Sed Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
relief
how dark the lines around the edges are
2
New cards
Cleavage
a preferred fracture orientation
3
New cards
Pleochroism
grain changes color when rotated under plane-polarized light
4
New cards
Birefringence
distinctive colors seen in anisotropic minerals under cross-polarized light
5
New cards
twinning
crystals in the same grain formed with opposite orientation of their crystal lattice
6
New cards
Quartz
Typically colorless in plane-polarized light, shades of gray in cross-polarized light, has low relief
7
New cards
Calcite in thin section
Two cleavage planes, high relief, pale green and pink birefringence
8
New cards
Easiest way to distinguish different types of feldspars
twinning
9
New cards
Besides the different types of individual mineral grains in a sandstone, other constituents may include:
lithic grains, matrix, cement
10
New cards
Laminar flow
low flow rates
11
New cards
Turbulent flow
high flow velocities
12
New cards
rolling
clasts move along the bottom of the fluid column and stay in contact with the bed
13
New cards
saltation
particles jump or bounce along the bed surface
14
New cards
Suspension
turbulence keeps the particles in the fluid column
15
New cards
bedload
particles being carried by rolling and saltation
16
New cards
suspended load
the sediment load being carried in the fluid column without interacting with the bed surface
17
New cards
Normal grading
Grain size decrease from the bottom to the top of a single bed
18
New cards
Reverse Grading
Increase in grain size upward within a single bed
19
New cards
Fining upward
pattern of overall smaller grain sized upward through a number of beds
20
New cards
coarsening upward
pattern of overall larger grain sizes upward through a number of beds
21
New cards
Bouma Sequence
associated with turbidity currents
22
New cards
Downstream
Ripples that form under unidirectional flow have asymmetric shapes and cross-lamination that dip
23
New cards
Current ripple produces
cross-lamination
24
New cards
straight-crested dune produces
planar cross-bedding
25
New cards
sinuous-crested dune produces
trough cross-bedding
26
New cards
plane bedding produces
planar lamination
27
New cards
interbedded
alternations of thin beds of different lithology
28
New cards
cross-stratification
any layering that is at an angle to the depositional horizon
29
New cards
primary current lineation
ridges on bedding planes parallel to flow direction
30
New cards
stoss
upstream side of a ripple
31
New cards
lee
downstream side of a ripple
32
New cards
wave base
the depth to which surface waves affect a water body is the
33
New cards
Wave ripples
