351 Test #1: MedSurg
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
1
New cards
speciality practice of med-surg nursing
* Promote, restore, or maintain optimal health for patients > age 18
* Nurses must have knowledge, skills, & attitudes (KSAs) to be:
* Care coordinators
* Transition managers
* Caregivers
* Patient educators
* Leaders
* Advocates for the patient and family
* Locations: skilled nursing facilities, hospitals, ambulatory clinics, patient’s home
* Nurses must have knowledge, skills, & attitudes (KSAs) to be:
* Care coordinators
* Transition managers
* Caregivers
* Patient educators
* Leaders
* Advocates for the patient and family
* Locations: skilled nursing facilities, hospitals, ambulatory clinics, patient’s home
2
New cards
Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN)
* Patient-centered care
* Safety
* Teamwork and interprofessional collaboration
* Evidence-based practice
* Quality improvement
* Informatics and technology
* Safety
* Teamwork and interprofessional collaboration
* Evidence-based practice
* Quality improvement
* Informatics and technology
3
New cards
Patient-centered care
* The patient or designee (person who makes decisions on behalf of the patient) is source of control and full partner (QSEN, 2011)
* Cultural competence
* Family-centered care
* Respect for patients’ values, preferences, and expressed needs
* Interdisciplinary
* Teamwork
* Care coordination
* Transitional care
* Access
* Cultural competence
* Family-centered care
* Respect for patients’ values, preferences, and expressed needs
* Interdisciplinary
* Teamwork
* Care coordination
* Transitional care
* Access
4
New cards
Safety
* The ability to keep the patient and staff free from harm and minimize errors in care
* The Joint Commission (hospital compliance): A Culture of Safety
* National Patient Safety Goals
* Requires a culture of safety: blame-free approach
* Serious (sentinel) events must be reported.
* The Joint Commission (hospital compliance): A Culture of Safety
* National Patient Safety Goals
* Requires a culture of safety: blame-free approach
* Serious (sentinel) events must be reported.
5
New cards
Common causes of harm and error
* Lack of clear communication
* Lack of attentiveness
* Lack of clinical judgment
* Errors in medication admin.
* Inadequate prevention of complications
* Lack of attentiveness
* Lack of clinical judgment
* Errors in medication admin.
* Inadequate prevention of complications
6
New cards
Teamwork and interprofessional collaboration
* Function effectively within interprofessional health care teams, fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making (QSEN, 2011)
* Includes:
* Ethics for interprofessional practice - Mutual respect & shared values
* Knowledge of role responsibilities (ours and others)
* Communication (including strategies such as SBAR)
* Teamwork – relationship-building values
* Includes:
* Ethics for interprofessional practice - Mutual respect & shared values
* Knowledge of role responsibilities (ours and others)
* Communication (including strategies such as SBAR)
* Teamwork – relationship-building values
7
New cards
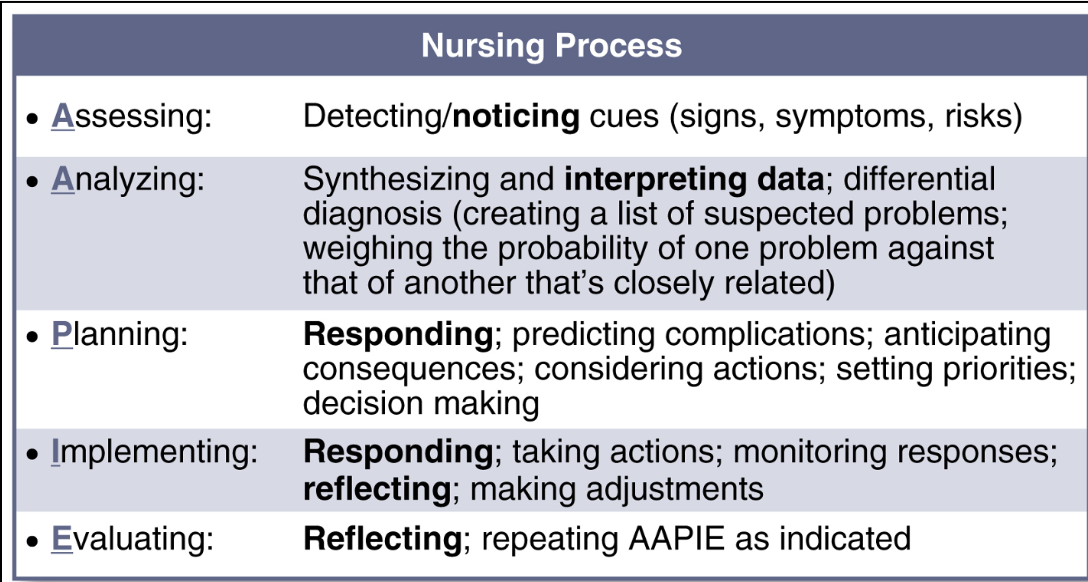
Teamwork nursing process
assessing, analyzing, planning, implementing, evaluating
8
New cards
Delegation
* Process of transferring a selected nursing task or activity to a competent UAP (unlicensed assistive personnel): nurse tech, medical assistant
* The nurse is always accountable for the task/activity delegated!
* Not necessarily the actions, just the fact that you delegated the task
* The nurse is always accountable for the task/activity delegated!
