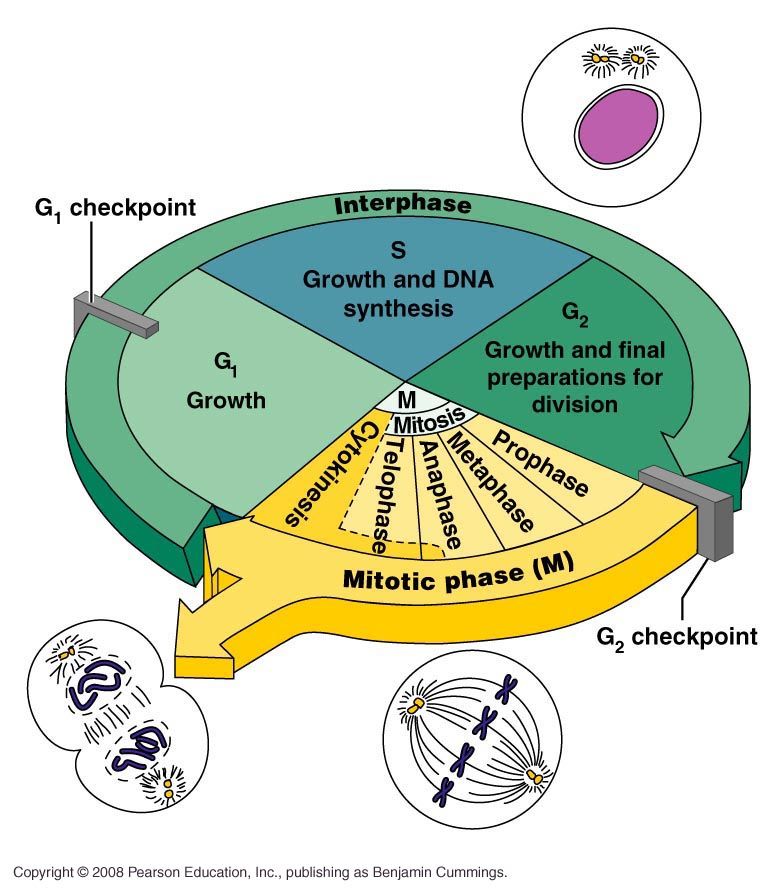
what happens in G2?
the cell grows even larger and reorganizes its genetic material
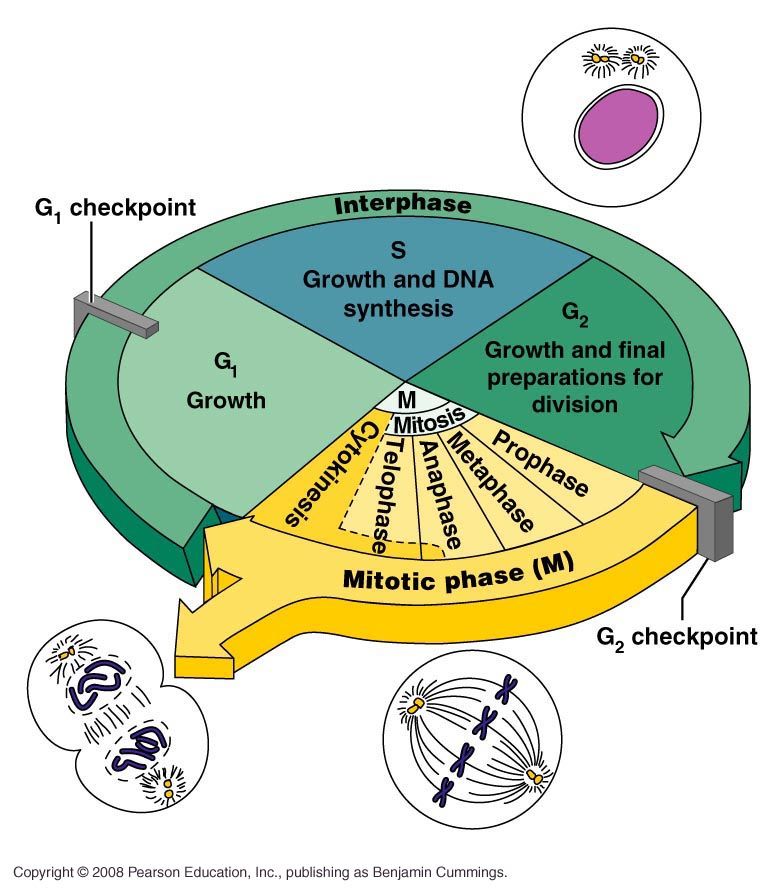
what are some things to remember about interphase?