symmetric
34
New cards
Tidal currents which move water onshore
flood tides
35
New cards
Ebb tides
Tidal currents which move water offshore
36
New cards
mud drapes
thin layer of mud on foresets of cross-stratified sand
37
New cards
reactivation surface
a minor erosion surface within cross-stratification reflecting current reversals
38
New cards
Tidal bundle
a cyclical variation of thickness in foreset laminae in cross-beds reflecting variations in flow strength
39
New cards
Herringbone cross stratification
bipolar cross-stratification produced by alternating directions of ripple migration
40
New cards
flaser bedding
isolated thin drapes of mud in a cross-laminated sand
41
New cards
Tidal bundle

42
New cards
Flaser bedding

43
New cards
cross bedding
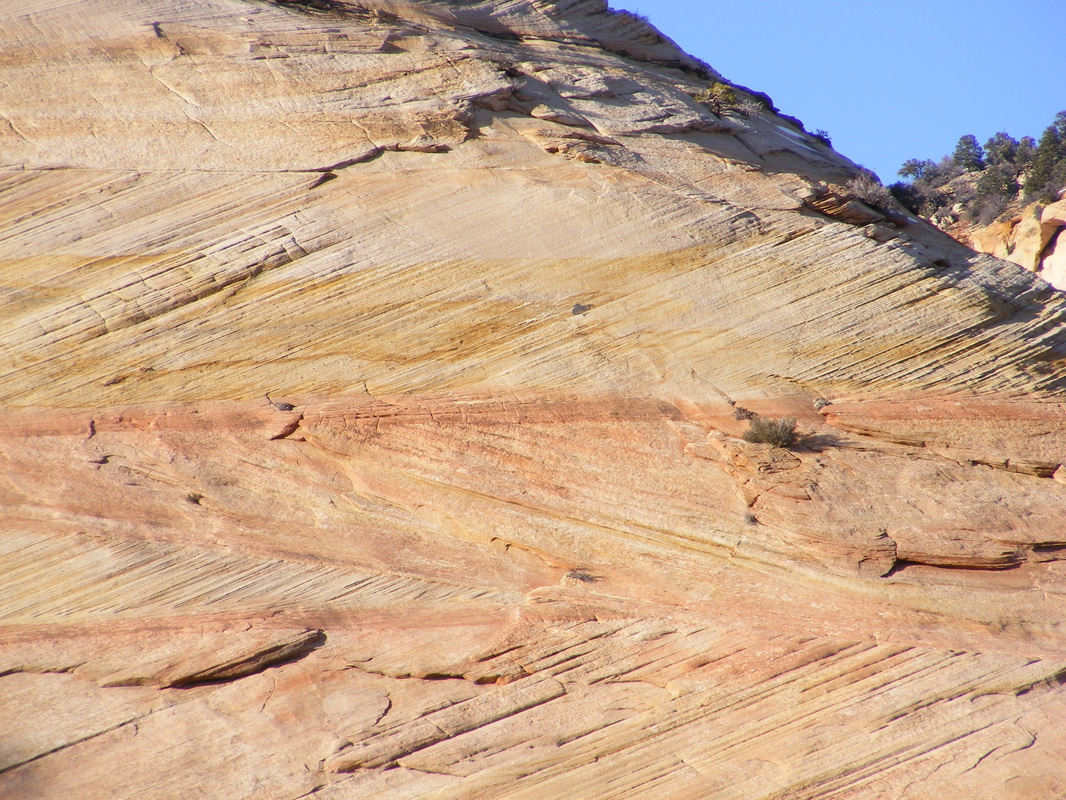

44
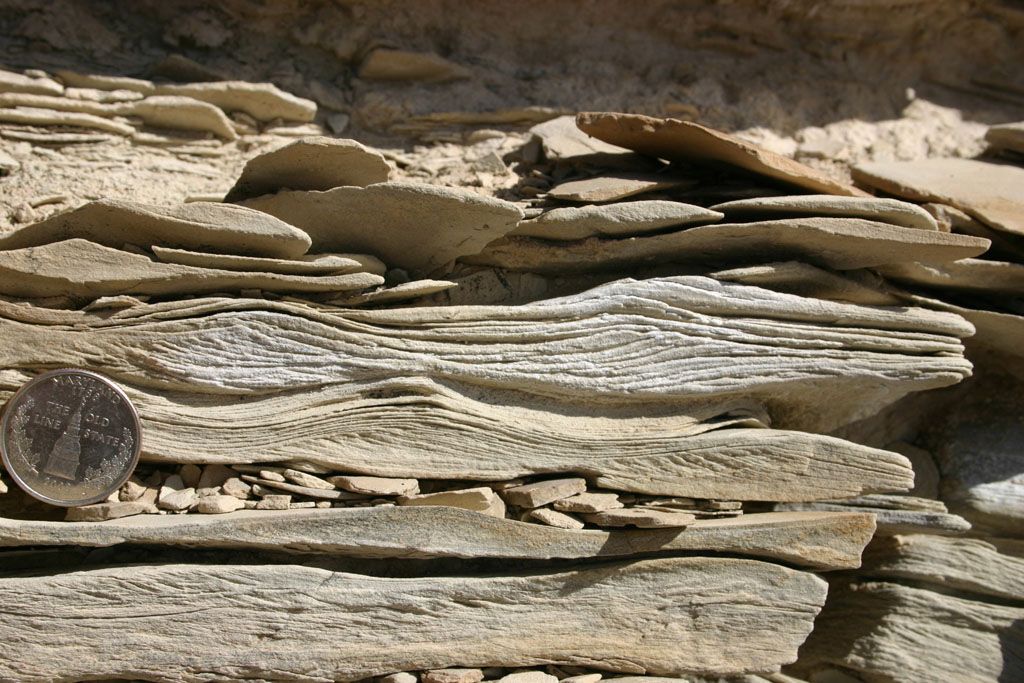
New cards
wave ripple-lamination

45
New cards
wavy bedding

46
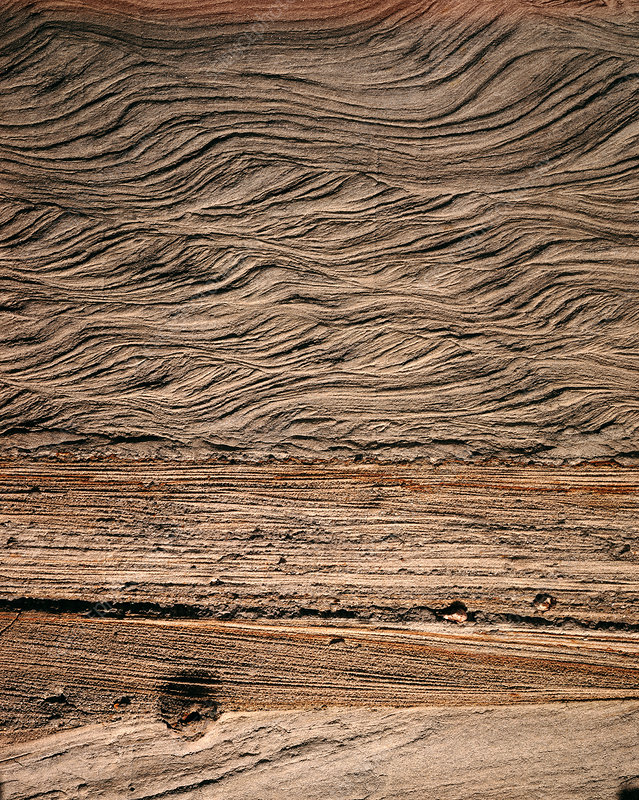
New cards
climbing ripples

47
New cards
hummocky cross-stratification

48
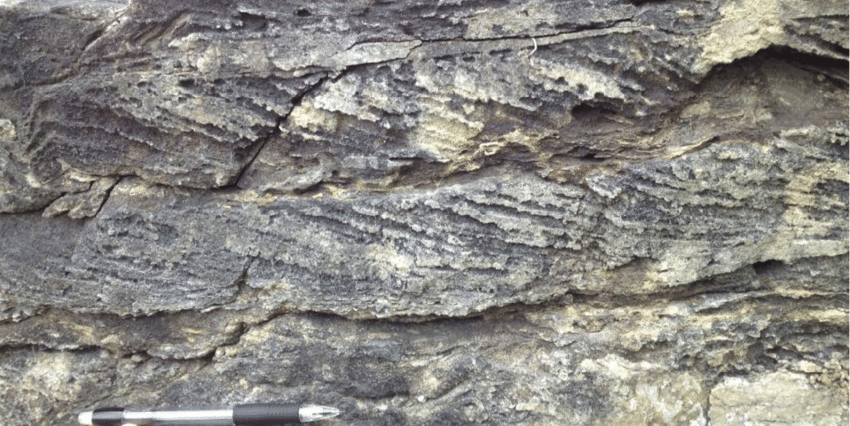
New cards
ripple cross-lamination

49
New cards
lenticular bedding

50
New cards
Trough Cross bedding
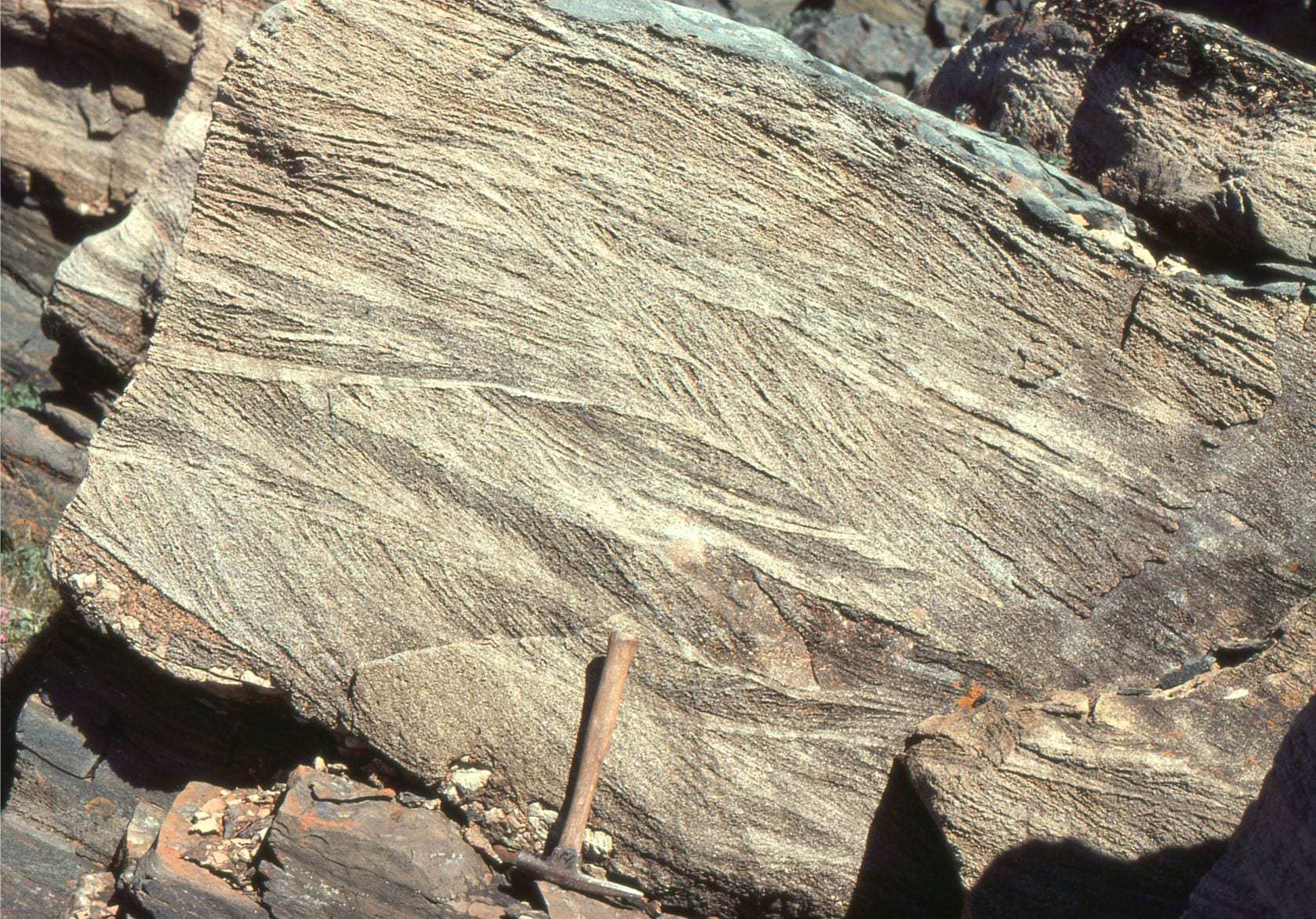

51
New cards
Tidal Rhythmite
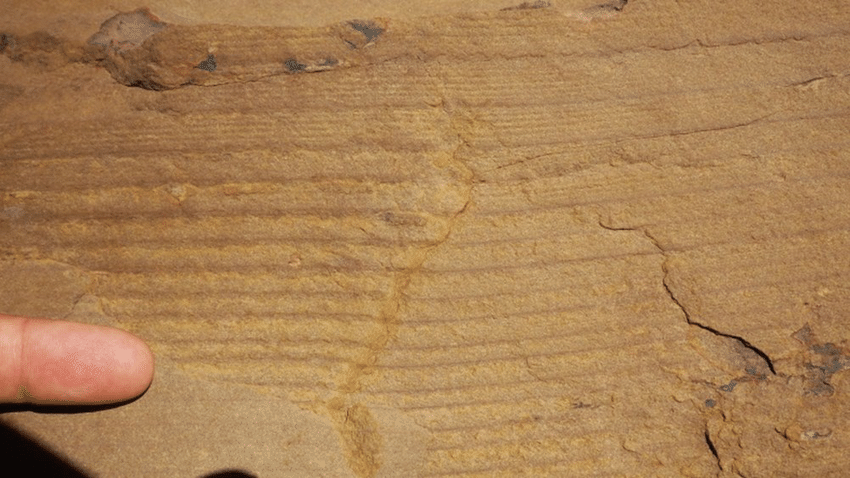

52
New cards
upstream
flute casts are elongated ridges with a steep narrow end that is oriented
53
New cards
scour marks
erosion of the underlying bed by turbulence in the flow
54
New cards
tool marks
an object carried in the flow marking the underlying bed
55
New cards
gutter cast
linear ridges and furrows on the bed surface
56
New cards
grooves
sharply defined elongate marks created by a dragging object
57
New cards
prod marks
indents in the lines of a bedding planes from a bouncing object
58
New cards
Flame Structure
type of deformation structure where mud projects into an overlying sandy bed
59
New cards
Dewatering structures
soft-sediment deformation structures formed by fluidization processes
60
New cards
Load Casts
Form when higher density sand partially sinks into the underlying mud to form downward-facing, bulbous structures
61
New cards
Skolithos
trace fossil assemblage that is dominantly characterized by small vertical tubes in sands
62
New cards
Zoophycos
trace fossil assemblage is mostly characterized by radial, sweeping forms on bedding plane surfaces
63
New cards
Cruziana
This trace fossil assemblage is the most diverse and contains complex networks of burrows that can be horizontal, vertical, and branching
64
New cards
Nereties
This trace fossil assemblage consists of intricate, regular patterns seen only on bedding planes and are typically feeding traces.