* Not necessarily the actions, just the fact that you delegated the task
9
New cards
Delegation requires:
* Supervision
* Guidance or direction, evaluation, and follow-up by the nurse to ensure a task/activity is performed appropriately
* There are some tasks that nurses cannot delegate to nursing assistants: assessment and evaluation (assessment of pain, evaluation of intervention), education, unstable patients (right circumstance)
* Nursing assistants can only gather data
* Guidance or direction, evaluation, and follow-up by the nurse to ensure a task/activity is performed appropriately
* There are some tasks that nurses cannot delegate to nursing assistants: assessment and evaluation (assessment of pain, evaluation of intervention), education, unstable patients (right circumstance)
* Nursing assistants can only gather data
10
New cards
Five rights of delegation
right task, circumstance, person, communication, supervision
11
New cards
RNs can’t delegate
pain level
12
New cards
Evidence-based practice
* Integration of the best current evidence and practices to make decisions about patient care
* Considers patient preferences and values
* Considers one’s own clinical expertise for delivery of optimal health care
* Considers patient preferences and values
* Considers one’s own clinical expertise for delivery of optimal health care
13
New cards
Quality improvement
* Indicators (data) used to monitor care outcomes and develop solutions to change and improve care
* Models
* PDSA
* Models
* PDSA
14
New cards
Informatics and technology is used to:
communicate, manage knowledge, prevent errors, and support decision making
15
New cards
Development of clinical judgment
Nursing process + Tanner’s Model of Clinical Judgment (patterns of noticing, interpreting, responding, and reflecting)
16
New cards
Can use the NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model: considers the context of your patients
1. Recognize clues: assessment
2. Analyze clues: assessment
3. Prioritize hypotheses : nursing diagnosis (patient’s biggest problem)
4. Generate solutions: plan
5. Take action: implementation
6. Evaluate outcomes: evaluation
17
New cards
Critical thinking
The skill of using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative health care solutions, conclusions, or approaches to clinical or practice problems
18
New cards
Clinical reasoning
The process by which nurses collect cues, process the information, come to an understanding of a patient problem or situation, plan and implement interventions, evaluate outcomes, and reflect on and learn from the process
19
New cards
Clinical judgment
The skill of recognizing cues about a clinical situation, generating and weighing hypotheses, taking action, and evaluating outcomes for the purpose of arriving at a satisfactory clinical outcome. Clinical judgment is the observed outcome of two unobserved underlying mental processes, critical thinking and decision making
20
New cards
Acid-base balance
* Maintenance of arterial blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45
* Acidosis (DKA) and alkalosis (basic)
* Acidosis (DKA) and alkalosis (basic)
21
New cards
Cellular regulation
* Cell growth, replication, and differentiation
* Benign (non-cancerous) /Malignant (cancerous) cell growth
* Healthy People 2030 goal to reduce cancer risk
* Benign (non-cancerous) /Malignant (cancerous) cell growth
* Healthy People 2030 goal to reduce cancer risk
22
New cards
Clotting
* A complex, multi-step process by which blood forms a protein-based structure (clot)
* Thrombosis or embolus (increased clotting)
* DVT, PE, blood clot
* Prolonged internal or external bleeding (decreased ability to clot)
