MIS 180 Exam 2 review
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
NOT a principle of process re-engineering (BPR)?
New Processes increase controls, checks, and touchpoints
Data inconsistency
Poor data quality can result from data values being different for the same field in different systems
Effective approach to managing enterprise data
Model business data and store it in databases
Software application screens that support enterprise processes focus on capturing data
structured data, unstructured data, semi-structured data
Scenario analysis
Decision models created to probe the challenges and opportunities presented by plausible future worlds(ex: worst case, best case, most likely…)
NOT a true statement about Decision Support Systems (DSS)?
A DSS enables the real-time execution of large numbers of database transactions by a large number of people
Mission
A practical statement of what the organization does, for whom, and how., Focused on daily operations and how the business provides value. Ex:: "To offer customers the lowest possible prices, the best available selection, and the utmost convenience."
Vision
A long-term, aspirational view of what the organization wants to achieve. Ex: "To be the world’s most customer-centric company."
Values
Guiding principles or ethics the company follows, Influence corporate culture and behavior. Ex: Integrity, Innovation, Customer-focus.
SWOT analysis
assesses an enterprise by looking outside-in and inside-out
Enterprise
intentionally organized set of ppl, $, assets, and principles (ex: capabilities) to deliver some type of value to society
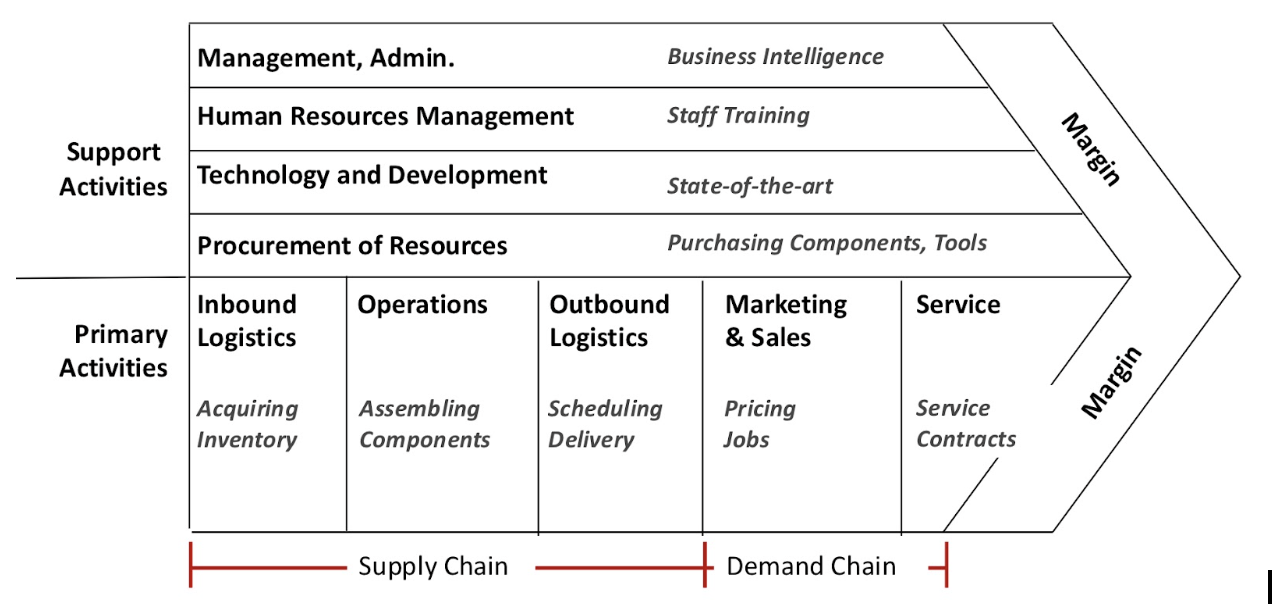
Michael Porter's Value Chain
concept that divides a company's activities into the technologically and economically distinct activities it performs to do business, primary and support activities, which contain both the supply chain and the demand chain.
Components of process
process, inputs, control, outputs, feedback, adjustment
Why enterprises model their business processes
transparency, governance, plan
Governance (could be: data, silos, tech)
Not a cause for bad data
Business Information System
GIGO
describes the phenomenon of bad data inputs resulting in bad data outputs
Data Accuracy
when data are what they are supposed to be and represent the real world, and do not include errors
Characteristics of big data
variety, volume, veracity, value, velocity
relational database
a particular design of a DBMS that stores its info in the form of logically related two-dimensional tables (how we organize the data).
Schemas
how data is organized, including logical constraints such as table names, and fields
File system
How unstructured data is typically stored
data item, field, record, table, database
Data granularity (low to high)
Each record has a foreign key
False
Dilemma
Paradox
a decision that is seemingly absurd or a self-contradictory statement of a proposition that, when investigated or explained, may prove to be well-founded or true
Utilitarian
saving 5 ppl at the cost of 1 person is the right choice because it maximizes the well-being of the greatest number of people
Problem
a decision that is required when a matter or situation that is regarded as unwelcome or harmful, and needs to be dealt with and overcome; usually has a quality of urgency
Structured decision
routine, well-defined procedures for making the decision
TPS
collect, organize, and store master data (ex: product, customer) and transaction data (ex: sales order) for business opportunities
Model
smth that lets you work with it (manipulate, adjust, change, get feedback)
Benefits measurement model
matrix used to evaluate the outcomes of potential choices based on weighted criteria
CSF Critical success factor
crucial steps companies perform to achieve their goals and objectives and implement their strategies.
KPI Key Performance Indicator
(compared to the inside target, strategic objective): quantifiable metrics a company uses to evaluate progress toward critical success factors.
Strategy
“a general plan or set of plans intended to achieve a goal,” it considers a longer timeframe. For every specific strategy, there are several tactics.
competitive business strategies
Cost leadership: offer the lowest prices
Differentiation: be different enough from competitors
Innovation: offer products no one else does
Growth: repeat a winning business model in new markets
Inorganic: through acquisition, organic: taking products to new markets or putting new products under a business model.
Alliances: partner with businesses that have complementary skills
Niche: serves a narrow market, often with high margins.
Support activities = “enterprise functions”
Required to run the business, not directly related to a given product, the cost associated has to be accounted for when selling, but they are not directly attributable to a product.