the nucleus and nucleolus are well defined
DNA is loosely packed into long chromatin fibers
what is mitosis?
the cell is actively dividing into 2 daughter cells
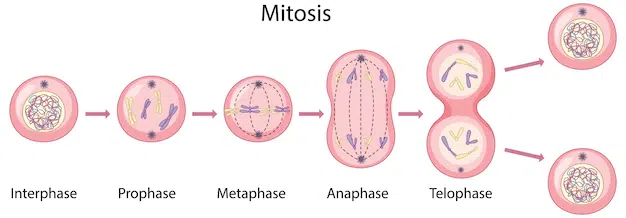
what are the stages of mitosis?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
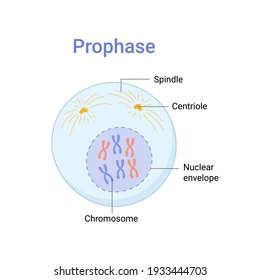
what happens in prophase?
the chromatin condenses and chromosomes become visible
the centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell
spindle fibers extend to the centrosome (where the centrioles are located)
the nucleus disappears
nuclear envelope breaks down
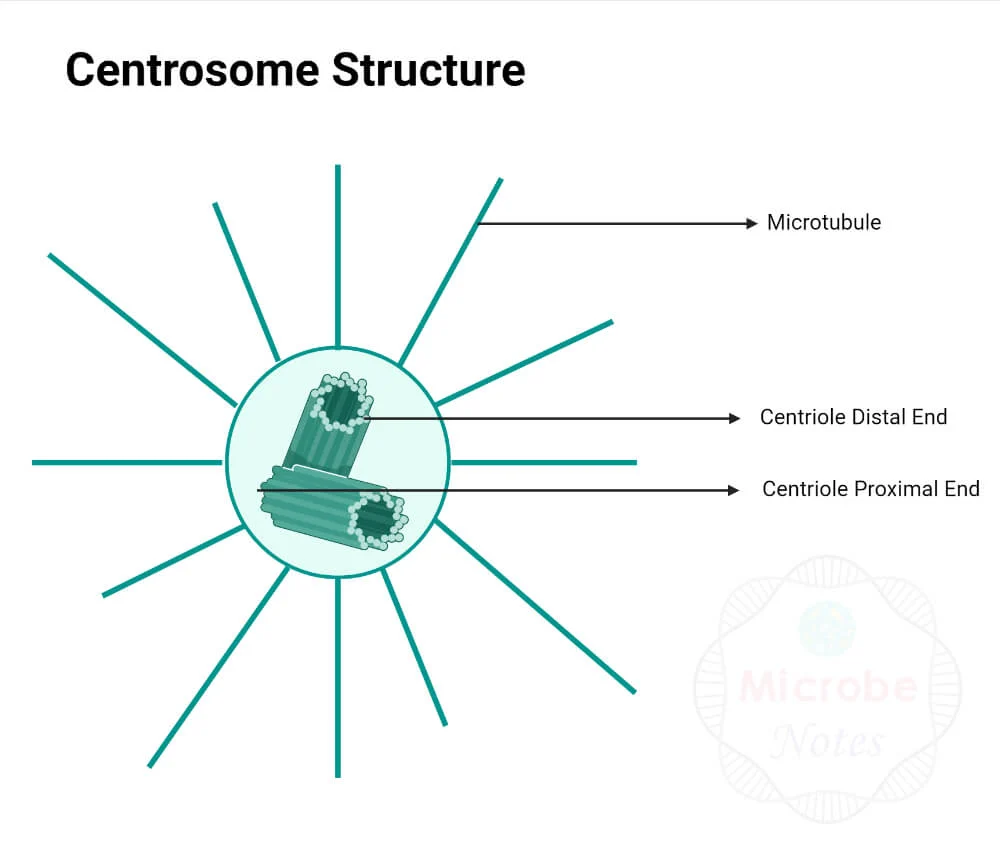
centrosome
where the centrioles are located
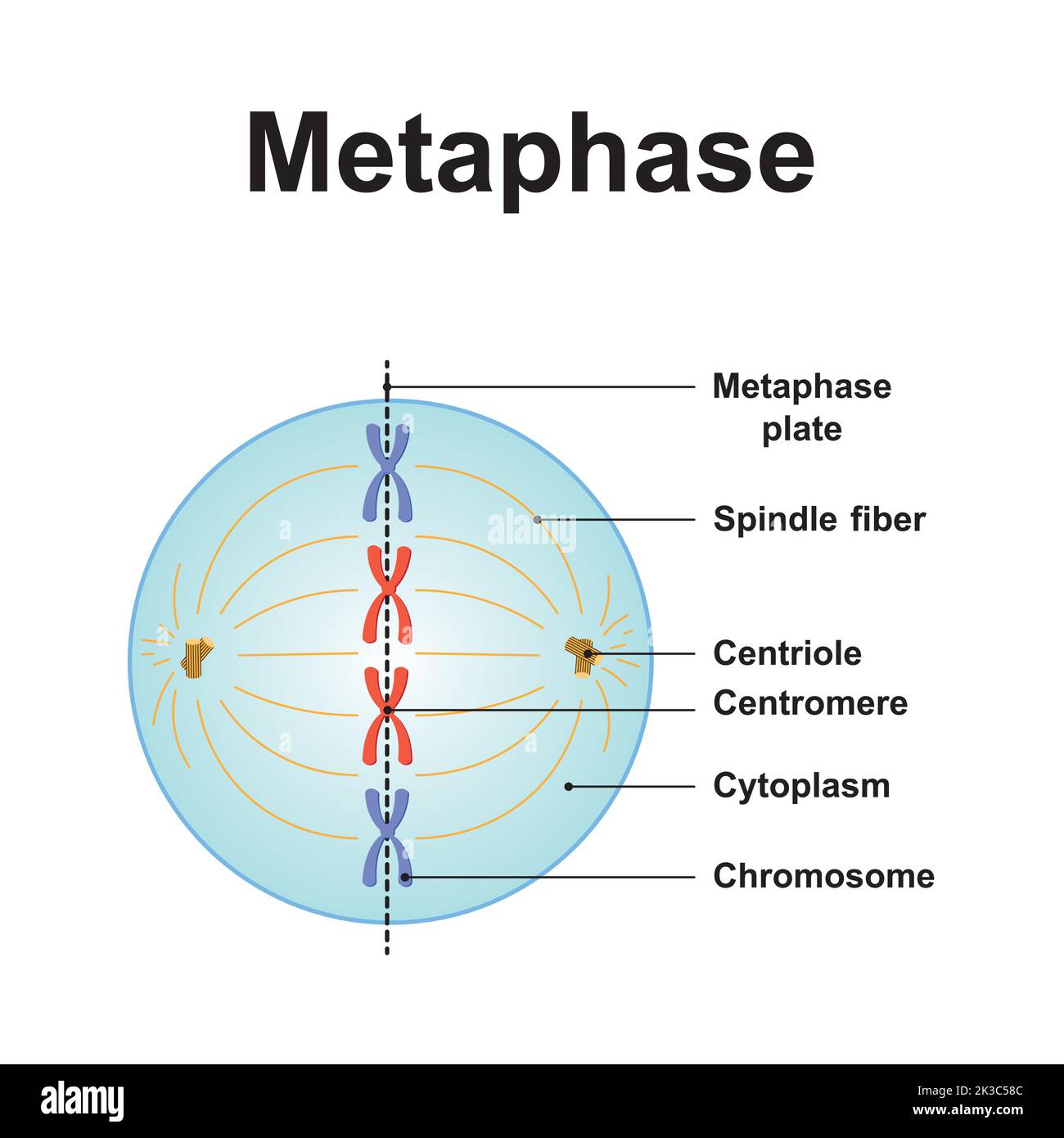
what happens in metaphase?