* hemorrhage
* Thrombosis or embolus (increased clotting)
* DVT, PE, blood clot
* Prolonged internal or external bleeding (decreased ability to clot)
* hemorrhage
23
New cards
Cognition
* Reasoning/Learning/memory
* May be intact/adequate, or impaired
* Delirium: acute, common in hospitals
* Dementia: prolonged, progressive
* Depression: prolonged, can look similar to dementia
* All seen in geriatrics and can appear similar
* Decreased blood sugar can cause LOC changes
* May be intact/adequate, or impaired
* Delirium: acute, common in hospitals
* Dementia: prolonged, progressive
* Depression: prolonged, can look similar to dementia
* All seen in geriatrics and can appear similar
* Decreased blood sugar can cause LOC changes
24
New cards
Comfort
emotional/physical, pain
25
New cards
Elimination: constipation/diarrhea
* Excretion of waste from the body (GI/Urinary)
* Continence versus incontinence
* Dysfunction of kidneys, bowels (GI), enlarged prostate (BPH)
* Continence versus incontinence
* Dysfunction of kidneys, bowels (GI), enlarged prostate (BPH)
26
New cards
Fluid and electrolyte balance
* Fluid volume excess or deficit (diuretics)
* Hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, etc.
* Hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, etc.
27
New cards
Gas exchange
* Inadequate transportation of oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide away from cells
* Ventilation & Diffusion (is oxygen reaching the blood?)
* Ventilation & Diffusion (is oxygen reaching the blood?)
28
New cards
Glucose regulation
* type II diabetes, tumor
* Maintenance of optimal blood glucose levels
* Maintenance of optimal blood glucose levels
29
New cards
Immunity
* Overactive: crohn's disease (autoimmune)
* Inactive: HIV
* Protection from illness or disease
* Active immunity/passive immunity
* Inactive: HIV
* Protection from illness or disease
* Active immunity/passive immunity
30
New cards
Infection
invasion of pathogens in the body
31
New cards
Inflammation
* Response to cellular injury, allergy, or invasion of pathogens
* Acute (sprained ankle) vs. Chronic (ulcerative colitis)
* Local vs. Systemic
* Acute (sprained ankle) vs. Chronic (ulcerative colitis)
* Local vs. Systemic
32
New cards
Mobility
* Dependent on central and peripheral nervous system & musculoskeletal system
* Aka “Functional Ability”
* Consider patients’ baselines in assessment
* Aka “Functional Ability”
* Consider patients’ baselines in assessment
33
New cards
Nutrition
* ill-fitting dentures, stomach flu, Crohn’s disease- malnutrition
* Process of ingesting and using food to maintain optimal body function
* Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals
* Process of ingesting and using food to maintain optimal body function
* Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals
34
New cards
Pain
* Unpleasant sensory or motor experience
* Acute vs. Persistent/Chronic Pain
* Acute vs. Persistent/Chronic Pain
35
New cards
Perfusion
* cast that’s too tight-obstructs blood flow
* Adequate arterial blood flow through peripheral tissues (peripheral perfusion)
* Blood pumped by the heart to oxygenate major body organs (central perfusion)
* Adequate arterial blood flow through peripheral tissues (peripheral perfusion)
* Blood pumped by the heart to oxygenate major body organs (central perfusion)
36
New cards
Sensory perception
* Receiving & interpreting sensory input
* Vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch
* Vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch
37
New cards
Sexuality
“Physiological, emotional, social aspects of well-being related to intimacy, self concept, and role relationships.”