65
New cards
The distribution of ichnofacies is controlled by several environmental factors. The factors are:
Hardness of substrate, sedimentation rate, oxygen levels in the water, salinity of the water, quality/quantity of nutrient supply
66
New cards
Tropical regions
Chemical weathering is enhanced because of the higher temperatures and abundance of water.
67
New cards
Subtropical regions
Limited availability of water and absence of soil and vegetation leads to rapid physical weathering.
68
New cards
Polar and cold mountain regions
Physical weathering is the dominant process here.
69
New cards
Temperate regions
Both physical and chemical weathering are subdued in these regions.
70
New cards
Erosion and transport under gravity through downslope movement
landslide, rock fall, slumping, soil creep
71
New cards
Denudation
The lowering of the land surface through the combination of weathering and erosion is called
72
New cards
limestone
rocks made of calcium carbonate
73
New cards
calcite
the most common carbonate mineral
74
New cards
dolomite
calcium magnesium carbonate
75
New cards
aragonite
denser and harder CaCO3 mineral
76
New cards
ooid
spherical CaCO3 grain
77
New cards
pisoids
spherical CaCO3 grain >2mm diameter
78
New cards
peloids
homogeneous grains - probably fecal pellets
79
New cards
intraclast
grain that is a recycled piece of CaCO3
80
New cards
aggregate
consists of several fragments
81
New cards
The most common evaporite minerals in sedimentary rocks are
gypsum and anhydrite
82
New cards
Halite
evaporite mineral that is distinguished by its salty taste.
83
New cards
Chert
A fine-grained siliceous sedimentary rock made up of interlocking microquartz grains is called
84
New cards
Sedimentary log
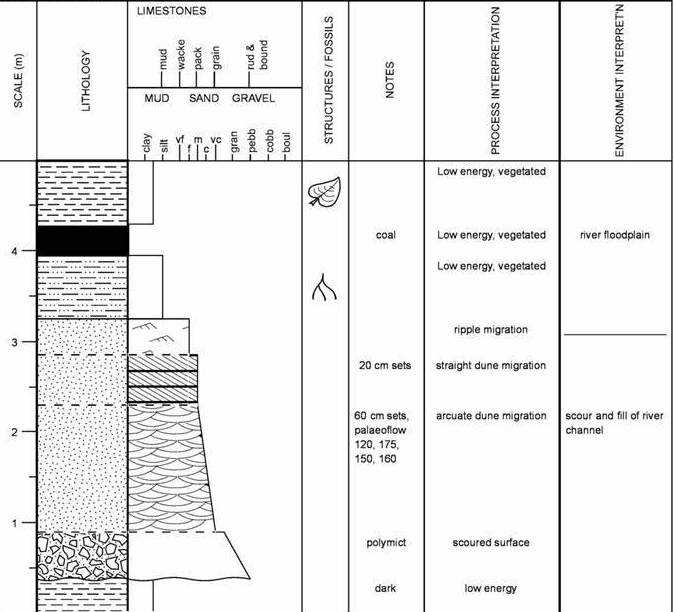
85
New cards
Unidirectional indicators
Which type of paleocurrent indicator gives the absolute direction of flow?
86
New cards
Fence diagram
A diagram that shows how different sedimentary logs can be correlated and linked across various distances is called a
87
New cards
Flow axis indicators
Which type of paleocurrent indicator gives the linear orientation of the flow but does not distinguish upcurrent from downcurrent?
88
New cards
Rose
Paleocurrent data are normally plotted on a ____ diagram, which is a circular histogram.