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
spindle fibers help to coordinate the movement of the chromosomes
it is the SHORTEST phase
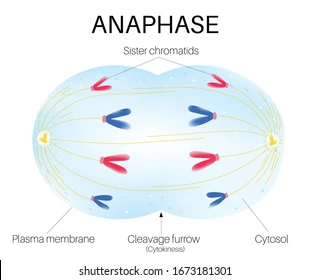
what happens during anaphase?
the sister chromatins separate from each other and move away from each other
chromosomes move along spindle fibers to opposite sides of the cell
once anaphase begins each sister chromosome is considered an INDIVIDUAL chromosome
at the end of anaphase, each side of the cell has a complete set of chromosomes
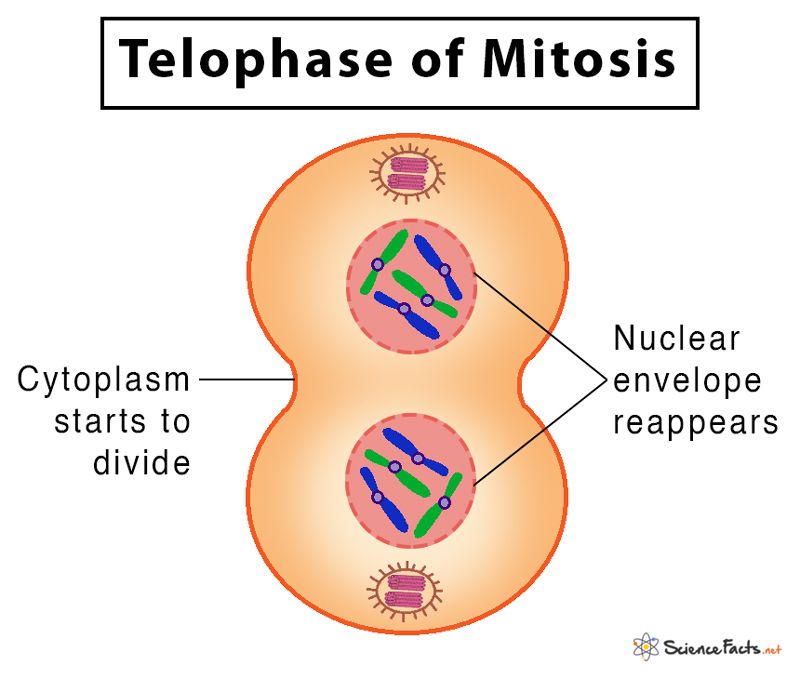
what happens in telophase?