38
New cards
Tissue integrity: pressure ulcer, wound, rash
* Intactness of structure and function of integument and mucous membranes
* Intact versus impaired
* Intact versus impaired
39
New cards
priority concepts for a perioperative patient
gas exchange, pain
40
New cards
interrelated concepts for a perioperative patient
infection, tissue integrity
41
New cards
Hemoglobin women values
12-16 g/dL
42
New cards
Hemoglobin men levels
14-18 g/dL
43
New cards
Hematocrit women values
37-47%
44
New cards
Hematocrit men values
42-52%
45
New cards
AB+ blood is the
universal recipient
46
New cards
O- is the
universal donor
47
New cards
\+blood
have Rh
48
New cards
\-blood
don’t have Rh
49
New cards
aPTT
* 30-60 seconds
* Patients receiving anticoagulant therapy: 1.5-2.5 times control value in seconds
* Patients receiving anticoagulant therapy: 1.5-2.5 times control value in seconds
50
New cards
PT
* 11-12.5 seconds; 85-100%
* Full anticoagulant therapy: >1.5-2 times control value; 20-30%
* INR: 0.8-1.1
* Full anticoagulant therapy: >1.5-2 times control value; 20-30%
* INR: 0.8-1.1
51
New cards
Platelet count for adults-elderly
150,000-400,000/ mm3
52
New cards
Perioperative assessment: pre-op history
* Review of systems (ROS) (head-toe assessment as a history)
* Medical history
* Surgical history
* Social history (alcohol, drugs, nicotine)
* Psychological status and support (who is going to help them at home)
* Cultural or spiritual needs (food requests or needs, see them chaplin, want a certain gender of care provider, may not accept blood products, how anxious the patient is)
* Medical history
* Surgical history
* Social history (alcohol, drugs, nicotine)
* Psychological status and support (who is going to help them at home)
* Cultural or spiritual needs (food requests or needs, see them chaplin, want a certain gender of care provider, may not accept blood products, how anxious the patient is)
53
New cards
Perioperative assessment: increased risk
* Age older than 65
* Medications: immunosuppressants, NSAIDs
* Medical history: cardiopulmonary disease, impaired immunity, active infection, DM, coagulation disorder, obesity, substance use/abuse, any chronic disease
* Prior surgical experiences: anesthesia reactions/complications, post-operative complications
* Type of planned procedure: head/neck surgery (airway occlusion), chest procedure (atelectasis-risk for pneumonia), abdominal surgery (paralytic ileus and DVT)
* Medications: immunosuppressants, NSAIDs
* Medical history: cardiopulmonary disease, impaired immunity, active infection, DM, coagulation disorder, obesity, substance use/abuse, any chronic disease
* Prior surgical experiences: anesthesia reactions/complications, post-operative complications
* Type of planned procedure: head/neck surgery (airway occlusion), chest procedure (atelectasis-risk for pneumonia), abdominal surgery (paralytic ileus and DVT)
54
New cards
Focused preoperative physical assessment: cardiopulmonary
* Hypotension/hypertension
* Bradycardia, tachycardia, dysrhythmia
* Chest pain
* Dyspnea or tachypnea
* Pulse ox
* Bradycardia, tachycardia, dysrhythmia
* Chest pain
* Dyspnea or tachypnea
* Pulse ox
55
New cards
Focused preoperative physical assessment: infection
* Fever, increased WBC
* Wounds, respiratory, or urinary symptoms
* Wounds, respiratory, or urinary symptoms
56
New cards
Focused preoperative physical assessment: contraindications for surgery
* Increased PT, INR, or aPTT
* May not even do surgery if these numbers are out of range
* Coagulation issues-inability to create clots after surgery
* Hypo/hyperkalemia
* Positive pregnancy test
* Recent PO intake (within 6 hours)
* May not even do surgery if these numbers are out of range
* Coagulation issues-inability to create clots after surgery
* Hypo/hyperkalemia
* Positive pregnancy test
* Recent PO intake (within 6 hours)
57
New cards
Focused preoperative physical assessment: conditions to evaluate further
* Change in mental status
* Vomiting
* Rash
* Recent anticoagulants
* Vomiting
* Rash
* Recent anticoagulants
58
New cards
Pre-op planning short-term outcomes
* The patient will demonstrate improvement in symptoms
* The patient will describe/demonstrate appropriate self-care strategies (to be used during post-op period)