89
New cards
lithostratigraphic unit
defined by rock type and stratigraphic position
90
New cards
biostratigraphic unit
defined by its fossil content
91
New cards
chronostratigraphic unit
defined by its absolute age
92
New cards
magnetostratigraphic
defined by magnetic properties
93
New cards
allostratigraphic unit
defined by its position relative to significant stratigraphic surfaces
94
New cards
isochronous
a surface representing a single moment in geologic time
95
New cards
Left side of diagram
angular unconformity
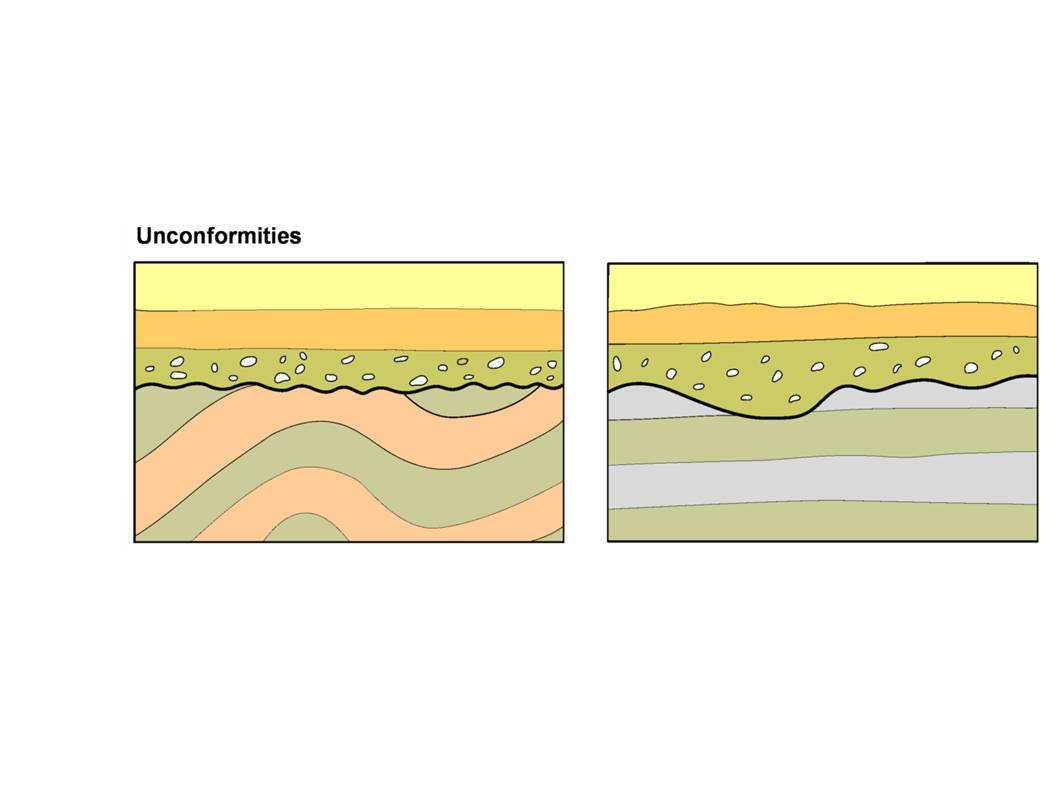