condensed chromosomes unwind and spread out into clusters of chromatin
the nuclear envelope reforms
the nucleus becomes visible again
the cell now has TWO IDENTICAL nuclei
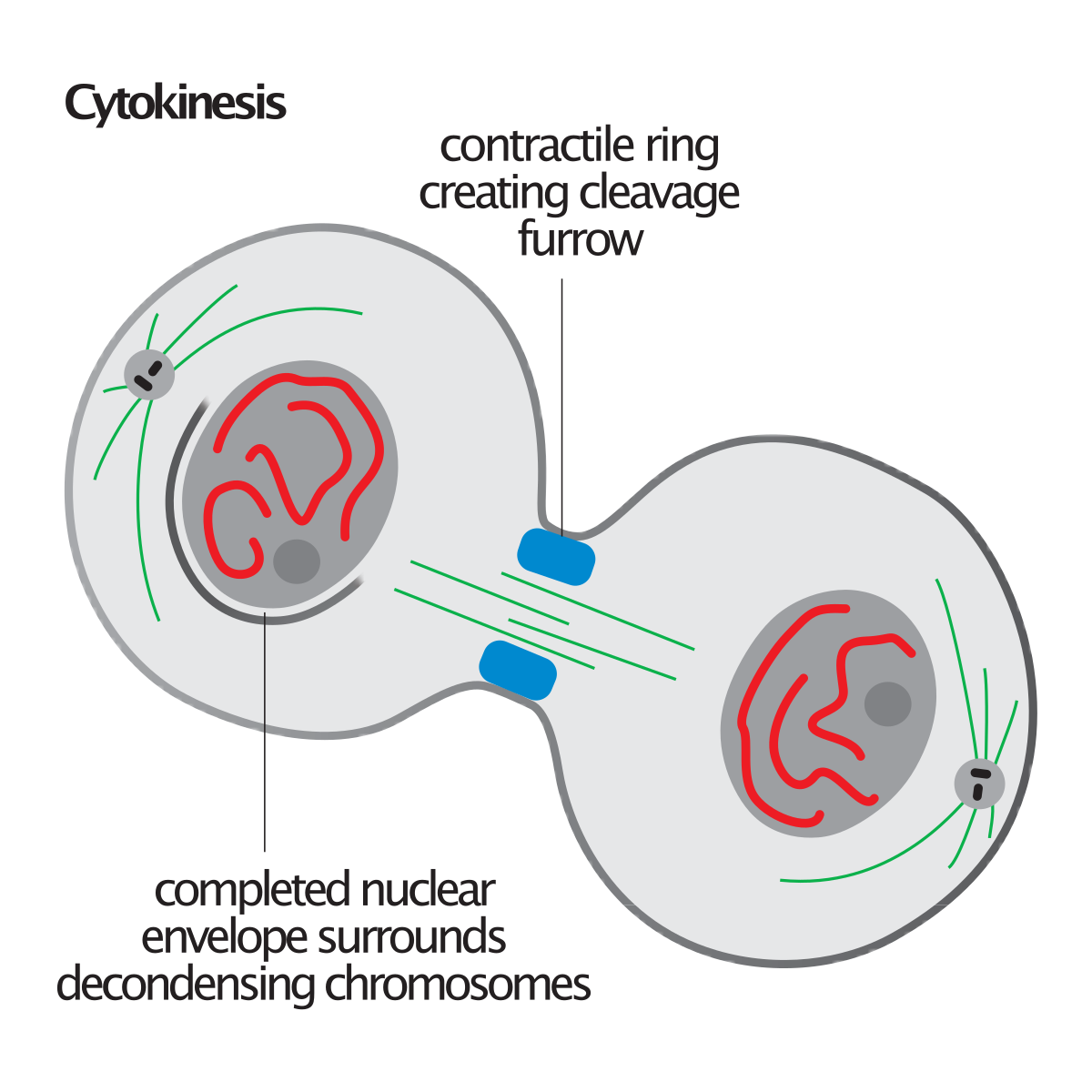
what happens in cytokinesis?
cell division completes by splitting the cytoplasm and dividing the cell into 2 identical cells
each daughter cell contains an identical set of chromosomes
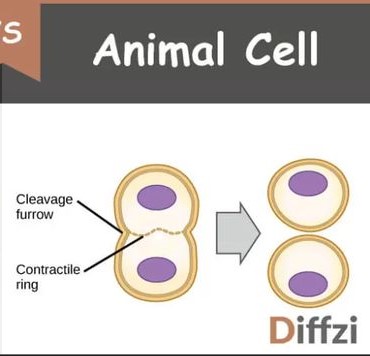
what happens in animal cell cytokinesis?
the cell membrane draws inward to create a cleavage furrow
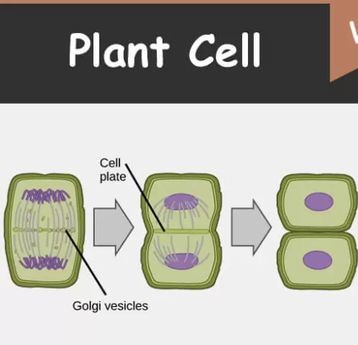
what happens in plant cell cytokinesis?
a cell plate forms between the 2 divided cells