* The patient will describe/demonstrate appropriate self-care strategies (to be used during post-op period)
59
New cards
Pre-op planning long-term outcomes
The patient will not experience any complications (of the surgery)
60
New cards
Perioperative implementation
pre-op teaching and anticipatory guidance
61
New cards
Perioperative implementation: prevent complications
* DVT (use SCDs-creates blood flow pumping motion), atelectasis (incentive spirometer (breath in) -bacteria can grow-pneumonia), paralytic ileus, early \*ambulation prevents these things
* Splitting helps with abdominal surgeries, holding a pillow to the chest to prevent pain
* Initially give meds on a scheduled basis to reach a therapeutic dose even if they are PRN
* Splitting helps with abdominal surgeries, holding a pillow to the chest to prevent pain
* Initially give meds on a scheduled basis to reach a therapeutic dose even if they are PRN
62
New cards

Perioperative planning for patient teaching
\*focus on early ambulation-prevents pressure ulcers, constipation
63
New cards
Perioperative implementation: informed consent by the surgeon
1. Nature of procedure
2. Risks and benefits
3. Reasonable alternatives
4. Assessment of the patient’s understanding
64
New cards
Perioperative implementation: informed consent by the nurse
* Verify form is signed
* May serve as witness to patient’s signature
* Is NOT witnessing that the patient understands
* Client confused about surgery: request surgeon
* May serve as witness to patient’s signature
* Is NOT witnessing that the patient understands
* Client confused about surgery: request surgeon
65
New cards
Post-op assessment: respiratory complications
atelectasis: listen to lung sounds (diminished, popping sounds), ask about dyspnea, O2 sats (low), elevated RR
66
New cards
Post-op assessment: cardiovascular complications
* VTE (warm skin, intermittent claudication-pain while walking), dysrhythmias or HF, hypo/hypertension, sepsis, SOB with PE
* HF right-sided: edema, left-sided: fluid in the lungs
* Skin assessment, turn every 2 hrs
* Blood pressure measurements
* Check wound drains
* HF right-sided: edema, left-sided: fluid in the lungs
* Skin assessment, turn every 2 hrs
* Blood pressure measurements
* Check wound drains
67
New cards
Post-op assessment: neurologic complications
* CVA, cognitive decline
* Neuro status assessment
* CVA: paralysis on one side of the body
* Changes in vision
* Neuro status assessment
* CVA: paralysis on one side of the body
* Changes in vision
68
New cards
Post-op assessment: neuromuscular complications
* nerve damage
* Monofilament test (lost of sensation, tingling)
* Slower reflexes
* Monofilament test (lost of sensation, tingling)
* Slower reflexes
69
New cards
Post-op assessment: GI complications
* stress ulcer (not caused by H.pylori, surgery causes physiologic stresser), paralytic ileus (intestines are paralyzed, peristalsis isn’t working, type of bowel obstruction, causes N/V)
* Constipated, incontinence
* PPI given to treat stress ulcer
* Paralytic ileus: nausea, won’t eat, not having BM because nothing is moving through
* Constipated, incontinence
* PPI given to treat stress ulcer
* Paralytic ileus: nausea, won’t eat, not having BM because nothing is moving through
70
New cards
Post-op assessment: renal/GU complications
* AKI (elevated creatinine or BUN-lab results, may require dialysis), acute urinary retention (medications we give), electrolyte imbalance (medications, IV fluids, dehydration)
* Concentrated urine, not voiding
* Potassium- EKG effects
* Concentrated urine, not voiding
* Potassium- EKG effects
71
New cards
Post-op assessment: skin complications
* pressure injuries, wound infection or dehiscence (separation of approximated wound edges)
* Skin assessment, non-blanchable redness, purulent drainage
* Skin assessment, non-blanchable redness, purulent drainage
72
New cards
Post-op focused assessment
PACU and then Med-Surg unit: make sure to get a full set of vitals and orient them to their room, how they would ask for help, who is taking care of them
73
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: neuro status
* Awake, arousable, oriented, aware?