96
New cards
Right side of diagram
disconformity
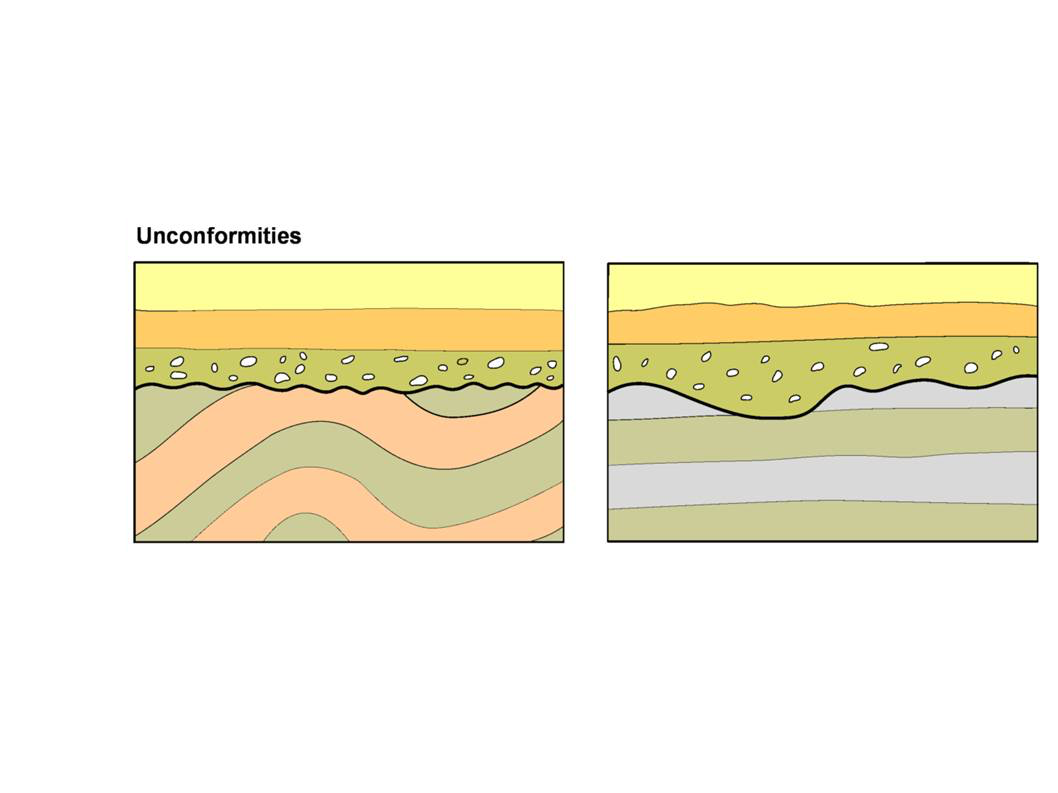
97
New cards
Cross cutting
where igneous rocks are younger than the strata
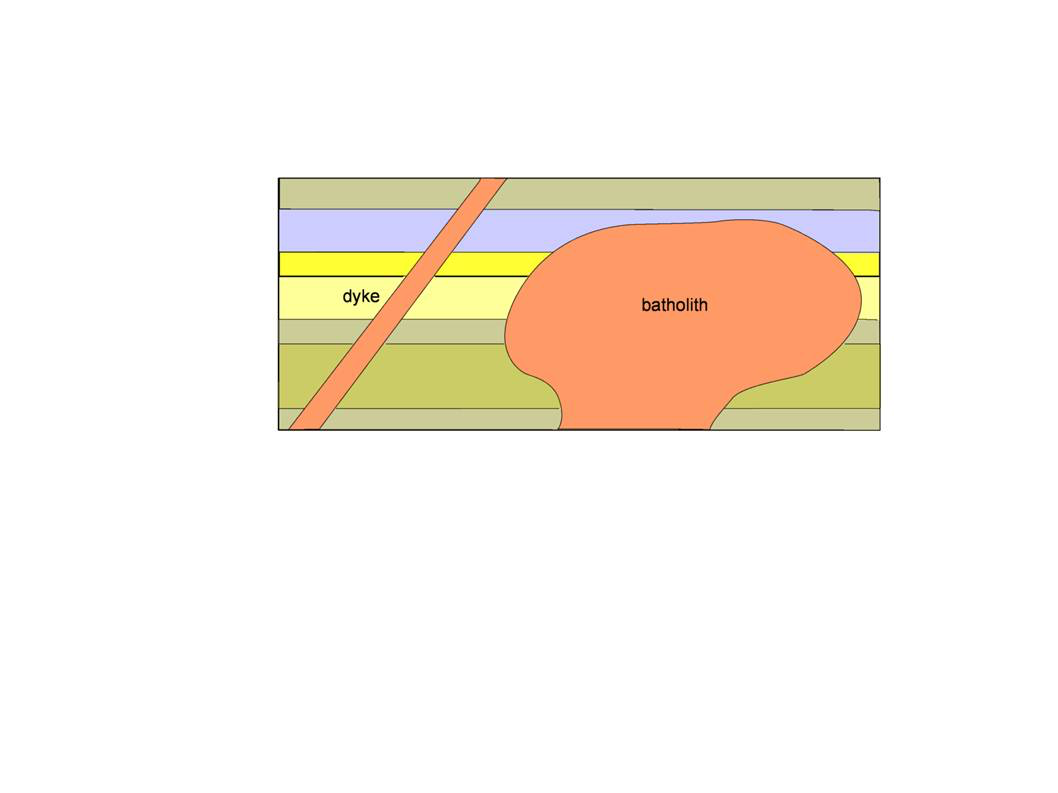
98
New cards
Which characteristic CANNOT be used to define a formation?
age
99
New cards
True or False: A bedding plane typically represent much more time than beds of strata themselves.
True
100
New cards
True or False: Interpretation of facies should be based on the processes, not the specific environment, that formed the beds under observation.
True