* Are peripheral pulses palpable?
* Are peripheral pulses palpable?
74
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: respiratory status
* Airway patent?
* RR and depth? LS CTA?
* Use of accessory muscles?
* O2 Sat? Setting and method of oxygen delivery?
* Incentive Spirometer?
* RR and depth? LS CTA?
* Use of accessory muscles?
* O2 Sat? Setting and method of oxygen delivery?
* Incentive Spirometer?
75
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: cardiovascular status
* BP/HR within baseline range?
* Values different than in (PACU)?
* VTE prophylaxis?
* Values different than in (PACU)?
* VTE prophylaxis?
76
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: GI/GU status
* Post-Op N/V (PONV)?
* Urine output?
* Urine output?
77
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: derm status
* Pressure ulcers? Redness?
* Check coccyx to see if there are pressure ulcers when the patient stands up or is transferred
* Check coccyx to see if there are pressure ulcers when the patient stands up or is transferred
78
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: surgical incision status
* Dressing? Drainage? Swelling?
* Bleeding/drainage under patient?
* Drains present? Quantity in container? Positioned properly & draining?
* Bleeding/drainage under patient?
* Drains present? Quantity in container? Positioned properly & draining?
79
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: IV fluid status
* Type? Additives?
* How much solution remaining?
* Rate of infusion? Ordered rate?
* How much solution remaining?
* Rate of infusion? Ordered rate?
80
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: other tube status
* NG or intestinal tube?
* Drainage color, consistency, and amount?
* Suction ordered?
* Foley? Draining properly?
* Urine color, clarity, and volume?
* Drainage color, consistency, and amount?
* Suction ordered?
* Foley? Draining properly?
* Urine color, clarity, and volume?
81
New cards
Post-op focused assessment: general status
lab results
82
New cards
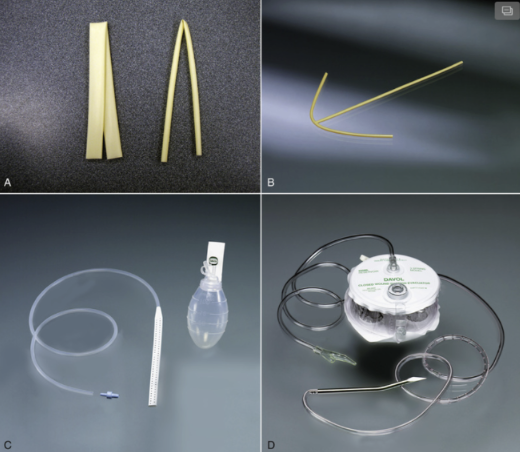
post-op assessment: drains
* A. Penrose: acts like a wick, used for a day
* B. T-tube
* C. Jackson-Pratt (JP): creating a vacuum and patients go home with them, teach how to track output, have to squeeze before you plug it in again
* D. Hemovac: greater volume for larger spaces, suction vacuum, maintain pressure, record volume and type of fluid
* B. T-tube
* C. Jackson-Pratt (JP): creating a vacuum and patients go home with them, teach how to track output, have to squeeze before you plug it in again
* D. Hemovac: greater volume for larger spaces, suction vacuum, maintain pressure, record volume and type of fluid
83
New cards
Post-op assessment: monitoring for complications of spinal or epidural anesthesia: paralysis and loss of sensation in the legs
* Respiratory depression
* Hypotension
* Post-dural puncture headache (spinal headache)-leak of cerebrospinal fluid, increased pressure in the brain, lie flat to resolve
* Hypotension
* Post-dural puncture headache (spinal headache)-leak of cerebrospinal fluid, increased pressure in the brain, lie flat to resolve
84
New cards
Post-op planning and interventions: addressing and preventing complications
outcome: patient is free of post-op complications
85
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: improve gas exchange
* Incentive spirometer
* Walking around
* Cough, deep breath, turn
* Walking around
* Cough, deep breath, turn
86
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: prevent wound infection/delayed wound healing
* Drain
* Cleaning dressing
* Increase protein intake to promote healing
* Increase hydration
* Cleaning dressing
* Increase protein intake to promote healing
* Increase hydration
87
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: promote peristalsis
* Walking around
* Stool softeners
* Fiber diet
* May have to wait around for body to work on its own or put in an NG tube
* Stool softeners
* Fiber diet
* May have to wait around for body to work on its own or put in an NG tube
88
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: manage pain
* Pain meds
* Music, dancing, acupuncture
* Pain assessment
* Music, dancing, acupuncture
* Pain assessment
89
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: prevent venous thromboembolus
* SCD
* Compression socks
* Walking around
* SQ heparin
* Compression socks
* Walking around
* SQ heparin
90
New cards
post-op planning/interventions: manage urinary retention and constipation
* Diuretic
* Catheter
* Laxative
* may have to wait around for body to keep working again, parasympathetic NS needs to start again
* Catheter
* Laxative
* may have to wait around for body to keep working again, parasympathetic NS needs to start again
91
New cards
post-op planing and implementation: moderate sedation, ED
Outcome: the patient will be free of symptoms of medication overdose
92
New cards
Opioids
* Prepare to administer naloxone hydrochloride (Narcan); may need to be repeated
* Have suction available
* Assess pain level, as naloxone reverses analgesic effect of opioids
* Have suction available
* Assess pain level, as naloxone reverses analgesic effect of opioids
93
New cards
Benzodiazepine: ativan
* Prepare to administer flumazenil (Romazicon); may need to repeat PRN
* Monitor for S/E of flumazenil: dizziness, HA, dry mouth, blurred vision
* Monitor for S/E of flumazenil: dizziness, HA, dry mouth, blurred vision
94
New cards
Opioids and benzodiazepines:
* Half-life is longer of drug than reversal agent: may need to give several doses
* Monitor and support airway
* Administer O2 if hypoxia or RR
* Monitor and support airway
* Administer O2 if hypoxia or RR
95
New cards
post-op planning/implementation: discharge teaching
* Outcome: the patient will demonstrate or restate ways to safely care for self at home
* Pain management
* Drug therapy with reconciliation of postoperative drugs
* SAFETY (e.g., understanding who to contact in case of complications, progressive increase in activity, needed assistive devices)
* Continuation of interventions to prevent post-op complications
* Management of drains or catheters
* Nutrition therapy
* Follow-up with the surgeon
* Pain management
* Drug therapy with reconciliation of postoperative drugs
* SAFETY (e.g., understanding who to contact in case of complications, progressive increase in activity, needed assistive devices)
* Continuation of interventions to prevent post-op complications
* Management of drains or catheters
* Nutrition therapy
* Follow-up with the surgeon
96
New cards
glucose normal adults ranges
74-106 mg/dL
97
New cards
glycoslyated hemoglobin normal ranges
good diabetic control:
98
New cards
diabetes typically occurs in
Native American populations with an education less than high school and family income in poverty
99
New cards
diabetes assessment: risk factors
* First degree relative with DM
* Physically inactive
* High risk ethnic populations
* African American, Hispanic American, American Indian, Pacific Islander
* Physically inactive
* High risk ethnic populations
* African American, Hispanic American, American Indian, Pacific Islander
100
New cards
diabetes assessment: history
* Gestational diabetes mellitus
* Infants more likely to have diabetes later in life
* Higher infant birth weight
* Vascular disease
* HTN
* Infants more likely to have diabetes later in life
* Higher infant birth weight
* Vascular disease
* HTN